Netty
Netty
一、概述
1、什么是Netty
Netty is an asynchronous event-driven network application framework
for rapid development of maintainable high performance protocol servers & clients.Copy
Netty 是一个异步的、基于事件驱动的网络应用框架,用于快速开发可维护、高性能的网络服务器和客户端
注意:netty的异步还是基于多路复用的,并没有实现真正意义上的异步IO
2、Netty的优势
如果使用传统NIO,其工作量大,bug 多
- 需要自己构建协议
- 解决 TCP 传输问题,如粘包、半包
- 因为bug的存在,epoll 空轮询导致 CPU 100%
Netty 对 API 进行增强,使之更易用,如
- FastThreadLocal => ThreadLocal
- ByteBuf => ByteBuffer
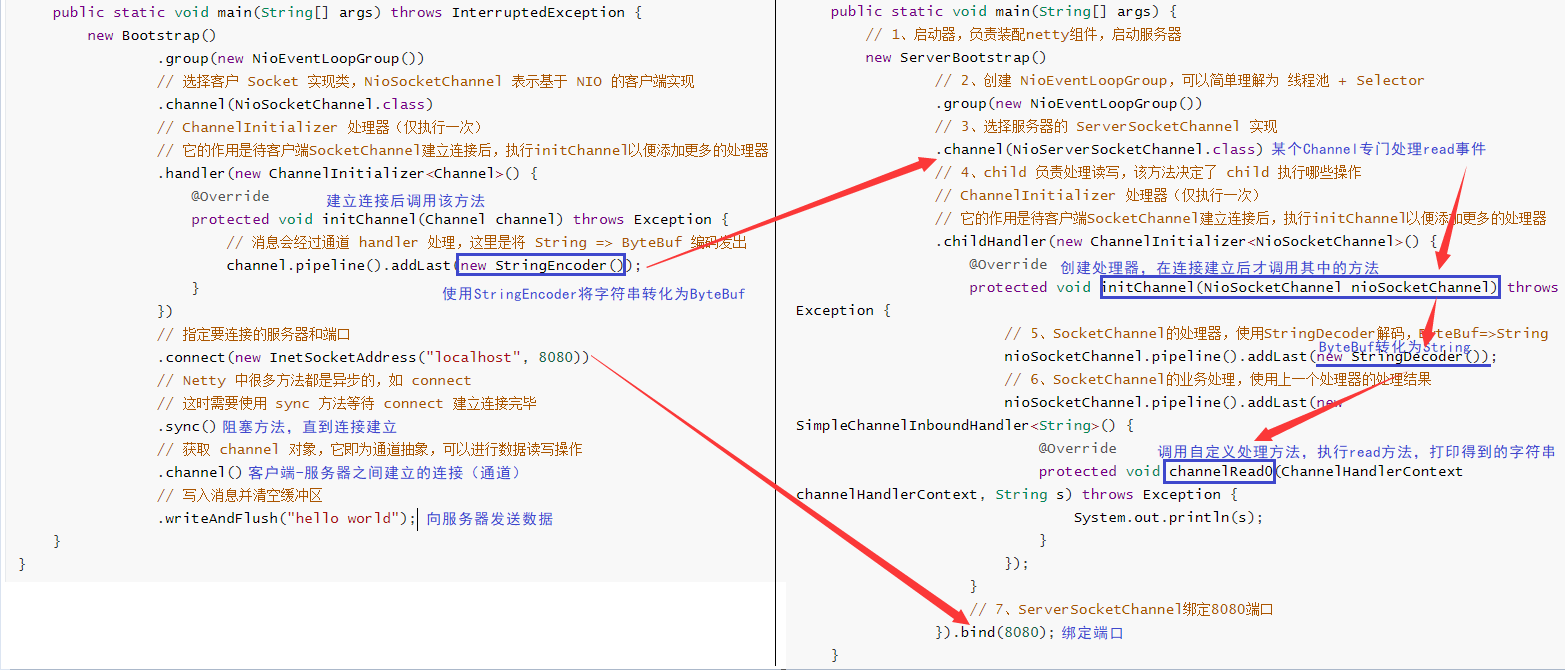
二、入门案例
1、服务器端代码
public class HelloServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、启动器,负责装配netty组件,启动服务器
new ServerBootstrap()
// 2、创建 NioEventLoopGroup,可以简单理解为 线程池 + Selector
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
// 3、选择服务器的 ServerSocketChannel 实现
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
// 4、child 负责处理读写,该方法决定了 child 执行哪些操作
// ChannelInitializer 处理器(仅执行一次)
// 它的作用是待客户端SocketChannel建立连接后,执行initChannel以便添加更多的处理器
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel nioSocketChannel) throws Exception {
// 5、SocketChannel的处理器,使用StringDecoder解码,ByteBuf=>String
nioSocketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
// 6、SocketChannel的业务处理,使用上一个处理器的处理结果
nioSocketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String>() {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, String s) throws Exception {
System.out.println(s);
}
});
}
// 7、ServerSocketChannel绑定8080端口
}).bind(8080);
}
}Copy
2、客户端代码
public class HelloClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
new Bootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
// 选择客户 Socket 实现类,NioSocketChannel 表示基于 NIO 的客户端实现
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
// ChannelInitializer 处理器(仅执行一次)
// 它的作用是待客户端SocketChannel建立连接后,执行initChannel以便添加更多的处理器
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel channel) throws Exception {
// 消息会经过通道 handler 处理,这里是将 String => ByteBuf 编码发出
channel.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder());
}
})
// 指定要连接的服务器和端口
.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080))
// Netty 中很多方法都是异步的,如 connect
// 这时需要使用 sync 方法等待 connect 建立连接完毕
.sync()
// 获取 channel 对象,它即为通道抽象,可以进行数据读写操作
.channel()
// 写入消息并清空缓冲区
.writeAndFlush("hello world");
}
}Copy
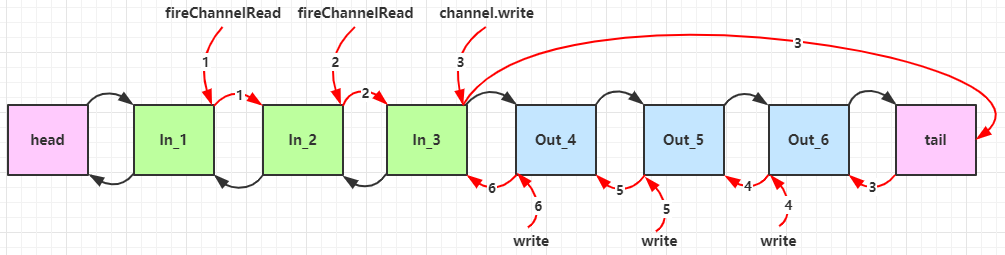
3、运行流程
左:客户端 右:服务器端
组件解释
-
channel 可以理解为数据的通道
-
msg 理解为流动的数据,最开始输入是 ByteBuf,但经过 pipeline 中的各个 handler 加工,会变成其它类型对象,最后输出又变成 ByteBuf
-
handler 可以理解为数据的处理工序
-
工序有多道,
合在一起就是 pipeline(传递途径)
,pipeline 负责发布事件(读、读取完成…)传播给每个 handler, handler 对自己感兴趣的事件进行处理(重写了相应事件处理方法)
- pipeline 中有多个 handler,处理时会依次调用其中的 handler
-
handler 分 Inbound 和 Outbound 两类
- Inbound 入站
- Outbound 出站
-
-
eventLoop 可以理解为处理数据的工人
- eventLoop 可以管理多个 channel 的 io 操作,并且一旦 eventLoop 负责了某个 channel,就会将其与channel进行绑定,以后该 channel 中的 io 操作都由该 eventLoop 负责
- eventLoop 既可以执行 io 操作,也可以进行任务处理,每个 eventLoop 有自己的任务队列,队列里可以堆放多个 channel 的待处理任务,任务分为普通任务、定时任务
- eventLoop 按照 pipeline 顺序,依次按照 handler 的规划(代码)处理数据,可以为每个 handler 指定不同的 eventLoop
三、组件
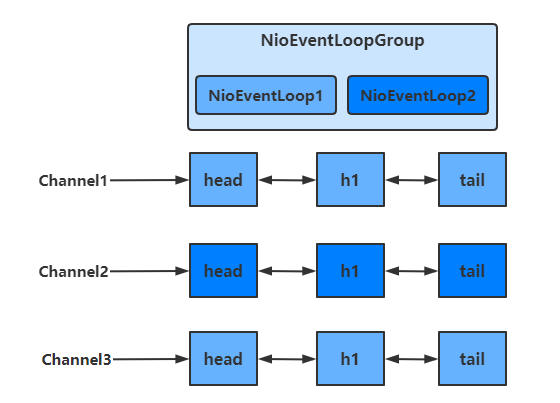
1、EventLoop
事件循环对象 EventLoop
EventLoop 本质是一个单线程执行器(同时维护了一个 Selector),里面有 run 方法处理一个或多个 Channel 上源源不断的 io 事件
它的继承关系如下
- 继承自 j.u.c.ScheduledExecutorService 因此包含了线程池中所有的方法
- 继承自 netty 自己的 OrderedEventExecutor
- 提供了 boolean inEventLoop(Thread thread) 方法判断一个线程是否属于此 EventLoop
- 提供了 EventLoopGroup parent() 方法来看看自己属于哪个 EventLoopGroup
事件循环组 EventLoopGroup
EventLoopGroup 是一组 EventLoop,Channel 一般会调用 EventLoopGroup 的 register 方法来绑定其中一个 EventLoop,后续这个 Channel 上的 io 事件都由此 EventLoop 来处理(保证了 io 事件处理时的线程安全)
- 继承自 netty 自己的 EventExecutorGroup
- 实现了 Iterable 接口提供遍历 EventLoop 的能力
- 另有 next 方法获取集合中下一个 EventLoop
处理普通与定时任务
public class TestEventLoop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建拥有两个EventLoop的NioEventLoopGroup,对应两个线程
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(2);
// 通过next方法可以获得下一个 EventLoop
System.out.println(group.next());
System.out.println(group.next());
// 通过EventLoop执行普通任务
group.next().execute(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " hello");
});
// 通过EventLoop执行定时任务
group.next().scheduleAtFixedRate(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " hello2");
}, 0, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 优雅地关闭
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}Copy
输出结果如下
io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop@7bb11784
io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop@33a10788
nioEventLoopGroup-2-1 hello
nioEventLoopGroup-2-2 hello2
nioEventLoopGroup-2-2 hello2
nioEventLoopGroup-2-2 hello2Copy
关闭 EventLoopGroup
优雅关闭 shutdownGracefully 方法。该方法会首先切换 EventLoopGroup 到关闭状态从而拒绝新的任务的加入,然后在任务队列的任务都处理完成后,停止线程的运行。从而确保整体应用是在正常有序的状态下退出的
处理IO任务
服务器代码
public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ServerBootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + buf.toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
});
}
})
.bind(8080);
}
}Copy
客户端代码
public class MyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Channel channel = new Bootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder());
}
})
.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080))
.sync()
.channel();
System.out.println(channel);
// 此处打断点调试,调用 channel.writeAndFlush(...);
System.in.read();
}
}Copy
分工
Bootstrap的group()方法可以传入两个EventLoopGroup参数,分别负责处理不同的事件
public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ServerBootstrap()
// 两个Group,分别为Boss 负责Accept事件,Worker 负责读写事件
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup(1), new NioEventLoopGroup(2))
...
}
}Copy
多个客户端分别发送 hello 结果
nioEventLoopGroup-3-1 hello1
nioEventLoopGroup-3-2 hello2
nioEventLoopGroup-3-1 hello3
nioEventLoopGroup-3-2 hello4
nioEventLoopGroup-3-2 hello4Copy
可以看出,一个EventLoop可以负责多个Channel,且EventLoop一旦与Channel绑定,则一直负责处理该Channel中的事件
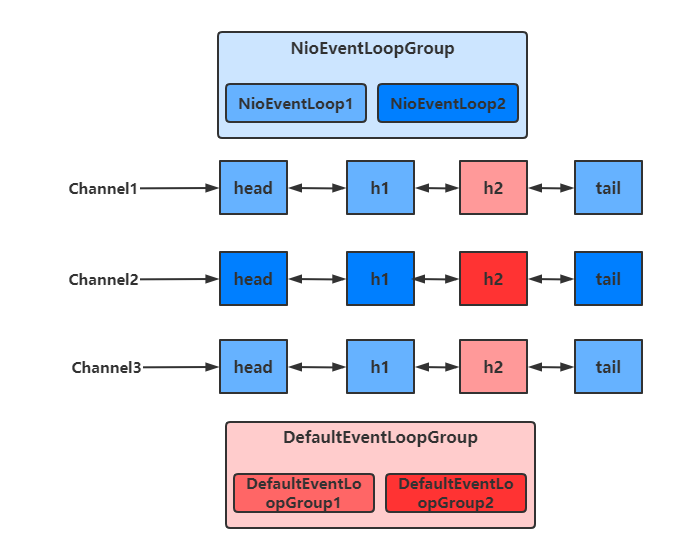
增加自定义EventLoopGroup
当有的任务需要较长的时间处理时,可以使用非NioEventLoopGroup,避免同一个NioEventLoop中的其他Channel在较长的时间内都无法得到处理
public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 增加自定义的非NioEventLoopGroup
EventLoopGroup group = new DefaultEventLoopGroup();
new ServerBootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup(1), new NioEventLoopGroup(2))
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
// 增加两个handler,第一个使用NioEventLoopGroup处理,第二个使用自定义EventLoopGroup处理
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast("nioHandler",new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + buf.toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
// 调用下一个handler
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
})
// 该handler绑定自定义的Group
.addLast(group, "myHandler", new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + buf.toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
});
}
})
.bind(8080);
}
}Copy
启动四个客户端发送数据
nioEventLoopGroup-4-1 hello1
defaultEventLoopGroup-2-1 hello1
nioEventLoopGroup-4-2 hello2
defaultEventLoopGroup-2-2 hello2
nioEventLoopGroup-4-1 hello3
defaultEventLoopGroup-2-3 hello3
nioEventLoopGroup-4-2 hello4
defaultEventLoopGroup-2-4 hello4Copy
可以看出,客户端与服务器之间的事件,被nioEventLoopGroup和defaultEventLoopGroup分别处理
切换的实现
不同的EventLoopGroup切换的实现原理如下
由上面的图可以看出,当handler中绑定的Group不同时,需要切换Group来执行不同的任务
static void invokeChannelRead(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next, Object msg) {
final Object m = next.pipeline.touch(ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(msg, "msg"), next);
// 获得下一个EventLoop, excutor 即为 EventLoopGroup
EventExecutor executor = next.executor();
// 如果下一个EventLoop 在当前的 EventLoopGroup中
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
// 使用当前 EventLoopGroup 中的 EventLoop 来处理任务
next.invokeChannelRead(m);
} else {
// 否则让另一个 EventLoopGroup 中的 EventLoop 来创建任务并执行
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
next.invokeChannelRead(m);
}
});
}
}Copy
- 如果两个 handler 绑定的是同一个EventLoopGroup,那么就直接调用
- 否则,把要调用的代码封装为一个任务对象,由下一个 handler 的 EventLoopGroup 来调用
2、Channel
Channel 的常用方法
- close() 可以用来关闭Channel
- closeFuture() 用来处理 Channel 的关闭
- sync 方法作用是同步等待 Channel 关闭
- 而 addListener 方法是异步等待 Channel 关闭
- pipeline() 方法用于添加处理器
- write() 方法将数据写入
- 因为缓冲机制,数据被写入到 Channel 中以后,不会立即被发送
- 只有当缓冲满了或者调用了flush()方法后,才会将数据通过 Channel 发送出去
- writeAndFlush() 方法将数据写入并立即发送(刷出)
ChannelFuture
连接问题
拆分客户端代码
public class MyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
ChannelFuture channelFuture = new Bootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder());
}
})
// 该方法为异步非阻塞方法,主线程调用后不会被阻塞,真正去执行连接操作的是NIO线程
// NIO线程:NioEventLoop 中的线程
.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));
// 该方法用于等待连接真正建立
channelFuture.sync();
// 获取客户端-服务器之间的Channel对象
Channel channel = channelFuture.channel();
channel.writeAndFlush("hello world");
System.in.read();
}
}Copy
如果我们去掉channelFuture.sync()方法,会服务器无法收到hello world
这是因为建立连接(connect)的过程是异步非阻塞的,若不通过sync()方法阻塞主线程,等待连接真正建立,这时通过 channelFuture.channel() 拿到的 Channel 对象,并不是真正与服务器建立好连接的 Channel,也就没法将信息正确的传输给服务器端
所以需要通过channelFuture.sync()方法,阻塞主线程,同步处理结果,等待连接真正建立好以后,再去获得 Channel 传递数据。使用该方法,获取 Channel 和发送数据的线程都是主线程
下面还有一种方法,用于异步获取建立连接后的 Channel 和发送数据,使得执行这些操作的线程是 NIO 线程(去执行connect操作的线程)
addListener方法
通过这种方法可以在NIO线程中获取 Channel 并发送数据,而不是在主线程中执行这些操作
public class MyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
ChannelFuture channelFuture = new Bootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder());
}
})
// 该方法为异步非阻塞方法,主线程调用后不会被阻塞,真正去执行连接操作的是NIO线程
// NIO线程:NioEventLoop 中的线程
.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));
// 当connect方法执行完毕后,也就是连接真正建立后
// 会在NIO线程中调用operationComplete方法
channelFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture channelFuture) throws Exception {
Channel channel = channelFuture.channel();
channel.writeAndFlush("hello world");
}
});
System.in.read();
}
}Copy
处理关闭
public class ReadClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 创建EventLoopGroup,使用完毕后关闭
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
ChannelFuture channelFuture = new Bootstrap()
.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder());
}
})
.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));
channelFuture.sync();
Channel channel = channelFuture.channel();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// 创建一个线程用于输入并向服务器发送
new Thread(()->{
while (true) {
String msg = scanner.next();
if ("q".equals(msg)) {
// 关闭操作是异步的,在NIO线程中执行
channel.close();
break;
}
channel.writeAndFlush(msg);
}
}, "inputThread").start();
// 获得closeFuture对象
ChannelFuture closeFuture = channel.closeFuture();
System.out.println("waiting close...");
// 同步等待NIO线程执行完close操作
closeFuture.sync();
// 关闭之后执行一些操作,可以保证执行的操作一定是在channel关闭以后执行的
System.out.println("关闭之后执行一些额外操作...");
// 关闭EventLoopGroup
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}Copy
关闭channel
当我们要关闭channel时,可以调用channel.close()方法进行关闭。但是该方法也是一个异步方法。真正的关闭操作并不是在调用该方法的线程中执行的,而是在NIO线程中执行真正的关闭操作
如果我们想在channel真正关闭以后,执行一些额外的操作,可以选择以下两种方法来实现
-
通过channel.closeFuture()方法获得对应的ChannelFuture对象,然后调用sync()方法阻塞执行操作的线程,等待channel真正关闭后,再执行其他操作
// 获得closeFuture对象 ChannelFuture closeFuture = channel.closeFuture(); // 同步等待NIO线程执行完close操作 closeFuture.sync();Copy -
调用closeFuture.addListener方法,添加close的后续操作
closeFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() { @Override public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture channelFuture) throws Exception { // 等待channel关闭后才执行的操作 System.out.println("关闭之后执行一些额外操作..."); // 关闭EventLoopGroup group.shutdownGracefully(); } });Copy
3、Future与Promise
概念
netty 中的 Future 与 jdk 中的 Future 同名,但是是两个接口
netty 的 Future 继承自 jdk 的 Future,而 Promise 又对 netty Future 进行了扩展
- jdk Future 只能同步等待任务结束(或成功、或失败)才能得到结果
- netty Future 可以同步等待任务结束得到结果,也可以异步方式得到结果,但都是要等任务结束
- netty Promise 不仅有 netty Future 的功能,而且脱离了任务独立存在,只作为两个线程间传递结果的容器
| 功能/名称 | jdk Future | netty Future | Promise |
|---|---|---|---|
| cancel | 取消任务 | - | - |
| isCanceled | 任务是否取消 | - | - |
| isDone | 任务是否完成,不能区分成功失败 | - | - |
