redis的搭建及应用(四)-redis哨兵机制
redis哨兵机制
Redis主从虽然能够增强Redis的高可用性,但是如果主(master)Redis服务忽然下线,需要提升某个从成为主来重新架构。如何判断下线,如何提升从为主,主重新上线后如何与其它redis交互… , redis哨兵策略比较好的处理了这一问题。这一节我们研究redis哨兵搭建及应用。
问题
如果主服务器(master)出现宕机,那么向从库写数据就会出现问题。
解决方案
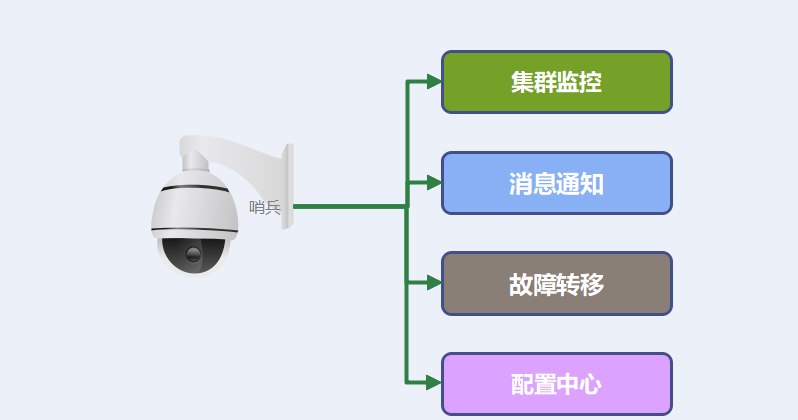
智能化节点监测-哨兵模式: Redis 在 2.8 版本以后提供的哨兵(Sentinel)机制,它的作用是实现主从节点故障转移。它会监测主节点是否存活,如果发现主节点挂了,它就会选举一个从节点切换为主节点,并且把新主节点的相关信息通知给从节点和客户端。
什么是哨兵机制
Sentinel(哨岗、哨兵)是Redis的高可用性(high availability)解决方案:由一个或多个Sentinel实例(instance)组成的Sentinel系统(system)可以监视任意多个主服务器,以及这些主服务器属下的所有从服务器,并在被监视的主服务器进入下线状态时,自动将下线主服务器属下的某个从服务器升级为新的主服务器,然后由新的主服务器代替已下线的主服务器继续处理命令请求。
哨兵架构
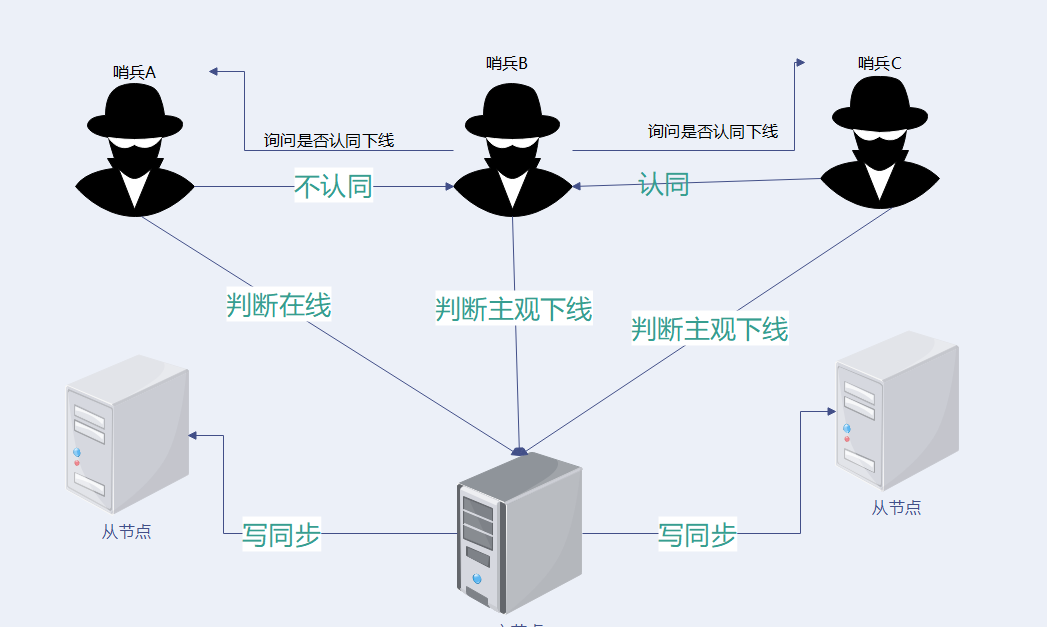
主观、客观下线
主观下线(Subjectively Down, 简称 SDOWN)指的是单个 Sentinel 实例对服务器做出的下线判断。
、客观下线(Objectively Down, 简称 ODOWN)指的是多个 Sentinel 实例在对同一个服务器做出 SDOWN 判断, 并且通过 SENTINEL is-master-down-by-addr 命令互相交流之后, 得出的服务器下线判断。 (一个 Sentinel 可以通过向另一个 Sentinel 发送 SENTINEL is-master-down-by-addr 命令来询问对方是否认为给定的服务器已下线。)
如果一个服务器没有在 master-down-after-milliseconds 选项所指定的时间内, 对向它发送 PING 命令的 Sentinel 返回一个有效回复(valid reply), 那么 Sentinel 就会将这个服务器标记为主观下线。
每个 Sentinel 都需要定期执行的任务
- 每个 Sentinel 以每秒钟一次的频率向它所知的主服务器、从服务器以及其他 Sentinel 实例发送一个 PING 命令。
- 如果一个实例(instance)距离最后一次有效回复 PING 命令的时间超过 down-after-milliseconds 选项所指定的值, 那么这个实例会被 Sentinel 标记为主观下线。 一个有效回复可以是: +PONG 、 -LOADING 或者 -MASTERDOWN 。
