第10章_多线程扩展练习(Thread类中的方法,线程创建,线程通信)
文章目录
第10章_多线程扩展练习
Thread类中的方法
1、新年倒计时
模拟新年倒计时,每隔1秒输出一个数字,依次输出10,9,8…1,最后输出:新年快乐!
public class Exercise1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 10; i>=0; i--) {
System.out.println(i);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("新年快乐!");
}
}
线程创建
2、奇偶数输出
案例:在子线程中输出1-100之间的偶数,主线程输出1-100之间的奇数。
效果如下:

public class Exercise2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread("子线程"){
public void run(){
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i+=2) {
System.out.println(getName() + "-->" + i);
}
}
}.start();
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i+=2) {
System.out.println("main主线程 -->" + i);
}
}
}
3、强行加塞
自定义线程类ChatThread:问是否结束(输入Y/y结束),如果输入的不是y,继续问是否结束,直到输入y才结束。
打印[1,10],每隔10毫秒打印一个数字,现在当主线程打印完5之后,就让自定义线程类加塞,直到自定义线程类结束,主线程再继续。
public class ChatThread extends Thread{
public void run(){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true){
System.out.print("是否结束(Y、N):");
String answer = input.nextLine();
if(!"".equals(answer) && Character.toUpperCase(answer.charAt(0))=='Y'){
break;
}
}
input.close();
}
}
public class Exercise3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
System.out.println("main:" + i);
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//当main打印到5之后,需要等join进来的线程停止后才会继续了。
if(i==5){
ChatThread t = new ChatThread();
t.start();
try {
t.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
4、奇偶数打印
声明一个PrintEvenThread线程类,继承Thread类,重写run方法,实现打印[1,100]之间的偶数,要求每隔1毫秒打印1个偶数。
声明一个PrintOddThread线程类,继承Thread类,重写run方法,实现打印[1,100]之间的奇数。
在main线程中:
(1)创建两个线程对象,并启动两个线程
(2)当打印奇数的线程结束了,让偶数的线程也停下来,就算偶数线程没有全部打印完[1,100]之间的偶数。
public class PrintEvenThread extends Thread{
private boolean flag = true;
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 2; i <= 100 && flag; i += 2) {
System.out.println("偶数线程:" + i);
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void setFlag(boolean flag) {
this.flag = flag;
}
}
public class PrintOddThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i += 2) {
System.out.println("奇数线程:" + i);
}
}
}
public class Exercise4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PrintEvenThread pe = new PrintEvenThread();
PrintOddThread po = new PrintOddThread();
pe.start();
po.start();
try {
po.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
pe.setFlag(false);
}
}
5、龟兔赛跑友谊赛
案例:编写龟兔赛跑多线程程序,设赛跑长度为30米
兔子的速度是10米每秒,兔子每跑完10米休眠的时间10秒
乌龟的速度是1米每秒,乌龟每跑完10米的休眠时间是1秒
要求:要等兔子和乌龟的线程结束,主线程(裁判)才能公布最后的结果。
//提示:System.currentTimeMillis()方法可以返回当前时间的毫秒值(long类型)
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//中间代码
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("中间代码运行耗时:" + (end - start) +"毫秒")
public class Racer extends Thread{
private long meterTime;//跑1米的时间
private long restTime;//跑完10米休息时间
private long time; //记录总用时
//有参构造
public Racer(String name, long meterTime, long restTime) {
super(name);
this.meterTime = meterTime;
this.restTime = restTime;
}
public void run(){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取时间值,现在距离1970-1-1 0.0.0 0的毫秒值
for (int i=1; i<=30; i++){//i单位是米
try {
Thread.sleep(meterTime);
System.out.println(getName() + "已经跑了" + i + "米");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(i==10 || i==20){
System.out.println(getName() +"正在休息....");
Thread.sleep(restTime);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(getName() + "到达终点.");
long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取时间值,现在距离1970-1-1 0.0.0 0的毫秒值
