odoo17 | 模型视图继承
前言
Odoo的强大之处在于它的模块化。模块专门用于满足业务需求,但模块也可以彼此交互。这对于扩展现有模块的功能非常有用。例如,在我们的房地产场景中,我们希望在常规用户视图中直接显示销售人员的属性列表。
但是在讨论特定的Odoo模块继承之前,让我们看看如何更改标准CRUD(创建、检索、更新或删除)方法的行为。
Python 继承
目标
- 设定不能删除非新建或已取消的属性。
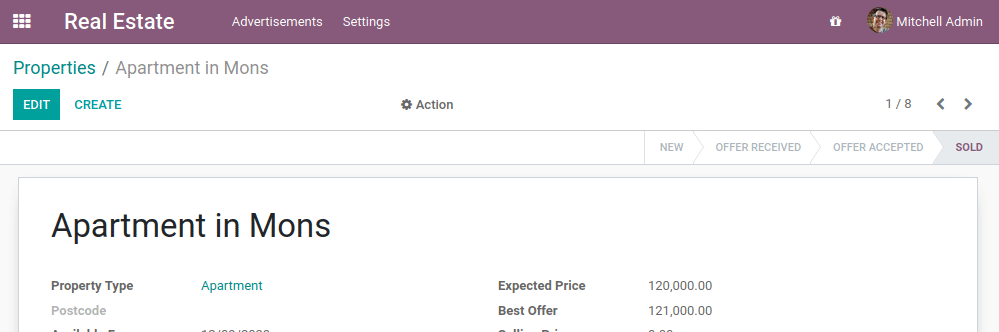