DBNet文本检测网络 (FPN、batch normalization、Transpose conv)
DB Net文本检测网络概述
DBNet论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1911.08947.pdf
DBNet是一种基于分割的文本检测网络,使用分割网络提供自适应的thresh用于二值化。
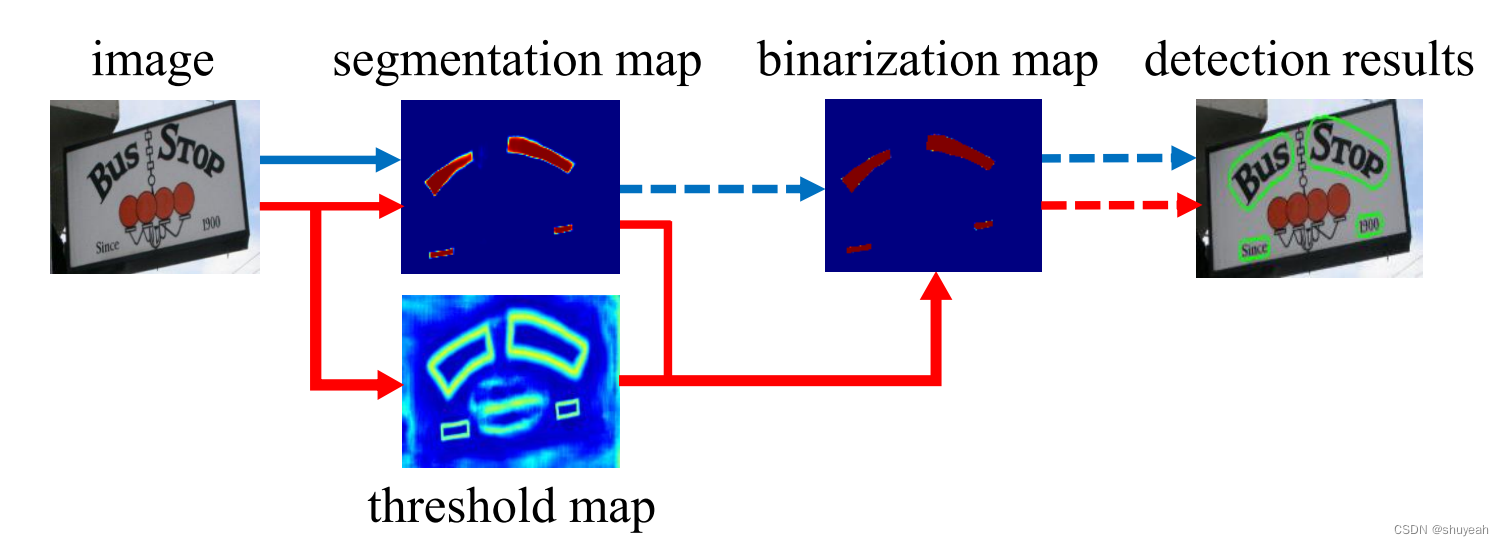
原始二值化方法和DBNet中的动态阈值
传统的基于分割的检测方法,对于分割后的特征层,使用直接二值化,生成检测结果。
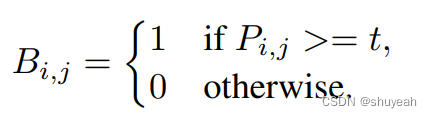
直接二值化的方法不可微分,不能参与到网络模型的训练中。
DB Net增加了threshold map,动态生成每一个像素点对应的阈值,得到二值化结果。
在训练阶段,probability map、threshold map和approximate binary map都参与计算,
其中probability map和approximate binary map受相同的变量监督
DB Net网络结构
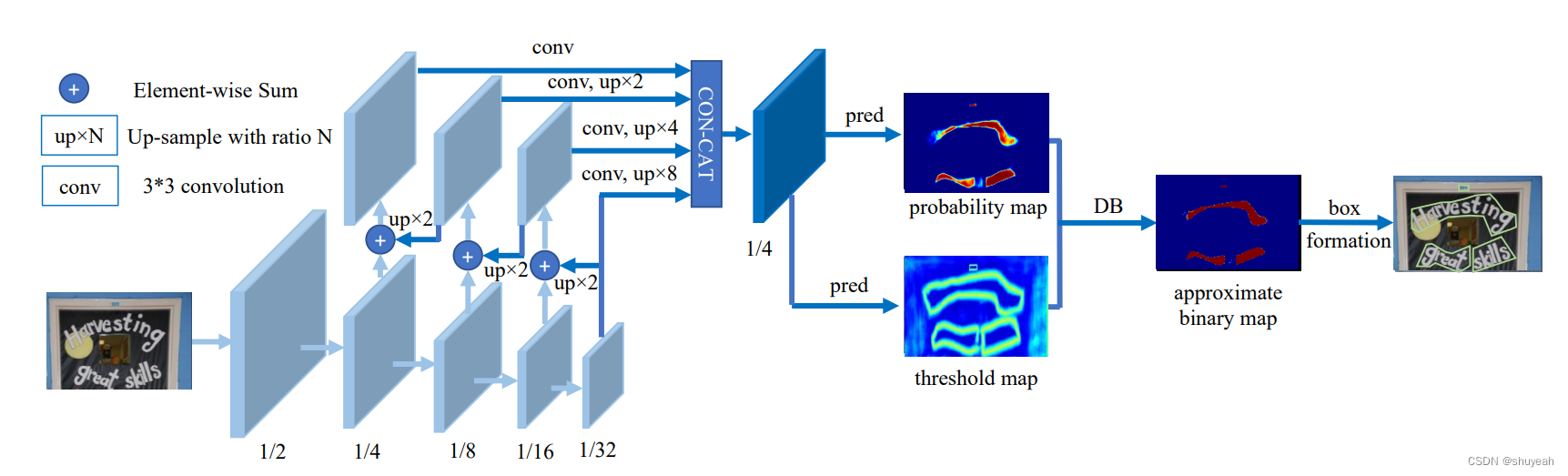
特征提取网络为FPN(Feature Pyramid Network)提取到不同尺度的特征,将深层的网络和浅层的网络特征层融合。
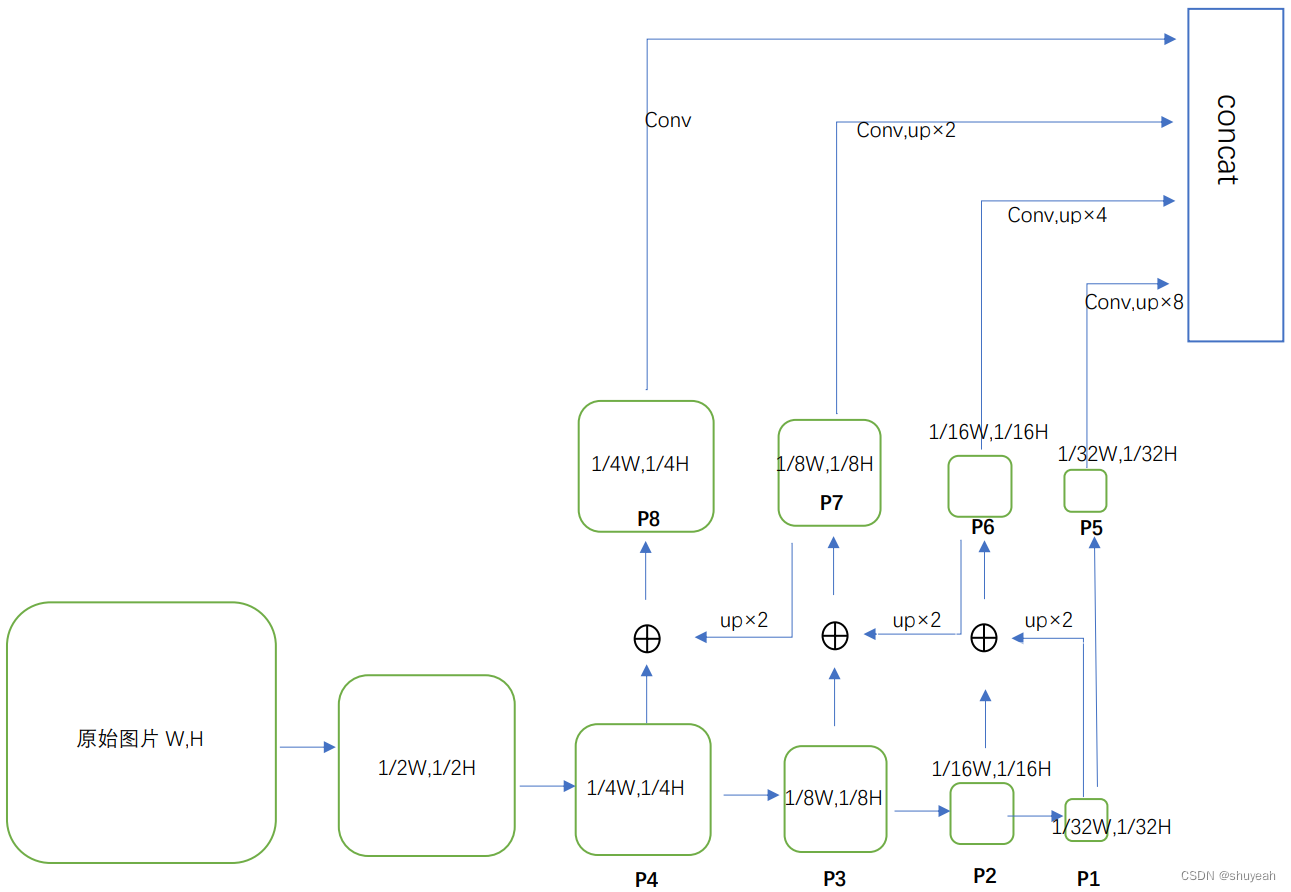
将原始图片经过卷积操作下采样,分别得到宽、高变为原来1/2,1/4,1/8,1/16,1/32大小的特征层;
将P1特征层经过两倍上采样,与P2特征层对应像素值相加,得到P6;
将P6特征层经过两倍上采样,与P3特征层对应像素值相加,得到P7;
将P7特征层经过两倍上采样,与P4特征层对应像素值相加,得到P8;
P8经过3×3卷积;
P7经过3×3卷积,再经过一次2倍上采样;
P6经过3×3卷积,再经过一次4倍上采样;
P5(P1)经过3×3卷积,再经过一次8倍上采样;
以上四个特征层宽高为原始图片的1/4,将四个特征层concat,完成FPN特征提取。
concat 后的特征层为原始图片宽高的1/4。
pred操作包含一个3×3卷积操作和两次stride为2的反卷积操作进行上采样。
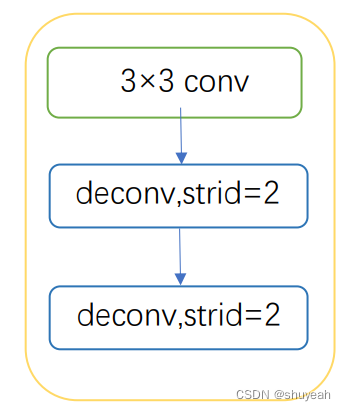
