数据库基础-多表查询
数据库笔记链接
? ? ? ? ?数据库基础-SQL语句
?????????数据库基础-函数
?????????数据库基础-约束
????????数据库基础-多表查询
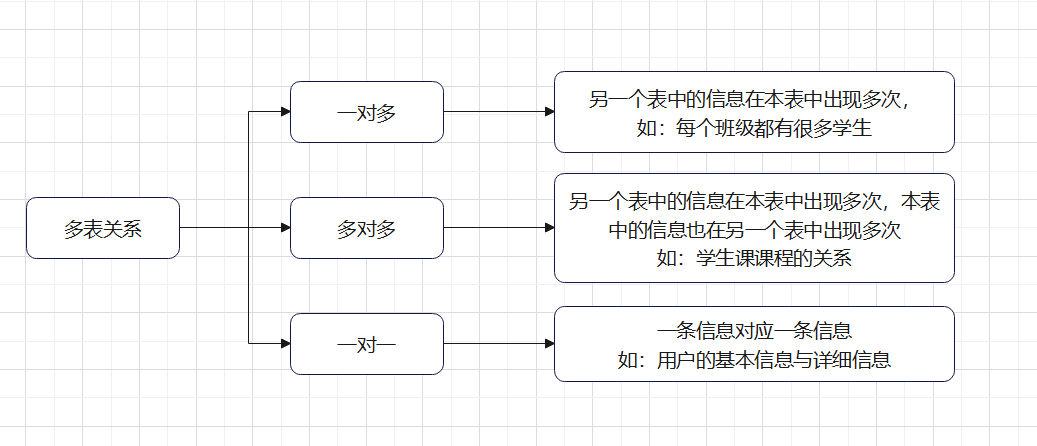
1.多表关系
? ? ? ? 项目开发中,在进行数据库结构设计时,会根据业务需求及业务模块之间的关系,分析并设计表结构,由于业务之间相互关联,以各个表结构之间也存在着各种联系,基本分为三种:
 ?
?
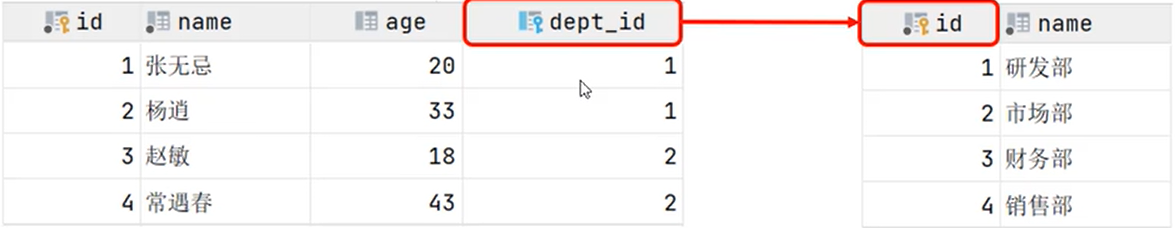
1.1一对多
比如部门和员工之间的关系,员工属于一个部门,但一个部门对应多个员工
实现:在多的一方建立外键,指向一的一方的主键
 ?
?