time = end - start;
}
public long getTime() {
return time;
}
}
public class Exercise5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//裁判线程执行(main线程)
Racer r = new Racer("兔子",100,10000);
Racer t = new Racer("乌龟",1000,1000);
r.start();
t.start();
//让r和t线程都结束了,才能继续main
try {
r.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
t.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("兔子用时:" + r.getTime());
System.out.println("乌龟用时:" + t.getTime());
if(r.getTime() < t.getTime()){
System.out.println("兔子赢");
}else if(r.getTime() > t.getTime()){
System.out.println("乌龟赢");
}else{
System.out.println("平局");
}
}
}
6、龟兔赛跑冠军赛
案例:编写龟兔赛跑多线程程序,设赛跑长度为30米
兔子的速度是10米每秒,兔子每跑完10米休眠的时间10秒
乌龟的速度是1米每秒,乌龟每跑完10米的休眠时间是1秒
要求:只要兔子和乌龟中有人到达终点,就宣布比赛结束,没到达终点的选手也要停下来。
public class Sporter extends Thread {
private long meterTime;//跑每米用时
private long restTime;//跑完10米休息的时间
private long time;//从跑到停的时间
private int distance;//当前运动员一共跑了几米
private final int MAX_DISTANCE = 30;
private static boolean flag = true;//true表示跑
//有参构造
public Sporter(String name, long meterTime, long restTime) {
super(name);
this.meterTime = meterTime;
this.restTime = restTime;
}
public void run() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取时间值,现在距离1970-1-1 0.0.0 0的毫秒值
while(distance < MAX_DISTANCE && flag){
try {
Thread.sleep(meterTime);
distance++;
System.out.println(getName() + "已经跑了" + distance + "米");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (distance == 10 || distance == 20) {
System.out.println(getName() + "正在休息....");
Thread.sleep(restTime);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(distance == MAX_DISTANCE){
flag = false;
System.out.println(getName() + "到达终点.");
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取时间值,现在距离1970-1-1 0.0.0 0的毫秒值
time = end - start;
System.out.println(getName() + "停止跑");
}
public long getTime() {
return time;
}
public static boolean isFlag() {
return flag;
}
public int getDistance() {
return distance;
}
}
public class Exercise6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sporter s1 = new Sporter("兔子",100,10000);
Sporter s2 = new Sporter("乌龟",1000,1000);
s1.start();
s2.start();
try {
s1.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
s2.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//宣布结果
if(s1.getDistance() > s2.getDistance()){
System.out.println("兔子赢");
}else if(s1.getDistance() <s2.getDistance()){
System.out.println("乌龟赢");
}else{
//距离一样
//System.out.println("平局");
//如果要再严格一点
if(s1.getTime() < s2.getTime()){
System.out.println("兔子赢");
}else if(s1.getTime() > s2.getTime()){
System.out.println("乌龟赢");
}else{
System.out.println("平局");
}
}
}
}
7、多人过山洞
案例:请按要求编写多线程应用程序,模拟多个人通过一个山洞:
? 1、这个山洞每次只能通过一个人,每个人通过山洞的时间为5秒;
? 2、随机生成10个人,同时准备过此山洞
? 3、定义一个变量用于记录通过隧道的人数
? 4、显示每次通过山洞人的姓名,和通过顺序;
案例运行效果如下:

开发提示:
(1)定义一个隧道类,例如Tunnel,实现Runnable接口:
-
定义一个int类型的变量crossNum,用来记录通过隧道的人数;
-
重写Runnable的run方法,调用通过隧道的方法cross()
-
定义通过隧道的方法void cross(),模拟每个人通过隧道需要5秒钟
- 打印“xx开始通过隧道…”
- 线程睡眠5秒钟,模拟每个人通过隧道需要5秒钟;
- 改变通过的人次;
- 打印线程名称及其通过隧道的顺序,模拟人通过隧道及其顺序;
(2)定义测试类
-
在main方法中创建一个隧道类对象;
-
在main方法中,循环创建10个子线程对象,通过构造方法把隧道对象和线程名(作为人的姓名)传递进去,并开启子线程;
public class Tunnel implements Runnable {
// 1.1 定义一个变量,用来记录通过隧道的人数
private int crossNum = 0;
/*
* 1.2 重写Runnable的run方法
*/
@Override
public void run() {
// 1.4 调用通过隧道的方法
cross();
}
/*
* 1.3 定义一个同步方法,模拟每个人通过隧道需要5秒钟
*/
public synchronized void cross() {
//1.3.1 打印 xx开始通过隧道...