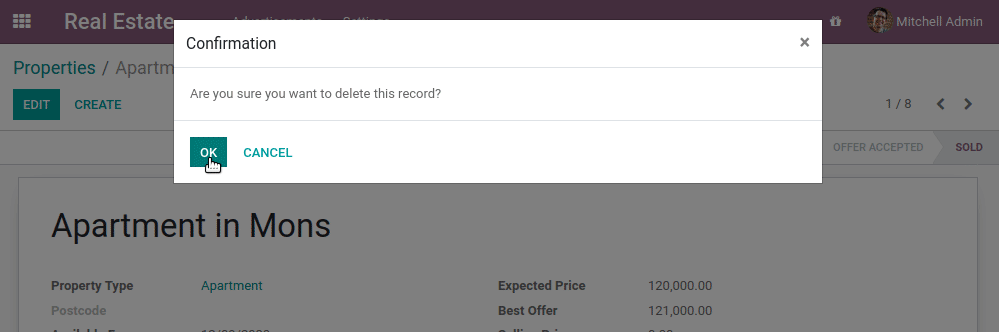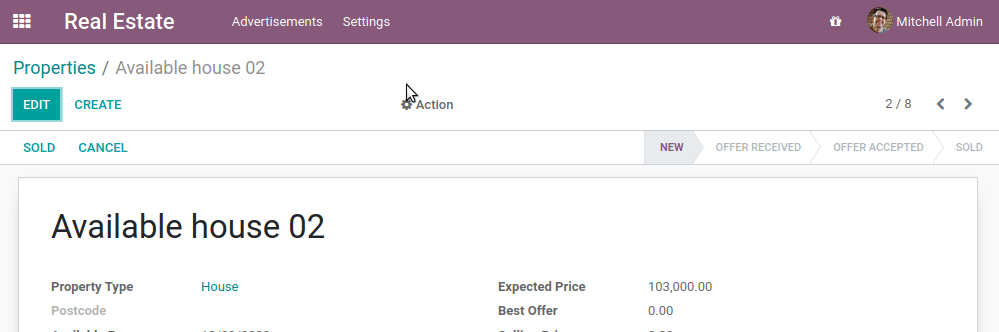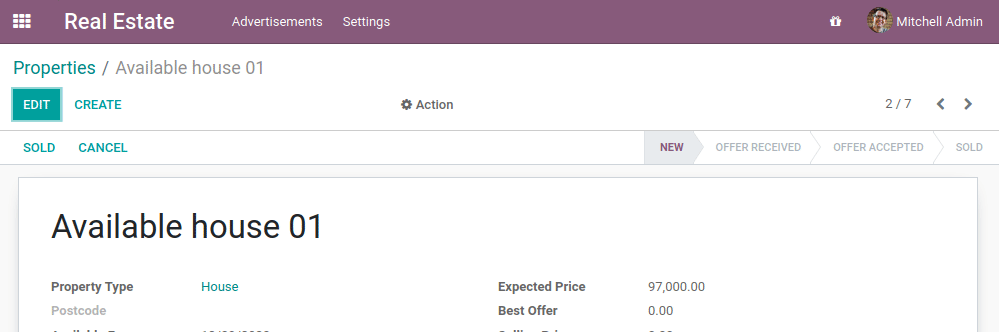
- 创建产品/服务后,属性状态应更改为“已收到产品/服务”
- 不能创建一个比现有报价更低的报价
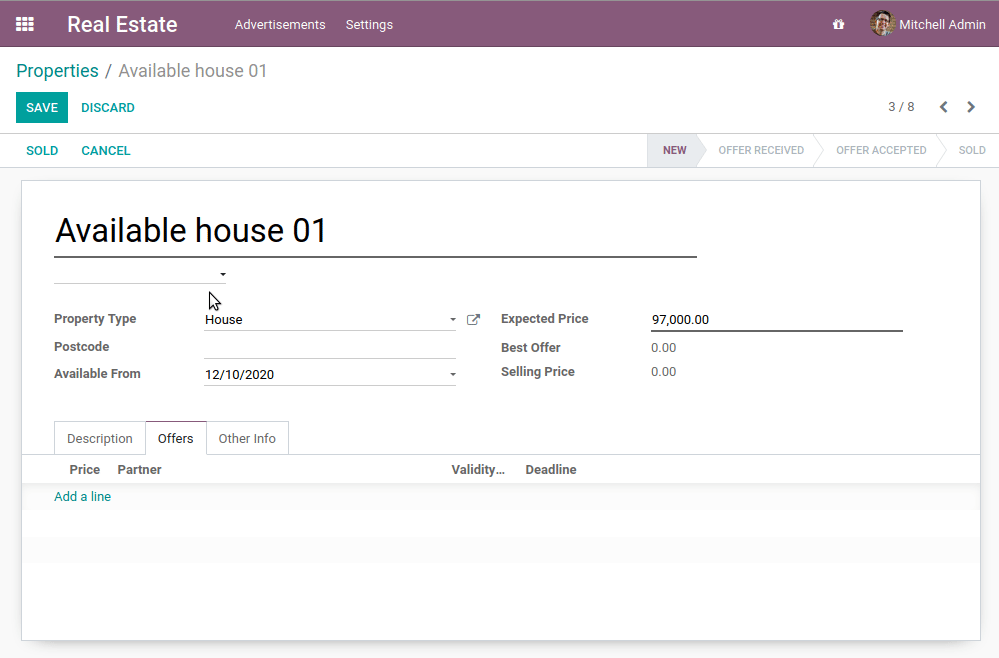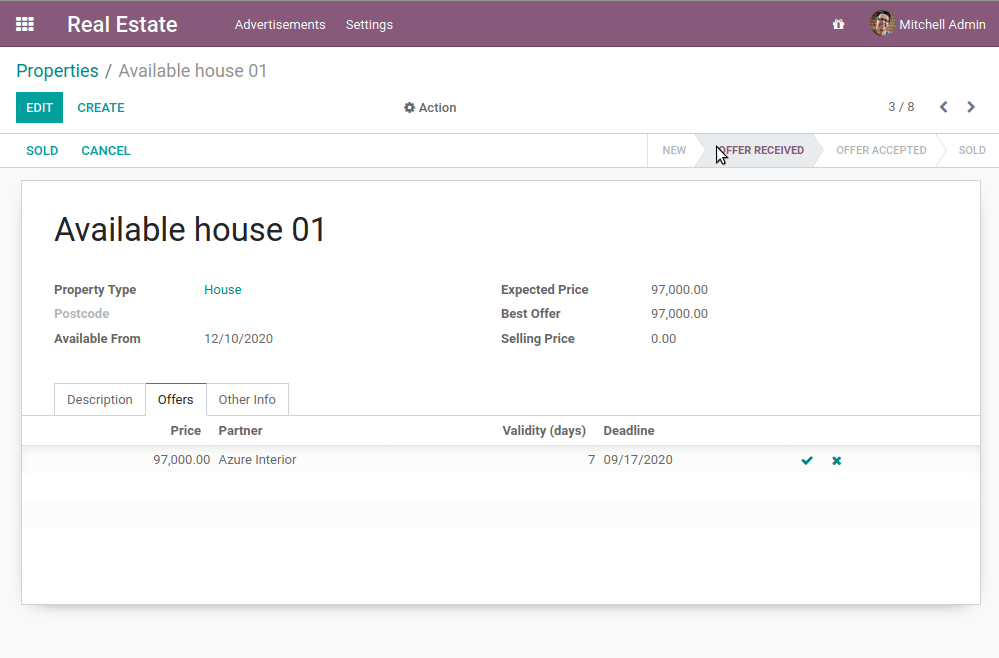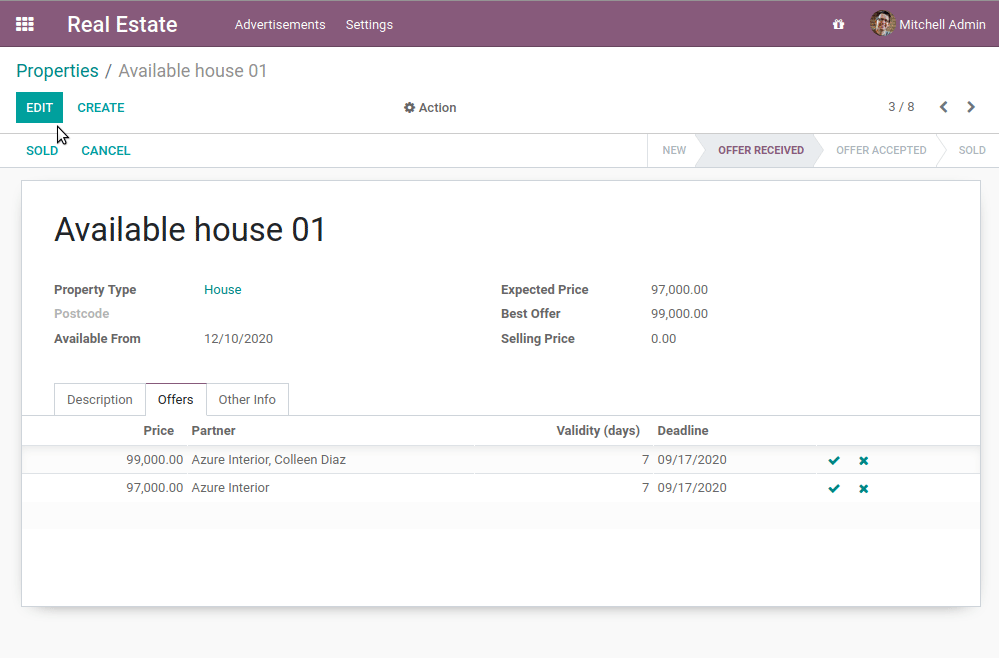