FFmpeg之SWScale
文章目录
??团队博客: 汽车电子社区
一、概述
??Libswscale里面实现了各种图像像素格式的转换,例如YUV与RGB之间的转换;以及图像大小缩放(例如640x360拉伸为1280x720)功能。而且libswscale还做了相应指令集的优化,因此它的转换效率比自己写的C语言的转换效率高很多。
??libswscale常用的函数数量很少,一般情况下就3个:
sws_getContext():初始化一个SwsContext。
sws_scale():处理图像数据。
sws_freeContext():释放一个SwsContext。
??其中sws_getContext()也可以用sws_getCachedContext()取代。
??尽管libswscale从表面上看常用函数的个数不多,它的内部却有一个大大的“世界”。做为一个几乎“万能”的图片像素数据处理类库,它的内部包含了大量的代码。因此计划写两篇文章分析它的源代码。本文首先分析它的初始化函数sws_getContext(),而下一篇文章则分析它的数据处理函数sws_scale()。
二、函数调用结构图
??分析得到的libswscale的函数调用关系如下图所示。

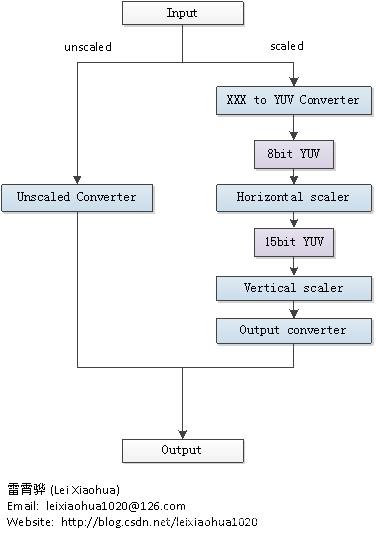
三、Libswscale处理数据流程
??Libswscale处理像素数据的流程可以概括为下图:
四、重要结构体
4.1、SwsContext
??SwsContext是使用libswscale时候一个贯穿始终的结构体。但是我们在使用FFmpeg的类库进行开发的时候,是无法看到它的内部结构的。在libswscale\swscale.h中只能看到一行定义:
typedef struct SwsContext {
/**
* info on struct for av_log
*/
const AVClass *av_class;
struct SwsContext *parent;
AVSliceThread *slicethread;
struct SwsContext **slice_ctx;
int *slice_err;
int nb_slice_ctx;
// values passed to current sws_receive_slice() call
int dst_slice_start;
int dst_slice_height;
/**
* Note that src, dst, srcStride, dstStride will be copied in the
* sws_scale() wrapper so they can be freely modified here.
*/
SwsFunc convert_unscaled;
int srcW; ///< Width of source luma/alpha planes.
int srcH; ///< Height of source luma/alpha planes.
int dstH; ///< Height of destination luma/alpha planes.
int chrSrcW; ///< Width of source chroma planes.
int chrSrcH; ///< Height of source chroma planes.
int chrDstW; ///< Width of destination chroma planes.
int chrDstH; ///< Height of destination chroma planes.
int lumXInc, chrXInc;
int lumYInc, chrYInc;
enum AVPixelFormat dstFormat; ///< Destination pixel format.
enum AVPixelFormat srcFormat; ///< Source pixel format.
int dstFormatBpp; ///< Number of bits per pixel of the destination pixel format.
int srcFormatBpp; ///< Number of bits per pixel of the source pixel format.
int dstBpc, srcBpc;
int chrSrcHSubSample; ///< Binary logarithm of horizontal subsampling factor between luma/alpha and chroma planes in source image.
int chrSrcVSubSample; ///< Binary logarithm of vertical subsampling factor between luma/alpha and chroma planes in source image.
int chrDstHSubSample; ///< Binary logarithm of horizontal subsampling factor between luma/alpha and chroma planes in destination image.
int chrDstVSubSample; ///< Binary logarithm of vertical subsampling factor between luma/alpha and chroma planes in destination image.
int vChrDrop; ///< Binary logarithm of extra vertical subsampling factor in source image chroma planes specified by user.
int sliceDir; ///< Direction that slices are fed to the scaler (1 = top-to-bottom, -1 = bottom-to-top).
int nb_threads; ///< Number of threads used for scaling
double param[2]; ///< Input parameters for scaling algorithms that need them.
AVFrame *frame_src;
AVFrame *frame_dst;
RangeList src_ranges;
/* The cascaded_* fields allow spliting a scaler task into multiple
* sequential steps, this is for example used to limit the maximum
* downscaling factor that needs to be supported in one scaler.
*/
struct SwsContext *cascaded_context[3];
int cascaded_tmpStride[4];
uint8_t *cascaded_tmp[4];
int cascaded1_tmpStride[4];
uint8_t *cascaded1_tmp[4];
int cascaded_mainindex;
double gamma_value;
int gamma_flag;
int is_internal_gamma;
uint16_t *gamma;
uint16_t *inv_gamma;
int numDesc;
int descIndex[2];
int numSlice;
struct SwsSlice *slice;
struct SwsFilterDescriptor *desc;
uint32_t pal_yuv[256];
uint32_t pal_rgb[256];
float uint2float_lut[256];
/**
* @name Scaled horizontal lines ring buffer.