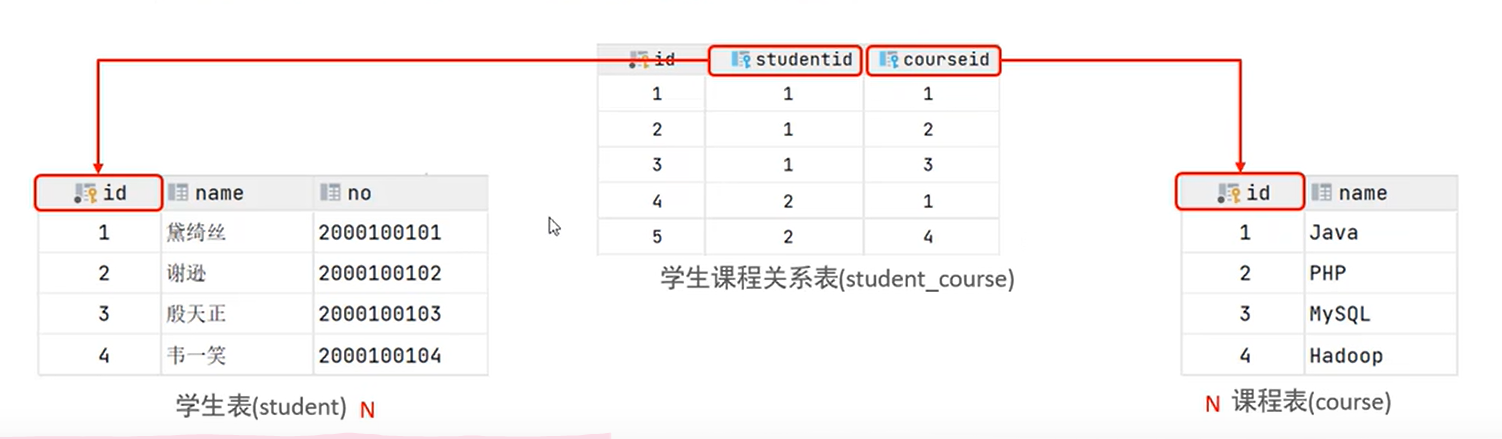
1.2多对多
举例:学生和课表的关系
关系:学生可以选择多门课程,课程可以被多名学生选择
实现:建立第三张中间表,中间表至少包含两个外键,分别关联两方主键
 ?
?
代码实现
create database test;
use test;
create table student(
id int primary key auto_increment comment '主键ID',
name varchar(10) comment '姓名',
no varchar(10) comment '学号'
)comment '学生表';
insert into student values(null, '我是一号', '2024001'),(null, '我是二号', '2024002'),(null, '我是三号', '2024003');
create table course(
id int auto_increment primary key comment '主键ID',
name varchar(10) comment '课程名称'
) comment '课程表';
insert into course(name) values('Python'), ('数据库概论'), ('离散数学'), ('Java');
create table student_course(
id int auto_increment primary key comment '主键ID',
studentid int not null comment '学生ID',
courseid int not null comment '课程ID',
constraint fk_studentid foreign key(studentid) references student(id),
constraint fk_sourseid foreign key(courseid) references course(id)
) comment '学生课程中间表'
insert into student_course values(null, 1, 1), (null, 1, 2), (null, 2, 1), (null, 2, 4), (null, 3, 2), (null, 3, 3); 1.3一对一
案例:用户与用户详细信息的情况
关系:一对一的关系,多用于单表拆分,将一张表的基础字段放在一张表中,其他详情字段放在另一张表中,以提升操作效率
 ?
?
经过才分后,变为基础信息表和学历信息表两部分
实现:在任意一方加入外键,关联另一方的主键,并且设置外键为唯一的(unique)
 ?
?
2.多表查询概念
 ?
?
-- 若直接查询就等于
select * from 表名1, 表名1; -- 这样会产生笛卡尔积,会输出大量无效信息 ?
?
-- 所以应该where在外键等于主键的时候输出
select * from emp, dept where emp.dept_id = dept.id;3.内连接
-- 内连接演示
-- 查询员工姓名,及关联的部门名称(隐式内连接实现)
-- 表结构emp, dept
-- 连接条件:emp.dept_id = dept.id
select emp.name, dept.name from emp, dept where emp.dept_id = dept.id;
-- 查询员工姓名,及关联的部门名称(显式内连接实现)
-- 表结构emp, dept
-- 连接条件:emp.dept_id = dept.id
select e.name, d.name from emp e [inner] join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;4.外连接
外连接和内连接的区别:
若表一中有些数据在外键那一栏为空,在表2中不存在空,那么就查不到这一条信息,但是外连接是首先查询出一个表的所有信息,然后再通过外键去另一个表找对应信息,无论是否为空都奖显示出来。
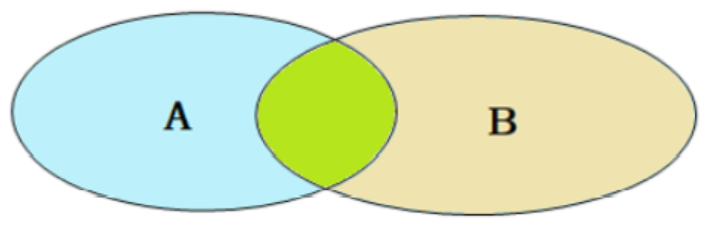 ?
?
