最小二乘法拟合二维点
发布时间:2024年01月19日
方法1:使用np.polyfit()函数进行拟合
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 模拟数据
x = np.array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
y = np.array([1, 3, 2, 4, 7, 10, 11, 15, 17, 20])
# 使用多项式拟合,这里选择二次多项式
coefficients = np.polyfit(x, y, 2)
polynomial = np.poly1d(coefficients)
print(polynomial)
# 计算拟合的y值
y_fit = polynomial(x)
# 绘图展示结果
plt.scatter(x, y, label='Data') # 原始数据点
plt.plot(x, y_fit, label='Fit', color='red') # 拟合曲线
plt.title('Polynomial Curve Fitting')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
运行结果:
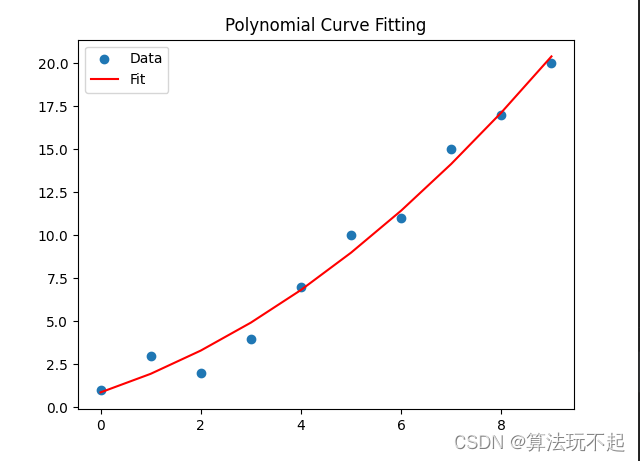
方法2:手动实现
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 模拟数据
x = np.array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
y = np.array([1, 3, 2, 4, 7, 10, 11, 15, 17, 20])
# 计算x的各次幂的和
x_sum = sum(x)
x2_sum = sum(xi**2 for xi in x)
x3_sum = sum(xi**3 for xi in x)
x4_sum = sum(xi**4 for xi in x)
# 计算x和y的乘积的和
xy_sum = sum(xi*yi for xi, yi in zip(x, y))
x2y_sum = sum(xi**2*yi for xi, yi in zip(x, y))
# 构建正规方程的系数矩阵和常数项向量
A = [[len(x), x_sum, x2_sum],
[x_sum, x2_sum, x3_sum],
[x2_sum, x3_sum, x4_sum]]
b = [sum(y), xy_sum, x2y_sum]
# 解正规方程
# 使用克莱默法则(Cramer's Rule)求解
def cramer_solve(A, b):
det_A = np.linalg.det(A)
coefficients = []
for i in range(len(b)):
Ai = [row[:i] + [b[j]] + row[i+1:] for j, row in enumerate(A)]
det_Ai = np.linalg.det(Ai)
coefficients.append(det_Ai / det_A)
return coefficients
a, b, c = cramer_solve(A, b)
print(a, b, c)
# 使用求得的系数计算拟合值
y_fit = [c*xi**2 + b*xi + a for xi in x]
# 绘图
plt.scatter(x, y, label='Data')
plt.plot(x, y_fit, label='Fit', color='red')
plt.title('Manual Polynomial Curve Fitting')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
运行结果:
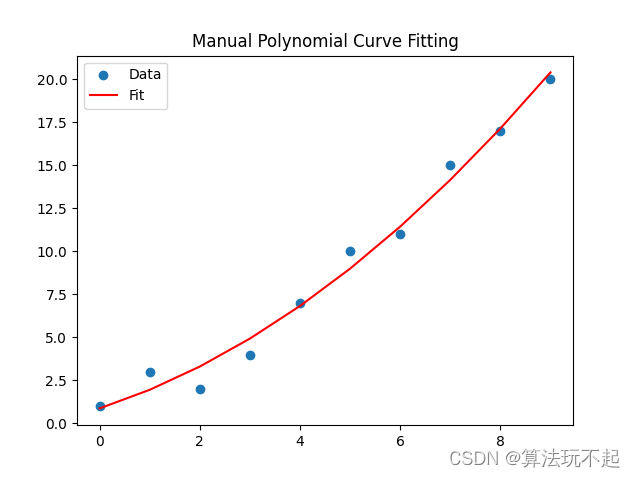
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_18566467/article/details/135706512
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!