* The horizontal scaler keeps just enough scaled lines in a ring buffer
* so they may be passed to the vertical scaler. The pointers to the
* allocated buffers for each line are duplicated in sequence in the ring
* buffer to simplify indexing and avoid wrapping around between lines
* inside the vertical scaler code. The wrapping is done before the
* vertical scaler is called.
*/
//@{
int lastInLumBuf; ///< Last scaled horizontal luma/alpha line from source in the ring buffer.
int lastInChrBuf; ///< Last scaled horizontal chroma line from source in the ring buffer.
//@}
uint8_t *formatConvBuffer;
int needAlpha;
/**
* @name Horizontal and vertical filters.
* To better understand the following fields, here is a pseudo-code of
* their usage in filtering a horizontal line:
* @code
* for (i = 0; i < width; i++) {
* dst[i] = 0;
* for (j = 0; j < filterSize; j++)
* dst[i] += src[ filterPos[i] + j ] * filter[ filterSize * i + j ];
* dst[i] >>= FRAC_BITS; // The actual implementation is fixed-point.
* }
* @endcode
*/
//@{
int16_t *hLumFilter; ///< Array of horizontal filter coefficients for luma/alpha planes.
int16_t *hChrFilter; ///< Array of horizontal filter coefficients for chroma planes.
int16_t *vLumFilter; ///< Array of vertical filter coefficients for luma/alpha planes.
int16_t *vChrFilter; ///< Array of vertical filter coefficients for chroma planes.
int32_t *hLumFilterPos; ///< Array of horizontal filter starting positions for each dst[i] for luma/alpha planes.
int32_t *hChrFilterPos; ///< Array of horizontal filter starting positions for each dst[i] for chroma planes.
int32_t *vLumFilterPos; ///< Array of vertical filter starting positions for each dst[i] for luma/alpha planes.
int32_t *vChrFilterPos; ///< Array of vertical filter starting positions for each dst[i] for chroma planes.
int hLumFilterSize; ///< Horizontal filter size for luma/alpha pixels.
int hChrFilterSize; ///< Horizontal filter size for chroma pixels.
int vLumFilterSize; ///< Vertical filter size for luma/alpha pixels.
int vChrFilterSize; ///< Vertical filter size for chroma pixels.
//@}
int lumMmxextFilterCodeSize; ///< Runtime-generated MMXEXT horizontal fast bilinear scaler code size for luma/alpha planes.
int chrMmxextFilterCodeSize; ///< Runtime-generated MMXEXT horizontal fast bilinear scaler code size for chroma planes.
uint8_t *lumMmxextFilterCode; ///< Runtime-generated MMXEXT horizontal fast bilinear scaler code for luma/alpha planes.
uint8_t *chrMmxextFilterCode; ///< Runtime-generated MMXEXT horizontal fast bilinear scaler code for chroma planes.
int canMMXEXTBeUsed;
int warned_unuseable_bilinear;
int dstY; ///< Last destination vertical line output from last slice.
int flags; ///< Flags passed by the user to select scaler algorithm, optimizations, subsampling, etc...
void *yuvTable; // pointer to the yuv->rgb table start so it can be freed()
// alignment ensures the offset can be added in a single
// instruction on e.g. ARM
DECLARE_ALIGNED(16, int, table_gV)[256 + 2*YUVRGB_TABLE_HEADROOM];
uint8_t *table_rV[256 + 2*YUVRGB_TABLE_HEADROOM];
uint8_t *table_gU[256 + 2*YUVRGB_TABLE_HEADROOM];
uint8_t *table_bU[256 + 2*YUVRGB_TABLE_HEADROOM];
DECLARE_ALIGNED(16, int32_t, input_rgb2yuv_table)[16+40*4]; // This table can contain both C and SIMD formatted values, the C vales are always at the XY_IDX points
#define RY_IDX 0
#define GY_IDX 1
#define BY_IDX 2
#define RU_IDX 3
#define GU_IDX 4
#define BU_IDX 5
#define RV_IDX 6
#define GV_IDX 7
#define BV_IDX 8
#define RGB2YUV_SHIFT 15
int *dither_error[4];
//Colorspace stuff
int contrast, brightness, saturation; // for sws_getColorspaceDetails
int srcColorspaceTable[4];
int dstColorspaceTable[4];
int srcRange; ///< 0 = MPG YUV range, 1 = JPG YUV range (source image).
int dstRange; ///< 0 = MPG YUV range, 1 = JPG YUV range (destination image).