左外连接
左外连接相当于查询表A(左表)的所有数据和中间绿色的交集部分的数据。
表1的位置为左表,表2的位置为右表
select 字段列表
from 表1
left 【outer】 join 表2
on 条件...
?查询emp表的所有数据, 和对应的部门信息
由于需求中提到,要查询emp的所有数据,所以是不能内连接查询的,因为有一些中间数据查询不到,需要考虑使用外连接查询。
表结构: emp, dept
连接条件: emp.dept_id = dept.id
(左外连接)
select e.*, d.name
from emp as e
left outer join dept as d
on e.dept_id = d.id
右外连接
右外连接相当于查询表B(右表)的所有数据和中间绿色的交集部分的数据。
表1的位置为左表,表2的位置为右表
select 字段列表
from 表1
right 【outer】 join 表2
on 条件...
?查询dept表的所有数据, 和对应的员工信息
?将右外改为左外
?想把右外连接改成左外连接,并且查询结果不改变,可以把right改为left,并且把表1和表2的位置调换一下
select d.*, e.*
from dept as d
left outer join emp as e
on e.dept_id = d.id;
5.自连接
-- 自连接查询语法
select 字段列表 from 表A 别名A join 表A 别名B on 条件;注意:自连接表一定要起别名
对于自连接查询,可以是内连接查询,也可以是外连接查询。
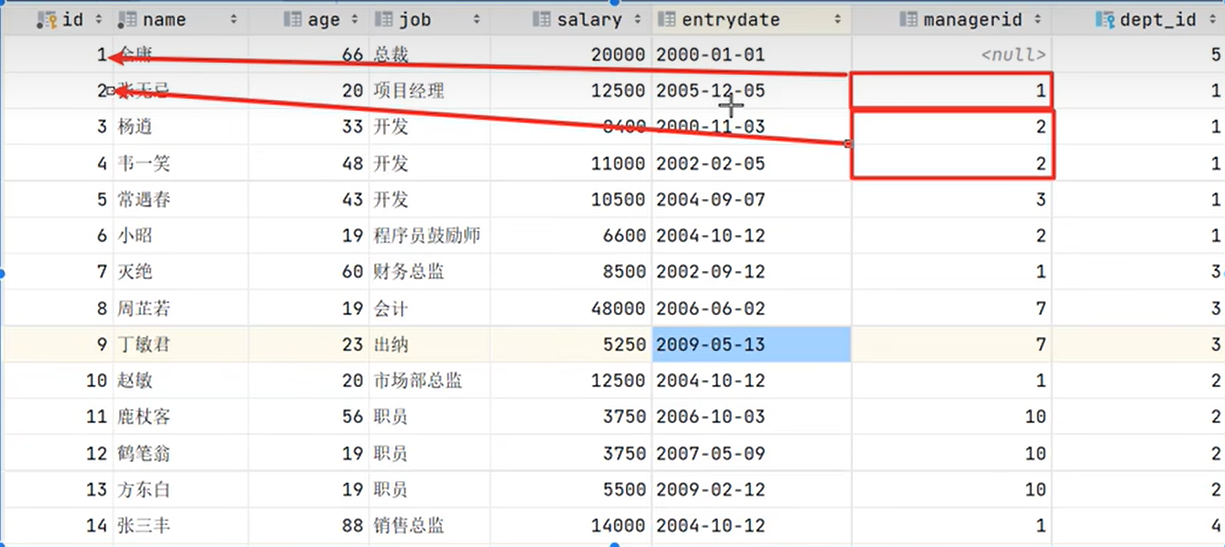 ?
?
例如上图:查询员工信息及其所属领导的名字
普通员工和领导其实都属于员工,都在员工表当中,每个员工又有一项manager_id记录这他的领导的id值
用内连接如下
select a.name, b.name
from
emp as a, emp as b
where a.managerid = b.id;当没有领导时也需要查询信息时用外连接如下:
select a.name, b.name
form emp as a
left outer join emp as b
on a.managerid = b.id;?6.联合查询-union, union all
对于union查询,就是吧多次查询的结果合并起来,形成一个新的查询结果集
select 字段列表 from 表A..
