几种常见的CSS三栏布局?介绍下粘性布局(sticky)?自适应布局?左边宽度固定,右边自适应?两种以上方式实现已知或者未知宽度的垂直水平居中?
几种常见的CSS三栏布局
流体布局
效果:

参考代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>流体布局</title>
<style>
.left {
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 200px;
background: lightcoral;
}
.right {
float: right;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: lightblue;
}
.main {
margin-left: 120px;
margin-right: 220px;
height: 200px;
background: lightgreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="right"></div>
<div class="main"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
圣杯布局
效果:

参考代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>圣杯布局</title>
<style>
.container {
margin-left: 120px;
margin-right: 220px;
}
.main {
float: left;
width: 100%;
height: 300px;
background: lightgreen;
}
.left {
position: relative;
left: -120px;
float: left;
height: 300px;
width: 100px;
margin-left: -100%;
background: lightcoral;
}
.right {
position: relative;
right: -220px;
float: right;
height: 300px;
width: 200px;
margin-left: -200px;
background: lightblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="main"></div>
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="right"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
双飞翼布局
效果:

参考代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>双飞翼布局</title>
<style>
.content {
float: left;
width: 100%;
}
.main {
height: 200px;
margin-left: 110px;
margin-right: 220px;
background: lightgreen;
}
.main::after {
content: '';
display: block;
font-size: 0;
height: 0;
zoom: 1;
clear: both;
}
.left {
float: left;
height: 200px;
width: 100px;
margin-left: -100%;
background: lightcoral;
}
.right {
float: right;
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
margin-left: -200px;
background: lightblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="content">
<div class="main"></div>
</div>
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="right"></div>
</body>
</html>
灵活布局(Flexbox)
效果:

代码参考:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>灵活布局(Flexbox)</title>
<style>
.container {
display: flex;
}
.left, .right {
flex: 0 0 200px; /* 不放大,不缩小,初始宽度 200px */
}
.left {
background-color: lightblue;
}
.right {
background-color: lightcoral;
}
.center {
flex: 1; /* 自适应宽度 */
background-color: lightgreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="left">Left</div>
<div class="center">Center</div>
<div class="right">Right</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
灵活布局:使用flex布局,设置display: flex,左右两栏flex: 0 0 200px,中间自适应。
定位布局
效果:

参考代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>定位布局 </title>
<style>
.container {
position: relative;
width: 100%;
}
.left, .right {
position: absolute;
width: 200px;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
}
.left {
left: 0;
background-color: lightblue;
}
.right {
right: 0;
background-color: lightcoral;
}
.center {
margin: 0 200px; /* 左右两栏宽度之和 */
background-color: lightgreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="left">Left</div>
<div class="right">Right</div>
<div class="center">Center</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
定位布局:使用position属性,左右两栏设置为position: absolute,中间自适应。
Grid 布局
效果:

代码参考:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Grid 布局</title>
<style>
.container {
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: 200px auto 200px;
}
.left {
background-color: lightblue;
}
.right {
background-color: lightcoral;
}
.center {
background-color: lightgreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="left">Left</div>
<div class="center">Center</div>
<div class="right">Right</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
使用 CSS Grid 属性,定义网格布局,可以轻松实现三栏布局。
介绍下粘性布局(sticky)
粘性布局(sticky)是 CSS3 中新增的一种定位方式。当一个元素被设置为 sticky 时,它会在页面滚动时保持在特定位置,直到滚动到指定的偏移值之后,此时元素将变成固定定位(fixed),并保持在屏幕上的位置。这样可以确保用户在浏览网页时能够轻松访问重要的导航或其他相关信息,提供更好的用户体验。
这里有几个要点需要注意:
-
文档流和定位影响:与 fixed 定位不同,sticky 元素并不脱离文档流,仍然保留元素原本在文档中的位置。
-
相对偏移计算:元素的固定位置是相对于离它最近的具有滚动功能的祖先元素计算的。如果没有滚动的祖先元素,那么偏移量将相对于视口(viewport)进行计算。
-
滚动过程中的行为:当页面滚动时,sticky 元素会固定在特定位置,直到滚动到指定的偏移值,然后它将变成固定定位。
自适应布局
自适应布局是指网页能够根据不同设备的屏幕尺寸和分辨率进行自动调整,以确保页面内容完整显示,而不会因为屏幕尺寸过小而导致出现滚动条。
在两栏布局中,常见的一种做法是将左侧栏设置为固定宽度,而右侧栏则会自动填充剩余空间。这可以通过以下方式实现:
- 将左侧栏使用浮动或者绝对定位固定在左侧,然后给右侧栏添加边距使其自动填充空间。
- 使用一个包裹性的
<div>标签将两栏包裹起来,然后给右侧栏添加负边距来创建块级格式化上下文(BFC),从而实现两栏自动排列。 - 使用 CSS 弹性盒子布局(Flexbox),可以简单地实现一栏固定宽度,一栏自动填充的两栏布局。
以上是一些常见的自适应布局方法,但具体实现还需根据实际情况选择合适的技术方案。总的来说,自适应布局可以让网页内容能够自动适应不同屏幕,从而给用户带来更好的阅读体验。
左边宽度固定,右边自适应
左边固定宽度,右边自适应的布局可以通过使用 float 或者 Flexbox 来实现。左侧元素设置固定宽度,而右侧元素则会根据剩余空间自动调整宽度。
HTML结构如下:
<div class="outer">
<div class="left">固定宽度</div>
<div class="right">自适应宽度</div>
</div>
在外层 div(类名为 outer)中,有两个子 div,类名分别为 left 和 right。其中 left 为固定宽度,而 right 为自适应宽度。
以下是几种常见的实现方法:
方法1: 使用浮动
效果:

参考代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<style>
.outer {
width: 100%;
height: 200px;
background-color: yellow;
}
.left {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: red;
float: left;
}
.right {
height: 200px;
background-color: blue;
overflow: hidden; /* 清除浮动 */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="outer">
<div class="left">固定宽度</div>
<div class="right">自适应宽度</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
方法2: 使用绝对定位
效果:

参考代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<style>
.outer {
width: 100%;
height: 200px;
background-color: yellow;
position: relative;
}
.left {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: red;
position: absolute;
}
.right {
height: 200px;
background-color: blue;
margin-left: 200px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="outer">
<div class="left">固定宽度</div>
<div class="right">自适应宽度</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
方法3: 使用绝对定位和 margin
效果:

参考代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<style>
.outer {
width: 100%;
height: 200px;
background-color: yellow;
position: relative;
}
.left {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: red;
position: absolute;
}
.right {
height: 200px;
background-color: blue;
margin-left: 200px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="outer">
<div class="left">固定宽度</div>
<div class="right">自适应宽度</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
方法4: 使用Flexbox布局
效果:

参考代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<style>
.outer {
width: 100%;
height: 200px;
background-color: yellow;
display: flex;
}
.left {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: red;
}
.right {
height: 200px;
background-color: blue;
flex: 1;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="outer">
<div class="left">固定宽度</div>
<div class="right">自适应宽度</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
这四种方法的优缺点:
方法1: 使用浮动
- 优点: 浏览器兼容性较好,适用于较为古老的浏览器。
- 缺点: 需要清除浮动以避免影响其他元素布局,可能导致一些意外的显示问题。
方法2: 使用绝对定位
- 优点: 可以精确地控制元素的位置,适合一些特定的布局需求。
- 缺点: 如果页面结构发生变化,需要手动调整绝对定位元素的位置,不够灵活。
方法3: 使用绝对定位和 margin
- 优点: 具有一定的灵活性,可以在保持左侧固定宽度的同时让右侧自适应。
- 缺点: 当页面结构复杂时,可能需要更多的调整来确保布局的稳定性。
方法4: 使用Flexbox布局
- 优点: 简单、直观,能够轻松实现左右布局,且支持响应式设计。
- 缺点: 对于一些较老版本的浏览器支持不够完善,需要额外处理兼容问题。