int src0Alpha;
int dst0Alpha;
int srcXYZ;
int dstXYZ;
int src_h_chr_pos;
int dst_h_chr_pos;
int src_v_chr_pos;
int dst_v_chr_pos;
int yuv2rgb_y_offset;
int yuv2rgb_y_coeff;
int yuv2rgb_v2r_coeff;
int yuv2rgb_v2g_coeff;
int yuv2rgb_u2g_coeff;
int yuv2rgb_u2b_coeff;
#define RED_DITHER "0*8"
#define GREEN_DITHER "1*8"
#define BLUE_DITHER "2*8"
#define Y_COEFF "3*8"
#define VR_COEFF "4*8"
#define UB_COEFF "5*8"
#define VG_COEFF "6*8"
#define UG_COEFF "7*8"
#define Y_OFFSET "8*8"
#define U_OFFSET "9*8"
#define V_OFFSET "10*8"
#define LUM_MMX_FILTER_OFFSET "11*8"
#define CHR_MMX_FILTER_OFFSET "11*8+4*4*"AV_STRINGIFY(MAX_FILTER_SIZE)
#define DSTW_OFFSET "11*8+4*4*"AV_STRINGIFY(MAX_FILTER_SIZE)"*2"
#define ESP_OFFSET "11*8+4*4*"AV_STRINGIFY(MAX_FILTER_SIZE)"*2+8"
#define VROUNDER_OFFSET "11*8+4*4*"AV_STRINGIFY(MAX_FILTER_SIZE)"*2+16"
#define U_TEMP "11*8+4*4*"AV_STRINGIFY(MAX_FILTER_SIZE)"*2+24"
#define V_TEMP "11*8+4*4*"AV_STRINGIFY(MAX_FILTER_SIZE)"*2+32"
#define Y_TEMP "11*8+4*4*"AV_STRINGIFY(MAX_FILTER_SIZE)"*2+40"
#define ALP_MMX_FILTER_OFFSET "11*8+4*4*"AV_STRINGIFY(MAX_FILTER_SIZE)"*2+48"
#define UV_OFF_PX "11*8+4*4*"AV_STRINGIFY(MAX_FILTER_SIZE)"*3+48"
#define UV_OFF_BYTE "11*8+4*4*"AV_STRINGIFY(MAX_FILTER_SIZE)"*3+56"
#define DITHER16 "11*8+4*4*"AV_STRINGIFY(MAX_FILTER_SIZE)"*3+64"
#define DITHER32 "11*8+4*4*"AV_STRINGIFY(MAX_FILTER_SIZE)"*3+80"
#define DITHER32_INT (11*8+4*4*MAX_FILTER_SIZE*3+80) // value equal to above, used for checking that the struct hasn't been changed by mistake
DECLARE_ALIGNED(8, uint64_t, redDither);
DECLARE_ALIGNED(8, uint64_t, greenDither);
DECLARE_ALIGNED(8, uint64_t, blueDither);
DECLARE_ALIGNED(8, uint64_t, yCoeff);
DECLARE_ALIGNED(8, uint64_t, vrCoeff);
DECLARE_ALIGNED(8, uint64_t, ubCoeff);
DECLARE_ALIGNED(8, uint64_t, vgCoeff);
DECLARE_ALIGNED(8, uint64_t, ugCoeff);
DECLARE_ALIGNED(8, uint64_t, yOffset);
DECLARE_ALIGNED(8, uint64_t, uOffset);
DECLARE_ALIGNED(8, uint64_t, vOffset);
int32_t lumMmxFilter[4 * MAX_FILTER_SIZE];
int32_t chrMmxFilter[4 * MAX_FILTER_SIZE];
int dstW; ///< Width of destination luma/alpha planes.
DECLARE_ALIGNED(8, uint64_t, esp);
DECLARE_ALIGNED(8, uint64_t, vRounder);
DECLARE_ALIGNED(8, uint64_t, u_temp);
DECLARE_ALIGNED(8, uint64_t, v_temp);
DECLARE_ALIGNED(8, uint64_t, y_temp);
int32_t alpMmxFilter[4 * MAX_FILTER_SIZE];
// alignment of these values is not necessary, but merely here
// to maintain the same offset across x8632 and x86-64. Once we
// use proper offset macros in the asm, they can be removed.
DECLARE_ALIGNED(8, ptrdiff_t, uv_off); ///< offset (in pixels) between u and v planes
DECLARE_ALIGNED(8, ptrdiff_t, uv_offx2); ///< offset (in bytes) between u and v planes
DECLARE_ALIGNED(8, uint16_t, dither16)[8];
DECLARE_ALIGNED(8, uint32_t, dither32)[8];
const uint8_t *chrDither8, *lumDither8;
#if HAVE_ALTIVEC
vector signed short CY;
vector signed short CRV;
vector signed short CBU;
vector signed short CGU;
vector signed short CGV;
vector signed short OY;
vector unsigned short CSHIFT;
vector signed short *vYCoeffsBank, *vCCoeffsBank;
#endif
int use_mmx_vfilter;
/* pre defined color-spaces gamma */
#define XYZ_GAMMA (2.6f)
#define RGB_GAMMA (2.2f)
int16_t *xyzgamma;
int16_t *rgbgamma;
int16_t *xyzgammainv;
int16_t *rgbgammainv;
int16_t xyz2rgb_matrix[3][4];
int16_t rgb2xyz_matrix[3][4];
/* function pointers for swscale() */
yuv2planar1_fn yuv2plane1;
yuv2planarX_fn yuv2planeX;
yuv2interleavedX_fn yuv2nv12cX;
yuv2packed1_fn yuv2packed1;
yuv2packed2_fn yuv2packed2;
yuv2packedX_fn yuv2packedX;
yuv2anyX_fn yuv2anyX;
/// Opaque data pointer passed to all input functions.