- 如果一个主服务器被标记为主观下线, 那么正在监视这个主服务器的所有 Sentinel 要以每秒一次的频率确认主服务器的确进入了主观下线状态。
- 如果一个主服务器被标记为主观下线, 并且有足够数量的 Sentinel (至少要达到配置文件指定的数量)在指定的时间范围内同意这一判断, 那么这个主服务器被标记为客观下线。
- 在一般情况下, 每个 Sentinel 会以每 10 秒一次的频率向它已知的所有主服务器和从服务器发送 INFO 命令。 当一个主服务器被 Sentinel 标记为客观下线时, Sentinel 向下线主服务器的所有从服务器发送 INFO 命令的频率会从 10 秒一次改为每秒一次。
- 当没有足够数量的 Sentinel 同意主服务器已经下线, 主服务器的客观下线状态就会被移除。 当主服务器重新向 Sentinel 的 PING 命令返回有效回复时, 主服务器的主观下线状态就会被移除。
Sentinel常用指令
| 序号 | 指令 | 解释 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | PING | 返回 PONG,判断是否联通 |
| 2 | SENTINEL masters | 列出所有被监视的主服务器,以及这些主服务器的当前状态。 |
| 3 | SENTINEL slaves | 列出给定主服务器的所有从服务器,以及这些从服务器的当前状态。 |
| 4 | SENTINEL get-master-addr-by-name | 返回给定名字的主服务器的 IP 地址和端口号。 如果这个主服务器正在执行故障转移操作, 或者针对这个主服务器的故障转移操作已经完成, 那么这个命令返回新的主服务器的 IP 地址和端口号。 |
哨兵搭建
redis主从服务ip地址及映射
| 序号 | 服务器名称 | 宿主ip | 宿主端口 | 容器ip | 容器端口 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | redis_6379 | 192.168.200.104 | 6379 | 172.18.12.10 | 6379 |
| 2 | redis_6380 | 192.168.200.104 | 6380 | 172.18.12.11 | 6379 |
| 3 | redis_6381 | 192.168.200.104 | 6381 | 172.18.12.12 | 6379 |
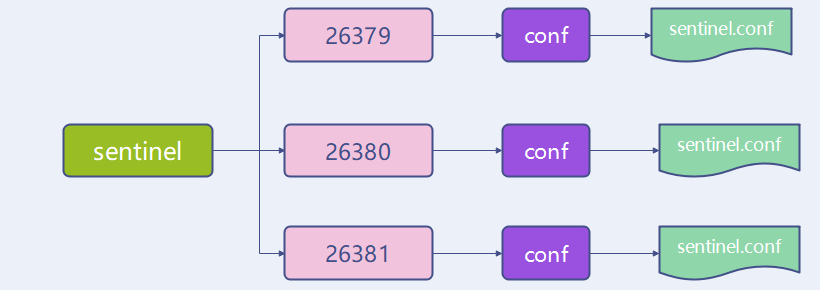
哨兵配置文件结构
创建哨兵文件存储哨兵配置文件 /usr/local/software/
mkdir -p sentinel/26379/conf
mkdir -p sentinel/26380/conf
mkdir -p sentinel/26381/conf
编辑配置文件(sentinel.conf)