| get | 获取任务结果,阻塞等待 | - | - |
| getNow | - | 获取任务结果,非阻塞,还未产生结果时返回 null | - |
| await | - | 等待任务结束,如果任务失败,不会抛异常,而是通过 isSuccess 判断 | - |
| sync | - | 等待任务结束,如果任务失败,抛出异常 | - |
| isSuccess | - | 判断任务是否成功 | - |
| cause | - | 获取失败信息,非阻塞,如果没有失败,返回null | - |
| addLinstener | - | 添加回调,异步接收结果 | - |
| setSuccess | - | - | 设置成功结果 |
| setFailure | - | - | 设置失败结果 |
JDK Future
public class JdkFuture {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ThreadFactory factory = new ThreadFactory() {
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, "JdkFuture");
}
};
// 创建线程池
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 10,10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(10), factory);
// 获得Future对象
Future<Integer> future = executor.submit(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
return 50;
}
});
// 通过阻塞的方式,获得运行结果
System.out.println(future.get());
}
}Copy
Netty Future
public class NettyFuture {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
// 获得 EventLoop 对象
EventLoop eventLoop = group.next();
Future<Integer> future = eventLoop.submit(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return 50;
}
});
// 主线程中获取结果
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 获取结果");
System.out.println("getNow " + future.getNow());
System.out.println("get " + future.get());
// NIO线程中异步获取结果
future.addListener(new GenericFutureListener<Future<? super Integer>>() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(Future<? super Integer> future) throws Exception {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 获取结果");
System.out.println("getNow " + future.getNow());
}
});
}
}Copy
运行结果
main 获取结果
getNow null
get 50
nioEventLoopGroup-2-1 获取结果
getNow 50Copy
Netty中的Future对象,可以通过EventLoop的sumbit()方法得到
- 可以通过Future对象的get方法,阻塞地获取返回结果
- 也可以通过getNow方法,获取结果,若还没有结果,则返回null,该方法是非阻塞的
- 还可以通过future.addListener方法,在Callable方法执行的线程中,异步获取返回结果
Netty Promise
Promise相当于一个容器,可以用于存放各个线程中的结果,然后让其他线程去获取该结果
public class NettyPromise {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// 创建EventLoop
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoop eventLoop = group.next();
// 创建Promise对象,用于存放结果
DefaultPromise<Integer> promise = new DefaultPromise<>(eventLoop);
new Thread(()->{
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 自定义线程向Promise中存放结果
promise.setSuccess(50);
}).start();
// 主线程从Promise中获取结果
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + promise.get());
}
}Copy
4、Handler与Pipeline
Pipeline
public class PipeLineServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ServerBootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
// 在socketChannel的pipeline中添加handler
// pipeline中handler是带有head与tail节点的双向链表,的实际结构为
// head <-> handler1 <-> ... <-> handler4 <->tail
// Inbound主要处理入站操作,一般为读操作,发生入站操作时会触发Inbound方法
// 入站时,handler是从head向后调用的
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast("handler1" ,new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Inbound handler 1");
// 父类该方法内部会调用fireChannelRead
// 将数据传递给下一个handler
super.channelRead(ctx, msg);
}
});
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast("handler2", new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Inbound handler 2");
// 执行write操作,使得Outbound的方法能够得到调用
socketChannel.writeAndFlush(ctx.alloc().buffer().writeBytes("Server...".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));
super.channelRead(ctx, msg);
}
});
// Outbound主要处理出站操作,一般为写操作,发生出站操作时会触发Outbound方法
// 出站时,handler的调用是从tail向前调用的
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast("handler3" ,new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Outbound handler 1");
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
}
});
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast("handler4" ,new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Outbound handler 2");
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
}
});
}
})
.bind(8080);
}
}Copy
运行结果如下
nioEventLoopGroup-2-2 Inbound handler 1
nioEventLoopGroup-2-2 Inbound handler 2
nioEventLoopGroup-2-2 Outbound handler 2
nioEventLoopGroup-2-2 Outbound handler 1Copy
通过channel.pipeline().addLast(name, handler)添加handler时,记得给handler取名字。这样可以调用pipeline的addAfter、addBefore等方法更灵活地向pipeline中添加handler
handler需要放入通道的pipeline中,才能根据放入顺序来使用handler
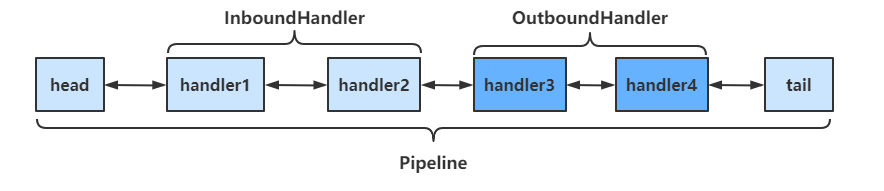
- pipeline是结构是一个带有head与tail指针的双向链表,其中的节点为handler
- 要通过ctx.fireChannelRead(msg)等方法,将当前handler的处理结果传递给下一个handler
- 当有入站(Inbound)操作时,会从head开始向后调用handler,直到handler不是处理Inbound操作为止
- 当有出站(Outbound)操作时,会从tail开始向前调用handler,直到handler不是处理Outbound操作为止
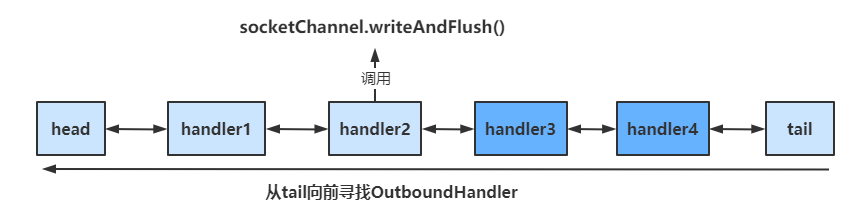
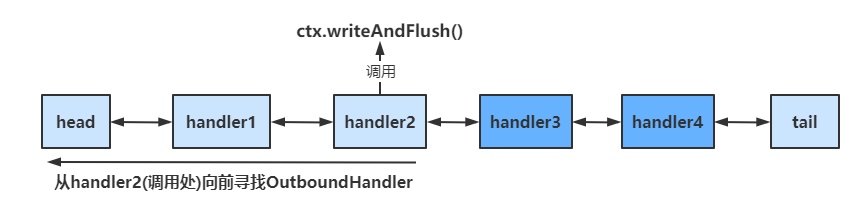
具体结构如下
调用顺序如下
OutboundHandler
socketChannel.writeAndFlush()
当handler中调用该方法进行写操作时,会触发Outbound操作,此时是从tail向前寻找OutboundHandler
ctx.writeAndFlush()
当handler中调用该方法进行写操作时,会触发Outbound操作,此时是从当前handler向前寻找OutboundHandler
EmbeddedChannel
EmbeddedChannel可以用于测试各个handler,通过其构造函数按顺序传入需要测试handler,然后调用对应的Inbound和Outbound方法即可
public class TestEmbeddedChannel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter h1 = new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("1");
super.channelRead(ctx, msg);
}
};
ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter h2 = new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("2");
super.channelRead(ctx, msg);
}
};
ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter h3 = new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
System.out.println("3");
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
}
};
ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter h4 = new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
System.out.println("4");
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
}
};
// 用于测试Handler的Channel
EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel(h1, h2, h3, h4);
// 执行Inbound操作
channel.writeInbound(ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer().writeBytes("hello".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));
// 执行Outbound操作
channel.writeOutbound(ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer().writeBytes("hello".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));
}
}Copy
5、ByteBuf
调试工具方法
private static void log(ByteBuf buffer) {
int length = buffer.readableBytes();
int rows = length / 16 + (length % 15 == 0 ? 0 : 1) + 4;
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(rows * 80 * 2)
.append("read index:").append(buffer.readerIndex())
.append(" write index:").append(buffer.writerIndex())
.append(" capacity:").append(buffer.capacity())
.append(NEWLINE);
appendPrettyHexDump(buf, buffer);
System.out.println(buf.toString());
}Copy
该方法可以帮助我们更为详细地查看ByteBuf中的内容
创建
public class ByteBufStudy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建ByteBuf
ByteBuf buffer = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer(16);
ByteBufUtil.log(buffer);
// 向buffer中写入数据
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
sb.append("a");
}
buffer.writeBytes(sb.toString().getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
// 查看写入结果
ByteBufUtil.log(buffer);
}
}Copy
运行结果
read index:0 write index:0 capacity:16
read index:0 write index:20 capacity:64
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 |aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa|
|00000010| 61 61 61 61 |aaaa |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+Copy
ByteBuf通过ByteBufAllocator选择allocator并调用对应的buffer()方法来创建的,默认使用直接内存作为ByteBuf,容量为256个字节,可以指定初始容量的大小
当ByteBuf的容量无法容纳所有数据时,ByteBuf会进行扩容操作
如果在handler中创建ByteBuf,建议使用ChannelHandlerContext ctx.alloc().buffer()来创建
直接内存与堆内存
通过该方法创建的ByteBuf,使用的是基于直接内存的ByteBuf
ByteBuf buffer = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer(16);Copy
可以使用下面的代码来创建池化基于堆的 ByteBuf
ByteBuf buffer = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.heapBuffer(16);Copy
也可以使用下面的代码来创建池化基于直接内存的 ByteBuf
ByteBuf buffer = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.directBuffer(16);Copy
- 直接内存创建和销毁的代价昂贵,但读写性能高(少一次内存复制),适合配合池化功能一起用
- 直接内存对 GC 压力小,因为这部分内存不受 JVM 垃圾回收的管理,但也要注意及时主动释放
验证
public class ByteBufStudy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuf buffer = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer(16);
System.out.println(buffer.getClass());
buffer = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.heapBuffer(16);
System.out.println(buffer.getClass());
buffer = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.directBuffer(16);
System.out.println(buffer.getClass());
}
}Copy
// 使用池化的直接内存
class io.netty.buffer.PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf
// 使用池化的堆内存
class io.netty.buffer.PooledUnsafeHeapByteBuf
// 使用池化的直接内存
class io.netty.buffer.PooledUnsafeDirectByteBufCopy
池化与非池化
池化的最大意义在于可以重用 ByteBuf,优点有
- 没有池化,则每次都得创建新的 ByteBuf 实例,这个操作对直接内存代价昂贵,就算是堆内存,也会增加 GC 压力
- 有了池化,则可以重用池中 ByteBuf 实例,并且采用了与 jemalloc 类似的内存分配算法提升分配效率
- 高并发时,池化功能更节约内存,减少内存溢出的可能
池化功能是否开启,可以通过下面的系统环境变量来设置
-Dio.netty.allocator.type={unpooled|pooled}Copy
- 4.1 以后,非 Android 平台默认启用池化实现,Android 平台启用非池化实现
- 4.1 之前,池化功能还不成熟,默认是非池化实现
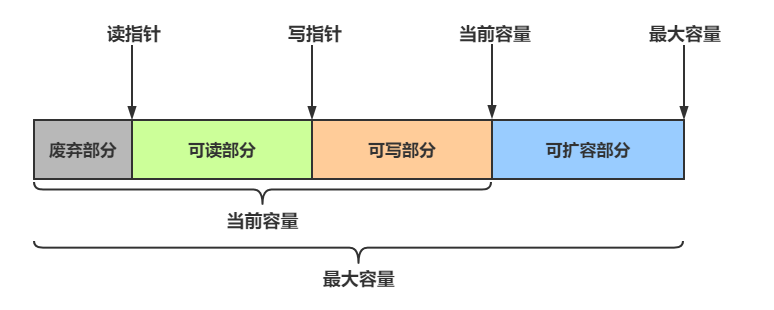
组成
ByteBuf主要有以下几个组成部分
-
最大容量与当前容量
- 在构造ByteBuf时,可传入两个参数,分别代表初始容量和最大容量,若未传入第二个参数(最大容量),最大容量默认为Integer.MAX_VALUE
- 当ByteBuf容量无法容纳所有数据时,会进行扩容操作,若超出最大容量,会抛出
java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException异常
-
读写操作不同于ByteBuffer只用position进行控制,
ByteBuf分别由读指针和写指针两个指针控制
。进行读写操作时,无需进行模式的切换
- 读指针前的部分被称为废弃部分,是已经读过的内容
- 读指针与写指针之间的空间称为可读部分
- 写指针与当前容量之间的空间称为可写部分
写入
常用方法如下
| 方法签名 | 含义 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| writeBoolean(boolean value) | 写入 boolean 值 | 用一字节 01|00 代表 true|false |
| writeByte(int value) | 写入 byte 值 | |
| writeShort(int value) | 写入 short 值 | |
| writeInt(int value) | 写入 int 值 | Big Endian(大端写入),即 0x250,写入后 00 00 02 50 |
| writeIntLE(int value) | 写入 int 值 | Little Endian(小端写入),即 0x250,写入后 50 02 00 00 |
| writeLong(long value) | 写入 long 值 | |
| writeChar(int value) | 写入 char 值 | |
| writeFloat(float value) | 写入 float 值 | |
| writeDouble(double value) | 写入 double 值 | |
| writeBytes(ByteBuf src) | 写入 netty 的 ByteBuf | |
| writeBytes(byte[] src) | 写入 byte[] | |
| writeBytes(ByteBuffer src) | 写入 nio 的 ByteBuffer | |
| int writeCharSequence(CharSequence sequence, Charset charset) | 写入字符串 | CharSequence为字符串类的父类,第二个参数为对应的字符集 |
注意
- 这些方法的未指明返回值的,其返回值都是 ByteBuf,意味着可以链式调用来写入不同的数据
- 网络传输中,默认习惯是 Big Endian,使用 writeInt(int value)
使用方法
public class ByteBufStudy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建ByteBuf
ByteBuf buffer = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer(16, 20);
ByteBufUtil.log(buffer);
// 向buffer中写入数据
buffer.writeBytes(new byte[]{1, 2, 3, 4});
ByteBufUtil.log(buffer);
buffer.writeInt(5);
ByteBufUtil.log(buffer);
buffer.writeIntLE(6);
ByteBufUtil.log(buffer);
buffer.writeLong(7);
ByteBufUtil.log(buffer);
}
}Copy
运行结果
read index:0 write index:0 capacity:16
read index:0 write index:4 capacity:16
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 01 02 03 04 |.... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
read index:0 write index:8 capacity:16
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 01 02 03 04 00 00 00 05 |........ |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
read index:0 write index:12 capacity:16
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 01 02 03 04 00 00 00 05 06 00 00 00 |............ |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
read index:0 write index:20 capacity:20
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 01 02 03 04 00 00 00 05 06 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
|00000010| 00 00 00 07 |.... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+Copy
还有一类方法是 set 开头的一系列方法,也可以写入数据,但不会改变写指针位置
扩容
当ByteBuf中的容量无法容纳写入的数据时,会进行扩容操作
buffer.writeLong(7);
ByteBufUtil.log(buffer);Copy
// 扩容前
read index:0 write index:12 capacity:16
...