void *input_opaque;
/// Unscaled conversion of luma plane to YV12 for horizontal scaler.
void (*lumToYV12)(uint8_t *dst, const uint8_t *src, const uint8_t *src2, const uint8_t *src3,
int width, uint32_t *pal, void *opq);
/// Unscaled conversion of alpha plane to YV12 for horizontal scaler.
void (*alpToYV12)(uint8_t *dst, const uint8_t *src, const uint8_t *src2, const uint8_t *src3,
int width, uint32_t *pal, void *opq);
/// Unscaled conversion of chroma planes to YV12 for horizontal scaler.
void (*chrToYV12)(uint8_t *dstU, uint8_t *dstV,
const uint8_t *src1, const uint8_t *src2, const uint8_t *src3,
int width, uint32_t *pal, void *opq);
/**
* Functions to read planar input, such as planar RGB, and convert
* internally to Y/UV/A.
*/
/** @{ */
void (*readLumPlanar)(uint8_t *dst, const uint8_t *src[4], int width, int32_t *rgb2yuv,
void *opq);
void (*readChrPlanar)(uint8_t *dstU, uint8_t *dstV, const uint8_t *src[4],
int width, int32_t *rgb2yuv, void *opq);
void (*readAlpPlanar)(uint8_t *dst, const uint8_t *src[4], int width, int32_t *rgb2yuv,
void *opq);
/** @} */
/**
* Scale one horizontal line of input data using a bilinear filter
* to produce one line of output data. Compared to SwsContext->hScale(),
* please take note of the following caveats when using these:
* - Scaling is done using only 7 bits instead of 14-bit coefficients.
* - You can use no more than 5 input pixels to produce 4 output
* pixels. Therefore, this filter should not be used for downscaling
* by more than ~20% in width (because that equals more than 5/4th
* downscaling and thus more than 5 pixels input per 4 pixels output).
* - In general, bilinear filters create artifacts during downscaling
* (even when <20%), because one output pixel will span more than one
* input pixel, and thus some pixels will need edges of both neighbor
* pixels to interpolate the output pixel. Since you can use at most
* two input pixels per output pixel in bilinear scaling, this is
* impossible and thus downscaling by any size will create artifacts.
* To enable this type of scaling, set SWS_FLAG_FAST_BILINEAR
* in SwsContext->flags.
*/
/** @{ */
void (*hyscale_fast)(struct SwsContext *c,
int16_t *dst, int dstWidth,
const uint8_t *src, int srcW, int xInc);
void (*hcscale_fast)(struct SwsContext *c,
int16_t *dst1, int16_t *dst2, int dstWidth,
const uint8_t *src1, const uint8_t *src2,
int srcW, int xInc);
/** @} */
/**
* Scale one horizontal line of input data using a filter over the input
* lines, to produce one (differently sized) line of output data.
*
* @param dst pointer to destination buffer for horizontally scaled
* data. If the number of bits per component of one
* destination pixel (SwsContext->dstBpc) is <= 10, data
* will be 15 bpc in 16 bits (int16_t) width. Else (i.e.
* SwsContext->dstBpc == 16), data will be 19bpc in
* 32 bits (int32_t) width.
* @param dstW width of destination image
* @param src pointer to source data to be scaled. If the number of
* bits per component of a source pixel (SwsContext->srcBpc)
* is 8, this is 8bpc in 8 bits (uint8_t) width. Else
* (i.e. SwsContext->dstBpc > 8), this is native depth
* in 16 bits (uint16_t) width. In other words, for 9-bit
* YUV input, this is 9bpc, for 10-bit YUV input, this is
* 10bpc, and for 16-bit RGB or YUV, this is 16bpc.
* @param filter filter coefficients to be used per output pixel for
* scaling. This contains 14bpp filtering coefficients.
* Guaranteed to contain dstW * filterSize entries.
* @param filterPos position of the first input pixel to be used for
* each output pixel during scaling. Guaranteed to
* contain dstW entries.
* @param filterSize the number of input coefficients to be used (and
* thus the number of input pixels to be used) for
* creating a single output pixel. Is aligned to 4
* (and input coefficients thus padded with zeroes)
* to simplify creating SIMD code.