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "开始通过隧道...");
// 1.3.2 子线程睡眠5秒钟,模拟每个人通过隧道需要5秒钟
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 1.3.3 改变通过的人次
crossNum++;
// 1.3.4 打印线程名称及其通过隧道的顺序,模拟人通过隧道及其顺序
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "已经通过隧道,TA是第" + crossNum + "通过的!");
}
}
public class Exercise7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 2.1 在main方法中创建一个隧道类对象
Tunnel tul = new Tunnel();
// 2.2 在main方法中,循环创建10个子线程对象,通过构造方法把隧道对象和// 线程名(作为人的姓名)传递进去,并开启子线程
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
Thread t = new Thread(tul, "p" + i);
t.start();
}
}
}
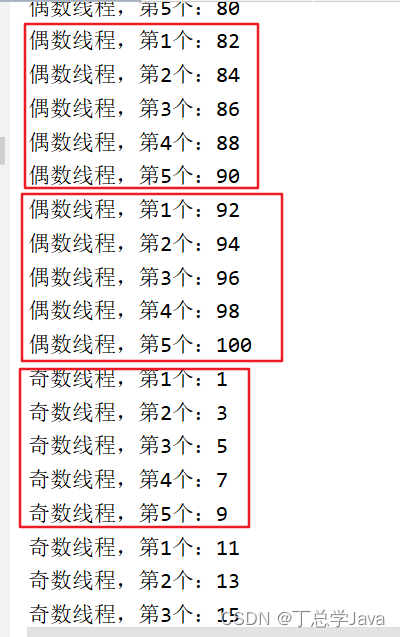
8、奇偶数连续打印
案例:创建和启动2个子线程,一个打印100以内的奇数,一个打印100以内的偶数,
(1)要求每个线程要么不打印,要么就连续打印5个数,每个数打印间隔50毫秒
(2)但两个线程不要求交替打印。
效果如下:
//方式1
public class Exercise8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new PrintEven().start();
new PrintOdd().start();
}
}
class PrintEven extends Thread {
private int num = 2;
public void run() {
while (num <= 100) {
synchronized (Thread.class) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println("偶数线程,第" + i + "个:" + num);
num += 2;
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
class PrintOdd extends Thread {
private int num = 1;
public void run() {
while (num <= 100) {
synchronized (Thread.class) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println("奇数线程,第" + i + "个:" + num);
num += 2;
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
//方式2
/*
(1)声明一个资源类,例如PrintNumber,
- 包含一个int类型的变量even,初始化为2
- 包含一个int类型的变量odd,初始化为1
- 包含void printEven()方法,循环输出5个偶数
- 包含void printOdd()方法,循环输出5个奇数
(2)在测试类中
- 创建资源类PrintNumber的对象
- 启动一个偶数线程,调用PrintNumber的对象printEven()方法
- 启动一个奇数数线程,调用printOdd的对象printEven()方法
*/
class PrintNumber {
private int even = 2;
private int odd = 1;
public synchronized void printEven(){
for (int i = 1; i <=5 ; i++,even += 2) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"本轮打印的第" + i + "个数字:" + even);
}
}
public synchronized void printOdd(){
for (int i = 1; i <=5 ; i++,odd+=2) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"本轮打印的第" + i + "个数字:" + odd);
}
}
}
public class Exercise8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PrintNumber p = new PrintNumber();
new Thread("偶数线程"){
@Override
public void run(){
while(true){
p.printEven();
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}.start();
new Thread("奇数线程"){
@Override
public void run(){
while(true){
p.printOdd();
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}.start();
}
}
9、字母连续打印
案例需求:
要求两个线程,同时打印字母,每个线程都能连续打印3个字母。两个线程交替打印,一个线程打印字母的小写形式,一个线程打印字母的大写形式,但是字母是连续的。当字母循环到z之后,回到a。
案例运行效果如下:

开发提示:
(1)声明一个资源类,例如:PrintLetter
- 包含一个char类型的成员变量letter,初始化为’a’,
- 包含void printLower() 负责打印小写字母,使用循环连续打印3个字母,如果letter的值已经是’z’里,重新赋值为’a’。唤醒其他线程,当前线程等待。
- 包含printUpper()负责打印大写字母,使用循环连续打印3个字母,并把letter中的字母转换为大写形式输出。唤醒其他线程,当前线程等待。
(2)在测试类中
- 创建资源类PrintLetter对象
- 创建并启动一个线程,负责调用资源类PrintLetter对象的printLower()
- 创建并启动另一个线程,负责调用资源类PrintLetter对象的printUpper()
public class PrintLetter {
private char letter = 'a';
public synchronized void printLower() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "->" + letter);
letter++;
if (letter > 'z') {
letter = 'a';
}
}
this.notify();
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public synchronized void printUpper() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "->" + (char) (letter - 32));