编辑26379下的配置文件
# 所以无需担心端口重复使用
# 如果需要在单机
port 26379
sentinel announce-ip 192.168.198.128
sentinel announce-port 26379
#
# The above two configuration directives are useful in environments where,
# because of NAT, Sentinel is reachable from outside via a non-local address.
#
# When announce-ip is provided, the Sentinel will claim the specified IP address
# in HELLO messages used to gossip its presence, instead of auto-detecting the
# local address as it usually does.
#
# Similarly when announce-port is provided and is valid and non-zero, Sentinel
# will announce the specified TCP port.
# 设定密码认证
# requirepass 123456
# 配置哨兵的监控参数
# 格式:sentinel monitor <master-name> <ip> <redis-port> <quorum>
# master-name是为这个被监控的master起的名字
# ip是被监控的master的IP或主机名。因为Docker容器之间可以使用容器名访问,所以这里写master节点的容器名
# 此处填写宿主机(linux)的ip地址
# redis-port是被监控节点所监听的端口号
# quorom设定了当几个哨兵判定这个节点失效后,才认为这个节点真的失效了
sentinel monitor redis_6379 192.168.200.104 6379 2
# 连接主节点的密码
# 格式:sentinel auth-pass <master-name> <password>
# sentinel auth-pass local-master 123456
# master在连续多长时间无法响应PING指令后,就会主观判定节点下线,默认是30秒
# 格式:sentinel down-after-milliseconds <master-name> <milliseconds>
sentinel down-after-milliseconds redis_6379 30000
编辑26380下的配置文件
# 所以无需担心端口重复使用
# 如果需要在单机
port 26380
sentinel announce-ip 192.168.198.128
sentinel announce-port 26380
#
# The above two configuration directives are useful in environments where,
# because of NAT, Sentinel is reachable from outside via a non-local address.
#
# When announce-ip is provided, the Sentinel will claim the specified IP address
# in HELLO messages used to gossip its presence, instead of auto-detecting the
# local address as it usually does.
