一个处理Range List的面试题解法
最近看到一个比较有意思的面试题。题目不算难,但是想把效率优化做好,也没那么容易。
我们先看下题目
题目
// Task: Implement a class named 'RangeList'
// A pair of integers define a range, for example: [1, 5). This range includes integers: 1, 2, 3, and 4.
// A range list is an aggregate of these ranges: [1, 5), [10, 11), [100, 201)
/**
*
* NOTE: Feel free to add any extra member variables/functions you like.
*/
class RangeList {
/**
*
* Adds a range to the list
* @param {Array<number>} range - Array of two integers that specify beginning and
end of range.
*/
add(range) {
// TODO: implement this
}
/**
*
* Removes a range from the list
* @param {Array<number>} range - Array of two integers that specify beginning and
end of range.
*/
remove(range) {
// TODO: implement this
}
/**
*
* Convert the list of ranges in the range list to a string
* @returns A string representation of the range list
*/
toString() {
// TODO: implement this
}
}
// Example run
const rl = new RangeList();
rl.toString(); // Should be ""
rl.add([1, 5]);
rl.toString(); // Should be: "[1, 5)"
rl.add([10, 20]);
rl.toString(); // Should be: "[1, 5) [10, 20)"
rl.add([20, 20]);
rl.toString(); // Should be: "[1, 5) [10, 20)"
rl.add([20, 21]);
rl.toString(); // Should be: "[1, 5) [10, 21)"