分别生成probability map 和threshold map,
其中probability map为分割结果,每个像素点属于哪一个类别;
threshold map动态设置每一个像素点的阈值。
接着通过可微分二值化操作,得出二值化的分割结果,得到approximate map;
最后经过box formation操作得到最终的文本检测结果。
DB可微分二值化
二值化过程了微分,可以使二值化过程与分割网络一同在训练过程中优化。
可微分二值化的方法:
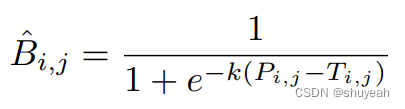
probability map 中的像素值与threshold map中的对应像素值做差,
如果值>0,B值=1;判断为文本区域
如果值<0,B值=0;判断为非文本区域
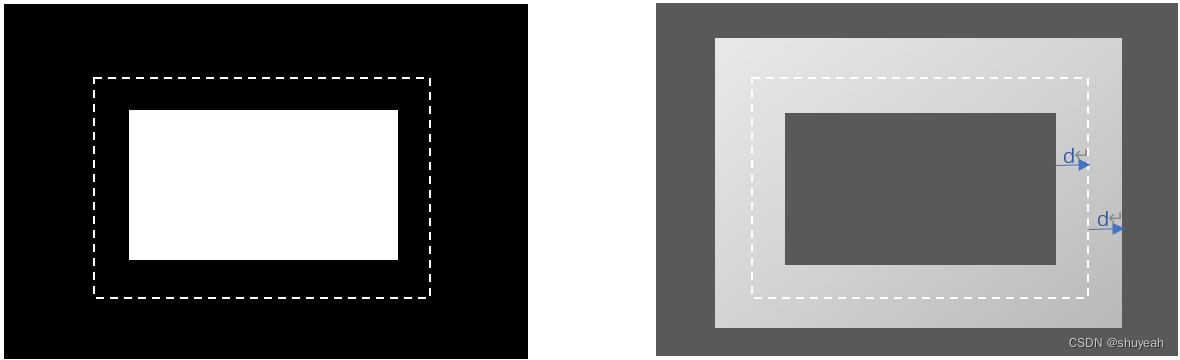
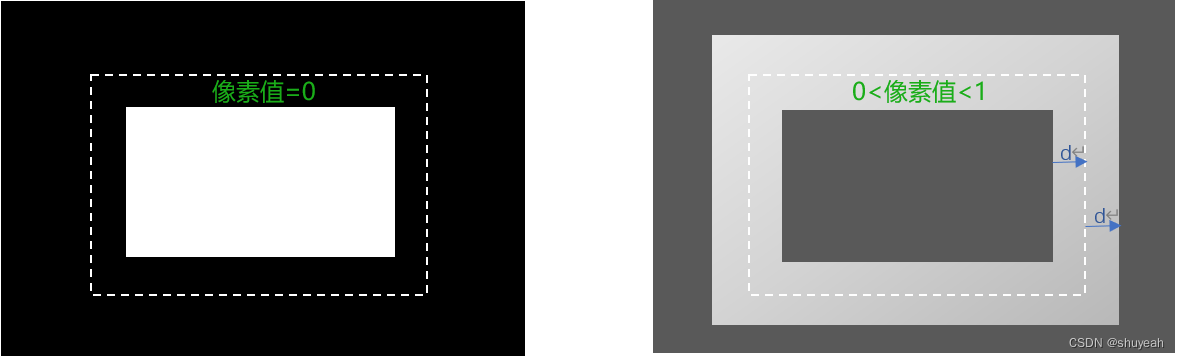
左侧为probability mapground truth标注,将原本文字区域(虚线部分)shrink 后标注为正样本,白色区域像素值为1,黑色区域像素值为0
右侧为threshold mapground truth标注,对于文本检测,文本与非文本的边界区域重点处理。通过threshold map来决定每一个像素点对应的阈值。
虚线为原文本区域的边界,分别向内shrink 和向外dilate距离为d,圆环区域对应的每一个像素点的阈值是动态变化的。
可微分二值化参数k取值为50,
(1)对于文本块内部,计算Pij-Tij>0,B=1
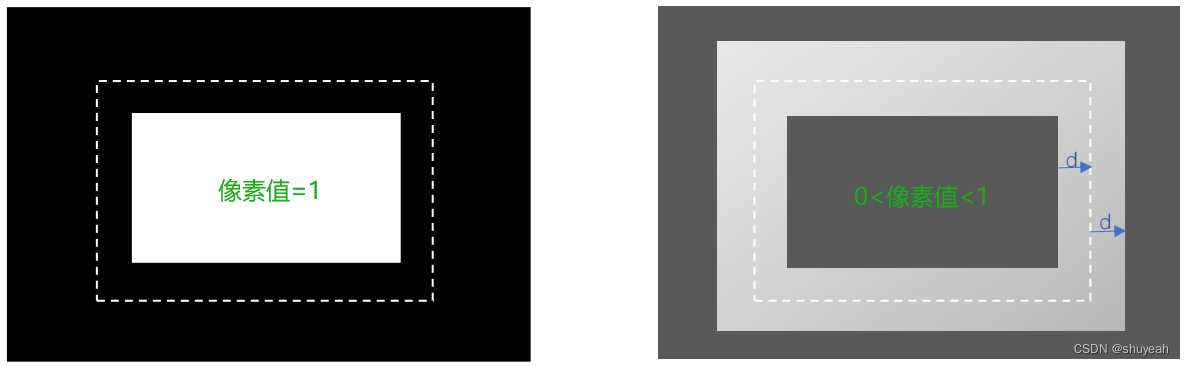
(2)对于文本块边缘,计算Pij-Tij<0,B=0
(3)对于非文本块区域,计算Pij-Tij<0,B=0
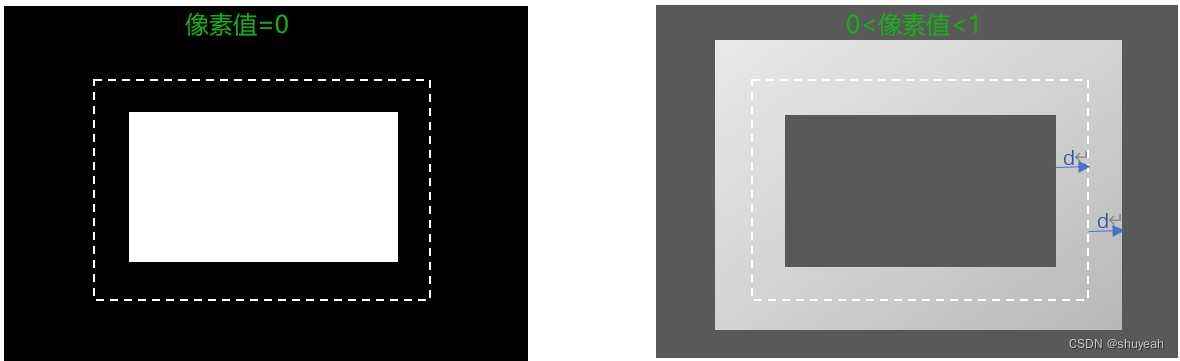
threshold map中的每一个值如何计算
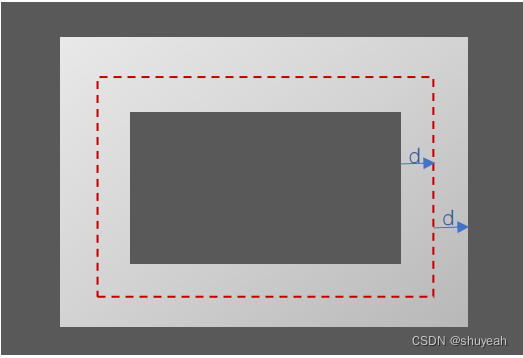
红色虚线为文本框区域,圆环区域为文本框分别向内shrink、向外dilate,
(1)区域内的每一个像素点,距离文本框的最短距离
(2)计算所有点得到,圆环中心区域像素值d(i,j)为0,圆环边缘区域值d(i,j)较大
(3)1-d(i,j),使得中间区域接近1,边缘区域接近0
(4)再将取值范围归一化到指定区域