#
# Similarly when announce-port is provided and is valid and non-zero, Sentinel
# will announce the specified TCP port.
# 设定密码认证
# requirepass 123456
# 配置哨兵的监控参数
# 格式:sentinel monitor <master-name> <ip> <redis-port> <quorum>
# master-name是为这个被监控的master起的名字
# ip是被监控的master的IP或主机名。因为Docker容器之间可以使用容器名访问,所以这里写master节点的容器名
# 此处填写宿主机(linux)的ip地址
# redis-port是被监控节点所监听的端口号
# quorom设定了当几个哨兵判定这个节点失效后,才认为这个节点真的失效了
sentinel monitor redis_6379 192.168.200.104 6379 2
# 连接主节点的密码
# 格式:sentinel auth-pass <master-name> <password>
# sentinel auth-pass local-master 123456
# master在连续多长时间无法响应PING指令后,就会主观判定节点下线,默认是30秒
# 格式:sentinel down-after-milliseconds <master-name> <milliseconds>
sentinel down-after-milliseconds redis_6379 30000
编辑26381下的配置文件
# 所以无需担心端口重复使用
# 如果需要在单机
port 26381
sentinel announce-ip 192.168.198.128
sentinel announce-port 26381
#
# The above two configuration directives are useful in environments where,
# because of NAT, Sentinel is reachable from outside via a non-local address.
#
# When announce-ip is provided, the Sentinel will claim the specified IP address
# in HELLO messages used to gossip its presence, instead of auto-detecting the
# local address as it usually does.
#
# Similarly when announce-port is provided and is valid and non-zero, Sentinel
# will announce the specified TCP port.
# 设定密码认证
# requirepass 123456
# 配置哨兵的监控参数
# 格式:sentinel monitor <master-name> <ip> <redis-port> <quorum>
# master-name是为这个被监控的master起的名字
# ip是被监控的master的IP或主机名。因为Docker容器之间可以使用容器名访问,所以这里写master节点的容器名
# 此处填写宿主机(linux)的ip地址
# redis-port是被监控节点所监听的端口号
# quorom设定了当几个哨兵判定这个节点失效后,才认为这个节点真的失效了
sentinel monitor redis_6379 192.168.200.104 6379 2