rl.add([2, 4]);
rl.toString(); // Should be: "[1, 5) [10, 21)"
rl.add([3, 8]);
rl.toString(); // Should be: "[1, 8) [10, 21)"
rl.remove([10, 10]);
rl.toString(); // Should be: "[1, 8) [10, 21)"
rl.remove([10, 11]);
rl.toString(); // Should be: "[1, 8) [11, 21)"
rl.remove([15, 17]);
rl.toString(); // Should be: "[1, 8) [11, 15) [17, 21)"
rl.remove([3, 19]);
rl.toString(); // Should be: "[1, 3) [19, 21)
这题大体的意思是:设计一个RangeList类,它保存了一批左闭右开的区间。它支持add操作,可以新增一个包含区间,但是可能会影响之前的区间,比如之前的区间是:[3,5) [7,9),新增区间[5,7)之后,区间就变成[3,9);它还支持remove操作,可以删除一个区间,也可能影响之前的区间,比如之前的区间是[3,9),删除[5,7)之后,变成[3,5) [7,9)。
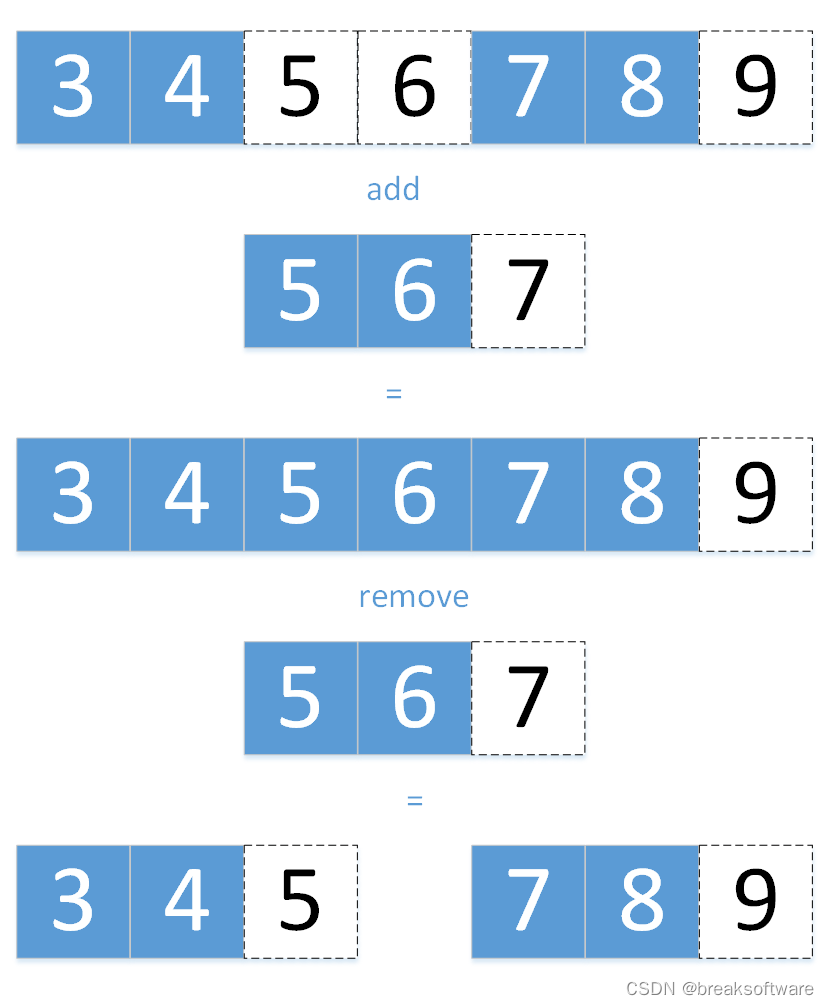
还有一种特殊区间需要考虑,就是左右值相等的区间。比如[5,5)代表的是一个空区间。
解法
Range
首先我们设计一个Range类,它只是单个区间。
add
如果对其进行add操作,即新增一个区间,则要考虑这两个区间是否相交。如果相交,则返回一个重新整合过的区间;如果不相交,则抛出异常。

# add the other range to this range.For example, [1, 5) add [5, 7) is [1, 7).
# @param other - the other range to add to this range
# @return - the new range after adding
# @throws TypeError if other is not a Range object or a list of integers
# @throws ValueError if other is not a list of 2 integers
# @throws TypeError if other range is not overlap with this range
def add(self, other) -> object:
other = self.conv(other)