// 扩容后
read index:0 write index:20 capacity:20
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 01 02 03 04 00 00 00 05 06 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
|00000010| 00 00 00 07 |.... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+Copy
扩容规则
-
如何写入后数据大小未超过 512 字节,则选择下一个 16 的整数倍进行扩容
- 例如写入后大小为 12 字节,则扩容后 capacity 是 16 字节
-
如果写入后数据大小超过 512 字节,则选择下一个 2
n
- 例如写入后大小为 513 字节,则扩容后 capacity 是 210=1024 字节(29=512 已经不够了)
-
扩容不能超过 maxCapacity,否则会抛出
java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException异常
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException: writerIndex(20) + minWritableBytes(8) exceeds maxCapacity(20): PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf(ridx: 0, widx: 20, cap: 20/20)
...Copy
读取
读取主要是通过一系列read方法进行读取,读取时会根据读取数据的字节数移动读指针
如果需要重复读取,需要调用buffer.markReaderIndex()对读指针进行标记,并通过buffer.resetReaderIndex()将读指针恢复到mark标记的位置
public class ByteBufStudy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建ByteBuf
ByteBuf buffer = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer(16, 20);
// 向buffer中写入数据
buffer.writeBytes(new byte[]{1, 2, 3, 4});
buffer.writeInt(5);
// 读取4个字节
System.out.println(buffer.readByte());
System.out.println(buffer.readByte());
System.out.println(buffer.readByte());
System.out.println(buffer.readByte());
ByteBufUtil.log(buffer);
// 通过mark与reset实现重复读取
buffer.markReaderIndex();
System.out.println(buffer.readInt());
ByteBufUtil.log(buffer);
// 恢复到mark标记处
buffer.resetReaderIndex();
ByteBufUtil.log(buffer);
}
}Copy
1
2
3
4
read index:4 write index:8 capacity:16
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 00 00 00 05 |.... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
5
read index:8 write index:8 capacity:16
read index:4 write index:8 capacity:16
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 00 00 00 05 |.... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+Copy
还有以 get 开头的一系列方法,这些方法不会改变读指针的位置
释放
由于 Netty 中有堆外内存(直接内存)的 ByteBuf 实现,堆外内存最好是手动来释放,而不是等 GC 垃圾回收。
- UnpooledHeapByteBuf 使用的是 JVM 内存,只需等 GC 回收内存即可
- UnpooledDirectByteBuf 使用的就是直接内存了,需要特殊的方法来回收内存
- PooledByteBuf 和它的子类使用了池化机制,需要更复杂的规则来回收内存
Netty 这里采用了引用计数法来控制回收内存,每个 ByteBuf 都实现了 ReferenceCounted 接口
- 每个 ByteBuf 对象的初始计数为 1
- 调用 release 方法计数减 1,如果计数为 0,ByteBuf 内存被回收
- 调用 retain 方法计数加 1,表示调用者没用完之前,其它 handler 即使调用了 release 也不会造成回收
- 当计数为 0 时,底层内存会被回收,这时即使 ByteBuf 对象还在,其各个方法均无法正常使用
释放规则
因为 pipeline 的存在,一般需要将 ByteBuf 传递给下一个 ChannelHandler,如果在每个 ChannelHandler 中都去调用 release ,就失去了传递性(如果在这个 ChannelHandler 内这个 ByteBuf 已完成了它的使命,那么便无须再传递)
基本规则是,谁是最后使用者,谁负责 release
-
起点,对于 NIO 实现来讲,在 io.netty.channel.nio.AbstractNioByteChannel.NioByteUnsafe.read 方法中首次创建 ByteBuf 放入 pipeline(line 163 pipeline.fireChannelRead(byteBuf))
-
入站 ByteBuf 处理原则
- 对原始 ByteBuf 不做处理,调用 ctx.fireChannelRead(msg) 向后传递,这时无须 release
- 将原始 ByteBuf 转换为其它类型的 Java 对象,这时 ByteBuf 就没用了,必须 release
- 如果不调用 ctx.fireChannelRead(msg) 向后传递,那么也必须 release
- 注意各种异常,如果 ByteBuf 没有成功传递到下一个 ChannelHandler,必须 release
- 假设消息一直向后传,那么 TailContext 会负责释放未处理消息(原始的 ByteBuf)
-
出站 ByteBuf 处理原则
- 出站消息最终都会转为 ByteBuf 输出,一直向前传,由 HeadContext flush 后 release
-
异常处理原则
-
有时候不清楚 ByteBuf 被引用了多少次,但又必须彻底释放,可以循环调用 release 直到返回 true
while (!buffer.release()) {}Copy
-
当ByteBuf被传到了pipeline的head与tail时,ByteBuf会被其中的方法彻底释放,但前提是ByteBuf被传递到了head与tail中
TailConext中释放ByteBuf的源码
protected void onUnhandledInboundMessage(Object msg) {
try {
logger.debug("Discarded inbound message {} that reached at the tail of the pipeline. Please check your pipeline configuration.", msg);
} finally {
// 具体的释放方法
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
}
}Copy
判断传过来的是否为ByteBuf,是的话才需要释放
public static boolean release(Object msg) {
return msg instanceof ReferenceCounted ? ((ReferenceCounted)msg).release() : false;
}Copy
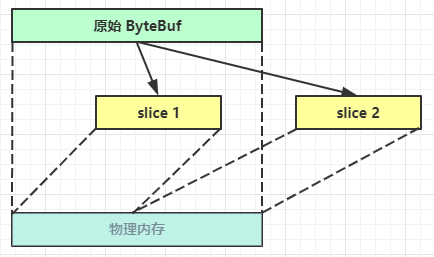
切片
ByteBuf切片是【零拷贝】的体现之一,对原始 ByteBuf 进行切片成多个 ByteBuf,切片后的 ByteBuf 并没有发生内存复制,还是使用原始 ByteBuf 的内存,切片后的 ByteBuf 维护独立的 read,write 指针
得到分片后的buffer后,要调用其retain方法,使其内部的引用计数加一。避免原ByteBuf释放,导致切片buffer无法使用
修改原ByteBuf中的值,也会影响切片后得到的ByteBuf
public class TestSlice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建ByteBuf
ByteBuf buffer = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer(16, 20);
// 向buffer中写入数据
buffer.writeBytes(new byte[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10});
// 将buffer分成两部分
ByteBuf slice1 = buffer.slice(0, 5);
ByteBuf slice2 = buffer.slice(5, 5);
// 需要让分片的buffer引用计数加一
// 避免原Buffer释放导致分片buffer无法使用
slice1.retain();
slice2.retain();
ByteBufUtil.log(slice1);
ByteBufUtil.log(slice2);
// 更改原始buffer中的值
System.out.println("===========修改原buffer中的值===========");
buffer.setByte(0,5);
System.out.println("===========打印slice1===========");
ByteBufUtil.log(slice1);
}
}Copy
运行结果
read index:0 write index:5 capacity:5
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 01 02 03 04 05 |..... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
read index:0 write index:5 capacity:5
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 06 07 08 09 0a |..... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
===========修改原buffer中的值===========
===========打印slice1===========
read index:0 write index:5 capacity:5
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 05 02 03 04 05 |..... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+Copy
优势
- 池化思想 - 可以重用池中 ByteBuf 实例,更节约内存,减少内存溢出的可能
- 读写指针分离,不需要像 ByteBuffer 一样切换读写模式
- 可以自动扩容
- 支持链式调用,使用更流畅
- 很多地方体现零拷贝,例如
- slice、duplicate、CompositeByteBuf
四、应用
1、粘包与半包
服务器代码
public class StudyServer {
static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(StudyServer.class);
void start() {
NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
serverBootstrap.group(boss, worker);
serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 连接建立时会执行该方法
log.debug("connected {}", ctx.channel());
super.channelActive(ctx);
}
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 连接断开时会执行该方法
log.debug("disconnect {}", ctx.channel());
super.channelInactive(ctx);
}
});
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8080);
log.debug("{} binding...", channelFuture.channel());
channelFuture.sync();
log.debug("{} bound...", channelFuture.channel());
// 关闭channel
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("server error", e);
} finally {
boss.shutdownGracefully();
worker.shutdownGracefully();
log.debug("stopped");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new StudyServer().start();
}
}Copy
粘包现象
客户端代码
public class StudyClient {
static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(StudyClient.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(worker);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
log.debug("connected...");
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
log.debug("sending...");
// 每次发送16个字节的数据,共发送10次
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
ByteBuf buffer = ctx.alloc().buffer();
buffer.writeBytes(new byte[]{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15});
ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer);
}
}
});
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 8080).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("client error", e);
} finally {
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}Copy
服务器接收结果
7999 [nioEventLoopGroup-3-1] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x5b43ecb0, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:53797] READ: 160B
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f |................|
|00000010| 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f |................|
|00000020| 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f |................|
|00000030| 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f |................|
|00000040| 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f |................|
|00000050| 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f |................|
|00000060| 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f |................|
|00000070| 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f |................|
|00000080| 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f |................|
|00000090| 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f |................|
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+Copy
可见虽然客户端是分别以16字节为单位,通过channel向服务器发送了10次数据,可是服务器端却只接收了一次,接收数据的大小为160B,即客户端发送的数据总大小,这就是粘包现象
半包现象
将客户端-服务器之间的channel容量进行调整
服务器代码
// 调整channel的容量
serverBootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, 10);Copy
注意
serverBootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, 10) 影响的底层接收缓冲区(即滑动窗口)大小,仅决定了 netty 读取的最小单位,netty 实际每次读取的一般是它的整数倍
服务器接收结果
5901 [nioEventLoopGroup-3-1] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0xc73284f3, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:49679] READ: 36B
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f |................|
|00000010| 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f |................|
|00000020| 00 01 02 03 |.... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
5901 [nioEventLoopGroup-3-1] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0xc73284f3, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:49679] READ: 40B
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f 00 01 02 03 |................|
|00000010| 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f 00 01 02 03 |................|
|00000020| 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b |........ |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
5901 [nioEventLoopGroup-3-1] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0xc73284f3, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:49679] READ: 40B
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 0c 0d 0e 0f 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b |................|
|00000010| 0c 0d 0e 0f 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b |................|
|00000020| 0c 0d 0e 0f 00 01 02 03 |........ |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
5901 [nioEventLoopGroup-3-1] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0xc73284f3, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:49679] READ: 40B
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f 00 01 02 03 |................|
|00000010| 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f 00 01 02 03 |................|
|00000020| 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b |........ |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
5901 [nioEventLoopGroup-3-1] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0xc73284f3, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:49679] READ: 4B
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 0c 0d 0e 0f |.... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+Copy
可见客户端每次发送的数据,因channel容量不足,无法将发送的数据一次性接收,便产生了半包现象
现象分析
粘包
- 现象
- 发送 abc def,接收 abcdef
- 原因
- 应用层
- 接收方 ByteBuf 设置太大(Netty 默认 1024)
- 传输层-网络层
- 滑动窗口:假设发送方 256 bytes 表示一个完整报文,但由于接收方处理不及时且**窗口大小足够大(大于256 bytes),这 256 bytes 字节就会缓冲在接收方的滑动窗口中,**当滑动窗口中缓冲了多个报文就会粘包
- Nagle 算法:会造成粘包
- 应用层
半包
- 现象
- 发送 abcdef,接收 abc def
- 原因
- 应用层
- 接收方 ByteBuf 小于实际发送数据量
- 传输层-网络层
- 滑动窗口:假设接收方的窗口只剩了 128 bytes,发送方的报文大小是 256 bytes,这时接收方窗口中无法容纳发送方的全部报文,发送方只能先发送前 128 bytes,等待 ack 后才能发送剩余部分,这就造成了半包
- 数据链路层
- MSS 限制:当发送的数据超过 MSS 限制后,会将数据切分发送,就会造成半包
- 应用层
本质
发生粘包与半包现象的本质是因为 TCP 是流式协议,消息无边界
解决方案
短链接
客户端每次向服务器发送数据以后,就与服务器断开连接,此时的消息边界为连接建立到连接断开。这时便无需使用滑动窗口等技术来缓冲数据,则不会发生粘包现象。但如果一次性数据发送过多,接收方无法一次性容纳所有数据,还是会发生半包现象,所以短链接无法解决半包现象
客户端代码改进
修改channelActive方法
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
log.debug("sending...");
ByteBuf buffer = ctx.alloc().buffer(16);
buffer.writeBytes(new byte[]{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15});
ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer);
// 使用短链接,每次发送完毕后就断开连接
ctx.channel().close();
}Copy
将发送步骤整体封装为send()方法,调用10次send()方法,模拟发送10次数据
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 发送10次
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
send();
}
}Copy
运行结果
6452 [nioEventLoopGroup-3-1] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x3eb6a684, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:65024] ACTIVE
6468 [nioEventLoopGroup-3-1] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x3eb6a684, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:65024] READ: 16B
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f |................|
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
6468 [nioEventLoopGroup-3-1] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x3eb6a684, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 ! R:/127.0.0.1:65024] INACTIVE
6483 [nioEventLoopGroup-3-2] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x7dcc31ff, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:65057] ACTIVE
6483 [nioEventLoopGroup-3-2] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x7dcc31ff, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:65057] READ: 16B
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f |................|
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
6483 [nioEventLoopGroup-3-2] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x7dcc31ff, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 ! R:/127.0.0.1:65057] INACTIVE
...Copy
客户端先于服务器建立连接,此时控制台打印ACTIVE,之后客户端向服务器发送了16B的数据,发送后断开连接,此时控制台打印INACTIVE,可见未出现粘包现象
定长解码器
客户端于服务器约定一个最大长度,保证客户端每次发送的数据长度都不会大于该长度。若发送数据长度不足则需要补齐至该长度
服务器接收数据时,将接收到的数据按照约定的最大长度进行拆分,即使发送过程中产生了粘包,也可以通过定长解码器将数据正确地进行拆分。服务端需要用到FixedLengthFrameDecoder对数据进行定长解码,具体使用方法如下
ch.pipeline().addLast(new FixedLengthFrameDecoder(16));Copy
客户端代码
客户端发送数据的代码如下
// 约定最大长度为16
final int maxLength = 16;
// 被发送的数据
char c = 'a';
// 向服务器发送10个报文
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
ByteBuf buffer = ctx.alloc().buffer(maxLength);
// 定长byte数组,未使用部分会以0进行填充
byte[] bytes = new byte[maxLength];
// 生成长度为0~15的数据
for (int j = 0; j < (int)(Math.random()*(maxLength-1)); j++) {
bytes[j] = (byte) c;
}
buffer.writeBytes(bytes);
c++;
// 将数据发送给服务器
ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer);
}Copy
服务器代码
使用FixedLengthFrameDecoder对粘包数据进行拆分,该handler需要添加在LoggingHandler之前,保证数据被打印时已被拆分
// 通过定长解码器对粘包数据进行拆分
ch.pipeline().addLast(new FixedLengthFrameDecoder(16));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));Copy
运行结果
8222 [nioEventLoopGroup-3-1] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0xbc122d07, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:52954] READ: 16B
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 61 61 61 61 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |aaaa............|
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
8222 [nioEventLoopGroup-3-1] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0xbc122d07, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:52954] READ: 16B
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 62 62 62 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |bbb.............|
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
8222 [nioEventLoopGroup-3-1] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0xbc122d07, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:52954] READ: 16B
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 63 63 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |cc..............|
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
...Copy
行解码器
行解码器的是通过分隔符对数据进行拆分来解决粘包半包问题的
可以通过LineBasedFrameDecoder(int maxLength)来拆分以换行符(\n)为分隔符的数据,也可以通过DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(int maxFrameLength, ByteBuf... delimiters)来指定通过什么分隔符来拆分数据(可以传入多个分隔符)
两种解码器都需要传入数据的最大长度,若超出最大长度,会抛出TooLongFrameException异常
以换行符 \n 为分隔符
客户端代码
// 约定最大长度为 64
final int maxLength = 64;
// 被发送的数据
char c = 'a';
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
ByteBuf buffer = ctx.alloc().buffer(maxLength);
// 生成长度为0~62的数据
Random random = new Random();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int j = 0; j < (int)(random.nextInt(maxLength-2)); j++) {
sb.append(c);
}
// 数据以 \n 结尾
sb.append("\n");
buffer.writeBytes(sb.toString().getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
c++;
// 将数据发送给服务器
ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer);
}Copy
服务器代码
// 通过行解码器对粘包数据进行拆分,以 \n 为分隔符
// 需要指定最大长度
ch.pipeline().addLast(new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(64));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));Copy
运行结果
4184 [nioEventLoopGroup-3-1] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x9d6ac701, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:58282] READ: 10B
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 |aaaaaaaaaa |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
4184 [nioEventLoopGroup-3-1] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x9d6ac701, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:58282] READ: 11B
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 62 62 62 62 62 62 62 62 62 62 62 |bbbbbbbbbbb |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
4184 [nioEventLoopGroup-3-1] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x9d6ac701, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:58282] READ: 2B
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 63 63 |cc |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
...Copy
以自定义分隔符 \c 为分隔符
客户端代码
...
// 数据以 \c 结尾
sb.append("\\c");
buffer.writeBytes(sb.toString().getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
...Copy
服务器代码
// 将分隔符放入ByteBuf中
ByteBuf bufSet = ch.alloc().buffer().writeBytes("\\c".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
// 通过行解码器对粘包数据进行拆分,以 \c 为分隔符
ch.pipeline().addLast(new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(64, ch.alloc().buffer().writeBytes(bufSet)));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));Copy
运行结果
8246 [nioEventLoopGroup-3-1] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x86215ccd, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:65159] READ: 14B
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 61 |aaaaaaaaaaaaaa |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
8247 [nioEventLoopGroup-3-1] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x86215ccd, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:65159] READ: 3B
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 62 62 62 |bbb |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
...Copy
长度字段解码器
在传送数据时可以在数据中添加一个用于表示有用数据长度的字段,在解码时读取出这个用于表明长度的字段,同时读取其他相关参数,即可知道最终需要的数据是什么样子的
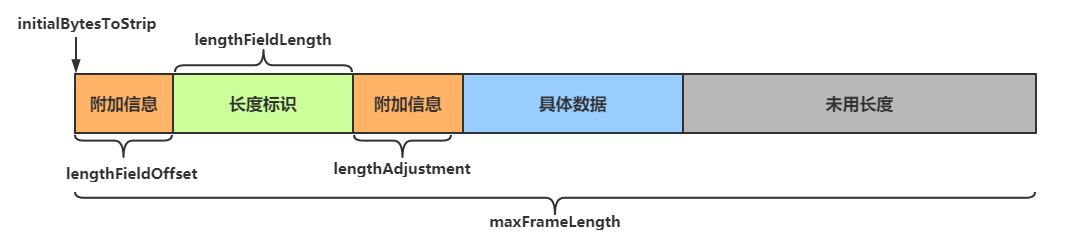
LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder解码器可以提供更为丰富的拆分方法,其构造方法有五个参数
public LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(
int maxFrameLength,
int lengthFieldOffset, int lengthFieldLength,
int lengthAdjustment, int initialBytesToStrip)Copy
参数解析
- maxFrameLength 数据最大长度
- 表示数据的最大长度(包括附加信息、长度标识等内容)
- lengthFieldOffset 数据长度标识的起始偏移量
- 用于指明数据第几个字节开始是用于标识有用字节长度的,因为前面可能还有其他附加信息
- lengthFieldLength 数据长度标识所占字节数(用于指明有用数据的长度)
- 数据中用于表示有用数据长度的标识所占的字节数
- lengthAdjustment 长度表示与有用数据的偏移量
- 用于指明数据长度标识和有用数据之间的距离,因为两者之间还可能有附加信息
- initialBytesToStrip 数据读取起点
- 读取起点,不读取 0 ~ initialBytesToStrip 之间的数据
参数图解
lengthFieldOffset = 0
lengthFieldLength = 2
lengthAdjustment = 0
initialBytesToStrip = 0 (= do not strip header)
BEFORE DECODE (14 bytes) AFTER DECODE (14 bytes)
+--------+----------------+ +--------+----------------+
| Length | Actual Content |----->| Length | Actual Content |
| 0x000C | "HELLO, WORLD" | | 0x000C | "HELLO, WORLD" |
+--------+----------------+ +--------+----------------+Copy
从0开始即为长度标识,长度标识长度为2个字节
0x000C 即为后面 HELLO, WORLD的长度
lengthFieldOffset = 0
lengthFieldLength = 2
lengthAdjustment = 0
initialBytesToStrip = 2 (= the length of the Length field)
BEFORE DECODE (14 bytes) AFTER DECODE (12 bytes)
+--------+----------------+ +----------------+
| Length | Actual Content |----->| Actual Content |
| 0x000C | "HELLO, WORLD" | | "HELLO, WORLD" |
+--------+----------------+ +----------------+Copy
从0开始即为长度标识,长度标识长度为2个字节,读取时从第二个字节开始读取(此处即跳过长度标识)
因为跳过了用于表示长度的2个字节,所以此处直接读取HELLO, WORLD
lengthFieldOffset = 2 (= the length of Header 1)
lengthFieldLength = 3
lengthAdjustment = 0
initialBytesToStrip = 0
BEFORE DECODE (17 bytes) AFTER DECODE (17 bytes)
+----------+----------+----------------+ +----------+----------+----------------+
| Header 1 | Length | Actual Content |----->| Header 1 | Length | Actual Content |
| 0xCAFE | 0x00000C | "HELLO, WORLD" | | 0xCAFE | 0x00000C | "HELLO, WORLD" |
+----------+----------+----------------+ +----------+----------+----------------+Copy
长度标识前面还有2个字节的其他内容(0xCAFE),第三个字节开始才是长度标识,长度表示长度为3个字节(0x00000C)
Header1中有附加信息,读取长度标识时需要跳过这些附加信息来获取长度
lengthFieldOffset = 0
lengthFieldLength = 3
lengthAdjustment = 2 (= the length of Header 1)
initialBytesToStrip = 0
BEFORE DECODE (17 bytes) AFTER DECODE (17 bytes)
+----------+----------+----------------+ +----------+----------+----------------+
| Length | Header 1 | Actual Content |----->| Length | Header 1 | Actual Content |
| 0x00000C | 0xCAFE | "HELLO, WORLD" | | 0x00000C | 0xCAFE | "HELLO, WORLD" |
+----------+----------+----------------+ +----------+----------+----------------+Copy
从0开始即为长度标识,长度标识长度为3个字节,长度标识之后还有2个字节的其他内容(0xCAFE)
长度标识(0x00000C)表示的是从其后lengthAdjustment(2个字节)开始的数据的长度,即HELLO, WORLD,不包括0xCAFE
lengthFieldOffset = 1 (= the length of HDR1)
lengthFieldLength = 2
lengthAdjustment = 1 (= the length of HDR2)
initialBytesToStrip = 3 (= the length of HDR1 + LEN)
BEFORE DECODE (16 bytes) AFTER DECODE (13 bytes)
+------+--------+------+----------------+ +------+----------------+
| HDR1 | Length | HDR2 | Actual Content |----->| HDR2 | Actual Content |
| 0xCA | 0x000C | 0xFE | "HELLO, WORLD" | | 0xFE | "HELLO, WORLD" |
+------+--------+------+----------------+ +------+----------------+Copy
长度标识前面有1个字节的其他内容,后面也有1个字节的其他内容,读取时从长度标识之后3个字节处开始读取,即读取 0xFE HELLO, WORLD
使用
通过 EmbeddedChannel 对 handler 进行测试
public class EncoderStudy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 模拟服务器
// 使用EmbeddedChannel测试handler
EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel(
// 数据最大长度为1KB,长度标识前后各有1个字节的附加信息,长度标识长度为4个字节(int)
new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(1024, 1, 4, 1, 0),
new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG)
);
// 模拟客户端,写入数据
ByteBuf buffer = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer();
send(buffer, "Hello");
channel.writeInbound(buffer);
send(buffer, "World");
channel.writeInbound(buffer);
}
private static void send(ByteBuf buf, String msg) {
// 得到数据的长度
int length = msg.length();
byte[] bytes = msg.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
// 将数据信息写入buf
// 写入长度标识前的其他信息
buf.writeByte(0xCA);
// 写入数据长度标识
buf.writeInt(length);
// 写入长度标识后的其他信息
buf.writeByte(0xFE);
// 写入具体的数据
buf.writeBytes(bytes);
}
}Copy
运行结果
146 [main] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0xembedded, L:embedded - R:embedded] READ: 11B
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| ca 00 00 00 05 fe 48 65 6c 6c 6f |......Hello |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
146 [main] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0xembedded, L:embedded - R:embedded] READ: 11B
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| ca 00 00 00 05 fe 57 6f 72 6c 64 |......World |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+Copy
2、协议设计与解析
协议的作用
TCP/IP 中消息传输基于流的方式,没有边界
协议的目的就是划定消息的边界,制定通信双方要共同遵守的通信规则
Redis协议
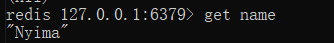
如果我们要向Redis服务器发送一条set name Nyima的指令,需要遵守如下协议
// 该指令一共有3部分,每条指令之后都要添加回车与换行符
*3\r\n
// 第一个指令的长度是3
$3\r\n
// 第一个指令是set指令
set\r\n
// 下面的指令以此类推
$4\r\n
name\r\n
$5\r\n
Nyima\r\nCopy
客户端代码如下
public class RedisClient {
static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(StudyServer.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ChannelFuture channelFuture = new Bootstrap()
.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
// 打印日志
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 回车与换行符
final byte[] LINE = {'\r','\n'};
// 获得ByteBuf
ByteBuf buffer = ctx.alloc().buffer();
// 连接建立后,向Redis中发送一条指令,注意添加回车与换行
// set name Nyima
buffer.writeBytes("*3".getBytes());
buffer.writeBytes(LINE);
buffer.writeBytes("$3".getBytes());
buffer.writeBytes(LINE);
buffer.writeBytes("set".getBytes());
buffer.writeBytes(LINE);
buffer.writeBytes("$4".getBytes());
buffer.writeBytes(LINE);
buffer.writeBytes("name".getBytes());
buffer.writeBytes(LINE);
buffer.writeBytes("$5".getBytes());
buffer.writeBytes(LINE);
buffer.writeBytes("Nyima".getBytes());
buffer.writeBytes(LINE);
ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer);
}
});
}
})
.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 6379));
channelFuture.sync();
// 关闭channel
channelFuture.channel().close().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 关闭group
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}Copy
控制台打印结果
1600 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x28c994f1, L:/127.0.0.1:60792 - R:localhost/127.0.0.1:6379] WRITE: 34B
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 2a 33 0d 0a 24 33 0d 0a 73 65 74 0d 0a 24 34 0d |*3..$3..set..$4.|
|00000010| 0a 6e 61 6d 65 0d 0a 24 35 0d 0a 4e 79 69 6d 61 |.name..$5..Nyima|
|00000020| 0d 0a |.. |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+Copy
Redis中查询执行结果
HTTP协议
HTTP协议在请求行请求头中都有很多的内容,自己实现较为困难,可以使用HttpServerCodec作为服务器端的解码器与编码器,来处理HTTP请求
// HttpServerCodec 中既有请求的解码器 HttpRequestDecoder 又有响应的编码器 HttpResponseEncoder
// Codec(CodeCombine) 一般代表该类既作为 编码器 又作为 解码器
public final class HttpServerCodec extends CombinedChannelDuplexHandler<HttpRequestDecoder, HttpResponseEncoder>
implements HttpServerUpgradeHandler.SourceCodecCopy
服务器代码
public class HttpServer {
static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(StudyServer.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
new ServerBootstrap()
.group(group)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));
// 作为服务器,使用 HttpServerCodec 作为编码器与解码器
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
// 服务器只处理HTTPRequest
ch.pipeline().addLast(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<HttpRequest>() {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpRequest msg) {
// 获得请求uri
log.debug(msg.uri());
// 获得完整响应,设置版本号与状态码
DefaultFullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(msg.protocolVersion(), HttpResponseStatus.OK);
// 设置响应内容
byte[] bytes = "<h1>Hello, World!</h1>".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
// 设置响应体长度,避免浏览器一直接收响应内容
response.headers().setInt(CONTENT_LENGTH, bytes.length);
// 设置响应体
response.content().writeBytes(bytes);
// 写回响应
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
}
});
}
})
.bind(8080);
}
}Copy
服务器负责处理请求并响应浏览器。所以只需要处理HTTP请求即可
// 服务器只处理HTTPRequest
ch.pipeline().addLast(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<HttpRequest>()Copy
获得请求后,需要返回响应给浏览器。需要创建响应对象DefaultFullHttpResponse,设置HTTP版本号及状态码,为避免浏览器获得响应后,因为获得CONTENT_LENGTH而一直空转,需要添加CONTENT_LENGTH字段,表明响应体中数据的具体长度
// 获得完整响应,设置版本号与状态码
DefaultFullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(msg.protocolVersion(), HttpResponseStatus.OK);
// 设置响应内容
byte[] bytes = "<h1>Hello, World!</h1>".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
// 设置响应体长度,避免浏览器一直接收响应内容
response.headers().setInt(CONTENT_LENGTH, bytes.length);
// 设置响应体
response.content().writeBytes(bytes);Copy
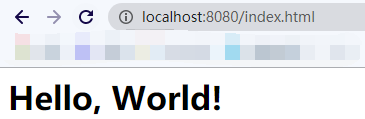
运行结果
浏览器
控制台
// 请求内容
1714 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-2] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x72630ef7, L:/0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1:8080 - R:/0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1:55503] READ: 688B
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 47 45 54 20 2f 66 61 76 69 63 6f 6e 2e 69 63 6f |GET /favicon.ico|
|00000010| 20 48 54 54 50 2f 31 2e 31 0d 0a 48 6f 73 74 3a | HTTP/1.1..Host:|
|00000020| 20 6c 6f 63 61 6c 68 6f 73 74 3a 38 30 38 30 0d | localhost:8080.|
|00000030| 0a 43 6f 6e 6e 65 63 74 69 6f 6e 3a 20 6b 65 65 |.Connection: kee|
|00000040| 70 2d 61 6c 69 76 65 0d 0a 50 72 61 67 6d 61 3a |p-alive..Pragma:|
....