# 连接主节点的密码
# 格式:sentinel auth-pass <master-name> <password>
# sentinel auth-pass local-master 123456
# master在连续多长时间无法响应PING指令后,就会主观判定节点下线,默认是30秒
# 格式:sentinel down-after-milliseconds <master-name> <milliseconds>
sentinel down-after-milliseconds redis_6379 30000
创建运行哨兵容器
运行26379容器
docker run -it \
--name sentinel_26379 \
--privileged \
--network wn_docker_net \
--sysctl net.core.somaxconn=1024 \
--ip 172.18.12.20 \
-p 26379:26379 \
-v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime \
-v /usr/local/software/sentinel/26379/conf:/user/local/etc/redis/conf/ \
-d redis \
redis-sentinel /user/local/etc/redis/conf/sentinel.conf
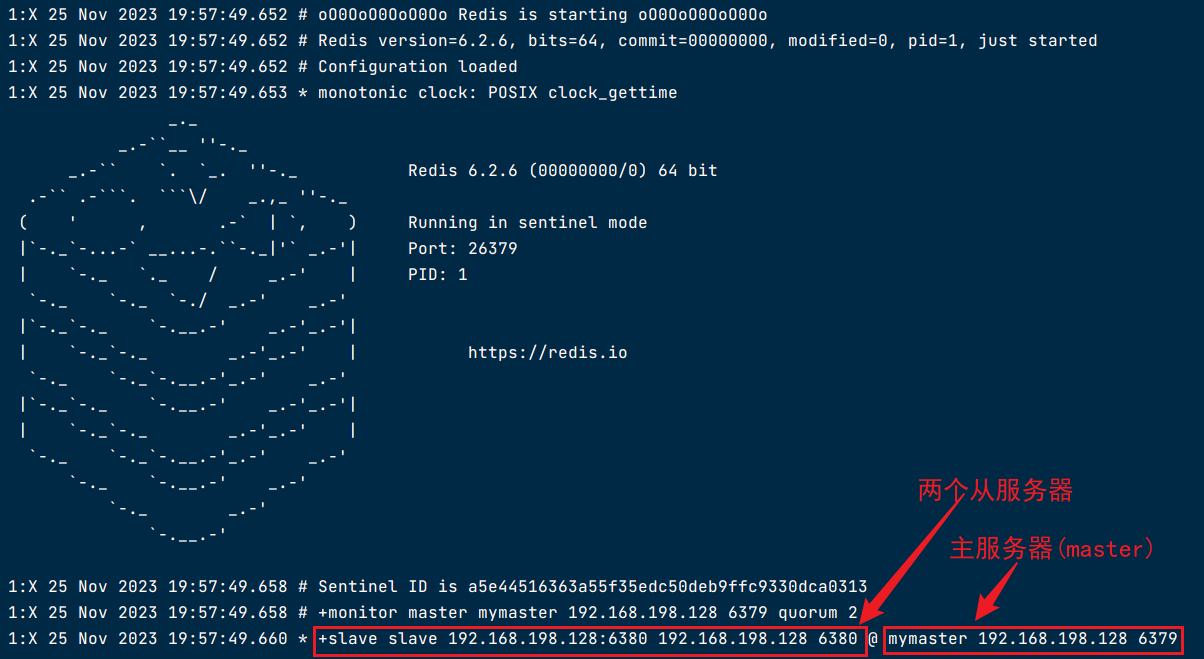
运行26380容器
docker run -it \
--name sentinel_26380 \
--privileged \
--network wn_docker_net \
--sysctl net.core.somaxconn=1024 \
--ip 172.18.12.21 \
-p 26380:26380 \
-v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime \
-v /usr/local/software/sentinel/26380/conf:/user/local/etc/redis/conf/ \
-d redis \
redis-sentinel /user/local/etc/redis/conf/sentinel.conf
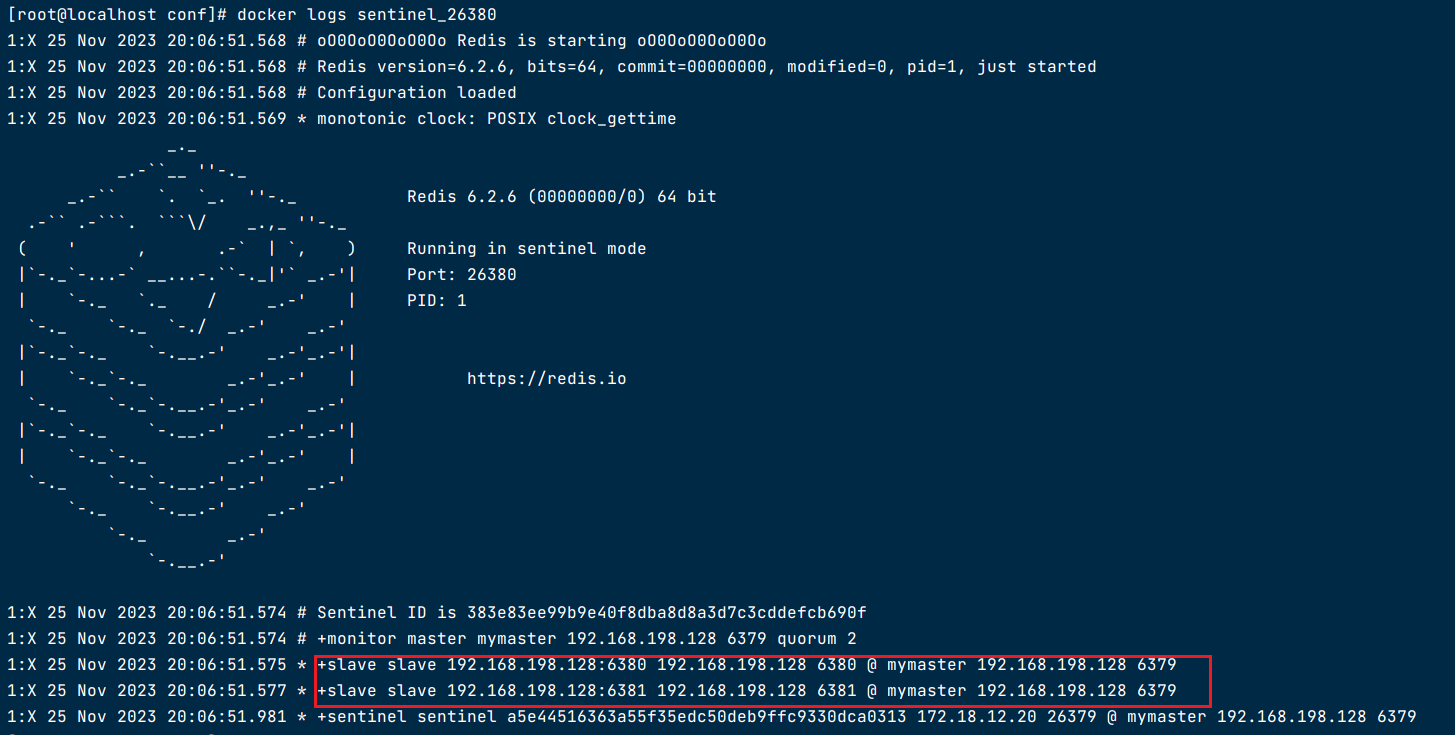
运行26381容器
docker run -it \
--name sentinel_26381 \
--privileged \
--network wn_docker_net \
--sysctl net.core.somaxconn=1024 \
--ip 172.18.12.22 \
-p 26381:26381 \
-v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime \
-v /usr/local/software/sentinel/26380/conf:/user/local/etc/redis/conf/ \
-d redis \
redis-sentinel /user/local/etc/redis/conf/sentinel.conf
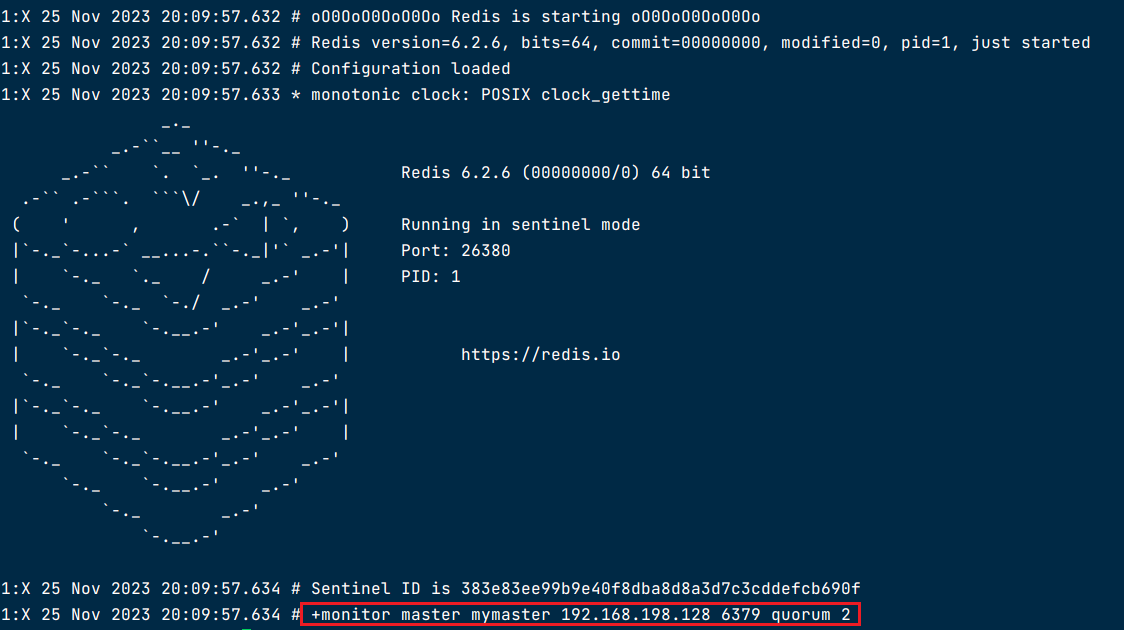
测试哨兵
关闭master容器
模拟服务器宕机状态,即redis_6379容器关闭。
docker stop redis_6379