*/
/** @{ */
void (*hyScale)(struct SwsContext *c, int16_t *dst, int dstW,
const uint8_t *src, const int16_t *filter,
const int32_t *filterPos, int filterSize);
void (*hcScale)(struct SwsContext *c, int16_t *dst, int dstW,
const uint8_t *src, const int16_t *filter,
const int32_t *filterPos, int filterSize);
/** @} */
/// Color range conversion function for luma plane if needed.
void (*lumConvertRange)(int16_t *dst, int width);
/// Color range conversion function for chroma planes if needed.
void (*chrConvertRange)(int16_t *dst1, int16_t *dst2, int width);
int needs_hcscale; ///< Set if there are chroma planes to be converted.
SwsDither dither;
SwsAlphaBlend alphablend;
// scratch buffer for converting packed rgb0 sources
// filled with a copy of the input frame + fully opaque alpha,
// then passed as input to further conversion
uint8_t *rgb0_scratch;
unsigned int rgb0_scratch_allocated;
// scratch buffer for converting XYZ sources
// filled with the input converted to rgb48
// then passed as input to further conversion
uint8_t *xyz_scratch;
unsigned int xyz_scratch_allocated;
unsigned int dst_slice_align;
atomic_int stride_unaligned_warned;
atomic_int data_unaligned_warned;
Half2FloatTables *h2f_tables;
} SwsContext;
??这个结构体的定义确实比较复杂,里面包含了libswscale所需要的全部变量。一一分析这些变量是不太现实的,在后文中会简单分析其中的几个变量。
??swscale这个变量的类型是SwsFunc,实际上就是一个函数指针。它是整个类库的核心。当我们从外部调用swscale()函数的时候。实际上就是调用了SwsContext中的这个名称为swscale的变量(注意外部函数接口和这个内部函数指针的名字是一样的,但不是一回事)。
4.2、SwsFilter
typedef struct SwsVector {
double *coeff; /* 滤波器系数 */
int length; /* 滤波器长度 */
} SwsVector;
// vectors can be shared
typedef struct SwsFilter {
SwsVector *lumH; /* 亮度水平处理 */
SwsVector *lumV; /* 亮度垂直处理 */
SwsVector *chrH; /* 色度水平处理 */
SwsVector *chrV; /* 色度垂直处理 */
} SwsFilter;
五、重要函数
5.1、sws_getContext
SwsContext *sws_getContext(int srcW, int srcH, enum AVPixelFormat srcFormat,
int dstW, int dstH, enum AVPixelFormat dstFormat,
int flags, SwsFilter *srcFilter,
SwsFilter *dstFilter, const double *param)
{
SwsContext *c;
c = sws_alloc_set_opts(srcW, srcH, srcFormat,
dstW, dstH, dstFormat,
flags, param);
if (!c)
return NULL;
if (sws_init_context(c, srcFilter, dstFilter) < 0) {
sws_freeContext(c);
return NULL;
}
return c;
}
??该函数包含以下参数:
????1. srcW:源图像的宽。
????2. srcH:源图像的高。
????3. srcFormat:源图像的像素格式。
????4. dstW:目标图像的宽。
????5. dstH:目标图像的高。
????6. dstFormat:目标图像的像素格式。
????7. flags:设定图像拉伸使用的算法 。
??成功执行的话返回生成的SwsContext,否则返回NULL。
从sws_getContext()的定义中可以看出,它首先调用了一个函数sws_alloc_context()用于给SwsContext分配内存。然后将传入的源图像,目标图像的宽高,像素格式,以及标志位分别赋值给该SwsContext相应的字段。最后调用一个函数sws_init_context()完成初始化工作。下面我们分别看一下sws_alloc_context()和sws_init_context()这两个函数。
5.1.1、sws_alloc_context
sws_alloc_context()是FFmpeg的一个API,用于给SwsContext分配内存,它的具体实现如下所示。
SwsContext *sws_alloc_context(void)
{
SwsContext *c = av_mallocz(sizeof(SwsContext));
av_assert0(offsetof(SwsContext, redDither) + DITHER32_INT == offsetof(SwsContext, dither32));
if (c) {
c->av_class = &ff_sws_context_class;
av_opt_set_defaults(c);
atomic_init(&c->stride_unaligned_warned, 0);
atomic_init(&c->data_unaligned_warned, 0);
}
return c;
}
??从代码中可以看出,sws_alloc_context()首先调用av_mallocz()为SwsContext结构体分配了一块内存;然后设置了该结构体的AVClass,并且给该结构体的字段设置了默认值。
5.1.2、sws_init_context
av_cold int sws_init_context(SwsContext *c, SwsFilter *srcFilter,
SwsFilter *dstFilter)
{
static AVOnce rgb2rgb_once = AV_ONCE_INIT;
enum AVPixelFormat src_format, dst_format;
