6.23删除二叉搜索树中的节点(LC450-M)
发布时间:2023年12月17日
算法:
一共有五种可能的情况:
- 第一种情况:没找到删除的节点,遍历到空节点直接返回了
- 找到删除的节点
- 第二种情况:左右孩子都为空(叶子节点),直接删除节点, 返回NULL为根节点
- 第三种情况:删除节点的左孩子为空,右孩子不为空,删除节点,右孩子补位,返回右孩子为根节点
- 第四种情况:删除节点的右孩子为空,左孩子不为空,删除节点,左孩子补位,返回左孩子为根节点
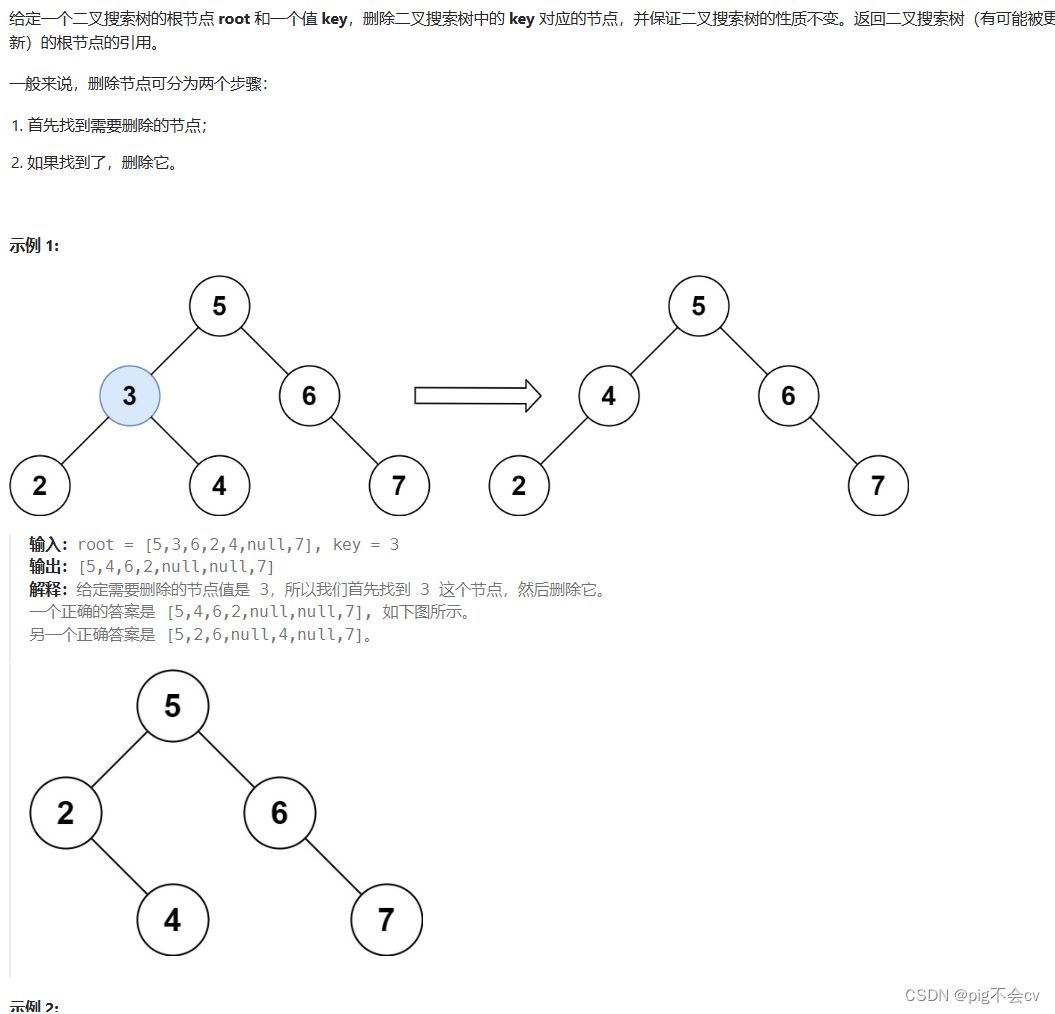
- 第五种情况:左右孩子节点都不为空,则将删除节点的左子树头结点(左孩子)放到删除节点的右子树的最左面节点的左孩子上,返回删除节点右孩子为新的根节点。
第五种情况,比如要删除节点7,可以让它的左孩子或者右孩子去继位。这里是让左孩子去继位,左孩子比7小,右孩子比7大,那左孩子应该继位在右孩子的最小的节点的左边,即8左边。然后,让3指向9。
调试过程:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if (root == null) return root;
//1.找不到key节点,自动返回原root
if (root.val == key) {
//2.左右都空,说明是叶子,直接删除
if (root.left==null && root.right==null) return null;
//3.左空右不空,右上移
if (root.left==null && root.right!=null) {
root = root.right;
return root;
}
//4.右空左不空,左上移
if (root.left!=null && root.right==null) {
root = root.left;
return root;
}
//5.左右都不空,root的左孩子移到右孩子的最左边
if (root.left!=null && root.right!=null){
TreeNode left = root.left;
root = root.right;
while (root.left!=null){
root = root.left;
}
root.left = left;
return root;
}
}
if (root.val < key) deleteNode(root.left, key);
if (root.val > key) deleteNode(root.right, key);
return root;
}
}
原因:
左右都不空时,代码有问题。
代码逻辑不对,没有中间变量cur,相当于少了个变量cur去实现交换操作。
而且,递归处没有赋值给root.left和root.right(因为这里的递归是有返回值TreeNode的)!!!!无法真正实现递归(这一点老是忘记)
修改后:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if (root == null) return root;
//1.找不到key节点,自动返回原root
if (root.val == key) {
//2.左右都空,说明是叶子,直接删除
if (root.left==null && root.right==null) return null;
//3.左空右不空,右上移
if (root.left==null && root.right!=null) {
root = root.right;
return root;
}
//4.右空左不空,左上移
if (root.left!=null && root.right==null) {