两种以上方式实现已知或者未知宽度的垂直水平居中
已知宽度的垂直水平居中、未知宽度的垂直水平居中(使用 Flexbox 布局)和未知宽度的垂直水平居中(使用表格布局)
效果:
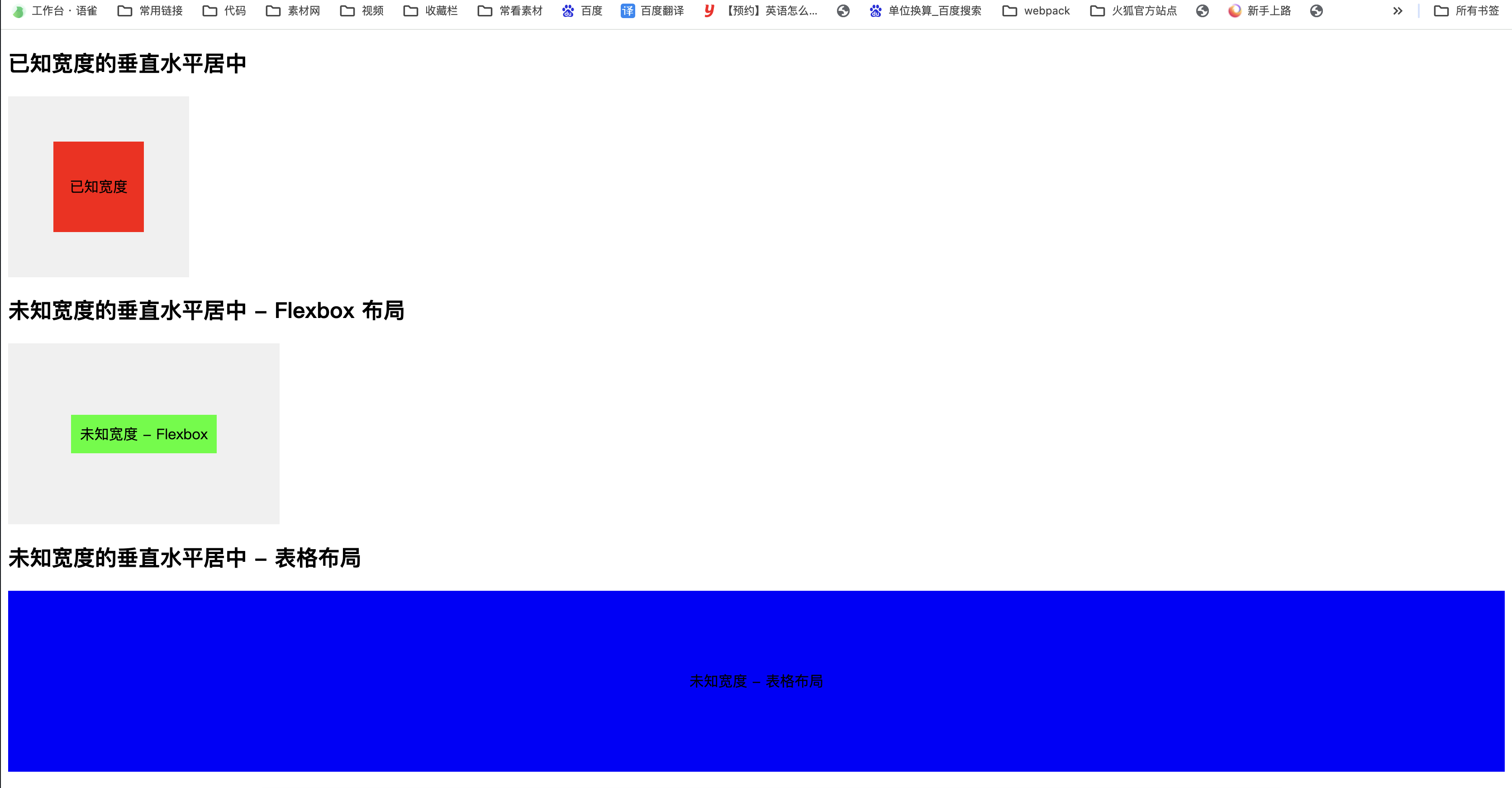
以下HTML 文件,包括已知宽度和未知宽度的垂直水平居中效果的示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<style>
/* 已知宽度的垂直水平居中 */
.wrapper {
position: relative;
width: 200px; /* 假设容器宽度为 200px */
height: 200px; /* 假设容器高度为 200px */
background-color: #f0f0f0;
}
.box {
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
margin-top: -50px; /* 将上边距设为自身高度的一半 */
margin-left: -50px; /* 将左边距设为自身宽度的一半 */
background-color: #ff0000;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
}
/* 未知宽度的垂直水平居中 - Flexbox 布局 */
.wrapper-flex {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
width: 300px; /* 假设容器宽度为 300px */
height: 200px; /* 假设容器高度为 200px */
background-color: #f0f0f0;
}
.box-flex {
background-color: #00ff00;
padding: 10px;
}
/* 未知宽度的垂直水平居中 - 表格布局 */
.wrapper-table {
display: table;
width: 100%;
height: 200px; /* 假设容器高度为 200px */
background-color: #f0f0f0;
}
.box-table {
display: table-cell;
text-align: center;
vertical-align: middle;
background-color: #0000ff;
}
</style>
<title>垂直水平居中示例</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>已知宽度的垂直水平居中</h2>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="box">已知宽度</div>
</div>
<h2>未知宽度的垂直水平居中 - Flexbox 布局</h2>
<div class="wrapper-flex">
<div class="box-flex">未知宽度 - Flexbox</div>
</div>
<h2>未知宽度的垂直水平居中 - 表格布局</h2>
<div class="wrapper-table">
<div class="box-table">未知宽度 - 表格布局</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
说出 space-between 和 space-around 的区别?
space-between 和 space-around 是 Flexbox 布局中的两种对齐方式,它们的区别在于间距的分配方式。
space-between:这个值会使得项目沿着主轴均匀分布,并且首个元素位于起始位置,末尾元素位于结束位置,中间的元素则平均分布在主轴上,没有额外的空白间隔。
space-around:该值会使得项目沿着主轴均匀分布,并且在每个项目周围均匀留有相等的空白空间,使得项目之间和项目与容器边界之间的空白空间大小相等。
这两种对齐方式的主要区别在于 space-around 在每个项目周围均匀留有空白空间,而 space-between 则只在首尾没有额外的空白空间。
持续学习总结记录中,回顾一下上面的内容:
几种常见的CSS三栏布局?介绍下粘性布局(sticky)?自适应布局?左边宽度固定,右边自适应?两种以上方式实现已知或者未知宽度的垂直水平居中?
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 如何防范采购过程中招投标隐患,泛微京桥通帮您建好“防护网”
- EI顶刊复现:考虑源荷不确定性的综合能源运行调度与容量配置两阶段随机优化模型程序代码!
- Android 12+ MQTT适配
- Go语言实现数据结构栈和队列
- MIT6.5840-2023-Lab4A: Sharded K/V Service-The Shard controller
- springboot整合swagger
- Web APIs知识点讲解
- 什么是跨站脚本攻击(XSS)?如何防止它?
- CTFhub-目录遍历
- L1-093:猜帽子游戏