计算损失Loss
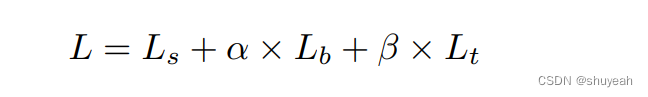
Ls表示probability map对应的损失
Lb表示approximate binary map对应的损失
Lt表示threshold map对应的损失
α、β分别取值1.0和10
网络模型部分代码
DBNet代码来自
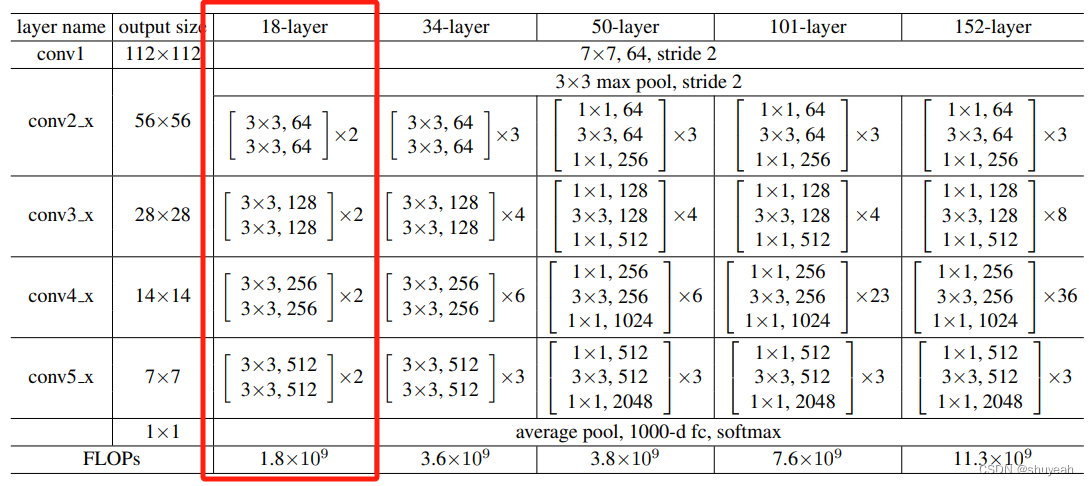
(1)backbone网络使用ResNet18
对于resnet18网络每一种卷积层的个数如图所示[2, 2, 2, 2]
def resnet18(pretrained=True, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-18 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
# 对应每一种卷积层在网络中的数量
model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [2, 2, 2, 2], **kwargs)
if pretrained:
assert kwargs['in_channels'] == 3, 'in_channels must be 3 whem pretrained is True'
print('load from imagenet')
model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet18']), strict=False)
return model
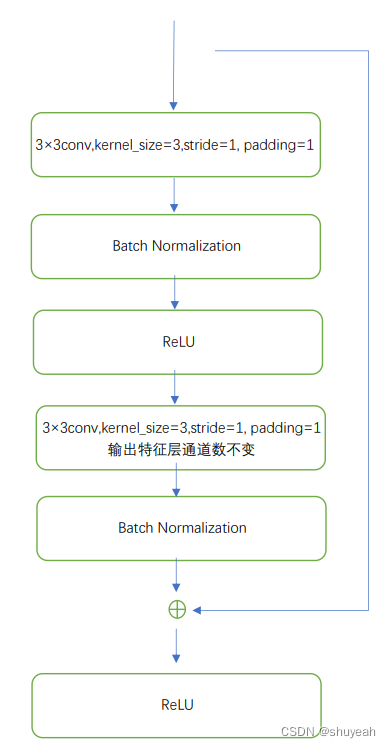
BasicBlock
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, dcn=None):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.with_dcn = dcn is not None # deformable convolution是否使用
self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride) # 3×3卷积操作,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1
