自定义线程池
发布时间:2024年01月19日
自定义线程池
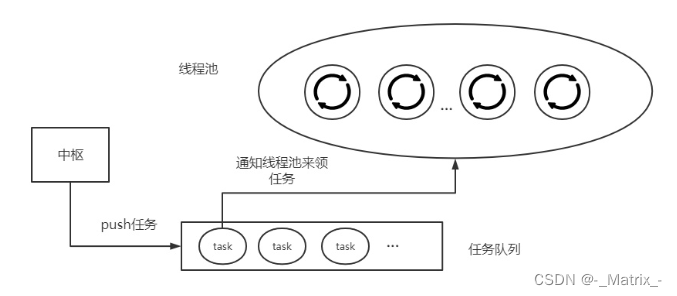
注意: 需要
c++17或c++20的支持
代码实现:
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <functional>
#include <future>
#include <atomic>
#include <iostream>
//线程池,单例类
class ThreadPool
{
public:
static ThreadPool& getInstance()
{
//std::thread::hardware_concurrency() //获取线程数 最小10个线程
static int size = std::max((int)std::thread::hardware_concurrency(),10);
static ThreadPool instance(size,size * 2);
return instance;
}
ThreadPool(ThreadPool const&) = delete;
void operator=(ThreadPool const&) = delete;
//增加运行的函数 动态获取类型
template<typename F, typename... Args>
auto enqueue(F&& f, Args&&... args) -> std::future<typename std::invoke_result<F,Args...>::type>
{
//返回类型
using return_type = typename std::invoke_result<F,Args...>::type;
//打包函数
auto task = std::make_shared<std::packaged_task<return_type()> >(
std::bind(std::forward<F>(f), std::forward<Args>(args)...)
);
std::future<return_type> res = task->get_future();
{
std::lock_guard <std::mutex> lock(m_queue_mutex);
if (m_stop)
{
//return res;
throw std::runtime_error("enqueue on stopped ThreadPool");
}
// // 添加线程来运行任务
// // 检查是否有空闲线程,否则创建新线程
// bool assigned = true;
// for (auto& worker : m_workers)
// {
// if (worker->status == Status::Idle)
// {
// assigned = false;
// break;
// }
// }
// 添加线程来运行任务
// 检查是否有空闲线程,否则创建新线程
bool assigned = true;
auto it = m_workers.begin();
while (it != m_workers.end())
{
// 使用循环来移除所有状态为 Status::Removed 的 Worker
if ((*it)->status == Status::Removed)
{
it = m_workers.erase(it); // erase 返回下一个有效迭代器
}
else if((*it)->status == Status::Idle)
{
//标记有空闲线程
assigned = false;
++it;
}
else
{
++it;
}
}
//创建新线程
if (assigned)
{
add_thread();
}
//添加任务
m_tasks.emplace([task]() { (*task)(); });
}
//随机唤醒一个线程
m_condition.notify_one();
return res;
}
~ThreadPool()
{
stop_all();
}
private:
ThreadPool(size_t min_threads,size_t max_thread,size_t timeout_ms = 60000)
:m_max_threads(max_thread),m_timeout_ms(timeout_ms), m_stop(false)
{
//创建
for (size_t i = 0; i < min_threads; ++i)
{
add_thread();
}
}
//添加线程
void add_thread()
{
//创建工作线程
std::shared_ptr<Worker> worker = std::make_shared<Worker>();
//默认状态 闲置
worker->status = Status::Idle;
worker->thread = std::thread([this,worker]() {
for(;;)
{
std::function<void()> task;
{
// std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(this->m_queue_mutex);
// this->m_condition.wait(lock, [this] {
// return this->m_stop || !this->m_tasks.empty();
// });
//当前线程超时处理(相对时间) 超时返回false
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(this->m_queue_mutex);
if (!this->m_condition.wait_for(lock, std::chrono::milliseconds(this->m_timeout_ms), [this] {
return this->m_stop || !this->m_tasks.empty();
}))
{
// 超时处理 大于最大线程数,标记移除 否则,跳过
if(this->m_workers.size() > this->m_max_threads)
{
worker->status = Status::Removed;
return;
}
else
{
continue;
}
}
//退出条件
if (this->m_stop && this->m_tasks.empty())
{
return;
}
//非空的情况下调用 重新判断
if(!this->m_tasks.empty())
{
task = std::move(this->m_tasks.front());
this->m_tasks.pop();
}
else
{
continue;
}
}
//设置线程运行状态 Running
worker->status = Status::Running;
//运行函数
task();
//函数运行完后 设置 闲置状态