查看6381,6380容器状态
让redis_6379重新上线,查看容器内的信息。
[root@localhost conf]# docker restart redis_6379
[root@localhost conf]# docker exec -it redis_6381 bash
root@a2ac20bad78b:/data# redis-lic
root@a2ac20bad78b:/data# redis-cli
127.0.0.1:6379> info replication
# Replication
role:master
connected_slaves:2
slave0:ip=192.168.200.104,port=6380,state=online,offset=3960084,lag=1
slave1:ip=192.168.200.104,port=6379,state=online,offset=3960084,lag=1
master_failover_state:no-failover
master_replid:eb8d2a448dbc1a01b694739627c9669ef2935375
master_replid2:410d195de210c3317b634790a5c237f150c30ca9
master_repl_offset:3960084
second_repl_offset:40914
repl_backlog_active:1
repl_backlog_size:1048576
repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:2911509
repl_backlog_histlen:1048576
防止“脑裂”
脑裂的主要原因其实就是哨兵集群认为主节点已经出现故障了,重新选举其它从节点作为主节点,而原主节点其实是假故障,从而导致短暂的出现两个主节点,那么在主从切换期间客户端一旦给原主节点发送命令,就会造成数据丢失。
修改redis.conf文件
- min-slaves-to-write:与主节点通信的从节点数量必须大于等于该值主节点,否则主节点拒绝写入。
- min-slaves-max-lag:主节点与从节点通信的ACK消息延迟必须小于该值,否则主节点拒绝写入。
684 # It is possible for a master to stop accepting writes if there are less than
685 # N replicas connected, having a lag less or equal than M seconds.
686 #
687 # The N replicas need to be in "online" state.
688 #
689 # The lag in seconds, that must be <= the specified value, is calculated from
690 # the last ping received from the replica, that is usually sent every second.
691 #
692 # This option does not GUARANTEE that N replicas will accept the write, but
693 # will limit the window of exposure for lost writes in case not enough replicas
694 # are available, to the specified number of seconds.