self.bn1 = BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.with_modulated_dcn = False
if not self.with_dcn:
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False)
else:
from torchvision.ops import DeformConv2d
deformable_groups = dcn.get('deformable_groups', 1)
offset_channels = 18 # 需要有18个偏移量的参数
self.conv2_offset = nn.Conv2d(planes, deformable_groups * offset_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.conv2 = DeformConv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
# out = self.conv2(out)
if not self.with_dcn:
out = self.conv2(out)
else:
offset = self.conv2_offset(out)
out = self.conv2(out, offset)
out = self.bn2(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
residual = self.downsample(x)
out += residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
BottleNeck
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
expansion = 4
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, dcn=None):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
self.with_dcn = dcn is not None
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.with_modulated_dcn = False
if not self.with_dcn:
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
else:
deformable_groups = dcn.get('deformable_groups', 1)
from torchvision.ops import DeformConv2d
offset_channels = 18
self.conv2_offset = nn.Conv2d(planes, deformable_groups * offset_channels, stride=stride, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.conv2 = DeformConv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=stride, bias=False)
self.bn2 = BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes * 4, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.bn3 = BatchNorm2d(planes * 4)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
self.dcn = dcn
self.with_dcn = dcn is not None
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
# out = self.conv2(out)
if not self.with_dcn:
out = self.conv2(out)
else:
offset = self.conv2_offset(out)
out = self.conv2(out, offset)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
residual = self.downsample(x)
out += residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
搭建ResNet网络结构
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, block, layers, in_channels=3, dcn=None):
self.dcn = dcn
self.inplanes = 64
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
self.out_channels = []
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3,
bias=False)
self.bn1 = BatchNorm2d(64)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0])
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=2, dcn=dcn)
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=2, dcn=dcn)
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, layers[3], stride=2, dcn=dcn)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
elif isinstance(m, BatchNorm2d):
m.weight.data.fill_(1)
m.bias.data.zero_()
if self.dcn is not None:
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, Bottleneck) or isinstance(m, BasicBlock):
if hasattr(m, 'conv2_offset'):
constant_init(m.conv2_offset, 0)
def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1, dcn=None):
downsample = None
# 使用一个conv block 接若干个identity block
if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
# 当输出的特征层通道数与输入特征层通道数不相等,需要使用1×1卷积来调整特征层维度
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion),
)
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample, dcn=dcn))
self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
for i in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, dcn=dcn))
self.out_channels.append(planes * block.expansion)
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x2 = self.layer1(x)
x3 = self.layer2(x2)
x4 = self.layer3(x3)
x5 = self.layer4(x4)
return x2, x3, x4, x5
deformable conv
使用deformable 卷积的作用:增大感受野
其中deformable convolution卷积再pytorch通过调用DeformConv2d实现
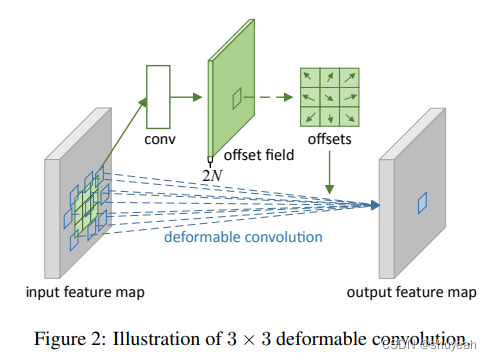
3×3卷积每一个kernel对应的9个值,每个值由两个坐标确定。
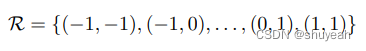
图片来自deformable 论文
每个坐标的偏移量都会有一个offset偏移量。在basicblock代码中,如果使用deformable convolution,18个偏移量参数有网络训练获得。
deformable_groups = dcn.get('deformable_groups', 1)
offset_channels = 18 # 需要有18个偏移量的参数
self.conv2_offset = nn.Conv2d(planes, deformable_groups * offset_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.conv2 = DeformConv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
