前端面试(5)
1、移动端适配
1.1、设置meta缩放比例,将设备窗口调整为设计图大小。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,
initial-scale=1, maximum-scale=1, user-scalable=no">
<title>Your Page Title</title>
<!-- 其他 head 元素 -->
</head>
<body>
<!-- 页面内容 -->
</body>
</html>
?在这里,<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, maximum-scale=1, user-scalable=no"> 的设置起到了关键作用:
width=device-width: 将页面的宽度设置为设备宽度。initial-scale=1: 初始缩放比例为 1,即不缩放。maximum-scale=1: 最大缩放比例为 1,防止用户手动放大。user-scalable=no: 禁止用户手动缩放。
这样设置后,页面将按照设备宽度来布局,而且用户将无法手动缩放。
1.2、媒体查询设置根节点字号 + rem
第一种:js动态计算屏幕宽度设置根节点字号 + rem+弹性布局(Flexbox)
第二种:js动态计算屏幕宽度设置根节点字号 + rem
字体相对单位: 使用相对单位(em、rem)定义字体大小,以确保在不同屏幕尺寸上的可读性。
// 屏幕大于 1440px 时应用该样式
@media screen and (min-width: 1441px) {
html{font-size: 16px;}
}
// 屏幕大于 1024px 或小于 1440px 时应用该样式
@media screen and (min-width: 1024px) and (max-width: 1440px) {
html{font-size: 14px;}
}
图片适配: 使用响应式图片或者通过 CSS 的 max-width 属性来确保图片在不同屏幕尺寸上适应
/* 示例图片适应 */
img {
max-width: 100%;
height: auto;
}
?优点:rem 布局能很好的实现在不同尺寸的屏幕横向填满屏幕,且在不同屏幕元素大小比例一致
缺点:在大屏设备(Pad)上,元素尺寸会很大,页面显示更少的内容。需要限制内容最大宽度
最大宽度限制: 对于一些容器或元素,可以设置最大宽度,防止在大屏幕上显示过宽。
1.3、postcss-px-to-viewport插件,将px转为vw,需要webpack配置
1、安装 postcss-px-to-viewport 插件和相应的 loader:
npm install postcss-px-to-viewport postcss-loader --save-dev
2、在项目根目录下创建 postcss.config.js 文件,配置 postcss-px-to-viewport 插件:?
// postcss.config.js
module.exports = {
plugins: {
'postcss-px-to-viewport': {
viewportWidth: 375, // 设计稿宽度
viewportHeight: 667, // 设计稿高度
unitPrecision: 5, // 单位精度
viewportUnit: 'vw', // 转换成的视口单位
selectorBlackList: [], // 需要忽略的CSS选择器
minPixelValue: 1, // 小于或等于 1px 不转换为视口单位
mediaQuery: false, // 是否允许在媒体查询中转换为vw
},
},
};
3、?在 webpack 配置中使用 postcss-loader:
// webpack.config.js
module.exports = {
// 其他配置项...
module: {
rules: [
// 其他 loader 配置...
{
test: /\.(css|postcss)$/,
use: [
'style-loader',
'css-loader',
'postcss-loader', // 添加 postcss-loader
],
},
],
},
};
1.5、流式布局:
使用相对单位(百分比、vw、vh)和相对单位来创建流式布局,使页面能够随着屏幕尺寸的变化而自适应。比较麻烦
-
子元素width、height的百分比:子元素的width或height中使用百分比,是相对于子元素的直接父元素
-
margin和padding的百分比:在垂直方向和水平方向都是相对于直接父亲元素的width,而与父元素的height无关
-
border-radius、
border-radius、background-size、transform: translate()、transform-origin的百分比:他们的百分比是相对于自身宽度,与父元素无关
2、瀑布流
参考:2022年了!再来手撕一下前端瀑布流代码吧!-阿里云开发者社区
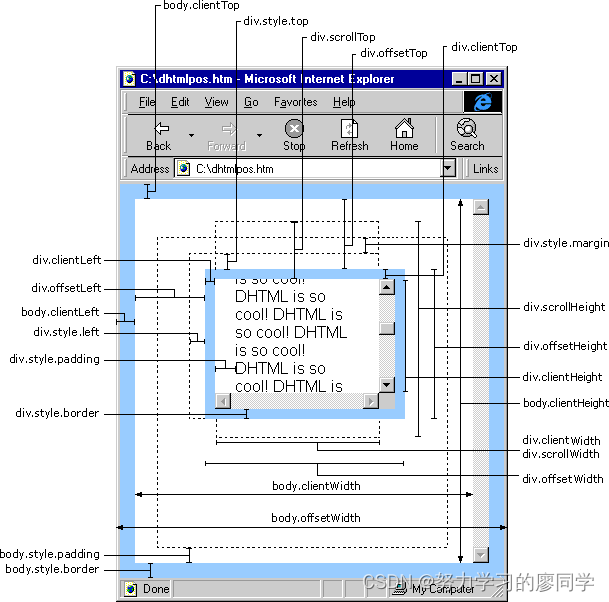
理解offsetleft offsetwidth:?offsetLeft,Left,clientLeft的区别 - 小顾问 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>瀑布流</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.item {
font-size: 30px;
font-weight: 700;
color: aliceblue;
width: 205px;
position: absolute;
}
.item-1 {
background-color: rgb(206, 169, 169);
height: 300px;
}
.item-2 {
background-color: rgb(131, 226, 174);
height: 150px;
}
.item-3 {
background-color: rgb(77, 30, 30);
height: 350px;
}
.item-4 {
background-color: rgb(49, 62, 134);
height: 300px;
}
.item-5 {
background-color: rgb(230, 99, 99);
height: 200px;
}
.item-6 {
background-color: rgb(206, 169, 169);
height: 300px;
}
.item-7 {
background-color: rgb(124, 126, 145);
height: 400px;
}
.item-8 {
background-color: rgb(169, 199, 38);
height: 230px;
}
.item-9 {
background-color: rgb(114, 128, 53);
height: 300px;
}
.item-10 {
background-color: rgb(48, 54, 18);
height: 260px;
}
.item-11 {
background-color: rgb(118, 122, 96);
height: 230px;
}
.item-12 {
background-color: rgb(118, 122, 96);
