KITTI数据集处理为COCO数据集格式
发布时间:2023年12月19日
KITTI作为自动驾驶常用数据集,被广泛的应用于自动驾驶目标检测等过程中。
首先是数据集类别合并,原始的KITTI数据集有九个类别,分别是:
Car
Van
Truck
Pedestrian
Person_sitting
Cyclist
Tram
Misc
而我们在使用过程中,通常会对某些类别进行合并,将Car,Van,Truck,Tram统一划分为Car,将Pedestrian与Person_setting统一设置为Pedestrian,保留Cyclist,去除Misc。
# modify_annotations_txt.py
import glob
import string
txt_list = glob.glob('./Labels/*.txt') # 存储Labels文件夹所有txt文件路径
def show_category(txt_list):
category_list= []
for item in txt_list:
try:
with open(item) as tdf:
for each_line in tdf:
labeldata = each_line.strip().split(' ') # 去掉前后多余的字符并把其分开
category_list.append(labeldata[0]) # 只要第一个字段,即类别
except IOError as ioerr:
print('File error:'+str(ioerr))
print(set(category_list)) # 输出集合
def merge(line):
each_line=''
for i in range(len(line)):
if i!= (len(line)-1):
each_line=each_line+line[i]+' '
else:
each_line=each_line+line[i] # 最后一条字段后面不加空格
each_line=each_line+'\n'
return (each_line)
print('before modify categories are:\n')
show_category(txt_list)
for item in txt_list:
new_txt=[]
try:
with open(item, 'r') as r_tdf:
for each_line in r_tdf:
labeldata = each_line.strip().split(' ')
if labeldata[0] in ['Truck','Van','Tram']: # 合并汽车类
labeldata[0] = labeldata[0].replace(labeldata[0],'Car')
if labeldata[0] == 'Person_sitting': # 合并行人类
labeldata[0] = labeldata[0].replace(labeldata[0],'Pedestrian')
if labeldata[0] == 'DontCare': # 忽略Dontcare类
continue
if labeldata[0] == 'Misc': # 忽略Misc类
continue
new_txt.append(merge(labeldata)) # 重新写入新的txt文件
with open(item,'w+') as w_tdf: # w+是打开原文件将内容删除,另写新内容进去
for temp in new_txt:
w_tdf.write(temp)
except IOError as ioerr:
print('File error:'+str(ioerr))
print('\nafter modify categories are:\n')
show_category(txt_list)
最终生成的数据集格式为txt,标注为YOLO格式。
一个txt文件对应一张图像,内容如下,分别对应类别,中心点坐标xy,标注框宽高wh。
1 0.6221936274509804 0.6093513513513513 0.08033496732026148 0.4457297297297298
随后对数据集进行划分,总共有7481张图像,按照4:1的比例划分训练集与验证集。代码如下:
import os
import random
import shutil
def mvfile(path,topath):
xmllist= os.listdir(path+"/annotations/")
xmlpath=path+"/annotations/"
imgpath=path+"/images/"
xmltopath=topath+"/val_annotations/"
if not os.path.exists(xmltopath):
os.makedirs(xmltopath)
imgtopath = topath + "val_images"
if not os.path.exists(imgtopath):
os.makedirs(imgtopath)
xmls = random.sample(xmllist, 1496)
for xml in xmls:
with open(topath+"抽取的标签.txt", "a") as f:
f.write(xml+"\n")
xmlfile=xmlpath+xml
print(xmlfile)
shutil.move(xmlfile,xmltopath)
imgfile=imgpath+xml.replace("txt","png")
print(imgfile)
shutil.move(imgfile,imgtopath)
if __name__ == '__main__':
path="D:\graduate\datasets\detection\kitti/"
mvfile(path,path+"val_images/")
通过上述程序会将验证集图像与标注文件提取出来。
数据集划分完成后需要将YOLO格式转换为COCO格式(JSON),即需要生成一个类别文件,里面标注的是类别名称,记得要与YOLO的类别编号一致。如下Car在YOLO中标注类别为0,Pedestrian为1,Cyclist为2。
Car
Pedestrian
Cyclist
随后将txt文件转换为COCO的json格式,在生成JSON文件时,需要原标注文件以及图像,因为要读取图像的大小等信息
import os
import json
import cv2
import random
import time
from PIL import Image