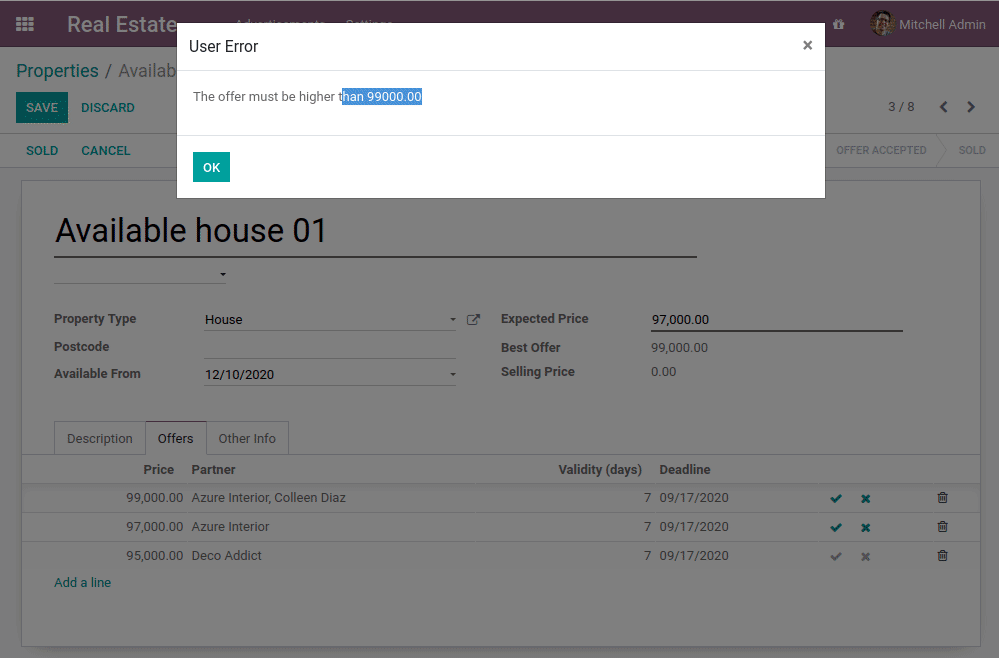
在我们的房地产模块中,我们不需要开发任何特定的东西来执行标准的CRUD操作。Odoo框架提供了完成这些任务所需的工具。事实上,由于经典的Python继承,这些操作已经包含在我们的模型中:
from odoo import fields, models
class TestModel(models.Model):
_name = "test_model"
_description = "Test Model"
...