union [all]
select 字段列表 from 表B...;
-- 加上all指吧两次查询结果全部输出
-- 不加则是去重之后输出
?对于联合查询的多张表的列数必须保持一致,字段类型也需要保持一致
union all会将全部的数据直接合并在一起,union会对合并之后的数据去重。
7.子查询
SQL语句中嵌套select语句, 称为嵌套查询, 又称子查询
select * from t1 where colum1 = (select column1 from t2);?子查询外部的语句可以是insert/update/delete/select的任何一个
根据子查询的位置可以分为where之后、from之后、select之后。
7.1标量子查询(子查询结果为单个值)
该查询返回的结果为单个值(数组、字符串、日期等), 最简单的形式,这种子查询称为标量子查询。
# 1.查询销售部的成员信息
-- dept是部门信息表
-- emp是员工信息表
a.从dept中查询销售表的主键ID
select id from dept where name = '销售部';
b.通过第一步查询到的ID到emp表中查询相关的员工信息
-- select * from emp where dept_id = id; 是这样的一个形式,id就是步骤a的查询结果
-- 两次操作合并后就等于
select * from emp where dept_id = (select id from dept where name = '销售部');
# 2.查询入职时间晚于李牛的入职时间
a.从emp中查询李牛的入职时间
select entrydate from emp where name = '李牛'; -- 返回结果为date
b.再根据查询到的入职时间date查询
select * from emp where entrydate > date;
-- 联合之后为
select * from emo where entrydate > (select entrydate from emp name = '李牛');7.2列子查询(子查询结果为一列)
子查询返回的结果是一列(可以是多行),这种查询称为列子查询.
常用的操作符:IN、NOT IN、ANY、SOME、ALL
 ?
?
# 1.查询销售部和市场部的所有员工信息
-- dept是部门信息表
-- emp是员工信息表
a.查询dept表中这两个部门的主键ID
select id from dept where name in('销售部', '市场部'); -- 得到结果2,4
b.根据部门ID在emp表中查询员工信息
select * from emp where dept_id in(2, 4);
-- 等价于
select * from emp where dept_id in(select id from dept where name in('销售部', '市场部'));
# 2.查询比财务部所有人工资都高的员工信息 -- 主要是使用all操作,可以用max更简单的操作
a.查询所有财务部人员工资
select id from dept where name = '财务部';
select salary from emp where dept_id = (select id from dept where name = '财务部');
b.比财务部所有人工资都高的员工信息
select * from emp where salary > all(select salary from emp where dept_id = (
select id from dept where name = '财务部'));
# 3.查询比财研发部任意一人工资高的员工信息 -- 使用any操作,同2
select * from emp where salsry > any(select salary from emp where dept_id = (
select id from dept where name = '研发部'));
7.3行子查询(子查询结果为一行)
子查询返回的结果是一行(可以是多列)
常用操作符: =、? <>、 IN、 NOT IN
# 查询和张无忌直属部门相同且领导相同的信息
a.查询张无忌的直属部门和领导
select dept_id, managerid from emp where name = '张无忌';
b.查询与张无忌部门与领导相同的信息
select * from emp where (dept_id, managerid) = (select dept_id, managerid
from emp where name = '张无忌');
7.4表子查询(子查询结果为多行多列)
子查询返回的是多行多列,有时将其作为一张表去查询
常用操作符为IN
# 1.查询和李牛,张无忌,职位和薪资相同的员工信息
a.查询他们的薪资和职位
select job, salary from emp where name in ( '李牛', '张无忌' );
b.查询信息相同的员工信息
select * fromm emp where (job, salary) in ( select job, salary from emp where
name in ( '李牛', '张无忌' ) );
# 2.查询入职信息在2006-01-01之后的员工信息,及其部门信息
a.查询入职时间在2006-01-01之后的员工信息
select * from emp where entrydate > '2006-01-01';
b.将上述信息作为一张表来处理
select e.*, d.name from (select * from emp where entrydate > '2006-01-01') as e left join
dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 轻量封装WebGPU渲染系统示例<50>- Json数据描述材质等3D渲染场景信息
- 微信小程序---如何创建分包
- MFC:CDC 类与成员
- 2.右值引用和移动语义
- 开源堡垒机JumpServer本地安装并配置公网访问地址
- Golang学习之路一七fmt的使用
- SOME/IP SubscriberEventGroup
- webpack如何把dist.js中某个模块js打包成一个全局变量,使得在html引入dist.js后可以直接访问
- 分块矩阵的定义、计算
- RC4加解密源码