coco_format_save_path='D:\graduate\datasets\detection\kitti\coco_annotations/val/' #要生成的标准coco格式标签所在文件夹
yolo_format_classes_path='D:\graduate/figures\images\Tools\Kitti2Coco\kitti.names' #类别文件,一行一个类
yolo_format_annotation_path='D:\graduate\datasets\detection\kitti\yolo_annotations/val' #yolo格式标签所在文件夹
img_pathDir='D:\graduate\datasets\detection\kitti/val\images/' #图片所在文件夹
with open(yolo_format_classes_path,'r') as fr: #打开并读取类别文件
lines1=fr.readlines()
# print(lines1)
categories=[] #存储类别的列表
for j,label in enumerate(lines1):
label=label.strip()
categories.append({'id':j,'name':label,'supercategory':'None'}) #将类别信息添加到categories中
# print(categories)
write_json_context=dict() #写入.json文件的大字典
write_json_context['info']= {'description': '', 'url': '', 'version': '', 'year': 2023, 'contributor': '', 'date_created': '2021-12-15'}
write_json_context['licenses']=[{'id':1,'name':None,'url':None}]
write_json_context['categories']=categories
write_json_context['images']=[]
write_json_context['annotations']=[]
#接下来的代码主要添加'images'和'annotations'的key值
imageFileList=os.listdir(img_pathDir) #遍历该文件夹下的所有文件,并将所有文件名添加到列表中
for i,imageFile in enumerate(imageFileList):
imagePath = os.path.join(img_pathDir,imageFile) #获取图片的绝对路径
image = Image.open(imagePath) #读取图片,然后获取图片的宽和高
W, H = image.size
img_context={} #使用一个字典存储该图片信息
#img_name=os.path.basename(imagePath) #返回path最后的文件名。如果path以/或\结尾,那么就会返回空值
img_context['file_name']=imageFile
img_context['height']=H
img_context['width']=W
img_context['date_captured']='2023-12-15'
img_context['id']=i #该图片的id
img_context['license']=1
img_context['color_url']=''
img_context['flickr_url']=''
write_json_context['images'].append(img_context) #将该图片信息添加到'image'列表中
txtFile=imageFile[:6]+'.txt' #获取该图片获取的txt文件
with open(os.path.join(yolo_format_annotation_path,txtFile),'r') as fr:
lines=fr.readlines() #读取txt文件的每一行数据,lines2是一个列表,包含了一个图片的所有标注信息
for j,line in enumerate(lines):
bbox_dict = {} #将每一个bounding box信息存储在该字典中
# line = line.strip().split()
# print(line.strip().split(' '))
class_id,x,y,w,h=line.strip().split(' ') #获取每一个标注框的详细信息
class_id,x, y, w, h = int(class_id), float(x), float(y), float(w), float(h) #将字符串类型转为可计算的int和float类型
xmin=(x-w/2)*W #坐标转换
ymin=(y-h/2)*H
xmax=(x+w/2)*W
ymax=(y+h/2)*H
w=w*W
h=h*H
bbox_dict['id']=i*10000+j #bounding box的坐标信息
bbox_dict['image_id']=i
bbox_dict['category_id']=class_id #注意目标类别要加一
bbox_dict['iscrowd']=0
height,width=abs(ymax-ymin),abs(xmax-xmin)
bbox_dict['area']=height*width
bbox_dict['bbox']=[xmin,ymin,w,h]
bbox_dict['segmentation']=[[xmin,ymin,xmax,ymin,xmax,ymax,xmin,ymax]]
write_json_context['annotations'].append(bbox_dict) #将每一个由字典存储的bounding box信息添加到'annotations'列表中
name = os.path.join(coco_format_save_path,"train"+ '.json')
with open(name,'w') as fw: #将字典信息写入.json文件中
json.dump(write_json_context,fw,indent=2)
生成的文件如下:
至此,KITTI数据集转换为COCO格式的数据集。
在运行时报错:
OSError: [WinError 1455] 页面文件太小,无法完成操作。 Error loading "D:\softwares\Anconda\envs\detr\lib\site-packages\torch\lib\cusparse64_11.dll" or one of its dependencies.
