leetcode—链表基础
发布时间:2024年01月11日
1 相交链表
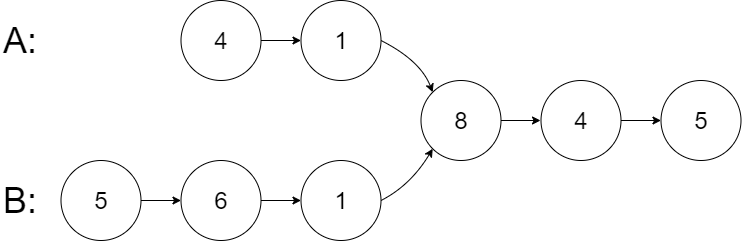
给你两个单链表的头节点?headA?和?headB?,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回?null?。
示例 1:
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 输出:Intersected at '8'
方法一:双指针
链表A的节点个数为a? 链表B的节点个数为b? ?公共链表节点个数为c
- 先遍历A/B链表,当遍历完本身时,再从头遍历B/A链表??
- A链表经过的节点数? a+(b-c)
- B链表经过的节点数 b+(a-c)
- 当A B重合时,找到公共节点? (null? 或者第一个公共节点)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
// 双指针方法
if(headA == null || headB == null){
return null;
}
ListNode pA = headA;
ListNode pB = headB;
// 当两指针相交时,即找到两链表的相交节点
while(pA != pB){
pA = pA == null ? headB : pA.next;
pB = pB == null ?headA : pB.next;
}
return pA;
}
}方法二:借助哈希集合
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
// 构造哈希集合存储链表节点
Set<ListNode> visited = new HashSet<>();
ListNode temp = headA;
// 循环将链表A的节点存入哈希集合中
while(temp != null ){
visited.add(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
temp = headB;
// 依次判断B链表的集合是否在哈希表中
while(temp != null){
// 如果当前节点在哈希表中, 那么B链表的后面节点都在链表中
if(visited.contains(temp)){
return temp;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
return null;
}
}2 反转链表
采用头插法创建一个新的链表? 得到的链表即为反转之后的链表
法一 : 超出时间限制
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// 新建一个链表 用头插法创建新的链表
while(head != null){
addFirst(head, head.val);
}
return head;
}
public void addFirst(ListNode head ,int data){
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
// 让node的地址指向头部
node.next = head;
// 原来的表头节点指向node
head = node;
}
}修改之后的代码
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// 新建一个头节点 用于保存反转之后 链表
ListNode newHead = null;
while(head != null){
// 暂存下一个节点
ListNode nextNode = head.next;
// 头插法 将当前节点插入到新链表的头部
head.next = newHead;
newHead = head;
head = nextNode;
}
return newHead;
}
}3 回文链表
方法一
思路:遍历链表,将链表节点中的值存入数组中,然后在使用双指针判断数组中的值是否为回文数
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
// 创建数组 存放链表中节点的值
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 遍历链表
ListNode currNode = head;
while(currNode != null){
list.add(currNode.val);
currNode = currNode.next;
}
// 判断数组中的值是否是回文数
int pre = 0;
int last = list.size() - 1;
while(pre <= last){
if(! list.get(pre).equals(list.get(last))){
return false;
}
pre++;
last--;
}
return true;
}
}方法二:递归
class Solution {
ListNode frontNode;
public boolean isPalindromeHelp(ListNode currNode){
if(currNode != null){
if(! isPalindromeHelp(currNode.next)){
return false;
}
if(currNode.val != frontNode.val){
return false;
}
frontNode = frontNode.next;
}
return true;
}
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
frontNode = head;
return isPalindromeHelp(head);
}
}?4?合并两个有序链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的?升序?链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。?
示例 1:

输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4] 输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
// 若list1 或者 list2 有其中一个为空 则返回另一个有序链表
if(list1 == null){
return list2;
}else if(list2 == null){
return list1;
}else if(list1.val < list2.val){
// 若链表1的节点小于2 则链接到链表1 然后用1的下一个节点同链表2的当前节点进行递归比较
list1.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next, list2);
return list1;
}else {
list2.next = mergeTwoLists(list2.next, list1);
return list2;
}
}
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_67281369/article/details/135462782
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 扎根底层技术,推动机器人换代式升级
- 新手怎么入行SEM
- 深度学习笔记(八)——构建网络的常用辅助增强方法:数据增强扩充、断点续训、可视化和部署预测
- 如何阅读论文?
- VMware设置
- 如何使用Idea生成war包-创建工件
- 《高教学刊》是什么级别的期刊?是正规期刊吗?是核心期刊吗?
- 06、Kafka ------ 各个功能的作用解释(ISR 同步副本、非同步副本、自动创建主题、修改主题、删除主题)
- 盲盒商城源码/ 盲盒开箱源码/ 仿CSGO盲盒开箱源码/盲盒商城源码系统附源码
- 人话说LightGBM