(Spring学习12)Spring 6.0及SpringBoot 3.0新特性解析
主要内容:
1、GraalVM介绍与基本使用
2、Spring Boot 3.0新特性介绍与实战
3、Docker SpringBoot3.0 新特性实战
4、RuntimeHints介绍与实战
5、Spring AOT作用与核心原理源码分析
GraalVM体验
https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/wiki/What%27s-New-in-Spring-Framework-6.x
最核心的就是Spring AOT
下载压缩包
打开https://github.com/graalvm/graalvm-ce-builds/releases,按JDK版本下载GraalVM对应的压缩包,请下载Java 17对应的版本,不然后面运行SpringBoot3可能会有问题。
下载完后,就解压,
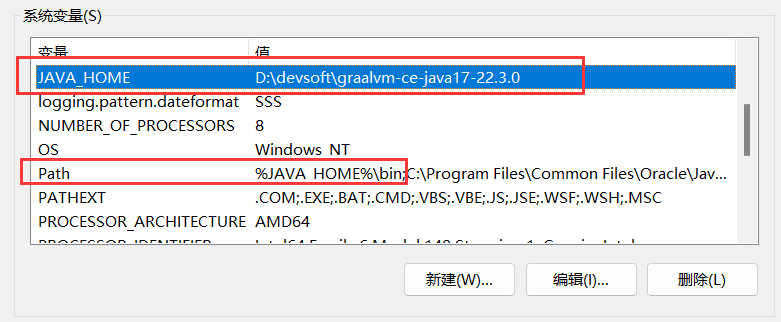
配置环境变量
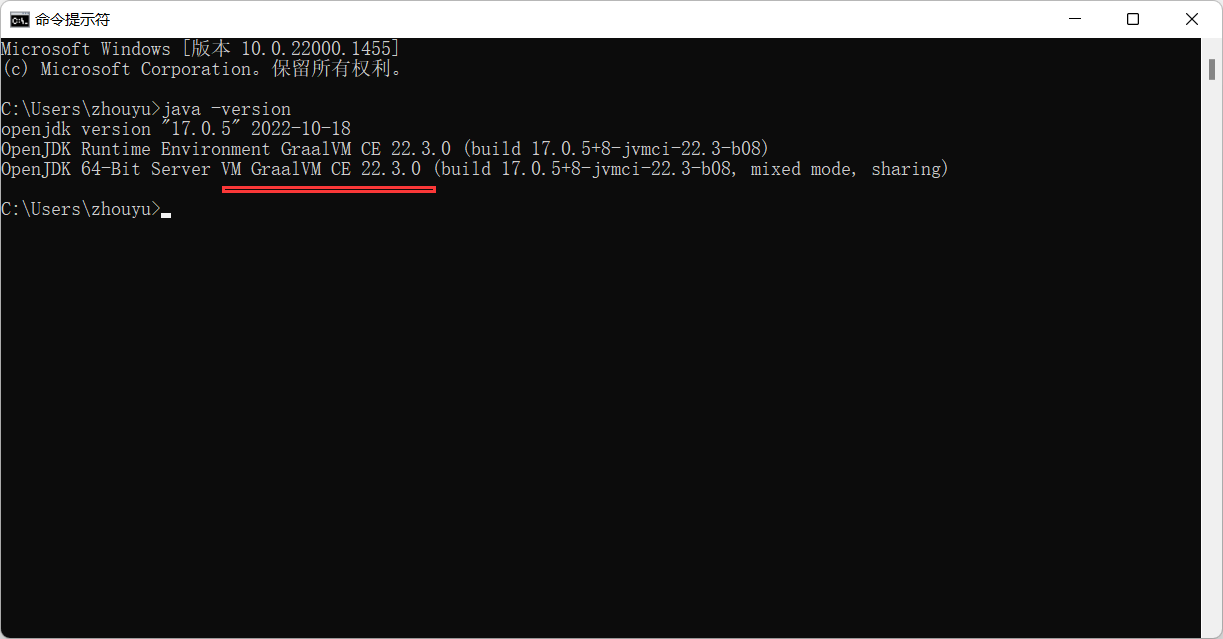
新开一个cmd测试:
java -version
安装Visual Studio Build Tools
因为需要C语言环境,所以需要安装Visual Studio Build Tools。
打开visualstudio.microsoft.com,下载Visual Studio Installer。
选择C++桌面开发,和Windows 11 SDK,然后进行下载和安装,安装后重启操作系统。
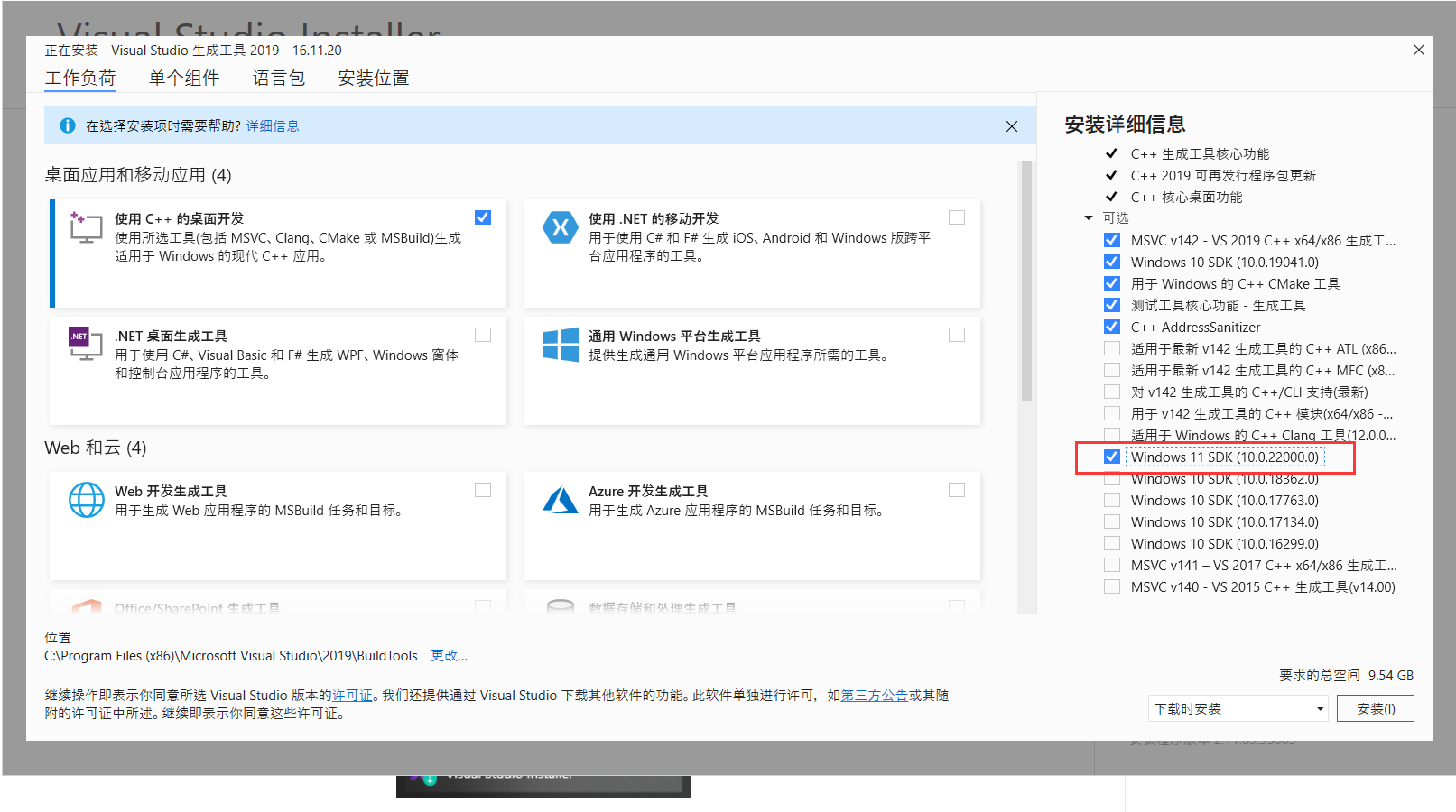
要使用GraalVM,不能使用普通的windows自带的命令行窗口,得使用VS提供的 x64 Native Tools Command Prompt for VS 