// 响应内容
1716 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-2] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x72630ef7, L:/0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1:8080 - R:/0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1:55503] WRITE: 61B
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 48 54 54 50 2f 31 2e 31 20 32 30 30 20 4f 4b 0d |HTTP/1.1 200 OK.|
|00000010| 0a 43 6f 6e 74 65 6e 74 2d 4c 65 6e 67 74 68 3a |.Content-Length:|
|00000020| 20 32 32 0d 0a 0d 0a 3c 68 31 3e 48 65 6c 6c 6f | 22....<h1>Hello|
|00000030| 2c 20 57 6f 72 6c 64 21 3c 2f 68 31 3e |, World!</h1> |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+Copy
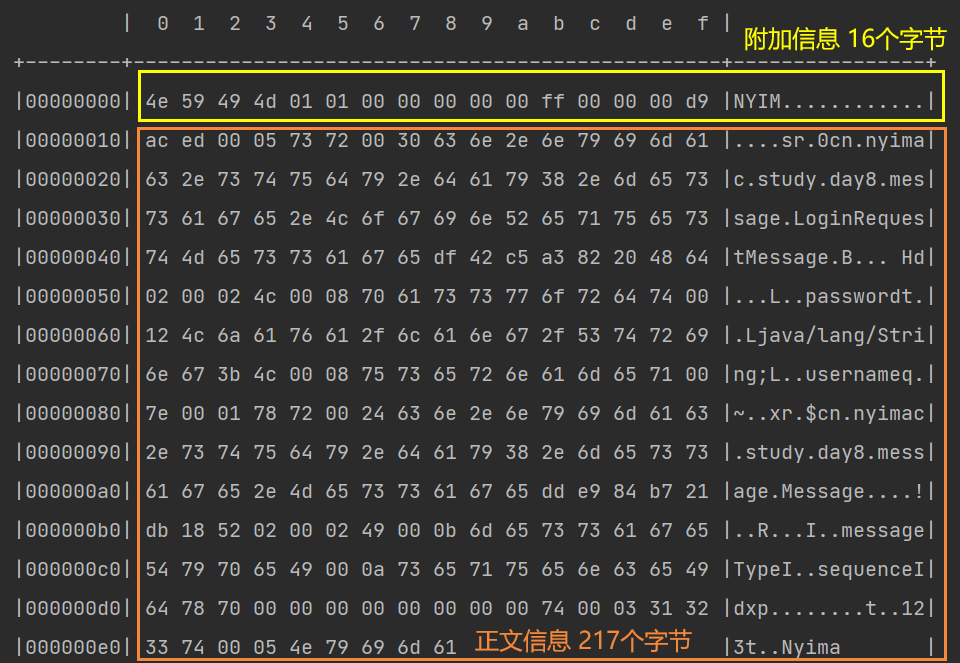
自定义协议
组成要素
-
魔数:用来在第一时间判定接收的数据是否为无效数据包
-
版本号:可以支持协议的升级
-
序列化算法
:消息正文到底采用哪种序列化反序列化方式
- 如:json、protobuf、hessian、jdk
-
指令类型:是登录、注册、单聊、群聊… 跟业务相关
-
请求序号:为了双工通信,提供异步能力
-
正文长度
-
消息正文
编码器与解码器
public class MessageCodec extends ByteToMessageCodec<Message> {
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Message msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception {
// 设置魔数 4个字节
out.writeBytes(new byte[]{'N','Y','I','M'});
// 设置版本号 1个字节
out.writeByte(1);
// 设置序列化方式 1个字节
out.writeByte(1);
// 设置指令类型 1个字节
out.writeByte(msg.getMessageType());
// 设置请求序号 4个字节
out.writeInt(msg.getSequenceId());
// 为了补齐为16个字节,填充1个字节的数据
out.writeByte(0xff);
// 获得序列化后的msg
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(msg);
byte[] bytes = bos.toByteArray();
// 获得并设置正文长度 长度用4个字节标识
out.writeInt(bytes.length);
// 设置消息正文
out.writeBytes(bytes);
}
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
// 获取魔数
int magic = in.readInt();
// 获取版本号
byte version = in.readByte();
// 获得序列化方式
byte seqType = in.readByte();
// 获得指令类型
byte messageType = in.readByte();
// 获得请求序号
int sequenceId = in.readInt();
// 移除补齐字节
in.readByte();
// 获得正文长度
int length = in.readInt();
// 获得正文
byte[] bytes = new byte[length];
in.readBytes(bytes, 0, length);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes));
Message message = (Message) ois.readObject();
// 将信息放入List中,传递给下一个handler
out.add(message);
// 打印获得的信息正文
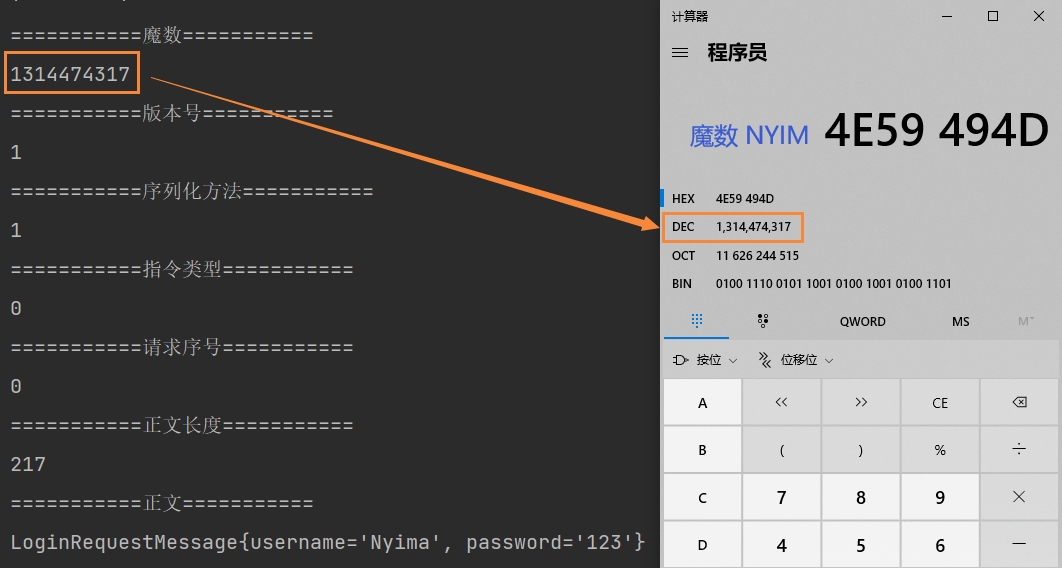
System.out.println("===========魔数===========");
System.out.println(magic);
System.out.println("===========版本号===========");
System.out.println(version);
System.out.println("===========序列化方法===========");
System.out.println(seqType);
System.out.println("===========指令类型===========");
System.out.println(messageType);
System.out.println("===========请求序号===========");
System.out.println(sequenceId);
System.out.println("===========正文长度===========");
System.out.println(length);
System.out.println("===========正文===========");
System.out.println(message);
}
}Copy
-
编码器与解码器方法源于父类ByteToMessageCodec,通过该类可以自定义编码器与解码器,泛型类型为被编码与被解码的类。此处使用了自定义类Message,代表消息
public class MessageCodec extends ByteToMessageCodec<Message>Copy -
编码器负责将附加信息与正文信息写入到ByteBuf中,其中附加信息总字节数最好为2n,不足需要补齐。正文内容如果为对象,需要通过序列化将其放入到ByteBuf中
-
解码器负责将ByteBuf中的信息取出,并放入List中,该List用于将信息传递给下一个handler
编写测试类
public class TestCodec {
static final org.slf4j.Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(StudyServer.class);
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel();
// 添加解码器,避免粘包半包问题
channel.pipeline().addLast(new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(1024, 12, 4, 0, 0));
channel.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));
channel.pipeline().addLast(new MessageCodec());
LoginRequestMessage user = new LoginRequestMessage("Nyima", "123");
// 测试编码与解码
ByteBuf byteBuf = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer();
new MessageCodec().encode(null, user, byteBuf);
channel.writeInbound(byteBuf);
}
}Copy
- 测试类中用到了LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder,避免粘包半包问题
- 通过MessageCodec的encode方法将附加信息与正文写入到ByteBuf中,通过channel执行入站操作。入站时会调用decode方法进行解码
运行结果
@Sharable注解
为了提高handler的复用率,可以将handler创建为handler对象,然后在不同的channel中使用该handler对象进行处理操作
LoggingHandler loggingHandler = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG);
// 不同的channel中使用同一个handler对象,提高复用率
channel1.pipeline().addLast(loggingHandler);
channel2.pipeline().addLast(loggingHandler);Copy
但是并不是所有的handler都能通过这种方法来提高复用率的,例如LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder。如果多个channel中使用同一个LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder对象,则可能发生如下问题
- channel1中收到了一个半包,LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder发现不是一条完整的数据,则没有继续向下传播
- 此时channel2中也收到了一个半包,因为两个channel使用了同一个LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder,存入其中的数据刚好拼凑成了一个完整的数据包。LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder让该数据包继续向下传播,最终引发错误
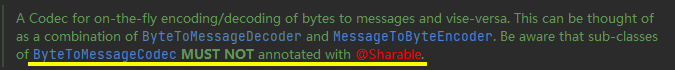
为了提高handler的复用率,同时又避免出现一些并发问题,Netty中原生的handler中用@Sharable注解来标明,该handler能否在多个channel中共享。
只有带有该注解,才能通过对象的方式被共享,否则无法被共享
自定义编解码器能否使用@Sharable注解
这需要根据自定义的handler的处理逻辑进行分析
我们的MessageCodec本身接收的是LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder处理之后的数据,那么数据肯定是完整的,按分析来说是可以添加@Sharable注解的
但是实际情况我们并不能添加该注解,会抛出异常信息ChannelHandler cn.nyimac.study.day8.protocol.MessageCodec is not allowed to be shared
-
因为MessageCodec继承自ByteToMessageCodec,ByteToMessageCodec类的注解如下
这就意味着ByteToMessageCodec不能被多个channel所共享的
- 原因:因为该类的目标是:将ByteBuf转化为Message,意味着传进该handler的数据还未被处理过。所以传过来的ByteBuf可能并不是完整的数据,如果共享则会出现问题
如果想要共享,需要怎么办呢?
继承MessageToMessageDecoder即可。该类的目标是:将已经被处理的完整数据再次被处理。传过来的Message如果是被处理过的完整数据,那么被共享也就不会出现问题了,也就可以使用@Sharable注解了。实现方式与ByteToMessageCodec类似
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class MessageSharableCodec extends MessageToMessageCodec<ByteBuf, Message> {
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Message msg, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
...
}
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
...