695 #
696 # For example to require at least 3 replicas with a lag <= 10 seconds use:
697 #
698 min-replicas-to-write 2
699 min-replicas-max-lag 10
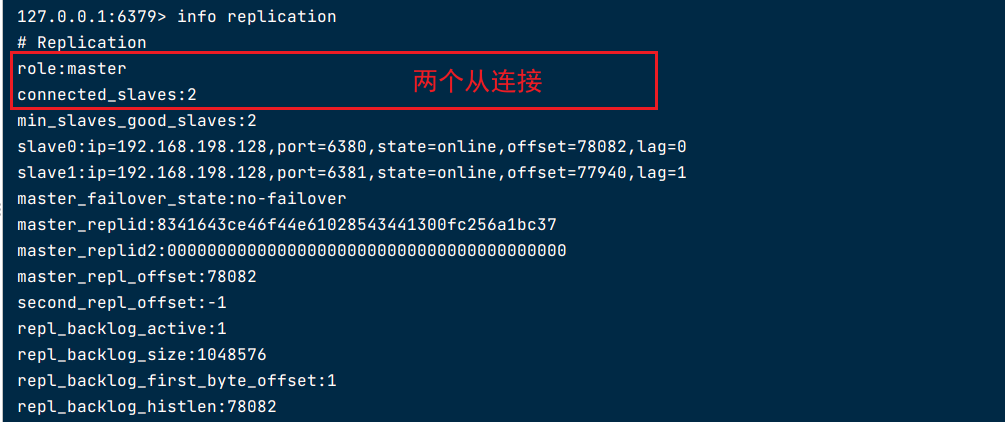
减少从(slave)redis_6381
将redis_6381关闭
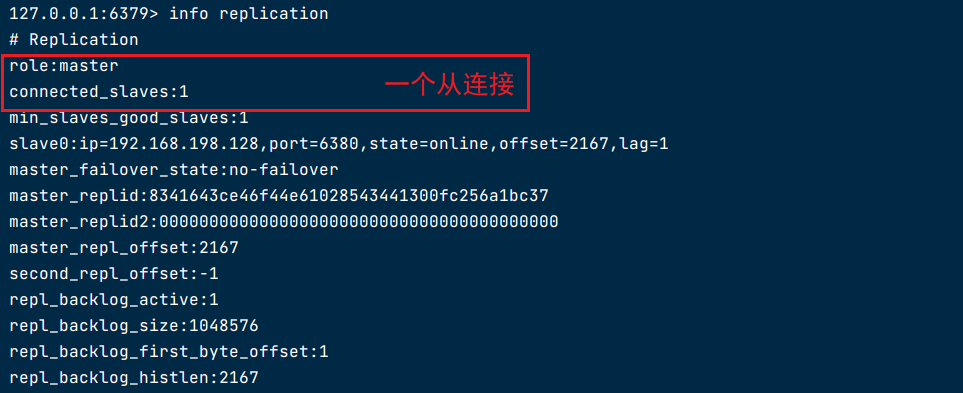

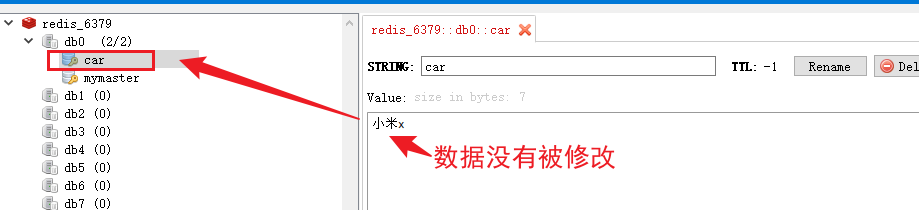
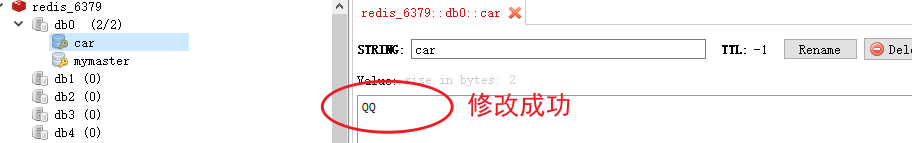
重新上线redis_6381
重新上线从,将从的数量达到 “min-replicas-to-write 2” 的要求。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 什么情况下需要版权登记呢?都有哪些费用?
- [pkg-config] 第三方软件包/库管理工具 pkg-config
- Day18 226翻转二叉树 101对称二叉树 100相同的树 572另一棵树的子树
- 积极拥抱信创,思迈特软件与麒麟软件NeoCertify完成认证
- 腾讯云主机活动内容:领取总面值2000元代金券礼包
- 【JavaEE】线程安全的集合类
- java freemarker 动态生成excel文件
- html渲染优先级
- Java连接数据库的各种细节错误(细节篇)
- CMU15-445-Spring-2023-Project #3 - 前置知识(lec10-14)