root = root.left;
return root;
}
//5.左右都不空,root的左孩子移到右孩子的最左边
if (root.left!=null && root.right!=null){
TreeNode cur = root.right;
while (cur.left!=null){
cur = cur.left;
}
cur.left = root.left;
root = root.right;
return root;
}
}
if (root.val < key) root.left=deleteNode(root.left, key);
if (root.val > key) root.right=deleteNode(root.right, key);
return root;
}
}原因:
递归处逻辑不对。
应该是key比root.val小时,向左搜索
应该是key比root.val大时,向右搜索
正确代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if (root == null) return root;
//1.找不到key节点,自动返回原root
if (root.val == key) {
//2.左右都空,说明是叶子,直接删除
if (root.left==null && root.right==null) return null;
//3.左空右不空,右上移
if (root.left==null && root.right!=null) {
root = root.right;
return root;
}
//4.右空左不空,左上移
if (root.left!=null && root.right==null) {
root = root.left;
return root;
}
//5.左右都不空,root的左孩子移到右孩子的最左边
if (root.left!=null && root.right!=null){
TreeNode cur = root.right;
while (cur.left!=null){
cur = cur.left;
}
cur.left = root.left;
root = root.right;
return root;
}
}
if (key< root.val) root.left=deleteNode(root.left, key);
if (key> root.val) root.right=deleteNode(root.right, key);
return root;
}
}时间空间复杂度:
时间复杂度:
O(n),其中 n为 root的节点个数。最差情况下,寻找和删除 cur各需要遍历一次树。
空间复杂度:
O(n),其中 n为 root的节点个数。递归的深度最深为 O(n)。
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_50696252/article/details/134953200
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- jmeter压力测试工具简介
- 视觉检测系统:工厂生产零部件的智能检测
- 139:leafle加载here地图(v3软件多种形式)
- 用 Python 制作可视化 GUI 界面,一键实现自动分类管理文件!
- Squid代理服务器
- PyQt5基础知识第一天
- SpringBoot整合ActiveMQ
- CAS:并发编程的关键技术
- 三分钟学完科研论文常用统计图
- 《剑指 Offer》专项突破版 - 面试题 23 : 两个链表的第 1 个重合节点(C++ 实现)