}
}Copy
3、在线聊天室
聊天室业务
用户登录接口
public interface UserService {
/**
* 登录
* @param username 用户名
* @param password 密码
* @return 登录成功返回 true, 否则返回 false
*/
boolean login(String username, String password);
}Copy
用户会话接口
public interface Session {
/**
* 绑定会话
* @param channel 哪个 channel 要绑定会话
* @param username 会话绑定用户
*/
void bind(Channel channel, String username);
/**
* 解绑会话
* @param channel 哪个 channel 要解绑会话
*/
void unbind(Channel channel);
/**
* 获取属性
* @param channel 哪个 channel
* @param name 属性名
* @return 属性值
*/
Object getAttribute(Channel channel, String name);
/**
* 设置属性
* @param channel 哪个 channel
* @param name 属性名
* @param value 属性值
*/
void setAttribute(Channel channel, String name, Object value);
/**
* 根据用户名获取 channel
* @param username 用户名
* @return channel
*/
Channel getChannel(String username);
}Copy
群聊会话接口
public interface GroupSession {
/**
* 创建一个聊天组, 如果不存在才能创建成功, 否则返回 null
* @param name 组名
* @param members 成员
* @return 成功时返回组对象, 失败返回 null
*/
Group createGroup(String name, Set<String> members);
/**
* 加入聊天组
* @param name 组名
* @param member 成员名
* @return 如果组不存在返回 null, 否则返回组对象
*/
Group joinMember(String name, String member);
/**
* 移除组成员
* @param name 组名
* @param member 成员名
* @return 如果组不存在返回 null, 否则返回组对象
*/
Group removeMember(String name, String member);
/**
* 移除聊天组
* @param name 组名
* @return 如果组不存在返回 null, 否则返回组对象
*/
Group removeGroup(String name);
/**
* 获取组成员
* @param name 组名
* @return 成员集合, 如果群不存在或没有成员会返回 empty set
*/
Set<String> getMembers(String name);
/**
* 获取组成员的 channel 集合, 只有在线的 channel 才会返回
* @param name 组名
* @return 成员 channel 集合
*/
List<Channel> getMembersChannel(String name);
/**
* 判断群聊是否一被创建
* @param name 群聊名称
* @return 是否存在
*/
boolean isCreated(String name);
}Copy
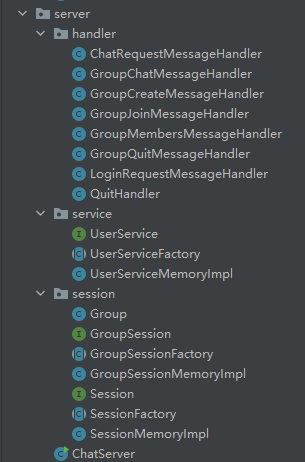
整体结构
- client包:存放客户端相关类
- message包:存放各种类型的消息
- protocol包:存放自定义协议
- server包:存放服务器相关类
- service包:存放用户相关类
- session包:单聊及群聊相关会话类
客户端代码结构
public class ChatClient {
static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ChatClient.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
LoggingHandler loggingHandler = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG);
MessageSharableCodec messageSharableCodec = new MessageSharableCodec();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group);
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ProtocolFrameDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(loggingHandler);
ch.pipeline().addLast(messageSharableCodec);
}
});
Channel channel = bootstrap.connect().sync().channel();
channel.closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}Copy
服务器代码结构
public class ChatServer {
static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ChatServer.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
LoggingHandler loggingHandler = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG);
MessageSharableCodec messageSharableCodec = new MessageSharableCodec();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(boss, worker);
bootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ProtocolFrameDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(loggingHandler);
ch.pipeline().addLast(messageSharableCodec);
}
});
Channel channel = bootstrap.bind(8080).sync().channel();
channel.closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
boss.shutdownGracefully();
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}Copy
登录
客户端代码
客户端添加如下handler,分别处理登录、聊天等操作
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
/**
* 创建连接时执行的处理器,用于执行登陆操作
*/
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 开辟额外线程,用于用户登陆及后续操作
new Thread(()->{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名");
String username = scanner.next();
System.out.println("请输入密码");
String password = scanner.next();
// 创建包含登录信息的请求体
LoginRequestMessage message = new LoginRequestMessage(username, password);
// 发送到channel中
ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
System.out.println("等待后续操作...");
// 阻塞,直到登陆成功后CountDownLatch被设置为0
try {
waitLogin.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 执行后续操作
if (!loginStatus.get()) {
// 登陆失败,关闭channel并返回
ctx.channel().close();
return;
}
// 登录成功后,执行其他操作
while (true) {
System.out.println("==================================");
System.out.println("send [username] [content]");
System.out.println("gsend [group name] [content]");
System.out.println("gcreate [group name] [m1,m2,m3...]");
System.out.println("gmembers [group name]");
System.out.println("gjoin [group name]");
System.out.println("gquit [group name]");
System.out.println("quit");
System.out.println("==================================");
String command = scanner.nextLine();
// 获得指令及其参数,并发送对应类型消息
String[] commands = command.split(" ");
switch (commands[0]){
case "send":
ctx.writeAndFlush(new ChatRequestMessage(username, commands[1], commands[2]));
break;
case "gsend":
ctx.writeAndFlush(new GroupChatRequestMessage(username,commands[1], commands[2]));
break;
case "gcreate":
// 分割,获得群员名
String[] members = commands[2].split(",");
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(members));
// 把自己加入到群聊中
set.add(username);
ctx.writeAndFlush(new GroupCreateRequestMessage(commands[1],set));
break;
case "gmembers":
ctx.writeAndFlush(new GroupMembersRequestMessage(commands[1]));
break;
case "gjoin":
ctx.writeAndFlush(new GroupJoinRequestMessage(username, commands[1]));
break;
case "gquit":
ctx.writeAndFlush(new GroupQuitRequestMessage(username, commands[1]));
break;
case "quit":
ctx.channel().close();
return;
default:
System.out.println("指令有误,请重新输入");
continue;
}
}
}, "login channel").start();
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
log.debug("{}", msg);
if (msg instanceof LoginResponseMessage) {
// 如果是登录响应信息
LoginResponseMessage message = (LoginResponseMessage) msg;
boolean isSuccess = message.isSuccess();
// 登录成功,设置登陆标记
if (isSuccess) {
loginStatus.set(true);
}
// 登陆后,唤醒登陆线程
waitLogin.countDown();
}
}
});Copy
服务器代码
服务器添加如下handler,并添加到对应的channel中,负责处理登录请求信息,并作出响应
@ChannelHandler.Sharable // 必须添加该注解
public class LoginRequestMessageHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<LoginRequestMessage> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, LoginRequestMessage msg) throws Exception {
// 获得登录信息
String username = msg.getUsername();
String password = msg.getPassword();
// 校验登录信息
boolean login = UserServiceFactory.getUserService().login(username, password);
LoginResponseMessage message;
if (login) {
message = new LoginResponseMessage(true, "登陆成功");
// 绑定channel与user
SessionFactory.getSession().bind(ctx.channel(), username);
} else {
message = new LoginResponseMessage(false, "登陆失败");
}
ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
}
}Copy
// 该handler处理登录请求
LoginRequestMessageHandler loginRequestMessageHandler = new LoginRequestMessageHandler();
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoginRequestMessageHandler());Copy
运行结果
客户端
5665 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] DEBUG cn.nyimac.study.day8.protocol.MessageSharableCodec - 1314474317, 1, 1, 1, 0, 279
5667 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] DEBUG cn.nyimac.study.day8.protocol.MessageSharableCodec - message:AbstractResponseMessage{success=true, reason='登陆成功'}
5667 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] DEBUG cn.nyimac.study.day8.client.ChatClient - AbstractResponseMessage{success=true, reason='登陆成功'}
successCopy
服务器
11919 [nioEventLoopGroup-3-1] DEBUG cn.nyimac.study.day8.protocol.MessageSharableCodec - 1314474317, 1, 1, 0, 0, 217
11919 [nioEventLoopGroup-3-1] DEBUG cn.nyimac.study.day8.protocol.MessageSharableCodec - message:LoginRequestMessage{username='Nyima', password='123'}
7946 [nioEventLoopGroup-3-1] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x8e7c07f6, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:60572] WRITE: 295B
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 4e 59 49 4d 01 01 01 00 00 00 00 ff 00 00 01 17 |NYIM............|
|00000010| ac ed 00 05 73 72 00 31 63 6e 2e 6e 79 69 6d 61 |....sr.1cn.nyima|
|00000020| 63 2e 73 74 75 64 79 2e 64 61 79 38 2e 6d 65 73 |c.study.day8.mes|
|00000030| 73 61 67 65 2e 4c 6f 67 69 6e 52 65 73 70 6f 6e |sage.LoginRespon|
|00000040| 73 65 4d 65 73 73 61 67 65 e2 34 49 24 72 52 f3 |seMessage.4I$rR.|
|00000050| 07 02 00 00 78 72 00 34 63 6e 2e 6e 79 69 6d 61 |....xr.4cn.nyima|
|00000060| 63 2e 73 74 75 64 79 2e 64 61 79 38 2e 6d 65 73 |c.study.day8.mes|
|00000070| 73 61 67 65 2e 41 62 73 74 72 61 63 74 52 65 73 |sage.AbstractRes|
|00000080| 70 6f 6e 73 65 4d 65 73 73 61 67 65 b3 7e 19 32 |ponseMessage.~.2|
|00000090| 9b 88 4d 7b 02 00 02 5a 00 07 73 75 63 63 65 73 |..M{...Z..succes|
|000000a0| 73 4c 00 06 72 65 61 73 6f 6e 74 00 12 4c 6a 61 |sL..reasont..Lja|
|000000b0| 76 61 2f 6c 61 6e 67 2f 53 74 72 69 6e 67 3b 78 |va/lang/String;x|
|000000c0| 72 00 24 63 6e 2e 6e 79 69 6d 61 63 2e 73 74 75 |r.$cn.nyimac.stu|
|000000d0| 64 79 2e 64 61 79 38 2e 6d 65 73 73 61 67 65 2e |dy.day8.message.|
|000000e0| 4d 65 73 73 61 67 65 dd e9 84 b7 21 db 18 52 02 |Message....!..R.|
|000000f0| 00 02 49 00 0b 6d 65 73 73 61 67 65 54 79 70 65 |..I..messageType|
|00000100| 49 00 0a 73 65 71 75 65 6e 63 65 49 64 78 70 00 |I..sequenceIdxp.|
|00000110| 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 01 74 00 0c e7 99 bb e9 99 |........t.......|
|00000120| 86 e6 88 90 e5 8a 9f |....... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+Copy
单聊
客户端输入send username content即可发送单聊消息,需要服务器端添加处理ChatRequestMessage的handler
@ChannelHandler.Sharable // 必须添加该注解
public class ChatRequestMessageHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ChatRequestMessage> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ChatRequestMessage msg) throws Exception {
// 获得user所在的channel
Channel channel = SessionFactory.getSession().getChannel(msg.getTo());
// 如果双方都在线
if (channel != null) {
// 通过接收方与服务器之间的channel发送信息
channel.writeAndFlush(new ChatResponseMessage(msg.getFrom(), msg.getContent()));
} else {
// 通过发送方与服务器之间的channel发送消息
ctx.writeAndFlush(new ChatResponseMessage(false, "对方用户不存在或离线,发送失败"));
}
}
}Copy
// 该handler处理单聊请求
ChatRequestMessageHandler chatRequestMessageHandler = new ChatRequestMessageHandler();
ch.pipeline().addLast(chatRequestMessageHandler);Copy
运行结果
发送方(zhangsan)
send Nyima helloCopy
接收方(Nyima)
// 收到zhangsan发来的消息
20230 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] DEBUG cn.nyimac.study.day8.client.ChatClient - ChatResponseMessage{from='zhangsan', content='hello'}Copy
群聊
创建
添加处理GroupCreateRequestMessage的handler
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class GroupCreateMessageHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<GroupCreateRequestMessage> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, GroupCreateRequestMessage msg) throws Exception {
// 获得要创建的群聊名
String groupName = msg.getGroupName();
// 获得要创建的群聊的成员组
Set<String> members = msg.getMembers();
// 判断该群聊是否创建过,未创建返回null并创建群聊
Group group = GroupSessionFactory.getGroupSession().createGroup(groupName, members);
if (group == null) {
// 发送创建成功消息
GroupCreateResponseMessage groupCreateResponseMessage = new GroupCreateResponseMessage(true, groupName + "创建成功");
ctx.writeAndFlush(groupCreateResponseMessage);
// 获得在线群员的channel,给群员发送入群聊消息
List<Channel> membersChannel = GroupSessionFactory.getGroupSession().getMembersChannel(groupName);
groupCreateResponseMessage = new GroupCreateResponseMessage(true, "您已被拉入"+groupName);
// 给每个在线群员发送消息
for(Channel channel : membersChannel) {
channel.writeAndFlush(groupCreateResponseMessage);
}
} else {
// 发送失败消息
GroupCreateResponseMessage groupCreateResponseMessage = new GroupCreateResponseMessage(false, groupName + "已存在");
ctx.writeAndFlush(groupCreateResponseMessage);
}
}
}Copy
// 该handler处理创建群聊请求
GroupCreateMessageHandler groupCreateMessageHandler = new GroupCreateMessageHandler();
ch.pipeline().addLast(groupCreateMessageHandler);Copy
运行结果
创建者客户端
// 首次创建
gcreate Netty学习 zhangsan,lisi
31649 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] DEBUG cn.nyimac.study.day8.client.ChatClient - AbstractResponseMessage{success=true, reason='Netty学习创建成功'}
15244 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] DEBUG cn.nyimac.study.day8.client.ChatClient - AbstractResponseMessage{success=true, reason='您已被拉入Netty学习'}
// 再次创建
gcreate Netty学习 zhangsan,lisi
40771 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] DEBUG cn.nyimac.study.day8.client.ChatClient - AbstractResponseMessage{success=false, reason='Netty学习已存在'}Copy
群员客户端
28788 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] DEBUG cn.nyimac.study.day8.client.ChatClient - AbstractResponseMessage{success=true, reason='您已被拉入Netty学习'}Copy
聊天
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class GroupChatMessageHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<GroupChatRequestMessage> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, GroupChatRequestMessage msg) throws Exception {
String groupName = msg.getGroupName();
GroupSession groupSession = GroupSessionFactory.getGroupSession();
// 判断群聊是否存在
boolean isCreated = groupSession.isCreated(groupName);
if (isCreated) {
// 给群员发送信息
List<Channel> membersChannel = groupSession.getMembersChannel(groupName);
for(Channel channel : membersChannel) {
channel.writeAndFlush(new GroupChatResponseMessage(msg.getFrom(), msg.getContent()));
}
} else {
ctx.writeAndFlush(new GroupChatResponseMessage(false, "群聊不存在"));
}
}
}Copy
// 该handler处理群聊聊天
GroupChatMessageHandler groupChatMessageHandler = new GroupChatMessageHandler();
ch.pipeline().addLast(groupChatMessageHandler);Copy
运行结果
发送方(群聊存在)
gsend Netty学习 你们好
45408 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] DEBUG cn.nyimac.study.day8.client.ChatClient - GroupChatResponseMessage{from='zhangsan', content='你们好'}Copy
接收方
48082 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] DEBUG cn.nyimac.study.day8.client.ChatClient - GroupChatResponseMessage{from='zhangsan', content='你们好'}Copy
发送方(群聊不存在)
gsend Spring学习 你们好
25140 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] DEBUG cn.nyimac.study.day8.client.ChatClient - AbstractResponseMessage{success=false, reason='群聊不存在'}Copy
加入
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class GroupJoinMessageHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<GroupJoinRequestMessage> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, GroupJoinRequestMessage msg) throws Exception {
GroupSession groupSession = GroupSessionFactory.getGroupSession();
// 判断该用户是否在群聊中
Set<String> members = groupSession.getMembers(msg.getGroupName());
boolean joinFlag = false;
// 群聊存在且用户未加入,才能加入
if (!members.contains(msg.getUsername()) && groupSession.isCreated(msg.getGroupName())) {
joinFlag = true;
}
if (joinFlag) {
// 加入群聊
groupSession.joinMember(msg.getGroupName(), msg.getUsername());
ctx.writeAndFlush(new GroupJoinResponseMessage(true,"加入"+msg.getGroupName()+"成功"));
} else {
ctx.writeAndFlush(new GroupJoinResponseMessage(false, "加入失败,群聊未存在或您已加入该群聊"));
}
}
}Copy
// 该handler处理加入群聊
GroupJoinMessageHandler groupJoinMessageHandler = new GroupJoinMessageHandler();
ch.pipeline().addLast(groupJoinMessageHandler);Copy
运行结果
正常加入群聊
94921 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] DEBUG cn.nyimac.study.day8.client.ChatClient - AbstractResponseMessage{success=true, reason='加入Netty学习成功'}Copy
加入不能存在或已加入的群聊
44025 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] DEBUG cn.nyimac.study.day8.client.ChatClient - AbstractResponseMessage{success=false, reason='加入失败,群聊未存在或您已加入该群聊'}Copy
退出
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class GroupQuitMessageHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<GroupQuitRequestMessage> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, GroupQuitRequestMessage msg) throws Exception {
GroupSession groupSession = GroupSessionFactory.getGroupSession();
String groupName = msg.getGroupName();
Set<String> members = groupSession.getMembers(groupName);
String username = msg.getUsername();
// 判断用户是否在群聊中以及群聊是否存在
boolean joinFlag = false;
if (groupSession.isCreated(groupName) && members.contains(username)) {
// 可以退出
joinFlag = true;
}
if (joinFlag) {
// 退出成功
groupSession.removeMember(groupName, username);
ctx.writeAndFlush(new GroupQuitResponseMessage(true, "退出"+groupName+"成功"));
} else {
// 退出失败
ctx.writeAndFlush(new GroupQuitResponseMessage(false, "群聊不存在或您未加入该群,退出"+groupName+"失败"));
}
}
}Copy
// 该handler处理退出群聊
GroupQuitMessageHandler groupQuitMessageHandler = new GroupQuitMessageHandler();
ch.pipeline().addLast(groupQuitMessageHandler);Copy
运行结果
正常退出
32282 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] DEBUG cn.nyimac.study.day8.client.ChatClient - AbstractResponseMessage{success=true, reason='退出Netty学习成功'}Copy
退出不存在或未加入的群聊
67404 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] DEBUG cn.nyimac.study.day8.client.ChatClient - AbstractResponseMessage{success=false, reason='群聊不存在或您未加入该群,退出Netty失败'}Copy
查看成员
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class GroupMembersMessageHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<GroupMembersRequestMessage> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, GroupMembersRequestMessage msg) throws Exception {
ctx.writeAndFlush(new GroupMembersResponseMessage(GroupSessionFactory.getGroupSession().getMembers(msg.getGroupName())));
}
}Copy
// 该handler处理查看成员
GroupMembersMessageHandler groupMembersMessageHandler = new GroupMembersMessageHandler();
ch.pipeline().addLast(groupMembersMessageHandler);Copy
运行结果
46557 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] DEBUG cn.nyimac.study.day8.client.ChatClient - GroupMembersResponseMessage{members=[zhangsan, Nyima]}Copy
退出聊天室
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class QuitHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
/**
* 断开连接时触发 Inactive事件
*/
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 解绑
SessionFactory.getSession().unbind(ctx.channel());
}
/**
* 异常退出,需要解绑
*/
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
// 解绑
SessionFactory.getSession().unbind(ctx.channel());
}
}Copy
// 该handler处理退出聊天室
ch.pipeline().addLast(quitHandler);
GroupMembersMessageHandler groupMembersMessageHandler = new GroupMembersMessageHandler();Copy
退出时,客户端会关闭channel并返回
case "quit":
// 关闭channel并返回
ctx.channel().close();
return;Copy
空闲检测
连接假死
原因
- 网络设备出现故障,例如网卡,机房等,底层的 TCP 连接已经断开了,但应用程序没有感知到,仍然占用着资源
- 公网网络不稳定,出现丢包。如果连续出现丢包,这时现象就是客户端数据发不出去,服务端也一直收不到数据,会白白地消耗资源
- 应用程序线程阻塞,无法进行数据读写
问题
- 假死的连接占用的资源不能自动释放
- 向假死的连接发送数据,得到的反馈是发送超时
解决方法
可以添加IdleStateHandler对空闲时间进行检测,通过构造函数可以传入三个参数
- readerIdleTimeSeconds 读空闲经过的秒数
- writerIdleTimeSeconds 写空闲经过的秒数
- allIdleTimeSeconds 读和写空闲经过的秒数
当指定时间内未发生读或写事件时,会触发特定事件
- 读空闲会触发
READER_IDLE - 写空闲会触发
WRITE_IDLE - 读和写空闲会触发
ALL_IDEL
想要处理这些事件,需要自定义事件处理函数
服务器端代码
// 用于空闲连接的检测,5s内未读到数据,会触发READ_IDLE事件
ch.pipeline().addLast(new IdleStateHandler(5, 0, 0));
// 添加双向处理器,负责处理READER_IDLE事件
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelDuplexHandler() {
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception {
// 获得事件
IdleStateEvent event = (IdleStateEvent) evt;
if (event.state() == IdleState.READER_IDLE) {
// 断开连接
ctx.channel().close();
}
}
});Copy
-
使用
IdleStateHandler进行空闲检测 -
使用双向处理器
ChannelDuplexHandler对入站与出站事件进行处理
IdleStateHandler中的事件为特殊事件,需要实现ChannelDuplexHandler的userEventTriggered方法,判断事件类型并自定义处理方式,来对事件进行处理
为避免因非网络等原因引发的READ_IDLE事件,比如网络情况良好,只是用户本身没有输入数据,这时发生READ_IDLE事件,直接让服务器断开连接是不可取的
为避免此类情况,需要在客户端向服务器发送心跳包,发送频率要小于服务器设置的IdleTimeSeconds,一般设置为其值的一半
客户端代码
// 发送心跳包,让服务器知道客户端在线
// 3s未发生WRITER_IDLE,就像服务器发送心跳包
// 该值为服务器端设置的READER_IDLE触发时间的一半左右
ch.pipeline().addLast(new IdleStateHandler(0, 3, 0));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelDuplexHandler() {
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception {
IdleStateEvent event = (IdleStateEvent) evt;
if (event.state() == IdleState.WRITER_IDLE) {
// 发送心跳包
ctx.writeAndFlush(new PingMessage());
}
}
});Copy
五、优化
1、拓展序列化算法
序列化接口
public interface Serializer {
/**
* 序列化
* @param object 被序列化的对象
* @param <T> 被序列化对象类型
* @return 序列化后的字节数组
*/
<T> byte[] serialize(T object);
/**
* 反序列化
* @param clazz 反序列化的目标类的Class对象
* @param bytes 被反序列化的字节数组
* @param <T> 反序列化目标类
* @return 反序列化后的对象
*/
<T> T deserialize(Class<T> clazz, byte[] bytes);
}Copy
枚举实现类
public enum SerializerAlgorithm implements Serializer {
// Java的序列化和反序列化
Java {
@Override
public <T> byte[] serialize(T object) {
// 序列化后的字节数组
byte[] bytes = null;
try (ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos)) {
oos.writeObject(object);
bytes = bos.toByteArray();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return bytes;
}
@Override
public <T> T deserialize(Class<T> clazz, byte[] bytes) {
T target = null;
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));
try (ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis)) {
target = (T) ois.readObject();
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 返回反序列化后的对象
return target;
}
}
// Json的序列化和反序列化
Json {
@Override
public <T> byte[] serialize(T object) {
String s = new Gson().toJson(object);
System.out.println(s);
// 指定字符集,获得字节数组
return s.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
}
@Override
public <T> T deserialize(Class<T> clazz, byte[] bytes) {
String s = new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println(s);
// 此处的clazz为具体类型的Class对象,而不是父类Message的
return new Gson().fromJson(s, clazz);
}
}
}Copy
修改原编解码器
编码
// 获得序列化后的msg
// 使用指定的序列化方式
SerializerAlgorithm[] values = SerializerAlgorithm.values();
// 获得序列化后的对象
byte[] bytes = values[out.getByte(5)-1].serialize(msg);Copy
解码
// 获得反序列化方式
SerializerAlgorithm[] values = SerializerAlgorithm.values();
// 通过指定方式进行反序列化
// 需要通过Message的方法获得具体的消息类型
Message message = values[seqType-1].deserialize(Message.getMessageClass(messageType), bytes);Copy
2、参数调优
CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS
- 属于 SocketChannal 的参数
- 用在客户端建立连接时,如果在指定毫秒内无法连接,会抛出 timeout 异常
- 注意:Netty 中不要用成了SO_TIMEOUT 主要用在阻塞 IO,而 Netty 是非阻塞 IO
使用
public class TestParam {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// SocketChannel 5s内未建立连接就抛出异常
new Bootstrap().option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, 5000);
// ServerSocketChannel 5s内未建立连接就抛出异常
new ServerBootstrap().option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS,5000);
// SocketChannel 5s内未建立连接就抛出异常
new ServerBootstrap().childOption(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, 5000);
}
}Copy
-
客户端通过
Bootstrap.option函数来配置参数,配置参数作用于 SocketChannel -
服务器通过
ServerBootstrap来配置参数,但是对于不同的 Channel 需要选择不同的方法
- 通过
option来配置 ServerSocketChannel 上的参数 - 通过
childOption来配置 SocketChannel 上的参数
- 通过
源码分析
客户端中连接服务器的线程是 NIO 线程,抛出异常的是主线程。这是如何做到超时判断以及线程通信的呢?
AbstractNioChannel.AbstractNioUnsafe.connect方法中
public final void connect(
final SocketAddress remoteAddress, final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
...
// Schedule connect timeout.
