ResNet网络分析与demo实例
参考自?
- up主的b站链接:霹雳吧啦Wz的个人空间-霹雳吧啦Wz个人主页-哔哩哔哩视频
- 这位大佬的博客?Fun'_机器学习,pytorch图像分类,工具箱-CSDN博客
?ResNet 详解
原论文地址?[1512.03385] Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition (arxiv.org)
ResNet 网络是在?2015年?由微软实验室提出,斩获当年ImageNet竞赛中分类任务第一名,目标检测第一名。获得COCO数据集中目标检测第一名,图像分割第一名。
在ResNet网络的创新点:
- 提出?Residual?结构(残差结构),并搭建超深的网络结构(可突破1000层)
- 使用?Batch Normalization?加速训练(丢弃dropout)
下图是ResNet34层模型的结构简图:

在ResNet网络提出之前,传统的卷积神经网络都是通过将一系列卷积层与池化层进行堆叠得到的。
一般我们会觉得网络越深,特征信息越丰富,模型效果应该越好。但是实验证明,当网络堆叠到一定深度时,会出现两个问题
梯度消失或梯度爆炸
退化问题
如下图所示,20层网络 反而比 56层网络 的误差更小:

对于梯度消失或梯度爆炸问题,ResNet论文提出通过数据的预处理以及在网络中使用
?BN(Batch Normalization)层来解决。
对于退化问题,ResNet论文提出了?residual结构(残差结构)来减轻退化问题,下图是使用residual结构的卷积网络,可以看到随着网络的不断加深,效果并没有变差,而是变的更好了。(虚线是train error,实线是test error)

为了解决深层网络中的退化问题,可以人为地让神经网络某些层跳过下一层神经元的连接,隔层相连,弱化每层之间的强联系。这种神经网络被称为 残差网络 (ResNets)。
残差网络由许多隔层相连的神经元子模块组成,我们称之为 残差块 Residual block。单个残差块的结构如下图所示:


原文的表注中已说明,conv3_x, conv4_x, conv5_x所对应的一系列残差结构的第一层残差结构都是虚线残差结构。因为这一系列残差结构的第一层都有调整输入特征矩阵shape的使命(将特征矩阵的高和宽缩减为原来的一半,将深度channel调整成下一层残差结构所需要的channel)
需要注意的是,对于ResNet50/101/152,其实conv2_x所对应的一系列残差结构的第一层也是虚线残差结构,因为它需要调整输入特征矩阵的channel。根据表格可知通过3x3的max pool之后输出的特征矩阵shape应该是[56, 56, 64],但conv2_x所对应的一系列残差结构中的实线残差结构它们期望的输入特征矩阵shape是[56, 56, 256](因为这样才能保证输入输出特征矩阵shape相同,才能将捷径分支的输出与主分支的输出进行相加)。所以第一层残差结构需要将shape从[56, 56, 64] --> [56, 56, 256]。注意,这里只调整channel维度,高和宽不变(而conv3_x, conv4_x, conv5_x所对应的一系列残差结构的第一层虚线残差结构不仅要调整channel还要将高和宽缩减为原来的一半)。
下面是 ResNet 18/34 和 ResNet 50/101/152 具体的实线/虚线残差结构图:
?
ResNet 18/34