这是由于虚拟内存不足导致的,看到有人说修改num_workers=0可以解决问题,但这是一种治标不治本的方法,正确方法是增大虚拟内存:
搜索 查看高级系统设置

找到虚拟内存
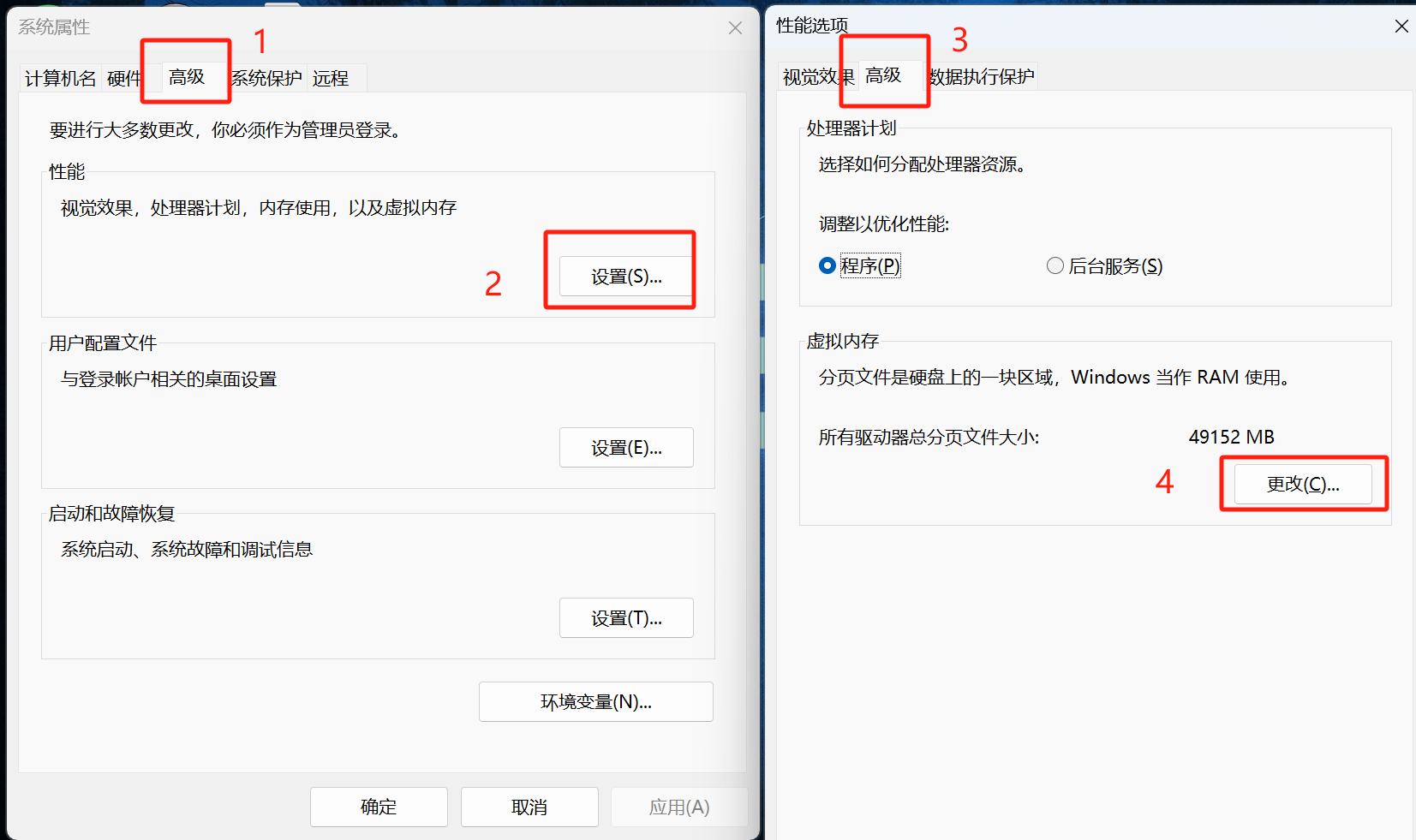
python安装在哪就修改哪个盘的分页文件大小。
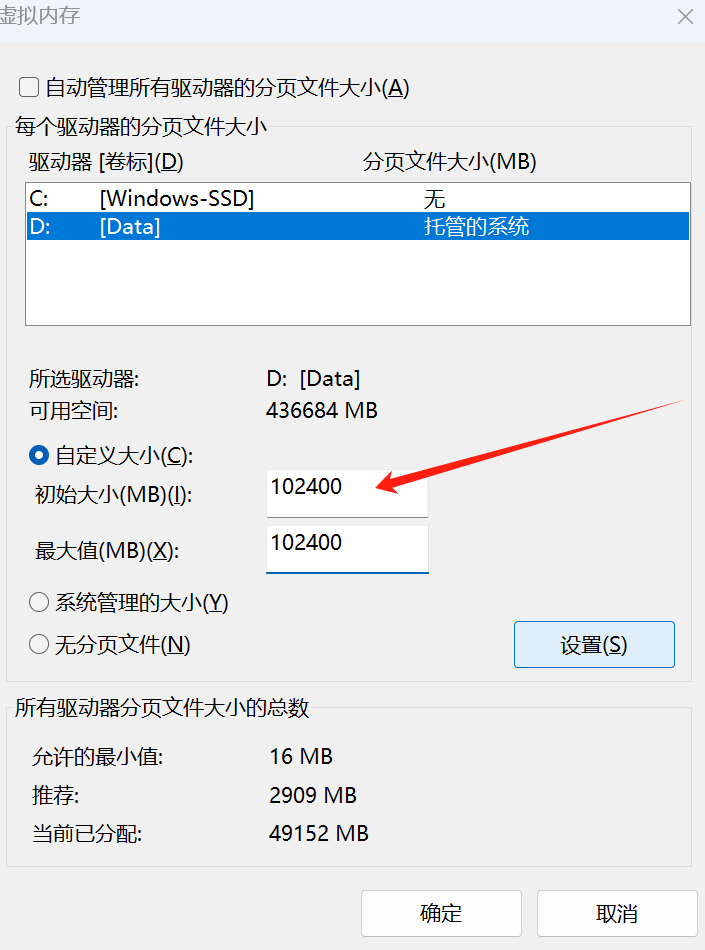
修改完内存后需要重启电脑才可以,重启后运行成功。
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/pengxiang1998/article/details/135003509
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- HTTPS证书有免费的吗?
- 许战海矩阵战略洞察 | 露露如何打造第二招牌实现突破增长
- docker - 常用容器部署命令大全(MySQL、Redis、RabbitMQ、ES、Kibana、Nacos、Sentinel)
- 百度POI分类 20231227记录
- 云架构师学习------腾讯云通识-网络与安全
- python入门小程序-账单管理系统
- Python 开源扫雷游戏 PyMine 发布介绍视频
- 5G阅信应用场景有哪些?
- 对象克隆学习
- SD-WAN网络建设:设备、服务与综合解决方案