// 设置超时时间,通过option方法传入的CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS参数进行设置
int connectTimeoutMillis = config().getConnectTimeoutMillis();
// 如果超时时间大于0
if (connectTimeoutMillis > 0) {
// 创建一个定时任务,延时connectTimeoutMillis(设置的超时时间时间)后执行
// schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit)
connectTimeoutFuture = eventLoop().schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 判断是否建立连接,Promise进行NIO线程与主线程之间的通信
// 如果超时,则通过tryFailure方法将异常放入Promise中
// 在主线程中抛出
ChannelPromise connectPromise = AbstractNioChannel.this.connectPromise;
ConnectTimeoutException cause = new ConnectTimeoutException("connection timed out: " + remoteAddress);
if (connectPromise != null && connectPromise.tryFailure(cause)) {
close(voidPromise());
}
}
}, connectTimeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
...
}Copy
超时的判断主要是通过 Eventloop 的 schedule 方法和 Promise 共同实现的
- schedule 设置了一个定时任务,延迟
connectTimeoutMillis秒后执行该方法 - 如果指定时间内没有建立连接,则会执行其中的任务
- 任务负责创建
ConnectTimeoutException异常,并将异常通过 Pormise 传给主线程并抛出
- 任务负责创建
SO_BACKLOG
该参数是 ServerSocketChannel 的参数
三次握手与连接队列
第一次握手时,因为客户端与服务器之间的连接还未完全建立,连接会被放入半连接队列中
当完成三次握手以后,连接会被放入全连接队列中
服务器处理Accept事件是在TCP三次握手,也就是建立连接之后。服务器会从全连接队列中获取连接并进行处理
在 linux 2.2 之前,backlog 大小包括了两个队列的大小,在 linux 2.2 之后,分别用下面两个参数来控制
- 半连接队列 - sync queue
- 大小通过 /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_max_syn_backlog 指定,在
syncookies启用的情况下,逻辑上没有最大值限制,这个设置便被忽略
- 大小通过 /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_max_syn_backlog 指定,在
- 全连接队列 - accept queue
- 其大小通过 /proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn 指定,在使用 listen 函数时,内核会根据传入的 backlog 参数与系统参数,取二者的较小值
- 如果 accpet queue 队列满了,server 将发送一个拒绝连接的错误信息到 client
作用
在Netty中,SO_BACKLOG主要用于设置全连接队列的大小。当处理Accept的速率小于连接建立的速率时,全连接队列中堆积的连接数大于SO_BACKLOG设置的值是,便会抛出异常
设置方式如下
// 设置全连接队列,大小为2
new ServerBootstrap().option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 2);Copy
默认值
backlog参数在NioSocketChannel.doBind方法被使用
@Override
protected void doBind(SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception {
if (PlatformDependent.javaVersion() >= 7) {
javaChannel().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog());
} else {
javaChannel().socket().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog());
}
}Copy
其中backlog被保存在了DefaultServerSocketChannelConfig配置类中
private volatile int backlog = NetUtil.SOMAXCONN;Copy
具体的赋值操作如下
SOMAXCONN = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer run() {
// Determine the default somaxconn (server socket backlog) value of the platform.
// The known defaults:
// - Windows NT Server 4.0+: 200
// - Linux and Mac OS X: 128
int somaxconn = PlatformDependent.isWindows() ? 200 : 128;
File file = new File("/proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn");
BufferedReader in = null;
try {
// file.exists() may throw a SecurityException if a SecurityManager is used, so execute it in the
// try / catch block.
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/4936
if (file.exists()) {
in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
// 将somaxconn设置为Linux配置文件中设置的值
somaxconn = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("{}: {}", file, somaxconn);
}
} else {
...
}
...
}
// 返回backlog的值
return somaxconn;
}
}Copy
-
backlog的值会根据操作系统的不同,来
选择不同的默认值
- Windows 200
- Linux/Mac OS 128
-
如果配置文件
/proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn存在,会读取配置文件中的值,并将backlog的值设置为配置文件中指定的
TCP_NODELAY
- 属于 SocketChannal 参数
- 因为 Nagle 算法,数据包会堆积到一定的数量后一起发送,这就可能导致数据的发送存在一定的延时
- 该参数默认为false,如果不希望的发送被延时,则需要将该值设置为true
SO_SNDBUF & SO_RCVBUF
- SO_SNDBUF 属于 SocketChannal 参数
- SO_RCVBUF 既可用于 SocketChannal 参数,也可以用于 ServerSocketChannal 参数(建议设置到 ServerSocketChannal 上)
- 该参数用于指定接收方与发送方的滑动窗口大小
ALLOCATOR
- 属于 SocketChannal 参数
- 用来配置 ByteBuf 是池化还是非池化,是直接内存还是堆内存
使用
// 选择ALLOCATOR参数,设置SocketChannel中分配的ByteBuf类型
// 第二个参数需要传入一个ByteBufAllocator,用于指定生成的 ByteBuf 的类型
new ServerBootstrap().childOption(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, new PooledByteBufAllocator());Copy
ByteBufAllocator类型
-
池化并使用直接内存
// true表示使用直接内存 new PooledByteBufAllocator(true);Copy -
池化并使用堆内存
// false表示使用堆内存 new PooledByteBufAllocator(false);Copy -
非池化并使用直接内存
// ture表示使用直接内存 new UnpooledByteBufAllocator(true);Copy -
非池化并使用堆内存
// false表示使用堆内存 new UnpooledByteBufAllocator(false);Copy
RCVBUF_ALLOCATOR
- 属于 SocketChannal 参数
- 控制 Netty 接收缓冲区大小
- 负责入站数据的分配,决定入站缓冲区的大小(并可动态调整),统一采用 direct 直接内存,具体池化还是非池化由 allocator 决定
3、RPC框架
准备工作
在聊天室代码的基础上进行一定的改进
Message中添加如下代码
public abstract class Message implements Serializable {
...
// 添加RPC消息类型
public static final int RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_REQUEST = 101;
public static final int RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_RESPONSE = 102;
static {
// 将消息类型放入消息类对象Map中
messageClasses.put(RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_REQUEST, RpcRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_RESPONSE, RpcResponseMessage.class);
}
}Copy
RPC请求消息
public class RpcRequestMessage extends Message {
/**
* 调用的接口全限定名,服务端根据它找到实现
*/
private String interfaceName;
/**
* 调用接口中的方法名
*/
private String methodName;
/**
* 方法返回类型
*/
private Class<?> returnType;
/**
* 方法参数类型数组
*/
private Class[] parameterTypes;
/**
* 方法参数值数组
*/
private Object[] parameterValue;
public RpcRequestMessage(int sequenceId, String interfaceName, String methodName, Class<?> returnType, Class[] parameterTypes, Object[] parameterValue) {
super.setSequenceId(sequenceId);
this.interfaceName = interfaceName;
this.methodName = methodName;
this.returnType = returnType;
this.parameterTypes = parameterTypes;
this.parameterValue = parameterValue;
}
@Override
public int getMessageType() {
return RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_REQUEST;
}
public String getInterfaceName() {
return interfaceName;
}
public String getMethodName() {
return methodName;
}
public Class<?> getReturnType() {
return returnType;
}
public Class[] getParameterTypes() {
return parameterTypes;
}
public Object[] getParameterValue() {
return parameterValue;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "RpcRequestMessage{" +
"interfaceName='" + interfaceName + '\'' +
", methodName='" + methodName + '\'' +
", returnType=" + returnType +
", parameterTypes=" + Arrays.toString(parameterTypes) +
", parameterValue=" + Arrays.toString(parameterValue) +
'}';
}
}Copy
想要远程调用一个方法,必须知道以下五个信息
- 方法所在的全限定类名
- 方法名
- 方法返回值类型
- 方法参数类型
- 方法参数值
RPC响应消息
public class RpcResponseMessage extends Message {
/**
* 返回值
*/
private Object returnValue;
/**
* 异常值
*/
private Exception exceptionValue;
@Override
public int getMessageType() {
return RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_RESPONSE;
}
public void setReturnValue(Object returnValue) {
this.returnValue = returnValue;
}
public void setExceptionValue(Exception exceptionValue) {
this.exceptionValue = exceptionValue;
}
public Object getReturnValue() {
return returnValue;
}
public Exception getExceptionValue() {
return exceptionValue;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "RpcResponseMessage{" +
"returnValue=" + returnValue +
", exceptionValue=" + exceptionValue +
'}';
}
}Copy
响应消息中只需要获取返回结果和异常值
服务器
public class RPCServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
LoggingHandler loggingHandler = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG);
MessageSharableCodec messageSharableCodec = new MessageSharableCodec();
// PRC 请求消息处理器
RpcRequestMessageHandler rpcRequestMessageHandler = new RpcRequestMessageHandler();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
serverBootstrap.group(boss, worker);
serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ProtocolFrameDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(loggingHandler);
ch.pipeline().addLast(messageSharableCodec);
ch.pipeline().addLast(rpcRequestMessageHandler);
}
});
Channel channel = serverBootstrap.bind(8080).sync().channel();
channel.closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
boss.shutdownGracefully();
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}Copy
服务器中添加了处理RPCRequest消息的handler
客户端
public class RPCClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
LoggingHandler loggingHandler = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG);
MessageSharableCodec messageSharableCodec = new MessageSharableCodec();
// PRC 请求消息处理器
RpcResponseMessageHandler rpcResponseMessageHandler = new RpcResponseMessageHandler();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(group);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ProtocolFrameDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(loggingHandler);
ch.pipeline().addLast(messageSharableCodec);
ch.pipeline().addLast(rpcResponseMessageHandler);
}
});
Channel channel = bootstrap.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080)).sync().channel();
channel.closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}Copy
通过接口Class获取实例对象的Factory
public class ServicesFactory {
static HashMap<Class<?>, Object> map = new HashMap<>(16);
public static Object getInstance(Class<?> interfaceClass) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
// 根据Class创建实例
try {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("cn.nyimac.study.day8.server.service.HelloService");
Object instance = Class.forName("cn.nyimac.study.day8.server.service.HelloServiceImpl").newInstance();
// 放入 InterfaceClass -> InstanceObject 的映射
map.put(clazz, instance);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return map.get(interfaceClass);
}
}Copy
RpcRequestMessageHandler
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class RpcRequestMessageHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RpcRequestMessage> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcRequestMessage rpcMessage) {
RpcResponseMessage rpcResponseMessage = new RpcResponseMessage();
try {
// 设置返回值的属性
rpcResponseMessage.setSequenceId(rpcMessage.getSequenceId());
// 返回一个实例
HelloService service = (HelloService) ServicesFactory.getInstance(Class.forName(rpcMessage.getInterfaceName()));
// 通过反射调用方法,并获取返回值
Method method = service.getClass().getMethod(rpcMessage.getMethodName(), rpcMessage.getParameterTypes());
// 获得返回值
Object invoke = method.invoke(service, rpcMessage.getParameterValue());
// 设置返回值
rpcResponseMessage.setReturnValue(invoke);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 设置异常
rpcResponseMessage.setExceptionValue(e);
}
}
// 向channel中写入Message
ctx.writeAndFlush(rpcResponseMessage);
}Copy
远程调用方法主要是通过反射实现的,大致步骤如下
- 通过请求消息传入被调入方法的各个参数
- 通过全限定接口名,在map中查询到对应的类并实例化对象
- 通过反射获取Method,并调用其invoke方法的返回值,并放入响应消息中
- 若有异常需要捕获,并放入响应消息中
RpcResponseMessageHandler
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class RpcResponseMessageHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RpcResponseMessage> {
static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ChatServer.class);
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcResponseMessage msg) throws Exception {
log.debug("{}", msg);
System.out.println((String)msg.getReturnValue());
}
}Copy
客户端发送消息
public class RPCClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
...
// 创建请求并发送
RpcRequestMessage message = new RpcRequestMessage(1,
"cn.nyimac.study.day8.server.service.HelloService",
"sayHello",
String.class,
new Class[]{String.class},
new Object[]{"Nyima"});
channel.writeAndFlush(message);
...
}
}Copy
运行结果
客户端
1606 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] DEBUG cn.nyimac.study.day8.server.ChatServer - RpcResponseMessage{returnValue=你好,Nyima, exceptionValue=null}Copy
改进客户端
public class RPCClientManager {
/**
* 产生SequenceId
*/
private static AtomicInteger sequenceId = new AtomicInteger(0);
private static volatile Channel channel = null;
private static final Object lock = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建代理对象
HelloService service = (HelloService) getProxy(HelloService.class);
// 通过代理对象执行方法
System.out.println(service.sayHello("Nyima"));
System.out.println(service.sayHello("Hulu"));
}
/**
* 单例模式创建Channel
*/
public static Channel getChannel() {
if (channel == null) {
synchronized (lock) {
if (channel == null) {
init();
}
}
}
return channel;
}
/**
* 使用代理模式,帮助我们创建请求消息并发送
*/
public static Object getProxy(Class<?> serviceClass) {
Class<?>[] classes = new Class<?>[]{serviceClass};
// 使用JDK代理,创建代理对象
Object o = Proxy.newProxyInstance(serviceClass.getClassLoader(), classes, new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 创建请求消息
int id = sequenceId.getAndIncrement();
RpcRequestMessage message = new RpcRequestMessage(id, serviceClass.getName(),
method.getName(), method.getReturnType(),
method.getParameterTypes(),
args);
// 发送消息
getChannel().writeAndFlush(message);
// 创建Promise,用于获取NIO线程中的返回结果,获取的过程是异步的
DefaultPromise<Object> promise = new DefaultPromise<>(getChannel().eventLoop());
// 将Promise放入Map中
RpcResponseMessageHandler.promiseMap.put(id, promise);
// 等待被放入Promise中结果
promise.await();
if (promise.isSuccess()) {
// 调用方法成功,返回方法执行结果
return promise.getNow();
} else {
// 调用方法失败,抛出异常
throw new RuntimeException(promise.cause());
}
}
});
return o;
}
private static void init() {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
LoggingHandler loggingHandler = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG);
MessageSharableCodec messageSharableCodec = new MessageSharableCodec();
// PRC 请求消息处理器
RpcResponseMessageHandler rpcResponseMessageHandler = new RpcResponseMessageHandler();
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(group);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ProtocolFrameDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(loggingHandler);
ch.pipeline().addLast(messageSharableCodec);
ch.pipeline().addLast(rpcResponseMessageHandler);
}
});
try {
channel = bootstrap.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080)).sync().channel();
// 异步关闭 group,避免Channel被阻塞
channel.closeFuture().addListener(future -> {
group.shutdownGracefully();
});
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Copy
获得Channel
- 建立连接,获取Channel的操作被封装到了
init方法中,当连接断开时,通过addListener方法异步关闭group - 通过单例模式创建与获取Channel
远程调用方法
- 为了让方法的调用变得简洁明了,将
RpcRequestMessage的创建与发送过程通过JDK的动态代理来完成 - 通过返回的代理对象调用方法即可,方法参数为被调用方法接口的Class类
远程调用方法返回值获取
-
调用方法的是主线程,处理返回结果的是NIO线程(RpcResponseMessageHandler)。要在不同线程中进行返回值的传递,需要用到Promise
-
在
RpcResponseMessageHandler中创建一个Map- Key为SequenceId
- Value为对应的Promise
-
主线程的代理类将RpcResponseMessage发送给服务器后,需要创建Promise对象,并将其放入到RpcResponseMessageHandler的Map中。需要使用await等待结果被放入Promise中。获取结果后,根据结果类型(判断是否成功)来返回结果或抛出异常
// 创建Promise,用于获取NIO线程中的返回结果,获取的过程是异步的 DefaultPromise<Object> promise = new DefaultPromise<>(getChannel().eventLoop()); // 将Promise放入Map中 RpcResponseMessageHandler.promiseMap.put(id, promise); // 等待被放入Promise中结果 promise.await(); if (promise.isSuccess()) { // 调用方法成功,返回方法执行结果 return promise.getNow(); } else { // 调用方法失败,抛出异常 throw new RuntimeException(promise.cause()); }Copy -
NIO线程负责通过SequenceId**获取并移除(remove)**对应的Promise,然后根据RpcResponseMessage中的结果,向Promise中放入不同的值
- 如果没有异常信息(ExceptionValue),就调用
promise.setSuccess(returnValue)放入方法返回值 - 如果有异常信息,就调用
promise.setFailure(exception)放入异常信息
// 将返回结果放入对应的Promise中,并移除Map中的Promise Promise<Object> promise = promiseMap.remove(msg.getSequenceId()); Object returnValue = msg.getReturnValue(); Exception exception = msg.getExceptionValue(); if (promise != null) { if (exception != null) { // 返回结果中有异常信息 promise.setFailure(exception); } else { // 方法正常执行,没有异常 promise.setSuccess(returnValue); } }Copy - 如果没有异常信息(ExceptionValue),就调用
改进RpcResponseMessageHandler
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class RpcResponseMessageHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RpcResponseMessage> {
static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ChatServer.class);
/**
* 用于存放Promise的集合,Promise用于主线程与NIO线程之间传递返回值
*/
public static Map<Integer, Promise<Object>> promiseMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcResponseMessage msg) throws Exception {
// 将返回结果放入对应的Promise中,并移除Map中的Promise
Promise<Object> promise = promiseMap.remove(msg.getSequenceId());
Object returnValue = msg.getReturnValue();
Exception exception = msg.getExceptionValue();
if (promise != null) {
if (exception != null) {
// 返回结果中有异常信息
promise.setFailure(exception);
} else {
// 方法正常执行,没有异常
promise.setSuccess(returnValue);
}
}
// 拿到返回结果并打印
log.debug("{}", msg);
}
}Copy
六、源码
1、启动流程
Netty启动流程可以简化成如下代码
// netty 中使用 NioEventLoopGroup (简称 nio boss 线程)来封装线程和 selector
Selector selector = Selector.open();
// 创建 NioServerSocketChannel,同时会初始化它关联的 handler,以及为原生 ssc 存储 config
NioServerSocketChannel attachment = new NioServerSocketChannel();
// 创建 NioServerSocketChannel 时,创建了 java 原生的 ServerSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 启动 nio boss 线程执行接下来的操作
//注册(仅关联 selector 和 NioServerSocketChannel),未关注事件
SelectionKey selectionKey = serverSocketChannel.register(selector, 0, attachment);
// head -> 初始化器 -> ServerBootstrapAcceptor -> tail,初始化器是一次性的,只为添加 acceptor
// 绑定端口
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
// 触发 channel active 事件,在 head 中关注 op_accept 事件
selectionKey.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);Copy
- 获得选择器Selector,Netty中使用NioEventloopGroup中的NioEventloop封装了线程和选择器
- 创建
NioServerSocketChannel,该Channel作为附件添加到ServerSocketChannel中 - 创建
ServerSocketChannel,将其设置为非阻塞模式,并注册到Selector中,此时未关注事件,但是添加了附件NioServerSocketChannel - 绑定端口
- 通过
interestOps设置感兴趣的事件
bind
选择器Selector的创建是在NioEventloopGroup中完成的。NioServerSocketChannel与ServerSocketChannel的创建,ServerSocketChannel注册到Selector中以及绑定操作都是由bind方法完成的
所以服务器启动的入口便是io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap.bind
public ChannelFuture bind(SocketAddress localAddress) {
validate();
return doBind(ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(localAddress, "localAddress"));
}Copy
doBind
真正完成初始化、注册以及绑定的方法是io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap.doBind
dobind方法在主线程中执行
private ChannelFuture doBind(final SocketAddress localAddress) {
// 负责NioServerSocketChannel和ServerSocketChannel的创建
// ServerSocketChannel的注册工作
// init由main线程完成,regisetr由NIO线程完成
final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister();
final Channel channel = regFuture.channel();
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
return regFuture;
}
// 因为register操作是异步的
// 所以要判断主线程执行到这里时,register操作是否已经执行完毕
if (regFuture.isDone()) {
// At this point we know that the registration was complete and successful.
ChannelPromise promise = channel.newPromise();
// 执行doBind0绑定操作
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
return promise;
} else {
// Registration future is almost always fulfilled already, but just in case it's not.
// 如果register操作还没执行完,就会到这个分支中来
final PendingRegistrationPromise promise = new PendingRegistrationPromise(channel);
// 添加监听器,NIO线程异步进行doBind0操作
regFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
Throwable cause = future.cause();
if (cause != null) {
// Registration on the EventLoop failed so fail the ChannelPromise directly to not cause an
// IllegalStateException once we try to access the EventLoop of the Channel.
promise.setFailure(cause);
} else {
// Registration was successful, so set the correct executor to use.