worker->status = Status::Idle;
}
});
m_workers.push_back(std::move(worker));
}
//停止所有线程
void stop_all()
{
{
std::lock_guard <std::mutex> lock(m_queue_mutex);
m_stop = true;
}
m_condition.notify_all();
for(auto& worker: m_workers)
{
if(worker->thread.joinable())
{
worker->thread.join();
}
}
m_workers.clear();
}
enum class Status
{
Running, //运行
Idle, //闲置
Removed //移除
};
//工作线程
struct Worker
{
Status status;
std::thread thread;
};
std::queue<std::function<void()>> m_tasks;//任务队列
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<Worker>> m_workers; //工作线程列表
std::mutex m_queue_mutex;
std::condition_variable m_condition;
std::atomic<bool> m_stop;
size_t m_max_threads; //最大线程数,闲置时 当前线程列表超出最大线程数时,标记 Removed
size_t m_timeout_ms; //超时 就把当前线程标记 Removed,下一轮添加任务把这个线程移除
};
//普通函数
int sub(int a,int b)
{
std::cout<<"sub: "<< a<<" - "<< b<<std::endl;
int i=0;
while((i++) != 200)
{
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::microseconds(1));
//耗时运算
}
return a - b;
}
//类函数
class Add
{
public:
int add(int a,int b)
{
std::cout<<"Add::add: "<< a<<" + "<< b<<std::endl;
int i=0;
while((i++) != 200)
{
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::microseconds(1));
//耗时运算
}
return a+b;
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int a = 60;
int b = 20;
int c = 30;
int d = 40;
//线程池运算 支持获取结果
//######################################### 普通函数使用 #########################################//
//方法1 - 直接调用
std::future<int> res = ThreadPool::getInstance().enqueue(sub,a,b);
//方法2 - lambda调用
std::future<int> res1 = ThreadPool::getInstance().enqueue([a,b](){
return sub(a,b);
});
//方法3 - std::bind绑定调用
//绑定
auto func = std::bind(sub,a,b);
std::future<int> res2 = ThreadPool::getInstance().enqueue(func);
std::cout<<"res:"<<res.get()<<std::endl;//先打印 res 然后等待线程函数结果
std::cout<<"res1:"<<res1.get()<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"res2:"<<res2.get()<<std::endl;
//######################################### 类函数使用 #########################################//
Add ddd;
//方法1 - 直接调用
std::future<int> res8 = ThreadPool::getInstance().enqueue(&Add::add,ddd,c,d);
//方法2 - lambda调用
std::future<int> res9 = ThreadPool::getInstance().enqueue([&ddd,c,d](){
return ddd.add(c,d);
});
//方法3 - std::bind绑定调用
//绑定
auto func2 = std::bind(&Add::add,&ddd,c,d);
std::future<int> res10 = ThreadPool::getInstance().enqueue(func2);
std::cout<<"res8:"<<res8.get()<<std::endl;//先打印 res8 然后等待线程函数结果
std::cout<<"res9:"<<res9.get()<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"res10:"<<res10.get()<<std::endl;
return 1;
}
运算结果
res:sub: 60 - 20
sub: 60sub: - 2060
- 20
40
res1:40
res2:40
Add::add: res8:30Add::add: + 4030
Add::add: 30 + + 4040
70
res9:70
res10:70
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43763292/article/details/135693441
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 硬件知识之ESD保护器件
- Ubuntu虚拟内存设置-----必成功!!!
- 【数据库原理】(32)数据库设计-数据库物理设计
- 数据安全问题困扰您吗?Zoho CRM帮您解决
- 操作系统复习 五、六章
- logstack 日志技术栈-01-ELK/EFK 入门介绍 ELK+filebeta
- Win11怎么重置系统?(小白专享篇)
- vue3完整的登录页面,element-plus
- 学生兼职中介管理系统(JSP+java+springmvc+mysql+MyBatis)
- [NSSRound#8 Basic]ez_node