我们的类TestModel继承自提供create()、read()、write()和unlink()功能的models.Model。
这些方法(以及Model类上定义的任何其他方法)可以扩展以添加特定的业务逻辑:
from odoo import fields, models
class TestModel(models.Model):
_name = "test_model"
_description = "Test Model"
...
@api.model
def create(self, vals):
# 做一些业务逻辑,修改值…
...
# 然后调用super来执行父方法
return super().create(vals)
装饰器model()对于create()方法是必需的,因为记录集本身的内容与创建上下文无关,但对于其他CRUD方法则不是必需的。
同样重要的是要注意,尽管我们可以直接覆盖**unlink()方法,但您几乎总是希望用ondelete()装饰器来编写一个新方法。带有此装饰符的方法将在unlink()期间被调用,从而避免了当unlink()**被直接覆盖时卸载模型模块时可能出现的一些问题。
在Python 3中,super()等价于super(TestModel, self)。当您需要使用修改后的记录集调用父方法时,后者可能是必需的。
注意
总是调用super()以避免中断流程是非常重要的。只有一些非常特殊的情况下你用调用super()。
确保始终返回与父方法一致的数据。例如,如果父方法返回dict(),则重写也必须返回dict()。
模型继承
在我们的房地产模块中,我们希望显示与销售人员相关的房地产列表 直接在“设置”/“用户和公司”/“用户”窗体视图中。为此,我们需要将一个字段添加到 模型并调整其视图以显示它。res.users
Odoo提供了两种继承机制,以模块化方式扩展现有模型。
第一种继承机制允许模块通过以下方式修改另一个模块中定义模型的行为
-
向模型添加字段,
-
覆盖模型中字段的定义,
-
向模型添加约束,
-
向模型添加方法,
-
重写模型中的现有方法。
第二种继承机制(委托)允许模型的每个记录链接到父模型的记录,并提供对该父记录字段的透明访问。
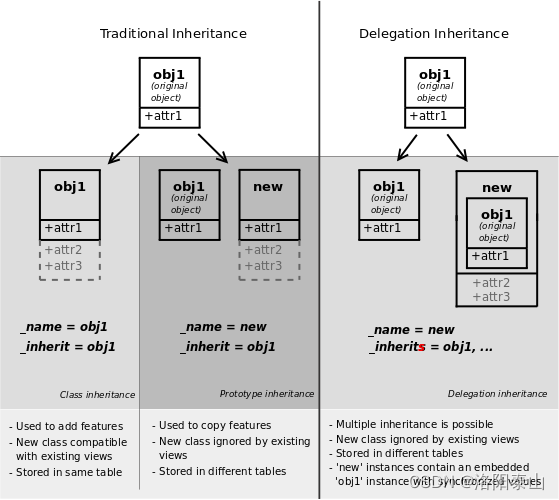
在Odoo中,第一种机制是目前使用最多的。在我们的示例中,我们希望向现有模型添加一个字段,这意味着我们将使用第一种机制。例如:
from odoo import fields, models
class InheritedModel(models.Model):
_inherit = "inherited.model"
new_field = fields.Char(string="New Field")
可以在此处找到向模型添加两个字段的实际示例。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Part of Odoo. See LICENSE file for full copyright and licensing details.
from odoo import models, fields, api, _
class AccountMove(models.Model):
_inherit = 'account.move'
def _post(self, soft=True):
vendor_bill_service = self.env.ref('account_fleet.data_fleet_service_type_vendor_bill', raise_if_not_found=False)
if not vendor_bill_service:
return super()._post(soft)
val_list = []
log_list = []
not_posted_before = self.filtered(lambda r: not r.posted_before)
posted = super()._post(soft) # We need the move name to be set, but we also need to know which move are posted for the first time.