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2586
promise.registered();
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
}
}
});
return promise;
}
}Copy
- doBind()中有两个重要方法
initAndRegister()和doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise) - initAndRegister主要负责NioServerSocketChannel和ServerSocketChannel的创建(主线程中完成)与ServerSocketChannel注册(NIO线程中完成)工作
- doBind0则负责连接的创建工作
initAndRegisterd
代码
final ChannelFuture initAndRegister() {
Channel channel = null;
try {
channel = channelFactory.newChannel();
init(channel);
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (channel != null) {
// channel can be null if newChannel crashed (eg SocketException("too many open files"))
channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
// as the Channel is not registered yet we need to force the usage of the GlobalEventExecutor
return new DefaultChannelPromise(channel, GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t);
}
// as the Channel is not registered yet we need to force the usage of the GlobalEventExecutor
return new DefaultChannelPromise(new FailedChannel(), GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t);
}
ChannelFuture regFuture = config().group().register(channel);
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
if (channel.isRegistered()) {
channel.close();
} else {
channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
}
}
// If we are here and the promise is not failed, it's one of the following cases:
// 1) If we attempted registration from the event loop, the registration has been completed at this point.
// i.e. It's safe to attempt bind() or connect() now because the channel has been registered.
// 2) If we attempted registration from the other thread, the registration request has been successfully
// added to the event loop's task queue for later execution.
// i.e. It's safe to attempt bind() or connect() now:
// because bind() or connect() will be executed *after* the scheduled registration task is executed
// because register(), bind(), and connect() are all bound to the same thread.
return regFuture;
}Copy
init
Channel channel = null;
try {
// 通过反射初始化NioServerSocketChannel
channel = channelFactory.newChannel();
init(channel);
}Copy
newChannel方法
@Override
public T newChannel() {
try {
// 通过反射调用NioServerSocketChannel的构造方法
// 创建NioServerSocketChannel对象
return constructor.newInstance();
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new ChannelException("Unable to create Channel from class " + constructor.getDeclaringClass(), t);
}
}Copy
NioServerSocketChannel构造方法
public NioServerSocketChannel() {
// 创建了ServerSocketChannel实例
this(newSocket(DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER));
}Copy
newSocket方法
private static ServerSocketChannel newSocket(SelectorProvider provider) {
try {
// ServerSocketChannel.open方法:
// SelectorProvider.provider().openServerSocketChannel()
// 所以此处相当于ServerSocketChannel.open()
// 创建了ServerSocketChannel实例
return provider.openServerSocketChannel();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ChannelException("Failed to open a server socket.", e);
}
}Copy
init方法
@Override
void init(Channel channel) {
...
// NioSocketChannl的Pipeline
ChannelPipeline p = channel.pipeline();
...
// 向Pipeline中添加了一个handler,该handler等待被调用
p.addLast(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {
@Override
// register之后才调用该方法
public void initChannel(final Channel ch) {
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
// 创建handler并加入到pipeline中
ChannelHandler handler = config.handler();
if (handler != null) {
pipeline.addLast(handler);
}
ch.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 添加新的handler,在发生Accept事件后建立连接
pipeline.addLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor(
ch, currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs));
}
});
}
});
}Copy
init主要完成了以下三个操作
-
创建NioServerSocketChannel
-
通过NioServerSocketChannel的构造器,创建了ServerSocketChannel
-
由
initChannel方法向NioServerSocketChannel中添加了两个handler,
添加操作在register之后被执行
- 一个handler负责设置配置
- 一个handler负责发生Accepet事件后建立连接
Register
init执行完毕后,便执行ChannelFuture regFuture = config().group().register(channel)操作
该方法最终调用的是promise.channel().unsafe().register(this, promise)方法
promise.channel().unsafe().register(this, promise)
@Override
public final void register(EventLoop eventLoop, final ChannelPromise promise) {
...
// 获取EventLoop
AbstractChannel.this.eventLoop = eventLoop;
// 此处完成了由 主线程 到 NIO线程 的切换
// eventLoop.inEventLoop()用于判断当前线程是否为NIO线程
if (eventLoop.inEventLoop()) {
register0(promise);
} else {
try {
// 向NIO线程中添加任务
eventLoop.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 该方法中会执行doRegister
// 执行真正的注册操作
register0(promise);
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
...
}
}
}Copy
register0方法
private void register0(ChannelPromise promise) {
try {
...
// 执行真正的注册操作
doRegister();
neverRegistered = false;
registered = true;
// Ensure we call handlerAdded(...) before we actually notify the promise. This is needed as the
// user may already fire events through the pipeline in the ChannelFutureListener.
// 调用init中的initChannel方法
pipeline.invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded();
...
} catch (Throwable t) {
...
}
}Copy
doRegister方法
@Override
protected void doRegister() throws Exception {
boolean selected = false;
for (;;) {
try {
// javaChannel()即为ServerSocketChannel
// eventLoop().unwrappedSelector()获取eventLoop中的Selector
// this为NIOServerSocketChannel,作为附件
selectionKey = javaChannel().register(eventLoop().unwrappedSelector(), 0, this);
return;
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
...
}
}
}Copy
回调initChannel
@Override
public void initChannel(final Channel ch) {
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
ChannelHandler handler = config.handler();
if (handler != null) {
pipeline.addLast(handler);
}
// 添加新任务,任务负责添加handler
// 该handler负责发生Accepet事件后建立连接
ch.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
pipeline.addLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor(
ch, currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs));
}
});
}Copy
Register主要完成了以下三个操作
-
完成了主线程到NIO的线程切换
- 通过
eventLoop.inEventLoop()进行线程判断,判断当前线程是否为NIO线程 - 切换的方式为让eventLoop执行register的操作
- register的操作在NIO线程中完成
- 通过
-
调用doRegister方法
// javaChannel()即为ServerSocketChannel // eventLoop().unwrappedSelector()获取eventLoop中的Selector // this为NIOServerSocketChannel,作为附件 selectionKey = javaChannel().register(eventLoop().unwrappedSelector(), 0, this);Copy- 将ServerSocketChannel注册到EventLoop的Selector中
- 此时还未关注事件
- 添加NioServerSocketChannel附件
-
通过
invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded调用init中的initChannel方法-
initChannel方法主要创建了
两个handler
- 一个handler负责设置配置
- 一个handler负责发生Accept事件后建立连接
-
doBind0
绑定端口
在doRegister和invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded操作中的完成后,会调用safeSetSuccess(promise)方法,向Promise中设置执行成功的结果。此时doBind方法中由initAndRegister返回的ChannelFuture对象regFuture便会由NIO线程异步执行doBind0绑定操作
// initAndRegister为异步方法,会返回ChannelFuture对象
final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister();
regFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
Throwable cause = future.cause();
if (cause != null) {
// Registration on the EventLoop failed so fail the ChannelPromise directly to not cause an
// IllegalStateException once we try to access the EventLoop of the Channel.
promise.setFailure(cause);
} else {
// Registration was successful, so set the correct executor to use.
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2586
promise.registered();
// 如果没有异常,则执行绑定操作
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
}
}
});Copy
doBind0最底层调用的是ServerSocketChannel的bind方法
NioServerSocketChannel.doBind方法
通过该方法,绑定了对应的端口
@SuppressJava6Requirement(reason = "Usage guarded by java version check")
@Override
protected void doBind(SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception {
if (PlatformDependent.javaVersion() >= 7) {
// 调用ServerSocketChannel的bind方法,绑定端口
javaChannel().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog());
} else {
javaChannel().socket().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog());
}
}Copy
关注事件
在绑定端口操作完成后,会判断各种所有初始化操作是否已经完成,若完成,则会添加ServerSocketChannel感兴趣的事件
if (!wasActive && isActive()) {
invokeLater(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
}
});
}Copy
最终在AbstractNioChannel.doBeginRead方法中,会添加ServerSocketChannel添加Accept事件
@Override
protected void doBeginRead() throws Exception {
// Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() was called
final SelectionKey selectionKey = this.selectionKey;
if (!selectionKey.isValid()) {
return;
}
readPending = true;
final int interestOps = selectionKey.interestOps();
// 如果ServerSocketChannel没有关注Accept事件
if ((interestOps & readInterestOp) == 0) {
// 则让其关注Accepet事件
// readInterestOp 取值是 16
// 在 NioServerSocketChannel 创建时初始化
selectionKey.interestOps(interestOps | readInterestOp);
}
}Copy
注意:此处设置interestOps时使用的方法,避免覆盖关注的其他事件
-
首先获取Channel所有感兴趣的事件
final int interestOps = selectionKey.interestOps();Copy -
然后再设置其感兴趣的事件
selectionKey.interestOps(interestOps | readInterestOp);Copy
各个事件对应的值
总结
通过上述步骤,完成了
- NioServerSocketChannel与ServerSocketChannel的创建
- ServerSocketChannel绑定到EventLoop的Selecot中,并添加NioServerSocketChannel附件
- 绑定了对应的端口
- 关注了Accept事件
2、NioEventLoop剖析
组成
NioEventLoop的重要组成部分有三个
-
Selector
public final class NioEventLoop extends SingleThreadEventLoop { ... // selector中的selectedKeys是基于数组的 // unwrappedSelector中的selectedKeys是基于HashSet的 private Selector selector; private Selector unwrappedSelector; private SelectedSelectionKeySet selectedKeys; ... }Copy -
Thread与TaskQueue
public abstract class SingleThreadEventExecutor extends AbstractScheduledEventExecutor implements OrderedEventExecutor { // 任务队列 private final Queue<Runnable> taskQueue; // 线程 private volatile Thread thread; }Copy
Selector的创建
Selector是在NioEventLoop的构造方法中被创建的
NioEventLoop(NioEventLoopGroup parent, Executor executor, SelectorProvider selectorProvider, SelectStrategy strategy, RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionHandler, EventLoopTaskQueueFactory queueFactory) {
...
// 初始化selector,初始化过程在openSelector中
final SelectorTuple selectorTuple = openSelector();
this.selector = selectorTuple.selector;
this.unwrappedSelector = selectorTuple.unwrappedSelector;
}
private SelectorTuple openSelector() {
final Selector unwrappedSelector;
try {
// 此处等同于 Selector.open()方法
// 创建了unwrappedSelector对象
unwrappedSelector = provider.openSelector();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ChannelException("failed to open a new selector", e);
}
}Copy
NioEventLoop的构造方法中,调用了openSelector()方法, 该方法会返回一个
SelectorTuple对象,该方法是创建Selector的核心方法。openSelector()方法内部调用了
unwrappedSelector = provider.openSelector();Copy
获得了Selector对象unwrappedSelector
后面会通过反射,修改unwrappedSelector中SelectedKeys的实现,然后通过SelectedSelectionKeySetSelector方法获得selector。最后通过SelectorTuple的构造方法,将该Selector的值赋给SelectorTuple类中的selector与unwrappedSelector
private static final class SelectorTuple {
final Selector unwrappedSelector;
final Selector selector;
SelectorTuple(Selector unwrappedSelector) {
this.unwrappedSelector = unwrappedSelector;
this.selector = unwrappedSelector;
}
/**
* 一般调用的是这个构造方法
*/
SelectorTuple(Selector unwrappedSelector, Selector selector) {
this.unwrappedSelector = unwrappedSelector;
this.selector = selector;
}
}Copy
再通过NioEventLoop的构造方法,将SelectorTuple中的Selector赋值给NioEventLoop中的Selector
两个Selector
NioEventLoop中有selector和unwrappedSelector两个Selector,它们的区别主要在于SelectedKeys的数据结构
- selector中的SelectedKeys是基于数组的
- unwrappedSelector中的是基于HashSet的
这样做的主要目的是,数组的遍历效率要高于HashSet
private SelectorTuple openSelector() {
final Selector unwrappedSelector;
try {
unwrappedSelector = provider.openSelector();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ChannelException("failed to open a new selector", e);
}
...
// 获得基于数组的selectedKeySet实现
final SelectedSelectionKeySet selectedKeySet = new SelectedSelectionKeySet();
Object maybeException = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() {
try {
// 通过反射拿到unwrappedSelector中的selectedKeys属性
Field selectedKeysField = selectorImplClass.getDeclaredField("selectedKeys");
Field publicSelectedKeysField = selectorImplClass.getDeclaredField("publicSelectedKeys");
...
// 暴力反射,修改私有属性
Throwable cause = ReflectionUtil.trySetAccessible(selectedKeysField, true);
if (cause != null) {
return cause;
}
cause = ReflectionUtil.trySetAccessible(publicSelectedKeysField, true);
if (cause != null) {
return cause;
}
// 替换为基于数组的selectedKeys实现
selectedKeysField.set(unwrappedSelector, selectedKeySet);
publicSelectedKeysField.set(unwrappedSelector, selectedKeySet);
return null;
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
return e;
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
return e;
}
}
});
selectedKeys = selectedKeySet;
// 调用构造函数,创建unwrappedSelector与selector
return new SelectorTuple(unwrappedSelector,
new SelectedSelectionKeySetSelector(unwrappedSelector, selectedKeySet));
}Copy
获得数组实现SelectedKeys的Selector的原理是反射,主要步骤如下
-
获得基于数组的selectedKeySet实现
// 获得基于数组的selectedKeySet实现 final SelectedSelectionKeySet selectedKeySet = new SelectedSelectionKeySet(); SelectedSelectionKeySet() { keys = new SelectionKey[1024]; }Copy -
通过反射拿到unwrappedSelector中的SelectedKeySet并将其替换为selectedKeySet
-
通过Selector的构造方法获得selector
new SelectedSelectionKeySetSelector(unwrappedSelector, selectedKeySet)Copy -
通过SelectorTuple的构造方法获得拥有两种Selector的SelectorTuple对象,并返回给NioEventLoop
// 调用构造函数,创建unwrappedSelector与selector return new SelectorTuple(unwrappedSelector, new SelectedSelectionKeySetSelector(unwrappedSelector, selectedKeySet));Copy
NIO线程启动时机
启动
NioEventLoop中的线程,在首次执行任务时,才会被创建,且只会被创建一次
测试代码
public class TestNioEventLoop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventLoop eventLoop = new NioEventLoopGroup().next();
// 使用NioEventLoop执行任务
eventLoop.execute(()->{
System.out.println("hello");
});
}
}Copy
进入execute执行任务
@Override
public void execute(Runnable task) {
// 检测传入的任务是否为空,为空会抛出NullPointerException
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(task, "task");
// 执行任务
// 此处判断了任务是否为懒加载任务,wakesUpForTask的返回值只会为true
execute(task, !(task instanceof LazyRunnable) && wakesUpForTask(task));
}Copy
进入上述代码的execute方法
private void execute(Runnable task, boolean immediate) {
// 判断当前线程是否为NIO线程
// 判断方法为 return thread == this.thread;
// this.thread即为NIO线程,首次执行任务时,其为null
boolean inEventLoop = inEventLoop();
// 向任务队列taskQueue中添加任务
addTask(task);
// 当前线程不是NIO线程,则进入if语句
if (!inEventLoop) {
// 启动NIO线程的核心方法
startThread();
...
}
// 有任务需要被执行时,唤醒阻塞的NIO线程
if (!addTaskWakesUp && immediate) {
wakeup(inEventLoop);
}
}Copy
进入startThread方法
private void startThread() {
// 查看NIO线程状态是否为未启动
// 该if代码块只会执行一次
// state一开始的值就是ST_NOT_STARTED
// private volatile int state = ST_NOT_STARTED;
if (state == ST_NOT_STARTED) {
// 通过原子属性更新器将状态更新为启动(ST_STARTED)
if (STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, ST_NOT_STARTED, ST_STARTED)) {
boolean success = false;
try {
// 执行启动线程
doStartThread();
success = true;
} finally {
if (!success) {
STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, ST_STARTED, ST_NOT_STARTED);
}
}
}
}
}Copy
进入doStartThread,真正创建NIO线程并执行任务
private void doStartThread() {
assert thread == null;
// 创建NIO线程并执行任务
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// thread即为NIO线程
thread = Thread.currentThread();
if (interrupted) {
thread.interrupt();
}
boolean success = false;
updateLastExecutionTime();
try {
// 执行内部run方法
SingleThreadEventExecutor.this.run();
success = true;
}
...
});
}Copy
通过SingleThreadEventExecutor.this.run()执行传入的任务(task)
该run方法是NioEvnetLoop的run方法
@Override
protected void run() {
int selectCnt = 0;
// 死循环,不断地从任务队列中获取各种任务来执行
for (;;) {
// 执行各种任务
try {
int strategy;
try {
strategy = selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks());
switch (strategy) {
case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE:
continue;
case SelectStrategy.BUSY_WAIT:
// fall-through to SELECT since the busy-wait is not supported with NIO
case SelectStrategy.SELECT:
long curDeadlineNanos = nextScheduledTaskDeadlineNanos();
if (curDeadlineNanos == -1L) {
curDeadlineNanos = NONE; // nothing on the calendar
}
nextWakeupNanos.set(curDeadlineNanos);
try {
if (!hasTasks()) {
strategy = select(curDeadlineNanos);
}
} finally {
// This update is just to help block unnecessary selector wakeups
// so use of lazySet is ok (no race condition)
nextWakeupNanos.lazySet(AWAKE);
}
// fall through
default:
}
}
}
}Copy
唤醒
NioEvnetLoop需要IO事件、普通任务以及定时任务,任务在run方法的for循环中
@Override
protected void run() {
int selectCnt = 0;
// 死循环,不断地从任务队列中获取各种任务来执行
for (;;) {
// 执行各种任务
...
}
}Copy
中被执行,但该循环不会空转,执行到某些代码时,会被阻塞
run方法中有SELECT分支
case SelectStrategy.SELECT:
long curDeadlineNanos = nextScheduledTaskDeadlineNanos();
if (curDeadlineNanos == -1L) {
curDeadlineNanos = NONE; // nothing on the calendar
}
nextWakeupNanos.set(curDeadlineNanos);
try {
if (!hasTasks()) {
// 执行select方法
strategy = select(curDeadlineNanos);
}
}
...Copy
会执行NioEvnetLoop的select方法,该方法内部会根据情况,执行selector的有参和无参的select方法
private int select(long deadlineNanos) throws IOException {
// 如果没有指定阻塞事件,就调用select()
if (deadlineNanos == NONE) {
return selector.select();
}
// 否则调用select(timeoutMillis),指定时间内未发生事件就停止阻塞
// Timeout will only be 0 if deadline is within 5 microsecs
long timeoutMillis = deadlineToDelayNanos(deadlineNanos + 995000L) / 1000000L;
return timeoutMillis <= 0 ? selector.selectNow() : selector.select(timeoutMillis);
}Copy
但需要注意的是,select方法是会阻塞线程的,当没有IO事件,但有其他任务需要执行时,需要唤醒线程
唤醒是通过execute最后的if代码块来完成的
// 有任务需要被执行时,唤醒阻塞的NIO线程
if (!addTaskWakesUp && immediate) {
wakeup(inEventLoop);
}Copy
NioEventLoop.wakeup唤醒被selector.select方法阻塞的NIO线程
@Override
protected void wakeup(boolean inEventLoop) {
// 只有当其他线程给当前NIO线程提交任务时(如执行execute),才会被唤醒
// 通过AtomicLong进行更新,保证每次只能有一个线程唤醒成功
if (!inEventLoop && nextWakeupNanos.getAndSet(AWAKE) != AWAKE) {
// 唤醒被selector.select方法阻塞的NIO线程
selector.wakeup();
}
}Copy
唤醒时需要进行两个判断
-
判断提交任务的
是否为NIO线程
- 若是其他线程,才能唤醒NIO线程
- 若是NIO线程自己,则不能唤醒
-
通过AtomicLong保证有多个线程同时提交任务时,只有一个线程能够唤醒NIO线程
SELECT分支
run方法的switch语句有多条分支,具体执行分支的代码由strategy变量控制
int strategy = selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks());
switch (strategy) {
...