letter++;
if (letter > 'z') {
letter = 'a';
}
}
this.notify();
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class Exercise9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建资源对象
PrintLetter p = new PrintLetter();
// 创建两个线程打印
new Thread("小写字母") {
public void run() {
while (true) {
p.printLower();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);// 控制节奏
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}.start();
new Thread("大写字母") {
public void run() {
while (true) {
p.printUpper();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);// 控制节奏
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}.start();
}
}
线程通信
10、奇偶数交替打印
案例:创建和启动2个子线程,一个打印奇数,一个打印偶数,
(1)要求实现交替打印。
(2)每个数打印间隔1秒
效果如下:

//方式1
public class Exercise10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new PrintNumber().start();
new PrintNumber().start();
}
}
class PrintNumber extends Thread{
private static int num;
public void run(){
while(true){
synchronized (PrintNumber.class) {
try {
PrintNumber.class.notify();
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(getName() + ":" + ++num);
PrintNumber.class.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
//方式2
/*
(1)编写一个资源类,例如:Number类,
- 包含1个int类型的num,用来记录线程要打印的数字,初始值为1。
- 包含1个boolean类型的odd,用来标记是奇数线程打印还是偶数线程打印,true表示奇数线程打印,false表示偶数线程打印。初始化为true。
- 包含void printOddNum()方法,判断odd为true,就打印num,之后修改odd为false,然后唤醒偶数线程,之后自己wait。
- 包含void printEvenNum()方法,判断odd为false,就打印num,之后修改odd为true,然后唤醒奇数线程,之后自己wait。
(2)在测试类中
- 创建Number类对象
- 创建一个奇数线程,并启动,重写run方法,循环调用Number类对象的printOddNum()方法。
- 创建一个偶数线程,并启动,重写run方法,循环调用Number类对象的printEvenNum()方法。
*/
class Number {
private int num = 1;
private boolean odd = true;
public synchronized void printOddNum(){
if(odd){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + num++);
}
odd = false;
this.notify();
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public synchronized void printEvenNum(){
if(!odd){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + num++);
}
odd = true;
this.notify();
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public int getNum() {
return num;
}
}
public class Exercise10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Number number = new Number();
new Thread(){
public void run(){
while(true){
number.printOddNum();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}.start();
new Thread(){
public void run(){
while(true){
number.printEvenNum();
}
}
}.start();
}
}
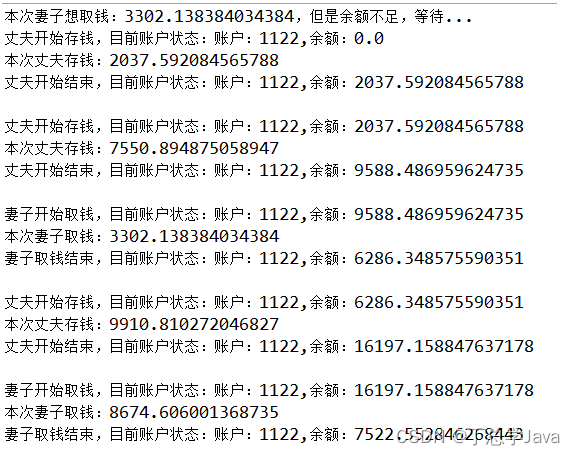
11、银行账户-1
案例:
? 1、创建一个银行账户类,
? (1)属性:账号,余额
? (2)get/set方法
? (3)toString():返回:账户:xxx,余额:xxx
? 2、创建一个丈夫类
? 负责往里存钱,每次存款[0,10000)以内不等
? 3、创建一个妻子类
? 负责取钱,每次取款[0,10000)以内不等,如果余额不足,要等丈夫存够了才能取
public class Exercise11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account a = new Account("1122",0);
new Wife(a).start();
new Husband(a).start();
}
}
class Account{
private String id;
private double balance;
public Account(String id, double balance) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.balance = balance;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "账户:" + id + ",余额:" + balance ;
}
}
class Wife extends Thread{
private Account account;
public Wife(Account account) {
super();
this.account = account;
}
public void run(){
while(true){
synchronized (Thread.class) {
double money = Math.random() * 10000;