for line in (not_posted_before & posted).line_ids.filtered(lambda ml: ml.vehicle_id):
val = {
'service_type_id': vendor_bill_service.id,
'vehicle_id': line.vehicle_id.id,
'amount': line.price_subtotal,
'vendor_id': line.partner_id.id,
'description': line.name,
}
log = _('Service Vendor Bill: <a href=# data-oe-model=account.move data-oe-id={move_id}>{move_name}</a>').format(
move_id=line.move_id.id,
move_name=line.move_id.name,
)
val_list.append(val)
log_list.append(log)
log_service_ids = self.env['fleet.vehicle.log.services'].create(val_list)
for log_service_id, log in zip(log_service_ids, log_list):
log_service_id.message_post(body=log)
return posted
class AccountMoveLine(models.Model):
_inherit = 'account.move.line'
vehicle_id = fields.Many2one('fleet.vehicle', string='Vehicle')
need_vehicle = fields.Boolean(compute='_compute_need_vehicle',
help="Technical field to decide whether the vehicle_id field is editable")
def _compute_need_vehicle(self):
self.need_vehicle = False
按照惯例,每个继承的模型都在自己的Python文件中定义。在我们的例子中,它将是models/inherited_model.py。
视图继承
目标
- 链接到销售人员的可用属性列表应显示在其用户窗体视图中
Odoo不是对现有视图进行修改(通过覆盖它们),而是提供视图继承,其中子“扩展”视图应用于根视图之上。这些扩展既可以添加也可以从父视图删除内容。
扩展视图使用 inherit_id 字段引用其父视图。与其单个视图不同,其 arch 字段包含多个 xpath 元素,用于选择和更改其父视图的内容
<record id="inherited_model_view_form" model="ir.ui.view">
<field name="name">inherited.model.form.inherit.test</field>
<field name="model">inherited.model</field>
<field name="inherit_id" ref="inherited.inherited_model_view_form"/>
<field name="arch" type="xml">
<!-- find field description and add the field
new_field after it -->
<xpath expr="//field[@name='description']" position="after">
<field name="new_field"/>
</xpath>
</field>
</record>
expr 表达式
一个XPath表达式,用于选择父视图中的一个元素。如果它没有匹配任何元素或匹配多个元素,则引发错误
position
应用于匹配元素的运算:
inside 在…内
将xpath的body附加到匹配元素的末尾
replace 代替
用xpath的body替换匹配的元素,将新body中出现的任何$0节点替换为原始元素
before 之前
将xpath的body作为同级插入到匹配的元素之前
after 之后
将xpath的body作为匹配元素之后的同级元素插入
attributes 属性,特征
使用XPath主体中的特殊属性元素更改匹配元素的属性
当匹配单个元素时,可以直接在要查找的元素上设置position属性。下面的两个继承具有相同的结果。
<xpath expr="//field[@name='description']" position="after">
<field name="idea_ids" />
</xpath>
<field name="description" position="after">
<field name="idea_ids" />
</field>
可以在这里找到一个视图继承扩展的示例。
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
<odoo>
<record id="view_move_form" model="ir.ui.view">
<field name="name">account.move.form</field>
<field name="model">account.move</field>
<field name="inherit_id" ref="account.view_move_form"/>
<field name="arch" type="xml">
<xpath expr="//field[@name='line_ids']//field[@name='account_id']" position="after">
<field name='need_vehicle' invisible='1'/>
<field name='vehicle_id' attrs="{'required': [('need_vehicle', '=', True), ('parent.move_type', '=', 'in_invoice')], 'column_invisible': [('parent.move_type', '!=', 'in_invoice')]}" optional='hidden'/>
</xpath>
<xpath expr="//field[@name='invoice_line_ids']//field[@name='account_id']" position="after">
<field name='need_vehicle' invisible='1'/>
<field name='vehicle_id' attrs="{'required': [('need_vehicle', '=', True), ('parent.move_type', '=', 'in_invoice')], 'column_invisible': [('parent.move_type', '!=', 'in_invoice')]}" optional='hidden'/>
</xpath>
</field>
</record>
</odoo>
在下一章中,我们将学习如何 与其他模块交互。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 20. C++ strcpy、snprintf、memcpy的区别
- 精度提升10个点!HD-Painter:无需训练的文本引导高分辨率图像修复方案!
- HealthKit 比我更懂大姨妈
- python获取文件的创建日期
- 车手互联是不是杀手锏,来听听一家头部手机厂的座舱方法论
- python--pyQt5 对话框使用(QInputDialog) PySide6
- 软件需求规格说明书
- MicroSD卡如何转接成SD卡?SD卡套
- 使用Python的requests库发送HTTP请求
- 融云获评「全球领航者·年度服务商」,自制《地图》引领行业风潮