}Copy
strategy的值由calculateStrategy方法确定
@Override
public int calculateStrategy(IntSupplier selectSupplier, boolean hasTasks) throws Exception {
// selectSupplier.get() 底层是 selector.selectNow();
return hasTasks ? selectSupplier.get() : SelectStrategy.SELECT;
}Copy
该方法会根据hasTaks变量判断任务队列中是否有任务
-
若有任务,则通过selectSupplier获得strategy的值
-
get方法会selectNow方法,顺便拿到IO事件
private final IntSupplier selectNowSupplier = new IntSupplier() { public int get() throws Exception { return NioEventLoop.this.selectNow(); } }; int selectNow() throws IOException { return this.selector.selectNow(); }Copy
-
-
若没有任务,就会进入SELECT分支
也就说,当任务队列中没有任务时,才会进入SELECT分支,让NIO线程阻塞,而不是空转。若有任务,则会通过get方法调用selector.selectNow方法,顺便拿到IO事件
Java NIO空轮询BUG
Java NIO空轮询BUG也就是JavaNIO在Linux系统下的epoll空轮询问题
在NioEventLoop中,因为run方法中存在一个死循环,需要通过selector.select方法来阻塞线程。但是select方法因为BUG,可能无法阻塞线程,导致循环一直执行,使得CPU负载升高
@Override
protected void run() {
...
for(;;){
...
// 可能发生空轮询,无法阻塞NIO线程
strategy = select(curDeadlineNanos);
...
if(...) {
...
} else if (unexpectedSelectorWakeup(selectCnt) ){
// 通过unexpectedSelectorWakeup方法中的rebuildSelector重建selector
// 并将selectCnt重置为0
selectCnt = 0;
}
}
}Copy
Netty中通过selectCnt变量来检测select方法是否发生空轮询BUG
若发生空轮询BUG,那么selectCnt的值会增长是十分迅速。当selectCnt的值大于等于SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD(默认512)时,Netty则判断其出现了空轮询BUG,进行如下处理
if (SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD > 0 && selectCnt >= SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD) {
// The selector returned prematurely many times in a row.
// Rebuild the selector to work around the problem.
logger.warn("Selector.select() returned prematurely {} times in a row; rebuilding Selector {}.",selectCnt, selector);
// 重建selector,将原selector的配置信息传给新selector
// 再用新selector覆盖旧selector
rebuildSelector();
return true;
}Copy
通过rebuildSelector方法重建selector,将原selector的配置信息传给新selector,再用新selector覆盖旧selector。同时将selectCnt的值设置为0
ioRatio
NioEventLoop可以处理IO事件和其他任务。不同的操作所耗费的时间是不同的,想要控制NioEventLoop处理IO事件花费时间占执行所有操作的总时间的比例,需要通过ioRatio来控制
NioEventLoop.run方法
// 处理IO事件时间比例,默认为50%
final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio;
// 如果IO事件时间比例设置为100%
if (ioRatio == 100) {
try {
// 如果需要去处理IO事件
if (strategy > 0) {
// 先处理IO事件
processSelectedKeys();
}
} finally {
// Ensure we always run tasks.
// 剩下的时间都去处理普通任务和定时任务
ranTasks = runAllTasks();
}
} else if (strategy > 0) { // 如果需要去处理IO事件
// 记录处理IO事件前的时间
final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime();
try {
// 去处理IO事件
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
// Ensure we always run tasks.
// ioTime为处理IO事件耗费的事件
final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime;
// 计算出处理其他任务的事件
// 超过设定的时间后,将会停止任务的执行,会在下一次循环中再继续执行
ranTasks = runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio);
}
} else { // 没有IO事件需要处理
// This will run the minimum number of tasks
// 直接处理普通和定时任务
ranTasks = runAllTasks(0);
}Copy
通过ioRatio控制各个任务执行的过程如下
-
判断ioRatio是否为100
-
若是,判断是否需要处理IO事件(strategy>0)
- 若需要处理IO事件,则先处理IO事件
-
若否(或IO事件已经处理完毕),接下来去执行所有的普通任务和定时任务,直到所有任务都被处理完
// 没有指定执行任务的时间 ranTasks = runAllTasks();Copy
-
-
若ioRatio不为100
-
先去处理IO事件,记录处理IO事件所花费的事件保存在ioTime中
-
接下来去处理其他任务,根据ioTime与ioRatio计算执行其他任务可用的时间
// 比如ioTime为10s,ioRatio为50 // 那么通过 10*(100-50)/50=10 计算出其他任务可用的时间为 10s // 处理IO事件占用的事件总比例为50% ranTasks = runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio);Copy -
执行其他任务一旦超过可用时间,则会停止执行,在下一次循环中再继续执行
-
-
若没有IO事件需要处理,则去执行最少数量的普通任务和定时任务
// 运行最少数量的任务 ranTasks = runAllTasks(0);Copy
处理事件
IO事件是通过NioEventLoop.processSelectedKeys()方法处理的
private void processSelectedKeys() {
// 如果selectedKeys是基于数组的
// 一般情况下都走这个分支
if (selectedKeys != null) {
// 处理各种IO事件
processSelectedKeysOptimized();
} else {
processSelectedKeysPlain(selector.selectedKeys());
}
}Copy
processSelectedKeysOptimized方法
private void processSelectedKeysOptimized() {
for (int i = 0; i < selectedKeys.size; ++i) {
// 拿到SelectionKeyec
final SelectionKey k = selectedKeys.keys[i];
// null out entry in the array to allow to have it GC'ed once the Channel close
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2363
selectedKeys.keys[i] = null;
// 获取SelectionKey上的附件,即NioServerSocketChannel
final Object a = k.attachment();
if (a instanceof AbstractNioChannel) {
// 处理事件,传入附件NioServerSocketChannel
processSelectedKey(k, (AbstractNioChannel) a);
} else {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
NioTask<SelectableChannel> task = (NioTask<SelectableChannel>) a;
processSelectedKey(k, task);
}
if (needsToSelectAgain) {
// null out entries in the array to allow to have it GC'ed once the Channel close
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2363
selectedKeys.reset(i + 1);
selectAgain();
i = -1;
}
}
}Copy
该方法中通过fori的方法,遍历基于数组的SelectedKey,通过
final SelectionKey k = selectedKeys.keys[i];Copy
获取到SelectionKey,然后获取其再Register时添加的附件NioServerSocketChannel
// 获取SelectionKey上的附件,即NioServerSocketChannel
final Object a = k.attachment();Copy
如果附件继承自AbstractNioChannel,则会调用
// 处理事件,传入附件NioServerSocketChannel
processSelectedKey(k, (AbstractNioChannel) a);Copy
去处理各个事件
真正处理各种事件的方法processSelectedKey
获取SelectionKey的事件,然后进行相应处理
private void processSelectedKey(SelectionKey k, AbstractNioChannel ch) {
final AbstractNioChannel.NioUnsafe unsafe = ch.unsafe();
if (!k.isValid()) {
final EventLoop eventLoop;
try {
eventLoop = ch.eventLoop();
} catch (Throwable ignored) {
// If the channel implementation throws an exception because there is no event loop, we ignore this
// because we are only trying to determine if ch is registered to this event loop and thus has authority
// to close ch.
return;
}
// Only close ch if ch is still registered to this EventLoop. ch could have deregistered from the event loop
// and thus the SelectionKey could be cancelled as part of the deregistration process, but the channel is
// still healthy and should not be closed.
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/5125
if (eventLoop == this) {
// close the channel if the key is not valid anymore
unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise());
}
return;
}
try {
int readyOps = k.readyOps();
// We first need to call finishConnect() before try to trigger a read(...) or write(...) as otherwise
// the NIO JDK channel implementation may throw a NotYetConnectedException.
if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT) != 0) {
// remove OP_CONNECT as otherwise Selector.select(..) will always return without blocking
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/924
int ops = k.interestOps();
ops &= ~SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT;
k.interestOps(ops);
unsafe.finishConnect();
}
// Process OP_WRITE first as we may be able to write some queued buffers and so free memory.
if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) {
// Call forceFlush which will also take care of clear the OP_WRITE once there is nothing left to write
ch.unsafe().forceFlush();
}
// Also check for readOps of 0 to workaround possible JDK bug which may otherwise lead
// to a spin loop
if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {
unsafe.read();
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException ignored) {
unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise());
}
}Copy
3、Accept剖析
NIO中处理Accept事件流程
NIO中处理Accept事件主要有以下六步
- selector.select()阻塞线程,直到事件发生
- 遍历selectionKeys
- 获取一个key,判断事件类型是否为Accept
- 创建SocketChannel,设置为非阻塞
- 将SocketChannel注册到selector中
- 关注selectionKeys的read事件
代码如下
// 阻塞直到事件发生
selector.select();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = selector.selectionKeys().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
// 拿到一个事件
SelectionKey key = iter.next();
// 如果是 accept 事件
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
// 执行accept,获得SocketChannel
SocketChannel channel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
channel.configureBlocking(false);
// 将SocketChannel注册到selector中,并关注read事件
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
// ...
}Copy
其中前三步,在NioEventLoop剖析中已经分析过了,所以接下来主要分析后三步
SocketChannel的创建与注册
发生Accept事件后,会执行NioEventLoop.run方法的如下if分支
if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {
unsafe.read();
}Copy
NioMessageUnsafe.read方法
public void read() {
...
try {
try {
do {
// doReadMessages中执行了accept获得了SocketChannel
// 并创建NioSocketChannel作为消息放入readBuf
// readBuf是一个ArrayList用来缓存消息
// private final List<Object> readBuf = new ArrayList<Object>();
int localRead = doReadMessages(readBuf);
...
// localRead值为1,就一条消息,即接收一个客户端连接
allocHandle.incMessagesRead(localRead);
} while (allocHandle.continueReading());
} catch (Throwable t) {
exception = t;
}
int size = readBuf.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i ++) {
readPending = false;
// 触发read事件,让pipeline上的handler处理
// ServerBootstrapAcceptor.channelRead
pipeline.fireChannelRead(readBuf.get(i));
}
...
} finally {
if (!readPending && !config.isAutoRead()) {
removeReadOp();
}
}
}Copy
NioSocketChannel.doReadMessages方法
该方法中处理accpet事件,获得SocketChannel,同时创建了NioSocketChannel,作为消息放在了readBuf中
@Override
protected int doReadMessages(List<Object> buf) throws Exception {
// 处理accpet事件,获得SocketChannel
SocketChannel ch = SocketUtils.accept(javaChannel());
try {
if (ch != null) {
// 创建了NioSocketChannel,作为消息放在了readBuf中
buf.add(new NioSocketChannel(this, ch));
return 1;
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
...
}
return 0;
}Copy
ServerBootstrapAcceptor.channelRead
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
// 这时的msg是NioSocketChannel
final Channel child = (Channel) msg;
// NioSocketChannel添加childHandler,即初始化器
child.pipeline().addLast(childHandler);
// 设置选项
setChannelOptions(child, childOptions, logger);
for (Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object> e: childAttrs) {
child.attr((AttributeKey<Object>) e.getKey()).set(e.getValue());
}
try {
// 注册 NioSocketChannel到nio worker线程,接下来的处理也移交至nio worker线程
childGroup.register(child).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
forceClose(child, future.cause());
}
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
forceClose(child, t);
}
}Copy
通过AbstractUnsafe.register 方法,将SocketChannel注册到了Selector中,过程与启动流程中的Register过程类似
public final void register(EventLoop eventLoop, final ChannelPromise promise) {
...
AbstractChannel.this.eventLoop = eventLoop;
if (eventLoop.inEventLoop()) {
register0(promise);
} else {
try {
// 这行代码完成的是nio boss -> nio worker线程的切换
eventLoop.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 真正的注册操作
register0(promise);
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
...
}
}
}Copy
AbstractChannel.AbstractUnsafe.register0
private void register0(ChannelPromise promise) {
try {
...
// 该方法将SocketChannel注册到Selector中
doRegister();
// 执行初始化器,执行前 pipeline 中只有 head -> 初始化器 -> tail
pipeline.invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded();
// 执行后就是 head -> logging handler -> my handler -> tail
safeSetSuccess(promise);
pipeline.fireChannelRegistered();
if (isActive()) {
if (firstRegistration) {
// 触发pipeline上active事件
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
} else if (config().isAutoRead()) {
beginRead();
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
closeForcibly();
closeFuture.setClosed();
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
}
}Copy
AbstractNioChannel.doRegister将SocketChannel注册到Selector中
@Override
protected void doRegister() throws Exception {
boolean selected = false;
for (;;) {
try {
// 将Selector注册到Selector中
selectionKey = javaChannel().register(eventLoop().unwrappedSelector(), 0, this);
return;
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
...
}
}
}Copy
HeadContext.channelActive
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
ctx.fireChannelActive();
// 触发read(NioSocketChannel这里read只是为了触发channel的事件注册,还未涉及数据读取)
readIfIsAutoRead();
}Copy
AbstractNioChannel.doBeginRead,通过该方法,SocketChannel关注了read事件
protected void doBeginRead() throws Exception {
// Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() was called
final SelectionKey selectionKey = this.selectionKey;
if (!selectionKey.isValid()) {
return;
}
readPending = true;
// 这时候 interestOps是0
final int interestOps = selectionKey.interestOps();
if ((interestOps & readInterestOp) == 0) {
// 关注read事件
selectionKey.interestOps(interestOps | readInterestOp);
}
}Copy
4、Read剖析
read事件的处理也是在
if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {
unsafe.read();
}Copy
分支中,通过unsafe.read()方法处理的,不过此处调用的方法在AbstractNioByteChannel.NioByteUnsafe类中
@Override
public final void read() {
// 获得Channel的配置
final ChannelConfig config = config();
if (shouldBreakReadReady(config)) {
clearReadPending();
return;
}
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline();
// 根据配置创建ByteBufAllocator(池化非池化、直接非直接内存)
final ByteBufAllocator allocator = config.getAllocator();
// 用来分配 byteBuf,确定单次读取大小
final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = recvBufAllocHandle();
allocHandle.reset(config);
ByteBuf byteBuf = null;
boolean close = false;
try {
do {
// 创建ByteBuf
byteBuf = allocHandle.allocate(allocator);
// 读取内容,放入ByteBUf中
allocHandle.lastBytesRead(doReadBytes(byteBuf));
if (allocHandle.lastBytesRead() <= 0) {
byteBuf.release();
byteBuf = null;
close = allocHandle.lastBytesRead() < 0;
if (close) {
readPending = false;
}
break;
}
allocHandle.incMessagesRead(1);
readPending = false;
// 触发read 事件,让pipeline上的handler处理
// 这时是处理NioSocketChannel上的handler
pipeline.fireChannelRead(byteBuf);
byteBuf = null;
}
// 是否要继续循环
while (allocHandle.continueReading());
allocHandle.readComplete();
// 触发 read complete事件
pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();
if (close) {
closeOnRead(pipeline);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleReadException(pipeline, byteBuf, t, close, allocHandle);
} finally {
// Check if there is a readPending which was not processed yet.
// This could be for two reasons:
// * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelRead(...) method
// * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelReadComplete(...) method
//
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2254
if (!readPending && !config.isAutoRead()) {
removeReadOp();
}
}
}Copy
DefaultMaxMessagesRecvByteBufAllocator.MaxMessageHandle.continueReading(io.netty.util.UncheckedBooleanSupplier)
public boolean continueReading(UncheckedBooleanSupplier maybeMoreDataSupplier) {
return
// 一般为true
config.isAutoRead() &&
// respectMaybeMoreData默认为true
// maybeMoreDataSupplier的逻辑是如果预期读取字节与实际读取字节相等,返回true
(!respectMaybeMoreData || maybeMoreDataSupplier.get()) &&
// 小于最大次数,maxMessagePerRead默认16
totalMessages < maxMessagePerRead &&
// 实际读到了数据
totalBytesRead > 0;
}Copy
entLoop.inEventLoop()) {
register0(promise);
} else {
try {
// 这行代码完成的是nio boss -> nio worker线程的切换
eventLoop.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 真正的注册操作
register0(promise);
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
…
}
}
}Copy
AbstractChannel.AbstractUnsafe.register0
private void register0(ChannelPromise promise) {
try {
...
// 该方法将SocketChannel注册到Selector中
doRegister();
// 执行初始化器,执行前 pipeline 中只有 head -> 初始化器 -> tail
pipeline.invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded();
// 执行后就是 head -> logging handler -> my handler -> tail
safeSetSuccess(promise);
pipeline.fireChannelRegistered();
if (isActive()) {
if (firstRegistration) {
// 触发pipeline上active事件
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
} else if (config().isAutoRead()) {
beginRead();
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
closeForcibly();
closeFuture.setClosed();
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
}
}Copy
`AbstractNioChannel.doRegister`将SocketChannel注册到Selector中
@Override
protected void doRegister() throws Exception {
boolean selected = false;
for (;😉 {
try {
// 将Selector注册到Selector中
selectionKey = javaChannel().register(eventLoop().unwrappedSelector(), 0, this);
return;
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
…
}
}
}Copy
HeadContext.channelActive
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
ctx.fireChannelActive();
// 触发read(NioSocketChannel这里read只是为了触发channel的事件注册,还未涉及数据读取)
readIfIsAutoRead();
}Copy
`AbstractNioChannel.doBeginRead`,通过该方法,SocketChannel关注了read事件
protected void doBeginRead() throws Exception {
// Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() was called
final SelectionKey selectionKey = this.selectionKey;
if (!selectionKey.isValid()) {
return;
}
readPending = true;
// 这时候 interestOps是0
final int interestOps = selectionKey.interestOps();
if ((interestOps & readInterestOp) == 0) {
// 关注read事件
selectionKey.interestOps(interestOps | readInterestOp);
}
}Copy
## 4、Read剖析
read事件的处理也是在
if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {
unsafe.read();
}Copy
分支中,通过`unsafe.read()`方法处理的,**不过此处调用的方法在AbstractNioByteChannel.NioByteUnsafe类中**
@Override
public final void read() {
// 获得Channel的配置
final ChannelConfig config = config();
if (shouldBreakReadReady(config)) {
clearReadPending();
return;
}
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline();
// 根据配置创建ByteBufAllocator(池化非池化、直接非直接内存)
final ByteBufAllocator allocator = config.getAllocator();
// 用来分配 byteBuf,确定单次读取大小
final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = recvBufAllocHandle();
allocHandle.reset(config);
ByteBuf byteBuf = null;
boolean close = false;
try {
do {
// 创建ByteBuf
byteBuf = allocHandle.allocate(allocator);
// 读取内容,放入ByteBUf中
allocHandle.lastBytesRead(doReadBytes(byteBuf));
if (allocHandle.lastBytesRead() <= 0) {
byteBuf.release();
byteBuf = null;
close = allocHandle.lastBytesRead() < 0;
if (close) {
readPending = false;
}
break;
}
allocHandle.incMessagesRead(1);
readPending = false;
// 触发read 事件,让pipeline上的handler处理
// 这时是处理NioSocketChannel上的handler
pipeline.fireChannelRead(byteBuf);
byteBuf = null;
}
// 是否要继续循环
while (allocHandle.continueReading());
allocHandle.readComplete();
// 触发 read complete事件
pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();
if (close) {
closeOnRead(pipeline);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleReadException(pipeline, byteBuf, t, close, allocHandle);
} finally {
// Check if there is a readPending which was not processed yet.
// This could be for two reasons:
// * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelRead(...) method
// * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelReadComplete(...) method
//
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2254
if (!readPending && !config.isAutoRead()) {
removeReadOp();
}
}
}Copy
DefaultMaxMessagesRecvByteBufAllocator.MaxMessageHandle.continueReading(io.netty.util.UncheckedBooleanSupplier)
public boolean continueReading(UncheckedBooleanSupplier maybeMoreDataSupplier) {
return
// 一般为true
config.isAutoRead() &&
// respectMaybeMoreData默认为true
// maybeMoreDataSupplier的逻辑是如果预期读取字节与实际读取字节相等,返回true
(!respectMaybeMoreData || maybeMoreDataSupplier.get()) &&
// 小于最大次数,maxMessagePerRead默认16
totalMessages < maxMessagePerRead &&
// 实际读到了数据
totalBytesRead > 0;
}Copy
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- vue:处理base64格式文件pdf、图片预览
- 重排和重绘的区别,什么情况下会触发这两种情况
- 真是一场酣畅淋漓的程序员Citywork!
- socket实现视频通话-WebRTC
- ifconfig 主机ip url记录
- iframe 与主应用页面之间如何互相通信传递数据
- 2024年G3锅炉水处理证模拟考试题库及G3锅炉水处理理论考试试题
- Python 如何获取当前时间是一年中的第几周
- 【大气】大气吸收损耗模型【含Matlab源码 2888期】
- jQuery 正则表达式 验证表单