int ret;
c->frame_src = av_frame_alloc();
c->frame_dst = av_frame_alloc();
if (!c->frame_src || !c->frame_dst)
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
if (ff_thread_once(&rgb2rgb_once, ff_sws_rgb2rgb_init) != 0)
return AVERROR_UNKNOWN;
src_format = c->srcFormat;
dst_format = c->dstFormat;
c->srcRange |= handle_jpeg(&c->srcFormat);
c->dstRange |= handle_jpeg(&c->dstFormat);
if (src_format != c->srcFormat || dst_format != c->dstFormat)
av_log(c, AV_LOG_WARNING, "deprecated pixel format used, make sure you did set range correctly\n");
if (c->nb_threads != 1) {
ret = context_init_threaded(c, srcFilter, dstFilter);
if (ret < 0 || c->nb_threads > 1)
return ret;
// threading disabled in this build, init as single-threaded
}
return sws_init_single_context(c, srcFilter, dstFilter);
}
??sws_init_context()除了对SwsContext中的各种变量进行赋值之外,主要按照顺序完成了以下一些工作:
????1. 通过sws_rgb2rgb_init()初始化RGB转RGB(或者YUV转YUV)的函数(注意不包含RGB与YUV相互转换的函数)。
????2. 通过判断输入输出图像的宽高来判断图像是否需要拉伸。如果图像需要拉伸,那么unscaled变量会被标记为1。
????3. 通过sws_setColorspaceDetails()初始化颜色空间。
????4. 一些输入参数的检测。例如:如果没有设置图像拉伸方法的话,默认设置为SWS_BICUBIC;如果输入和输出图像的宽高小于等于0的话,也会返回错误信息。
????5. 初始化Filter。这一步根据拉伸方法的不同,初始化不同的Filter。
????6. 如果flags中设置了“打印信息”选项SWS_PRINT_INFO,则输出信息。
????7. 如果不需要拉伸的话,调用ff_get_unscaled_swscale()将特定的像素转换函数的指针赋值给SwsContext中的swscale指针。
????8. 如果需要拉伸的话,调用ff_getSwsFunc()将通用的swscale()赋值给SwsContext中的swscale指针(这个地方有点绕,但是确实是这样的)。
5.2、sws_scale
??sws_scale()是用于转换像素的函数。它的声明位于libswscale\swscale.h,如下所示。
int attribute_align_arg sws_scale(struct SwsContext *c,
const uint8_t * const srcSlice[],
const int srcStride[], int srcSliceY,
int srcSliceH, uint8_t *const dst[],
const int dstStride[])
{
if (c->nb_slice_ctx)
c = c->slice_ctx[0];
return scale_internal(c, srcSlice, srcStride, srcSliceY, srcSliceH,
dst, dstStride, 0, c->dstH);
}
void ff_sws_slice_worker(void *priv, int jobnr, int threadnr,
int nb_jobs, int nb_threads)
{
SwsContext *parent = priv;
SwsContext *c = parent->slice_ctx[threadnr];
const int slice_height = FFALIGN(FFMAX((parent->dst_slice_height + nb_jobs - 1) / nb_jobs, 1),
c->dst_slice_align);
const int slice_start = jobnr * slice_height;
const int slice_end = FFMIN((jobnr + 1) * slice_height, parent->dst_slice_height);
int err = 0;
if (slice_end > slice_start) {
uint8_t *dst[4] = { NULL };
for (int i = 0; i < FF_ARRAY_ELEMS(dst) && parent->frame_dst->data[i]; i++) {
const int vshift = (i == 1 || i == 2) ? c->chrDstVSubSample : 0;
const ptrdiff_t offset = parent->frame_dst->linesize[i] *
((slice_start + parent->dst_slice_start) >> vshift);
dst[i] = parent->frame_dst->data[i] + offset;
}
err = scale_internal(c, (const uint8_t * const *)parent->frame_src->data,
parent->frame_src->linesize, 0, c->srcH,
dst, parent->frame_dst->linesize,
parent->dst_slice_start + slice_start, slice_end - slice_start);
}
parent->slice_err[threadnr] = err;
}
??参数说明:
????1. SwsContext *c:转换格式的上下文结构体,也就是 sws_getContext() 函数返回的结果。
????2. srcSlice[]:源图像的每个颜色通道的数据指针。其实就是解码后的 AVFrame 中的 data[] 数组。因为不同像素的存储格式不同,所以 srcSlice[] 数组也有可能不同。
????3. srcStride[]:源图像的每个颜色通道的跨度。也就是每个通道的行字节数,对应的是解码后的 AVFrame 中的 linesize[] 数组,根据它可以确立下一行的起始位置。
????4. srcSliceY、int srcSliceH:定义在源图像上处理区域,srcSliceY 是起始位置,srcSliceH 是处理多少行。如果 srcSliceY=0,srcSliceH=height,表示一次性处理完整个图像。这种设置是为了多线程并行,例如可以创建两个线程,第一个线程处理 [0, h/2-1] 行,第二个线程处理 [h/2, h-1] 行,并行处理加快速度。