ResNet 50/101/152s

在迁移学习中,我们希望利用源任务(Source Task)学到的知识帮助学习目标任务 (Target Task)。例如,一个训练好的图像分类网络能够被用于另一个图像相关的任务。再比如,一个网络在仿真环境学习的知识可以被迁移到真实环境的网络。迁移学习一个典型的例子就是载入训练好VGG网络,这个大规模分类网络能将图像分到1000个类别,然后把这个网络用于另一个任务,如医学图像分类。
为什么可以这么做呢?如下图所示,神经网络逐层提取图像的深层信息,这样,预训练网络就相当于一个特征提取器。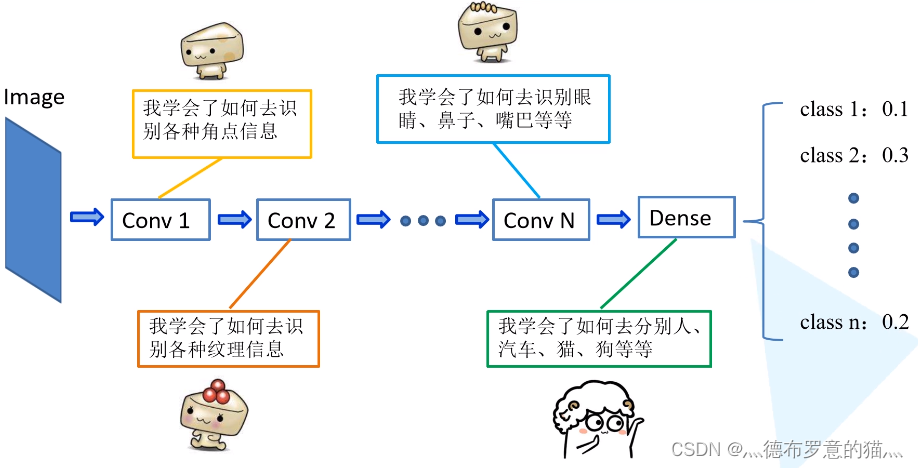
model.py
- 定义ResNet18/34的残差结构,即BasicBlock
- 定义ResNet50/101/152的残差结构,即Bottleneck
- 定义ResNet网络结构
- 定义resnet18/34/50/101/152
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
# ResNet18/34的残差结构,用的是2个3x3的卷积
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1 # 残差结构中,主分支的卷积核个数是否发生变化,不变则为1
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride=1, downsample=None): # downsample对应虚线残差结构
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.downsample = downsample
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
if self.downsample is not None: # 虚线残差结构,需要下采样
identity = self.downsample(x) # 捷径分支 short cut
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
# ResNet50/101/152的残差结构,用的是1x1+3x3+1x1的卷积
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
expansion = 4 # 残差结构中第三层卷积核个数是第一/二层卷积核个数的4倍
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride=1, downsample=None):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False) # squeeze channels
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
# -----------------------------------------
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3, stride=stride, bias=False, padding=1)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
# -----------------------------------------
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channel, out_channels=out_channel * self.expansion,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False) # unsqueeze channels
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel * self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x) # 捷径分支 short cut
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class ResNet(nn.Module):
# block = BasicBlock or Bottleneck
# block_num为残差结构中conv2_x~conv5_x中残差块个数,是一个列表
def __init__(self, block, blocks_num, num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
self.include_top = include_top
self.in_channel = 64
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, self.in_channel, kernel_size=7, stride=2,
padding=3, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.in_channel)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, blocks_num[0]) # conv2_x
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, blocks_num[1], stride=2) # conv3_x
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, blocks_num[2], stride=2) # conv4_x
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, blocks_num[3], stride=2) # conv5_x
if self.include_top:
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)) # output size = (1, 1)
self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
# channel为残差结构中第一层卷积核个数
def _make_layer(self, block, channel, block_num, stride=1):
downsample = None
# ResNet50/101/152的残差结构,block.expansion=4
if stride != 1 or self.in_channel != channel * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.in_channel, channel * block.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(channel * block.expansion))
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.in_channel, channel, downsample=downsample, stride=stride))
self.in_channel = channel * block.expansion
for _ in range(1, block_num):
layers.append(block(self.in_channel, channel))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
if self.include_top:
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
def resnet34(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
return ResNet(BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
def resnet101(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
train.py
由于ResNet网络较深,直接训练的话会非常耗时,因此用迁移学习的方法导入预训练好的模型参数:
在pycharm中输入import torchvision.models.resnet,ctrl+左键resnet跳转到pytorch官方实现resnet的源码中,下载预训练的模型参数:
?
model_urls = {
'resnet18': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet18-5c106cde.pth',
'resnet34': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet34-333f7ec4.pth',
'resnet50': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet50-19c8e357.pth',
'resnet101': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet101-5d3b4d8f.pth',
'resnet152': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet152-b121ed2d.pth',
'resnext50_32x4d': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnext50_32x4d-7cdf4587.pth',
'resnext101_32x8d': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnext101_32x8d-8ba56ff5.pth',
'wide_resnet50_2': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/wide_resnet50_2-95faca4d.pth',
'wide_resnet101_2': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/wide_resnet101_2-32ee1156.pth',
}
import torch
from model import resnet34
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import json
data_transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.Resize(256),
transforms.CenterCrop(224),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])])
# load image
img = Image.open("../tulip.jpg")
plt.imshow(img)
# [N, C, H, W]
img = data_transform(img)
# expand batch dimension
img = torch.unsqueeze(img, dim=0)
# read class_indict
try:
json_file = open('./class_indices.json', 'r')
class_indict = json.load(json_file)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
exit(-1)
# create model
model = resnet34(num_classes=5)
# load model weights
model_weight_path = "./resNet34.pth"
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_weight_path))
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
# predict class
output = torch.squeeze(model(img))
predict = torch.softmax(output, dim=0)
predict_cla = torch.argmax(predict).numpy()
print(class_indict[str(predict_cla)], predict[predict_cla].numpy())
plt.show()
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!