while(money > account.getBalance()){
System.out.println("本次妻子想取钱:" + money +",但是余额不足,等待...");
try {
Thread.class.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("妻子开始取钱,目前账户状态:" + account);
System.out.println("本次妻子取钱:" + money);
account.setBalance(account.getBalance() - money);
System.out.println("妻子取钱结束,目前账户状态:" + account);
System.out.println();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
class Husband extends Thread{
private Account account;
public Husband(Account account) {
super();
this.account = account;
}
public void run(){
while(true){
synchronized (Thread.class) {
double money = Math.random() * 10000;
System.out.println("丈夫开始存钱,目前账户状态:" + account);
System.out.println("本次丈夫存钱:" + money);
account.setBalance(account.getBalance() + money);
System.out.println("丈夫开始结束,目前账户状态:" + account);
System.out.println();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Thread.class.notify();
}
}
}
}
12、银行账户-2
(1)创建一个银行账户类Account
- 属性私有化:账号(声明为final的),余额
- 两个属性都只提供get方法
- 有参构造public Account(String id, double balance)
- toString():返回:账户:xxx,余额:xxx
- 提供存钱方法 public void save(double money)
- 提供取钱方法public void withdraw(double money),余额不足要等待
(2)创建一个丈夫线程类Husband
- 包含Account成员变量
- 包含public Husband(String name, Account account)构造器
- 重写run方法,调用Account对象的save方法,负责往里存钱,每次存款[100,10000)以内不等金额
(3)创建一个妻子线程类Wife
- 包含Account成员变量
- 包含public Wife(String name, Account account)构造器
- 重写run方法,调用Account对象的withdraw方法,负责取钱,每次取款[1000,20000)以内不等,如果余额不足,要等丈夫存够了才能取

public class Account {
private String id;
private double balance;
public Account(String id, double balance) {
this.id = id;
this.balance = balance;
}
public synchronized void save(double money){
if(money > 0){
balance += money;
System.out.println("丈夫" + Thread.currentThread().getName() +"本次存钱" + money +"元," + this );
}
this.notify();
}
public synchronized void withdraw(double money){
while(money > balance){
System.out.println("妻子" + Thread.currentThread().getName() +"本次想取钱" + money +"元,余额不足,等待...");
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(money > 0){
balance -= money;
System.out.println("妻子" + Thread.currentThread().getName() +"本次取钱" + money +"元," + this );
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "账号:" + id +",余额:" + balance;
}
}
public class Husband extends Thread {
private Account account;
public Husband(String name, Account account) {
super(name);
this.account = account;
}
@Override
public void run(){
while(true){
account.save(Math.random()*9900+100);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public class Wife extends Thread {
private Account account;
public Wife(String name, Account account) {
super(name);
this.account = account;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
account.withdraw(Math.random()*19000+1000);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public class Exercise12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account a = new Account("1122",0);
Husband h = new Husband("老王",a);
Wife w = new Wife("花花",a);
h.start();
w.start();
}
}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 公告确认!四维图新旗下杰发科技获得某国际知名电子厂商定点
- Linux平台下gcc安装升级
- python-docx+ LangChain
- k8s集群搭建
- 数据结构:组织和管理数据的艺术
- LED透镜粘接UV胶是一种特殊的UV固化胶
- Python爬虫中的代理IP设置与实战策略
- 【PCB专题】Allegro中Shape与line如何互相转换
- python2.x文件声明解释器编码方法
- 2023高教杯 数学建模 国赛参赛经历分享(经验/教训)