????5. dst[]、dstStride[]:定义目标图像信息(目标图像输出的每个颜色通道数据指针,每个颜色通道行字节数)。
??从sws_scale()的定义可以看出,它封装了SwsContext中的swscale()(注意这个函数中间没有“_”)。函数最重要的一句代码就是“c->swscale()”。除此之外,函数还做了一些增加“兼容性”的一些处理。函数的主要步骤如下所示。
????1. 检查输入的图像參数的合理性。
????2. 假设输入像素数据中使用了“调色板”(palette),则进行一些对应的处理。这一步通过函数usePal()来判定。
????3. 其他一些特殊格式的处理,比方说Alpha。XYZ等的处理(这方面没有研究过)。
????4. 假设输入的图像的扫描方式是从底部到顶部的(普通情况下是从顶部究竟部)。则将图像进行反转。
????5. 调用SwsContext中的swscale()。
5.2.1、SwsContext中的swscale()
??swscale这个变量的类型是SwsFunc,实际上就是一个函数指针。它是整个类库的核心。当我们从外部调用swscale()函数的时候。实际上就是调用了SwsContext中的这个名称为swscale的变量(注意外部函数接口和这个内部函数指针的名字是一样的,但不是一回事)。
??能够看一下SwsFunc这个类型的定义:
typedef int (*SwsFunc)(struct SwsContext *context, const uint8_t *src[],
int srcStride[], int srcSliceY, int srcSliceH,
uint8_t *dst[], int dstStride[]);
??能够看出SwsFunc的定义的參数类型和libswscale类库外部接口函数swscale()的參数类型一模一样。
??在libswscale中,该指针的指向能够分成2种情况:
????1. 图像没有伸缩的时候。指向专有的像素转换函数。
????2. 图像有伸缩的时候。指向swscale()函数。
??在调用sws_getContext()初始化SwsContext的时候。会在其子函数sws_init_context()中对swscale指针进行赋值。假设图像没有进行拉伸,则会调用ff_get_unscaled_swscale()对其进行赋值;假设图像进行了拉伸。则会调用ff_getSwsFunc()对其进行赋值。
5.2.2、check_image_pointers
??check_image_pointers()检查输入输出图像的内存是否正确分配。check_image_pointers()的定义例如以下所看到的
static int check_image_pointers(const uint8_t * const data[4], enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmt,
const int linesizes[4])
{
const AVPixFmtDescriptor *desc = av_pix_fmt_desc_get(pix_fmt);
int i;
av_assert2(desc);
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int plane = desc->comp[i].plane;
if (!data[plane] || !linesizes[plane])
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
5.2.3、usePal
static av_always_inline int usePal(enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmt)
{
switch (pix_fmt) {
case AV_PIX_FMT_PAL8:
case AV_PIX_FMT_BGR4_BYTE:
case AV_PIX_FMT_BGR8:
case AV_PIX_FMT_GRAY8:
case AV_PIX_FMT_RGB4_BYTE:
case AV_PIX_FMT_RGB8:
return 1;
default:
return 0;
}
}
??从定义能够看出该函数通过判定AVPixFmtDescriptor中的flag是否包括AV_PIX_FMT_FLAG_PAL来断定像素格式是否使用了“调色板”。
5.3、sws_freeContext
??sws_scale() 函数主要是用来做视频像素格式和分辨率的转换,其优势在于:可以在同一个函数里实现:
????1.图像色彩空间转换,
????2.分辨率缩放,
??3.前后图像滤波处理。
??不足之处在于:
????效率相对较低,不如 libyuv 或 shader,其关联的函数就是上面的sws_getContext() 和 sws_freeContext()。
??它的声明位于 libswscale\swscale.h,如下所示:
void sws_freeContext(SwsContext *c)
{
int i;
if (!c)
return;
for (i = 0; i < c->nb_slice_ctx; i++)
sws_freeContext(c->slice_ctx[i]);
av_freep(&c->slice_ctx);
av_freep(&c->slice_err);
avpriv_slicethread_free(&c->slicethread);
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++)
av_freep(&c->dither_error[i]);
av_frame_free(&c->frame_src);
av_frame_free(&c->frame_dst);
av_freep(&c->src_ranges.ranges);
av_freep(&c->vLumFilter);
av_freep(&c->vChrFilter);
av_freep(&c->hLumFilter);
av_freep(&c->hChrFilter);
#if HAVE_ALTIVEC
av_freep(&c->vYCoeffsBank);
av_freep(&c->vCCoeffsBank);
#endif
av_freep(&c->vLumFilterPos);
av_freep(&c->vChrFilterPos);
av_freep(&c->hLumFilterPos);
av_freep(&c->hChrFilterPos);
#if HAVE_MMX_INLINE
#if USE_MMAP
if (c->lumMmxextFilterCode)
munmap(c->lumMmxextFilterCode, c->lumMmxextFilterCodeSize);
if (c->chrMmxextFilterCode)
munmap(c->chrMmxextFilterCode, c->chrMmxextFilterCodeSize);
#elif HAVE_VIRTUALALLOC
if (c->lumMmxextFilterCode)
VirtualFree(c->lumMmxextFilterCode, 0, MEM_RELEASE);
if (c->chrMmxextFilterCode)
VirtualFree(c->chrMmxextFilterCode, 0, MEM_RELEASE);
#else
av_free(c->lumMmxextFilterCode);