height: 240px;
}
.item-13 {
background-color: rgb(118, 122, 96);
height: 250px;
}
.item-14 {
background-color: rgb(118, 122, 96);
height: 270px;
}
.item-15 {
background-color: rgb(118, 122, 96);
height: 330px;
}
.item-16 {
background-color: rgb(118, 122, 96);
height: 200px;
}
.item-17 {
background-color: rgb(118, 122, 96);
height: 100px;
}
.item-18 {
background-color: rgb(118, 122, 96);
height: 400px;
}
.item-19 {
background-color: rgb(118, 122, 96);
height: 340px;
}
.item-20 {
background-color: rgb(118, 122, 96);
height: 350px;
}
.item-21 {
background-color: rgb(118, 122, 96);
height: 360px;
}
.item-22 {
background-color: rgb(118, 122, 96);
height: 370px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<div class="item item-1">1</div>
<div class="item item-2">2</div>
<div class="item item-3">3</div>
<div class="item item-4">4</div>
<div class="item item-5">5</div>
<div class="item item-6">6</div>
<div class="item item-7">7</div>
<div class="item item-8">8</div>
<div class="item item-9">9</div>
<div class="item item-10">10</div>
<div class="item item-11">11</div>
<div class="item item-12">12</div>
<div class="item item-13">13</div>
<div class="item item-14">14</div>
<div class="item item-15">15</div>
<div class="item item-16">16</div>
<div class="item item-17">17</div>
<div class="item item-18">18</div>
<div class="item item-19">19</div>
<div class="item item-20">20</div>
<div class="item item-21">21</div>
<div class="item item-22">22</div>
</div>
</body>
<script>
var items = document.getElementsByClassName('item');
//定义间隙10像素
var gap = 10;
//进页面执行函数
window.onload = function() {
waterFall();
}
function waterFall() {
//首先确定列数 = 页面的宽度 / 图片的宽度
var pageWidth = getClient().width;
var itemWidth = items[0].offsetWidth;
var columns = parseInt(pageWidth / (itemWidth + gap));
var arr = []; //定义一个数组,用来存储元素的高度
console.log(columns)
for (var i = 0; i < items.length; i++) {
if (i < columns) {
//满足这个条件则说明在第一行,文章里面有提到
items[i].style.top = 0;
items[i].style.left = (itemWidth + gap) * i + 'px';
arr.push(items[i].offsetHeight);
} else {
//其他行,先找出最小高度列,和索引
//假设最小高度是第一个元素
var minHeight = arr[0];
var index = 0;
for (var j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) { //找出最小高度
if (minHeight > arr[j]) {
minHeight = arr[j];
index = j;
}
}
//设置下一行的第一个盒子的位置
//top值就是最小列的高度+gap
items[i].style.top = arr[index] + gap + 'px';
items[i].style.left = items[index].offsetLeft + 'px';
//修改最小列的高度
//最小列的高度 = 当前自己的高度 + 拼接过来的高度 + 间隙的高度
arr[index] = arr[index] + items[i].offsetHeight + gap;
}
}
}
//当页面尺寸发生变化时,触发函数,实现响应式
window.onresize = function() {
waterFall();
}
// clientWidth 处理兼容性
function getClient() {
return {
width: window.innerWidth || document.documentElement.clientWidth || document.body.clientWidth,
height: window.innerHeight || document.documentElement.clientHeight || document.body.clientHeight
}
}
// scrollTop兼容性处理
function getScrollTop() {
return window.pageYOffset || document.documentElement.scrollTop;
}
</script>
</html>3、vue原理解读,ele组件源码解读
4、canvas
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 学习JavaEE的日子 阶段回顾
- php物联网平台云监控WEB设备iot管理后台源码带文字安装教程
- Java21 + SpringBoot3集成WebSocket
- InnoDB引擎
- 优雅而高效的JavaScript——Promise 和 async/await
- [c语言]猜数字游戏
- 向华为学习:基于BLM模型的战略规划研讨会实操的详细说明,含研讨表单(五)
- UG沿引导线扫略
- Eureka整合seata分布式事务
- Java基础知识总结