Batch Normalization
在网络中添加Batch Normalization 来实现加速网络训练。
将一个batch(批量)特征层调整到满足均值为0方差为1
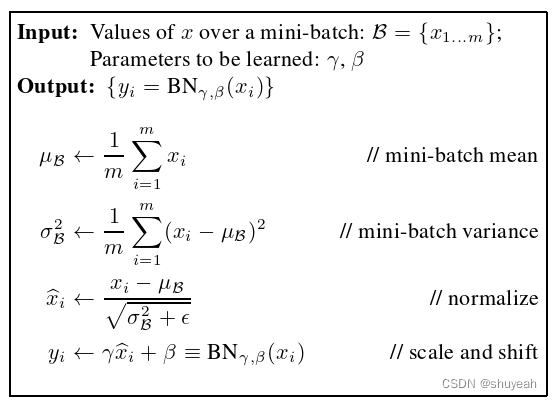
图片来自https://blog.csdn.net/qq_54185421/article/details/125429533
- 对于一个mini-batch数据,计算统计量μB;
- 对于一个mini-batch数据,计算统计量σ2B;
- 做归一化处理;
- 通过训练过程迭代γ和β
Transpose Conv
- 转置卷积不是卷积的逆运算
- 转置卷积也是卷积
转置卷积的作用:上采样(upsampling)
转置卷积可以将特征层的大小还原回卷积操作之前特征层的大小,但得到特征层的数值与原特征层的数值不同。
将卷积操作转化为矩阵相乘。
通过TransposeConv通过卷积实现上采样
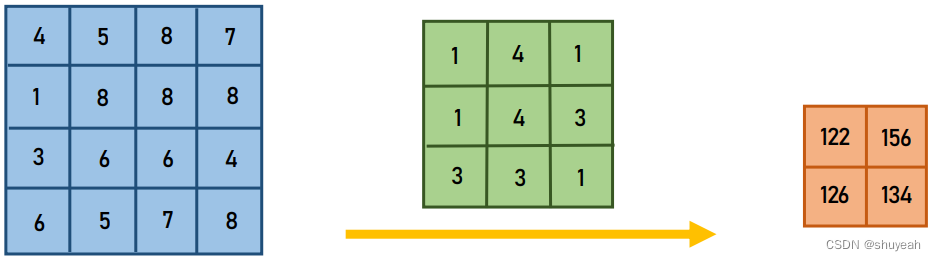
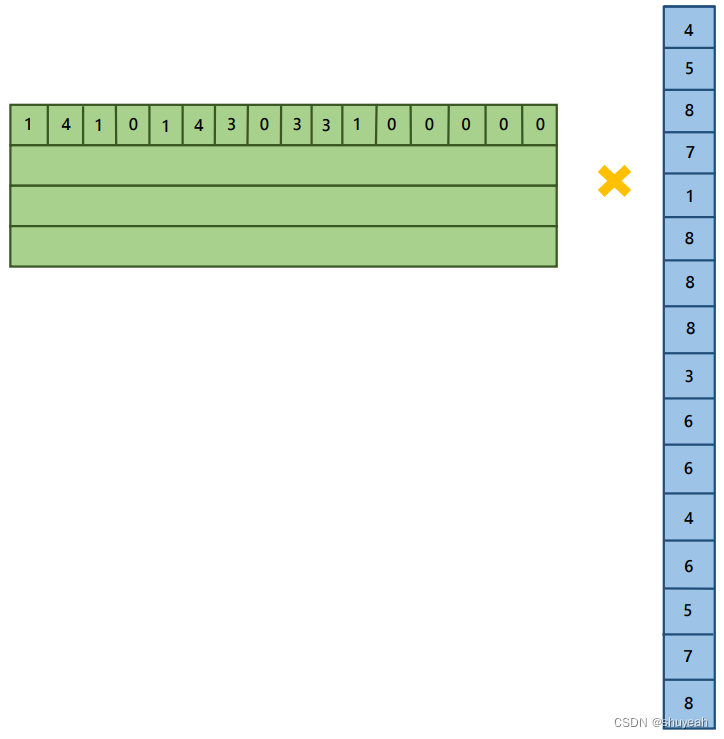
感谢:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1xf4y1p7Gf/?p=4&spm_id_from=pageDriver&vd_source=91cfed371d5491e2973d221d250b54ae
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 什么是超融合?
- 大模型实战营Day5 LMDeploy大模型量化部署实践
- 软件测评中心▏性能测试之压力测试、负载测试的区别和联系简析
- C语言实现八种排序算法
- 正则化(Regularization)
- 计算机毕业设计选题推荐-SpringBoot 大学新生报到系统
- SpringBoot应用开发的jar包,怎样在服务器重启情况下,自启动,从而实现远程无人值守
- MySQL第六讲·where和having的异同?
- vue3 element plus 查询输入框 实现输入就可以查询
- Impala-创建表详解(超详细)