av_free(c->chrMmxextFilterCode);
#endif
c->lumMmxextFilterCode = NULL;
c->chrMmxextFilterCode = NULL;
#endif /* HAVE_MMX_INLINE */
av_freep(&c->yuvTable);
av_freep(&c->formatConvBuffer);
sws_freeContext(c->cascaded_context[0]);
sws_freeContext(c->cascaded_context[1]);
sws_freeContext(c->cascaded_context[2]);
memset(c->cascaded_context, 0, sizeof(c->cascaded_context));
av_freep(&c->cascaded_tmp[0]);
av_freep(&c->cascaded1_tmp[0]);
av_freep(&c->gamma);
av_freep(&c->inv_gamma);
av_freep(&c->rgb0_scratch);
av_freep(&c->xyz_scratch);
ff_free_filters(c);
av_free(c);
}
六、实例
/*
* 需设定 SRCFILE 及 DSTFILE, 长宽等咨询
* 需 link libswscale
* 主要有三个 function
* sws_getContext() 是 initial 用, sws_freeContext() 是结束用
* sws_scale() 是主要运作的 function
*预设只会转换第一张 YUV, 如果要转换整个文档, 可以把 Decoding loop 的注解拿掉
*/
#include "libswscale/swscale.h"
#define SRCFILE "foreman_cif.yuv"
#define DSTFILE "out.yuv"
int main()
{
// 设定原始 YUV 的长宽
const int in_width = 352;
const int in_height = 288;
// 设定目的 YUV 的长宽
const int out_width = 640;
const int out_height = 480;
const int read_size = in_width * in_height * 3 / 2;
const int write_size = out_width * out_height * 3 / 2;
struct SwsContext *img_convert_ctx;
uint8_t *inbuf[4];
uint8_t *outbuf[4];
int inlinesize[4] = {in_width, in_width/2, in_width/2, 0};
int outlinesize[4] = {out_width, out_width/2, out_width/2, 0};
uint8_t in[352*288*3>>1];
uint8_t out[640*480*3>>1];
FILE *fin = fopen(SRCFILE, "rb");
FILE *fout = fopen(DSTFILE, "wb");
if(fin == NULL) {
printf("open input file %s error.\n", SRCFILE);
return -1;
}
if(fout == NULL) {
printf("open output file %s error.\n", DSTFILE);
return -1;
}
inbuf[0] = malloc(in_width*in_height);
inbuf[1] = malloc(in_width*in_height>>2);
inbuf[2] = malloc(in_width*in_height>>2);
inbuf[3] = NULL;
outbuf[0] = malloc(out_width*out_height);
outbuf[1] = malloc(out_width*out_height>>2);
outbuf[2] = malloc(out_width*out_height>>2);
outbuf[3] = NULL;
// ********* Initialize software scaling *********
// ********* sws_getContext **********************
img_convert_ctx = sws_getContext(in_width, in_height, PIX_FMT_YUV420P,
out_width, out_height, PIX_FMT_YUV420P, SWS_POINT,
NULL, NULL, NULL);
if(img_convert_ctx == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot initialize the conversion context!\n");
return -1;
}
fread(in, 1, read_size, fin);
memcpy(inbuf[0], in, in_width*in_height);
memcpy(inbuf[1], in+in_width*in_height, in_width*in_height>>2);
memcpy(inbuf[2], in+(in_width*in_height*5>>2), in_width*in_height>>2);
// ********* 主要的 function ******
// ********* sws_scale ************
sws_scale(img_convert_ctx, inbuf, inlinesize,
0, in_height, outbuf, outlinesize);
memcpy(out, outbuf[0], out_width*out_height);
memcpy(out+out_width*out_height, outbuf[1], out_width*out_height>>2);
memcpy(out+(out_width*out_height*5>>2), outbuf[2], out_width*out_height>>2);
fwrite(out, 1, write_size, fout);
// ********* 结束的 function *******
// ********* sws_freeContext *******
sws_freeContext(img_convert_ctx);
fclose(fin);
fclose(fout);
return 0;
}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 【Leetcode】最长连续序列
- 8.1 Centos安装部署Redis
- 【霹雳吧啦】手把手带你入门语义分割の番外14:U2-Net 源码讲解(PyTorch)—— 自定义数据集读取
- 企业如何实现合理定岗定编?
- 外贸人如何用AI找海外客户?分享一个新思路!
- springboot104学生网上请假系统设计与实现
- 数据库学习命令总结(持续更新)
- USB2.0 软件篇
- idea 专业版(学习版)安装windows/linux(ubuntu为例)通用
- 独立站的营销策略:吸引顾客的秘密武器