if self.end < other.start or self.start > other.end:
raise ValueError("other range must be overlap with this range")
if self.start >= other.start and self.end <= other.end:
return Range(other.start, other.end)
if self.start >= other.start and self.end > other.end:
return Range(other.start, self.end)
if self.start < other.start and self.end <= other.end:
return Range(self.start, other.end)
if self.start < other.start and self.end > other.end:
return Range(self.start, self.end)
remove
如果对其进行remove操作,即删除一个区间,也要考虑两个区间相交的情况。如果相交,则返回一个Range数组,其中可能0~2个区间。
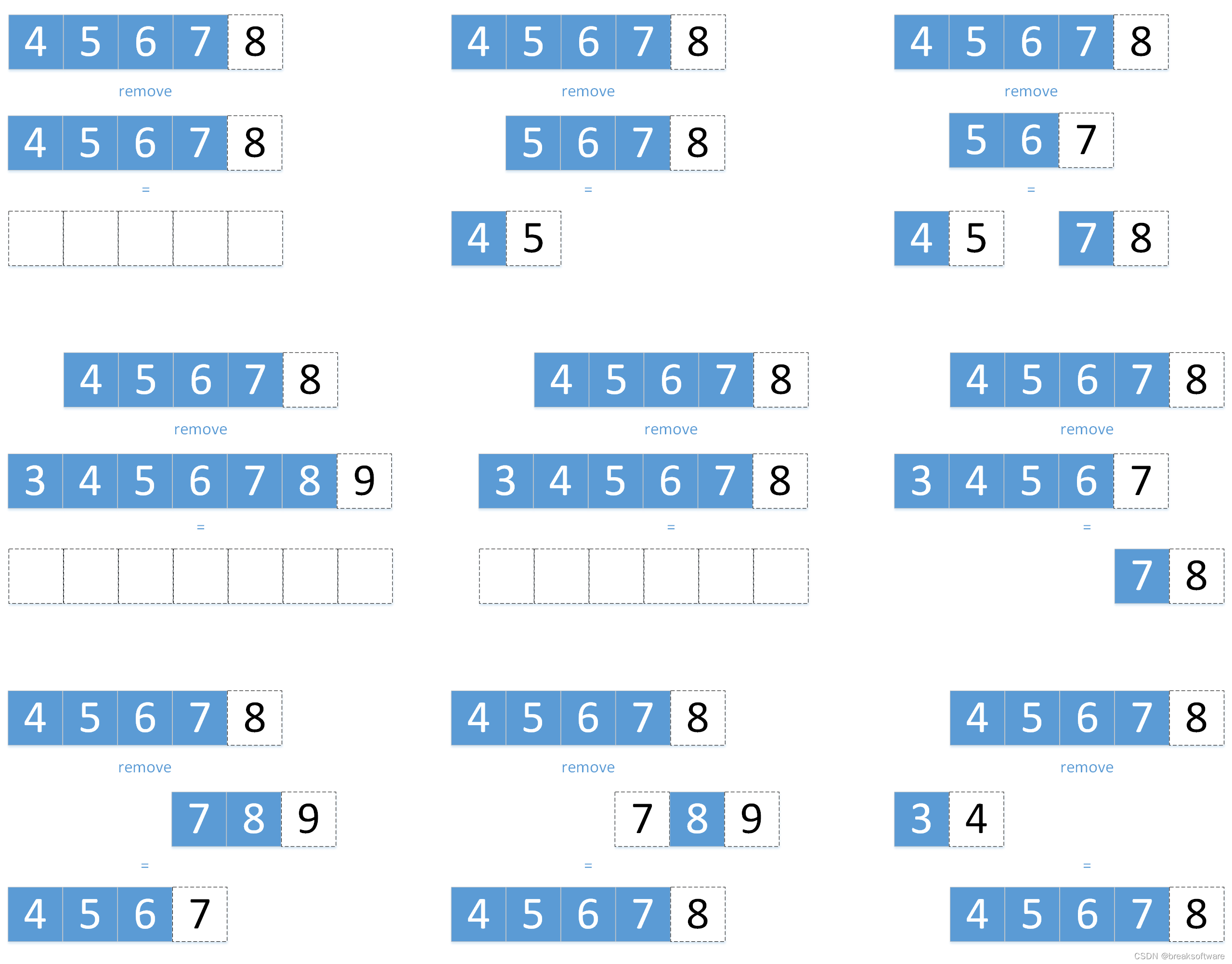
# remove the other range from this range.For example, [1, 5) remove [2, 3) is [1, 2) [3, 5).
# @param other - the other range to remove from this range.the other range must be a Range object or a list of 2 integers
# @return - a list of Range objects that are the result of removing other from this range
# @throws TypeError if other is not a Range object or a list of integers
# @throws ValueError if other is not a list of 2 integers
def remove(self, other) -> list:
other = self.conv(other)
if self.end < other.start or self.start > other.end:
return [self]
if self.start >= other.start and self.end <= other.end:
return []
if self.start >= other.start and self.end > other.end:
return [Range(other.end, self.end)]
if self.start < other.start and self.end <= other.end:
return [Range(self.start, other.start)]
if self.start < other.start and self.end > other.end:
return [Range(self.start, other.start), Range(other.end, self.end)]
Tools
在设计完Range类后,我们还需要解决下面两个问题:
- 被修正的区间有哪些
- 需要调整位置的区间有哪些
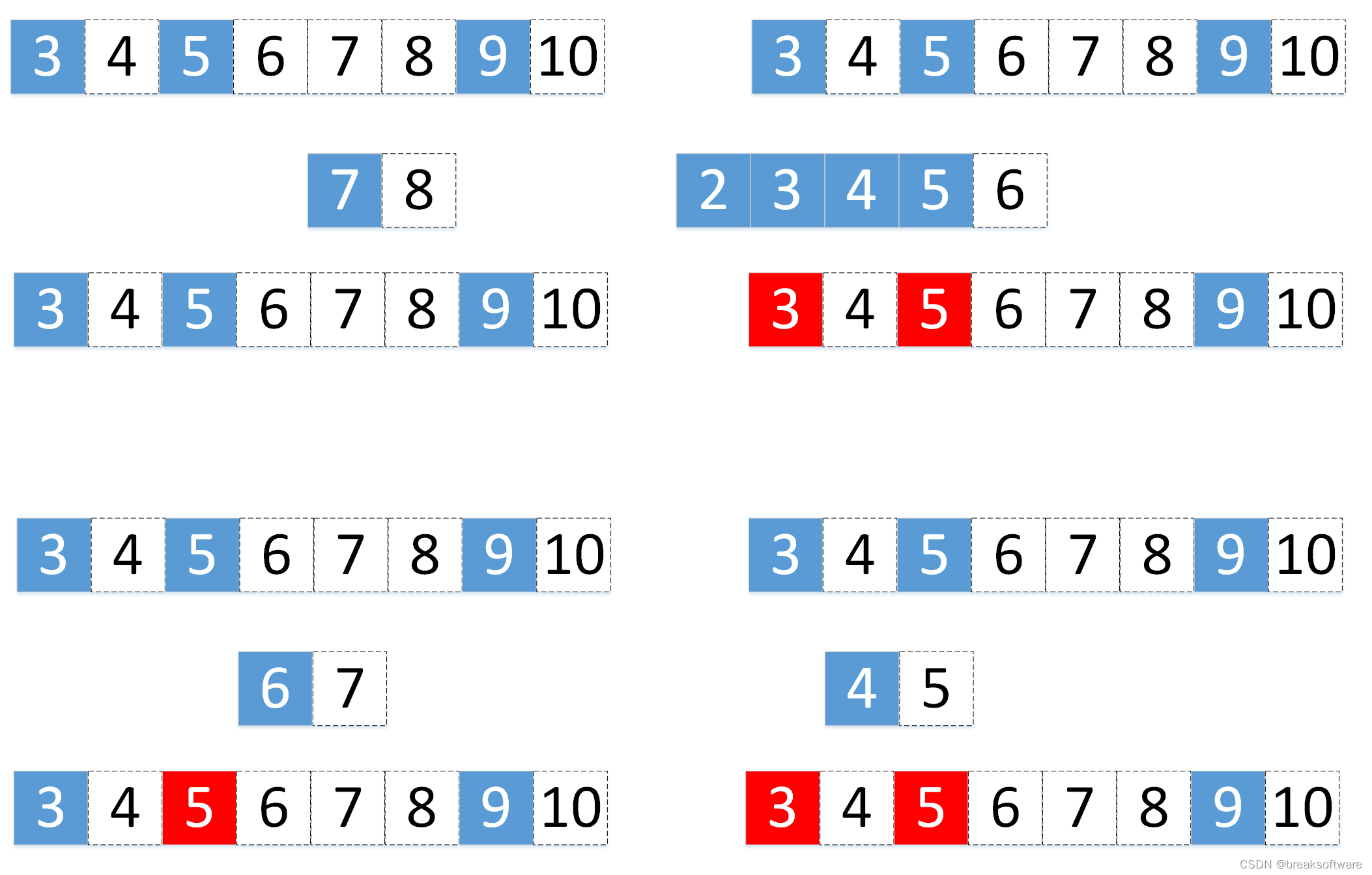
上图中标红的表示可能要调整区间的区域。
对于没有没有需要调整的区域,则要找到临近的区域。比如上图中第一组中,[7,8)需要找到[5,6)这组区间。如果是add操作,则需要将[7,8)插入到区间数组的[5,6)后面。
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8; py-indent-offset:4 -*-
# ======================================================================================================================
# Copyrigth (C) 2024 fangliang <304646673@qq.com>
#
# This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
# License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later
# version.
#
# ======================================================================================================================
from rangelist.range import Range
class Tools(object):
# search the index of the range which contains the value.First value is the index of the range where to compare with the value,
# second value is True if the range contains the value, False otherwise.
# @param ranges - the list of ranges
# @param value - the value to search
# @param start_index - the start index of the ranges to search
# @return the index of the range where to compare with the value, True if the range contains the value, False otherwise
@staticmethod
def search(ranges, value, start_index = 0):
if start_index < 0:
start_index = 0
end_index = len(ranges) - 1
while start_index <= end_index:
mid = (start_index + end_index) // 2
if ranges[mid].start <= value and ranges[mid].end >= value:
return (mid, True)
elif ranges[mid].end < value:
start_index = mid + 1
else:
end_index = mid - 1
return (end_index, False)
# search the index of the ranges which overlap with the search range.
# First value is the index of the range where to compare with the value, second value is True if the range contains the value,
# False otherwise.
# @param ranges - the list of ranges
# @param search_range - the range to search
# @return a list of (index, overlap) of the ranges which overlap with the search range
@staticmethod
def search_overlap(ranges, search_range):
if search_range.start == search_range.end:
return []
start = Tools.search(ranges, search_range.start)
end = Tools.search(ranges, search_range.end, start[0])
index_list = [start]
for i in range(start[0]+1, end[0]+1):
index_list.append((i, True))
return index_list
search_overlap方法返回的数据如下:
[(-1, False), (0, True), (1, True)]
-1代表对比的区间(可能是新增或者删除)的起始值在第0个区间的左侧。
True和False表示区间是否会调整(因为有覆盖)。
RangeList
RangeList用于保存一组Range序列。
这题的解法也主要依赖于其add和remove方法。
add
# add a range to the list.For example, [[1, 5)] add [2, 3) is [[1, 5)].[[1, 5)] add [6, 8) is [[1, 5) [6, 8)].
# @param other - the other range to compare with
# @return True if the other range is overlap with this range, False otherwise
# @throws TypeError if other is not a Range object or a list of integers
# @throws ValueError if other is not a list of 2 integers
def add(self, other):
other = Range.conv(other)
indexes = Tools.search_overlap(self.ranges, other)
del_start_index = -1
for i in indexes:
if i[1]:
other = self.ranges[i[0]].add(other)
if -1 == del_start_index:
del_start_index = i[0]
if -1 != del_start_index:
del self.ranges[del_start_index : indexes[-1][0]+1]
self.ranges.insert(del_start_index, other)
elif len(indexes) > 0:
self.ranges.insert(indexes[0][0]+1, other)
return self
add方法会让一个Range不停“合并”被其覆盖的Range。然后删除被覆盖的Range,把新组合的Range插入到第一个覆盖的Range位置。
如果没有覆盖的区间,则在适当的位置插入。
remove
# remove the other range from this range.For example, [[1, 5) [10, 14)]] remove [2, 3) is [[1, 2) [3, 5) [10, 14)]].
# @param other - the other range to remove from this range
# @return - the new range after removing
# @throws TypeError if other is not a Range object or a list of integers
# @throws ValueError if other is not a list of 2 integers
def remove(self, other):
other = Range.conv(other)
indexes = Tools.search_overlap(self.ranges, other)
del_start_index = -1
range_list_from_remove_all = []
for i in indexes:
if i[1]:
range_list_from_remove = self.ranges[i[0]].remove(other)
if range_list_from_remove != None:
range_list_from_remove_all.extend(range_list_from_remove)
if -1 == del_start_index:
del_start_index = i[0]
if -1 != del_start_index:
del self.ranges[del_start_index : indexes[-1][0]+1]
self.ranges[del_start_index:del_start_index] = range_list_from_remove_all
return self
remove方法则是让Range List中Range不停remove待删除Range,最后把切割的Range重新插入到Range List中。
代码
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 健康成长的基石:新生儿补充镁的关键
- Jmeter+ant+jenkins接口自动化测试
- MySQL深入——13
- 像专家一样使用TypeScript条件类型
- 20V升26V 600mA升压型LED驱动芯片,PWM调光芯片-AH1160
- PPT插件-好用的插件-超级对齐-大珩助手
- 【leetcode】力扣热门之反转链表【简单难度】
- Move_Certificates-v1.9安装-Magisk movecert模块安装时出现‘unzip error‘的解决办法
- java中Session的简单使用
- 【AI视野·今日CV 计算机视觉论文速览 第287期】Wed, 10 Jan 2024