2019,如果没有可以执行C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\BuildTools\VC\Auxiliary\Build\vcvars64.bat脚本来安装。
安装完之后其实就可以在 x64 Native Tools Command Prompt for VS 2019中去使用native-image命令去进行编译了。
但是,如果后续在编译过程中编译失败了,出现以下错误:
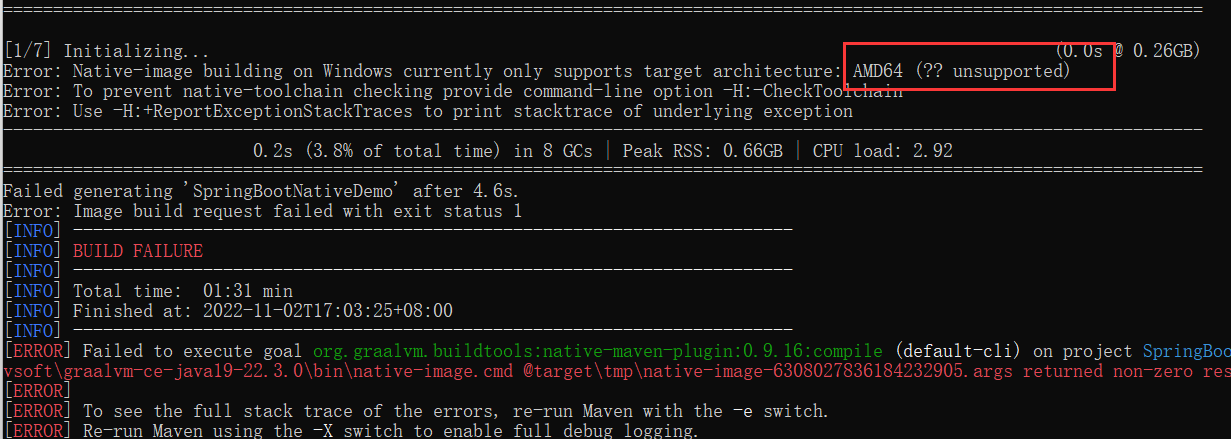
那么可以执行cl.exe,如果是中文,那就得修改为英文。
通过Visual Studio Installer来修改,比如:
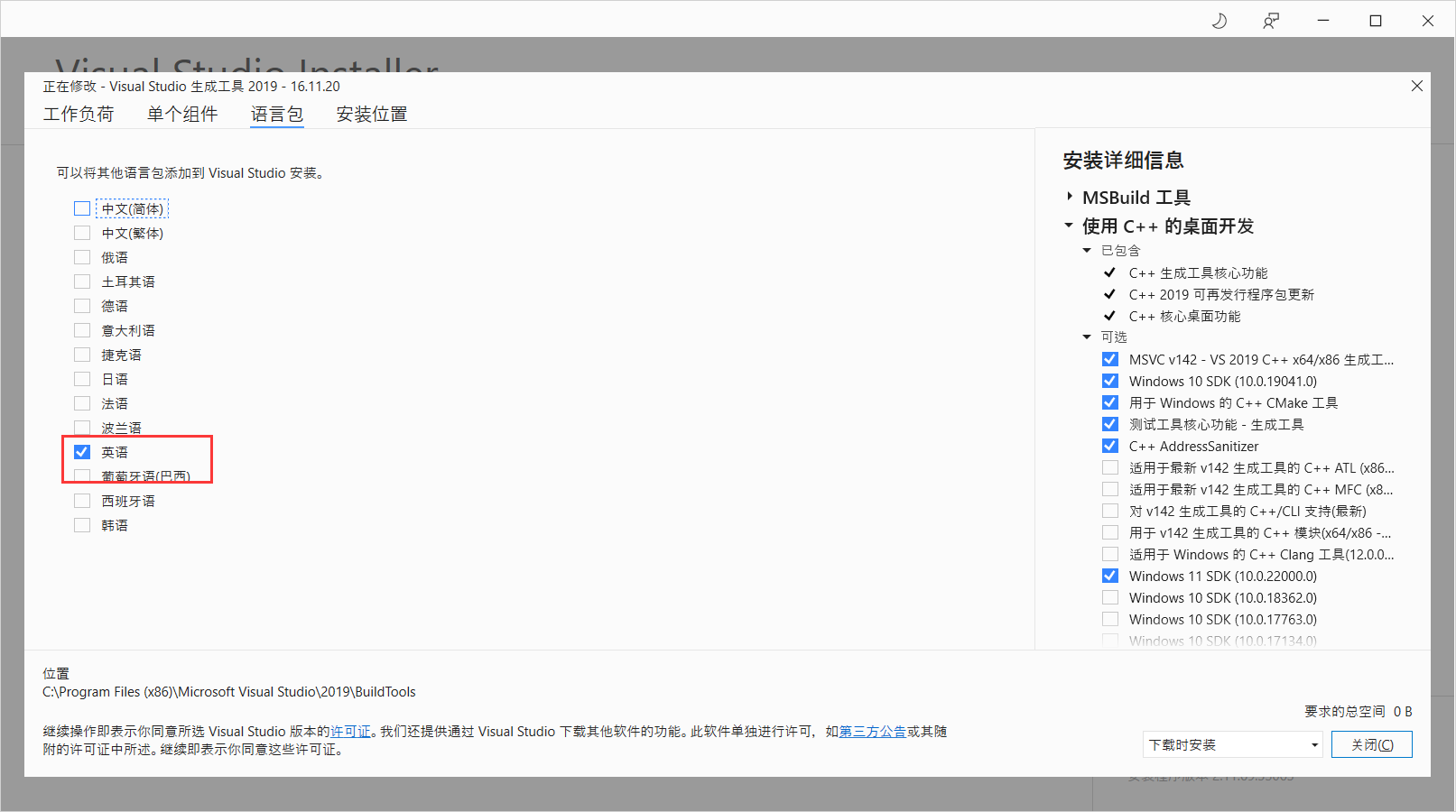
可能一开始只选择了中文,手动选择英文,去掉中文,然后安装即可。
再次检查
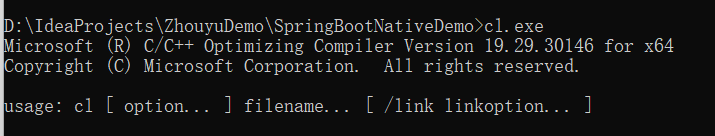
这样就可以正常的编译了。
Hello World实战
新建一个简单的Java工程:
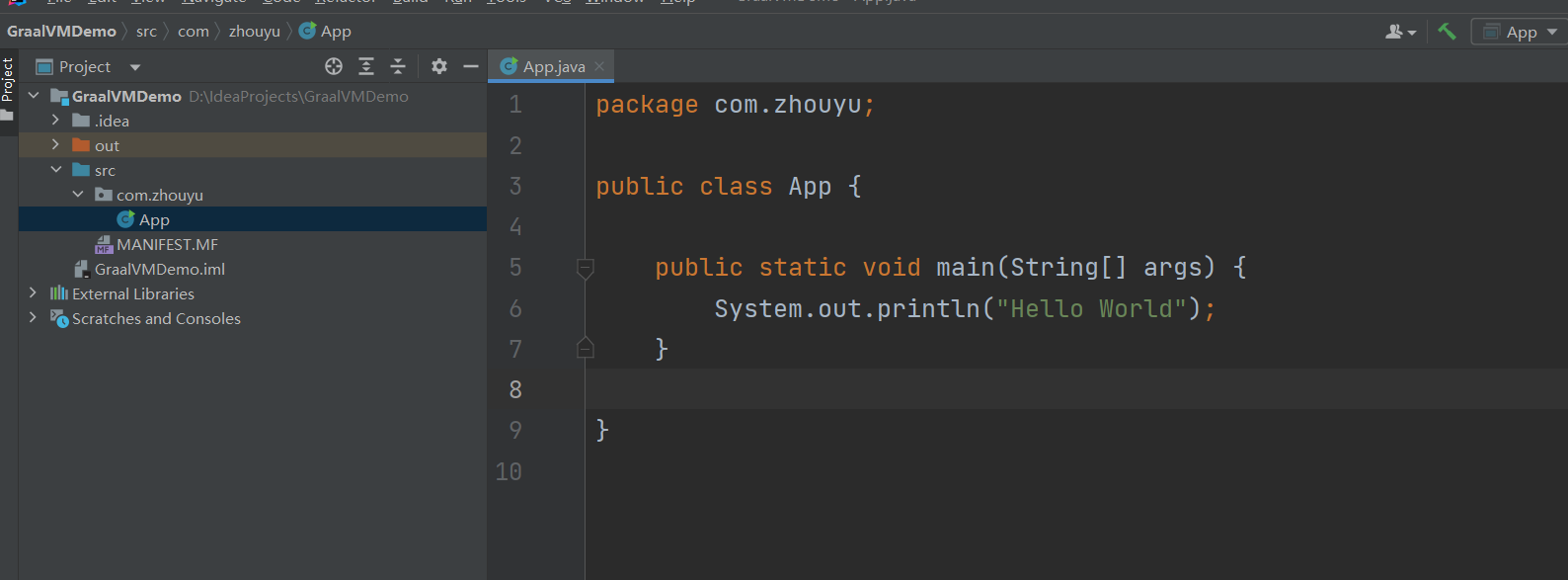
我们可以直接把graalvm当作普通的jdk的使用
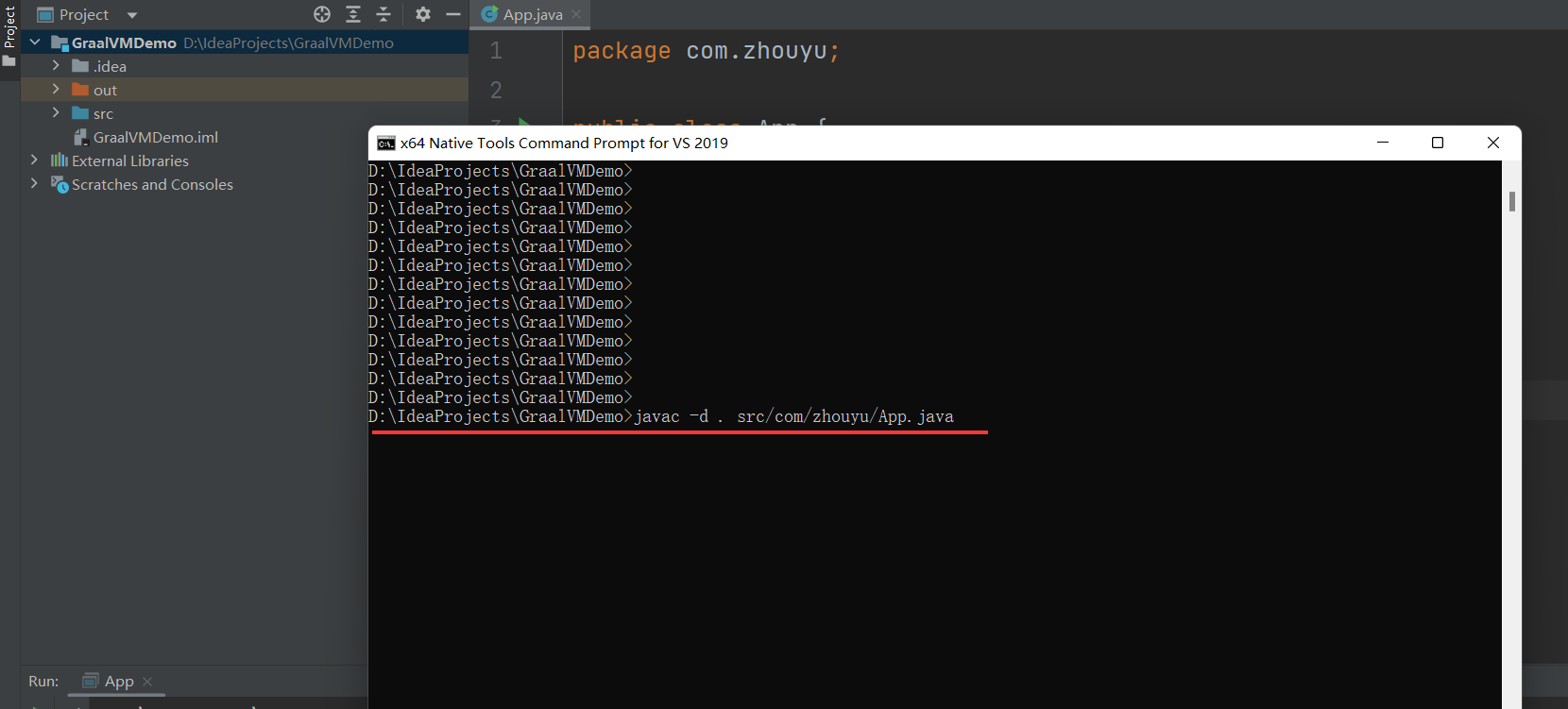
此时的class文件因为有main方法,所以用java命令可以运行
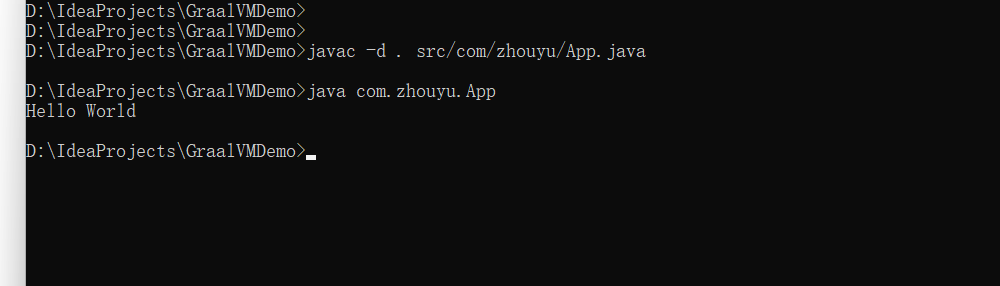
我们也可以利用native-image来编译
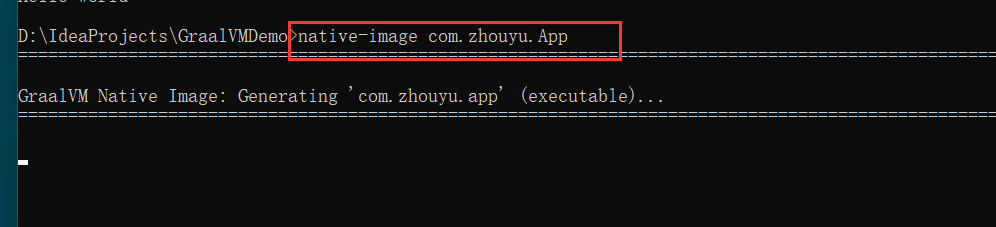
编译完了之后就会在当前目录生成一个exe文件:
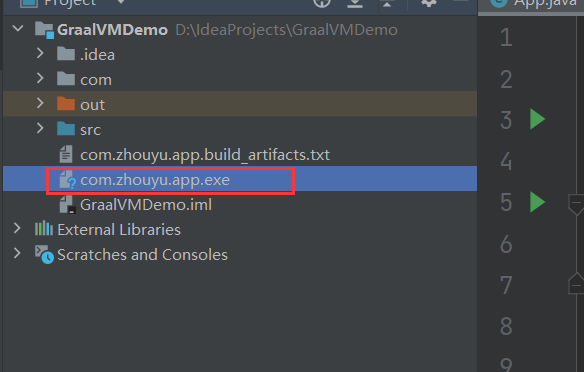
我们可以直接运行这个exe文件:
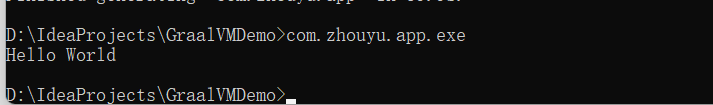
并且运行这个exe文件是不需要操作系统上安装了JDK环境的。
我们可以使用-o参数来指定exe文件的名字:
native-image com.zhouyu.App -o app
GraalVM的限制
GraalVM在编译成二进制可执行文件时,需要确定该应用到底用到了哪些类、哪些方法、哪些属性,从而把这些代码编译为机器指令(也就是exe文件)。但是我们一个应用中某些类可能是动态生成的,也就是应用运行后才生成的,为了解决这个问题,GraalVM提供了配置的方式,可以让我们在编译时告诉GraalVM哪些类会动态生成类,比如我们可以通过proxy-config.json、reflect-config.json来进行配置。
SpringBoot 3.0实战
然后新建一个Maven工程,添加SpringBoot依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
以及SpringBoot的插件
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.graalvm.buildtools</groupId>
<artifactId>native-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
以及一些代码
@RestController
public class ZhouyuController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@GetMapping("/demo")
public String test() {
return userService.test();
}
}
package com.zhouyu;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class UserService {
public String test(){
return "hello zhouyu";
}
}
package com.zhouyu;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args);
}
}
这本身就是一个普通的SpringBoot工程,所以可以使用我们之前的方式使用,同时也支持利用native-image命令把整个SpringBoot工程编译成为一个exe文件。
同样在 x64 Native Tools Command Prompt for VS 2019中,进入到工程目录下,执行mvn -Pnative native:compile进行编译就可以了,就能在target下生成对应的exe文件,后续只要运行exe文件就能启动应用了。
在执行命令之前,请确保环境变量中设置的时graalvm的路径。
编译完成截图:
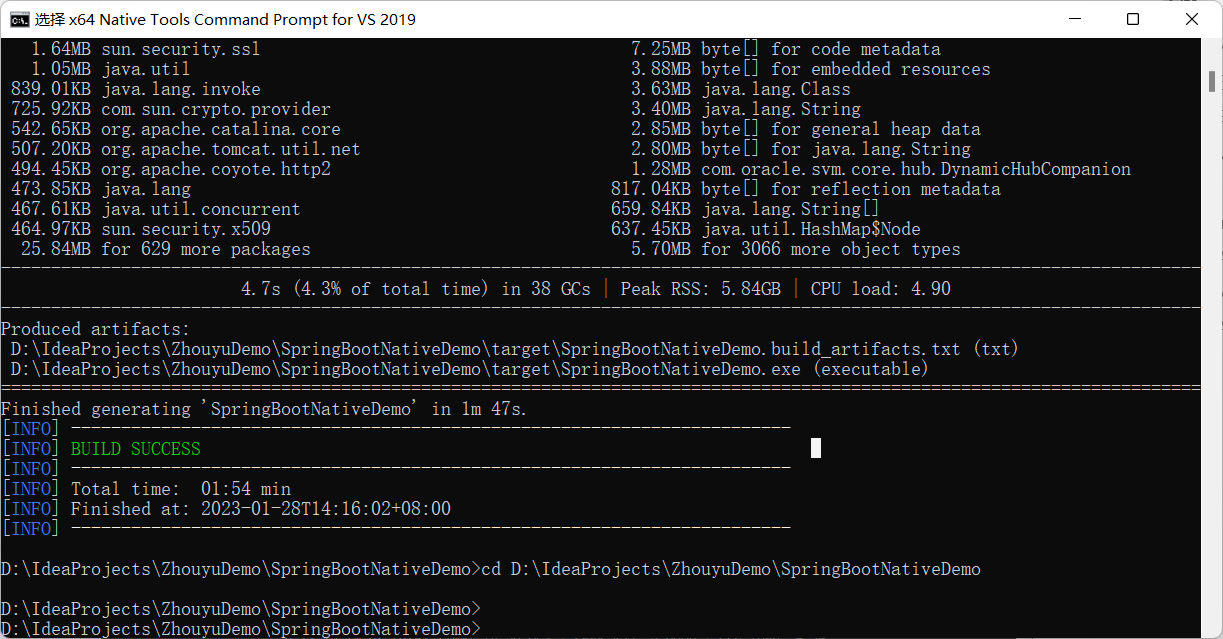
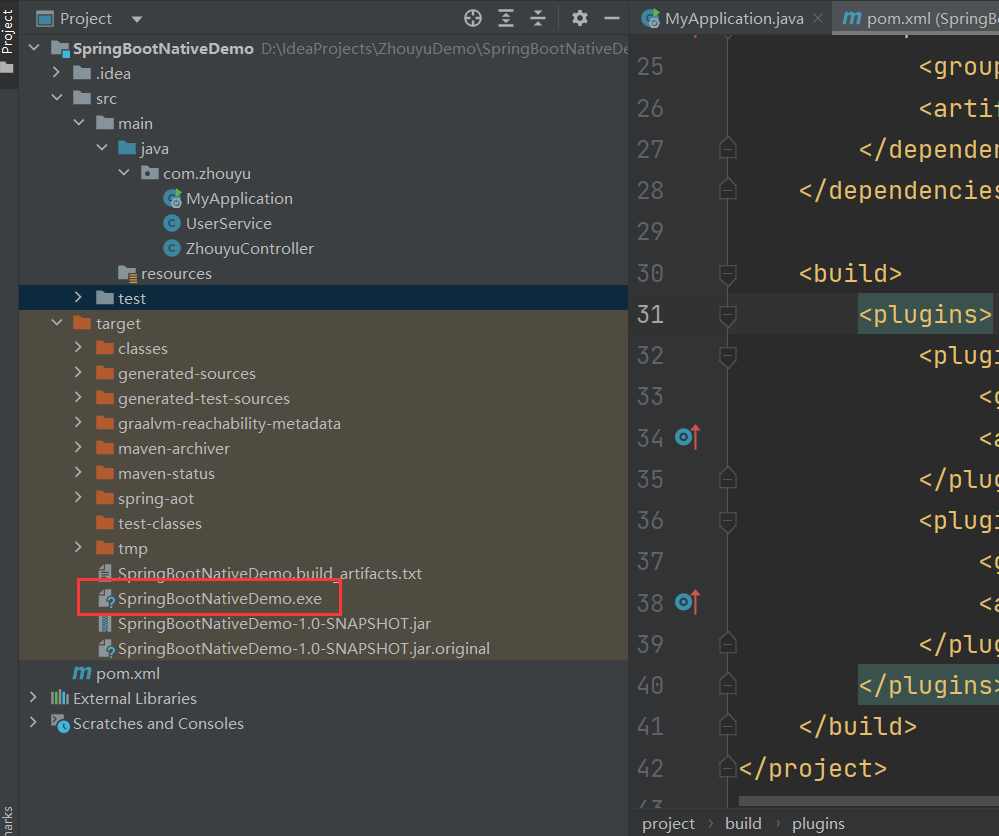
这样,我们就能够直接运行这个exe来启动我们的SpringBoot项目了。
Docker SpringBoot3.0 实战
我们可以直接把SpringBoot应用对应的本地可执行文件构建为一个Docker镜像,这样就能跨操作系统运行了。
Buildpacks,类似Dockerfile的镜像构建技术
注意要安装docker,并启动docker
注意这种方式并不要求你机器上安装了GraalVM,会由SpringBoot插件利用/paketo-buildpacks/native-image来生成本地可执行文件,然后打入到容器中
Docker镜像名字中不能有大写字母,我们可以配置镜像的名字:
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<spring-boot.build-image.imageName>springboot3demo</spring-boot.build-image.imageName>
</properties>
mvn -Pnative spring-boot:build-image
来生成Docker镜像,成功截图:
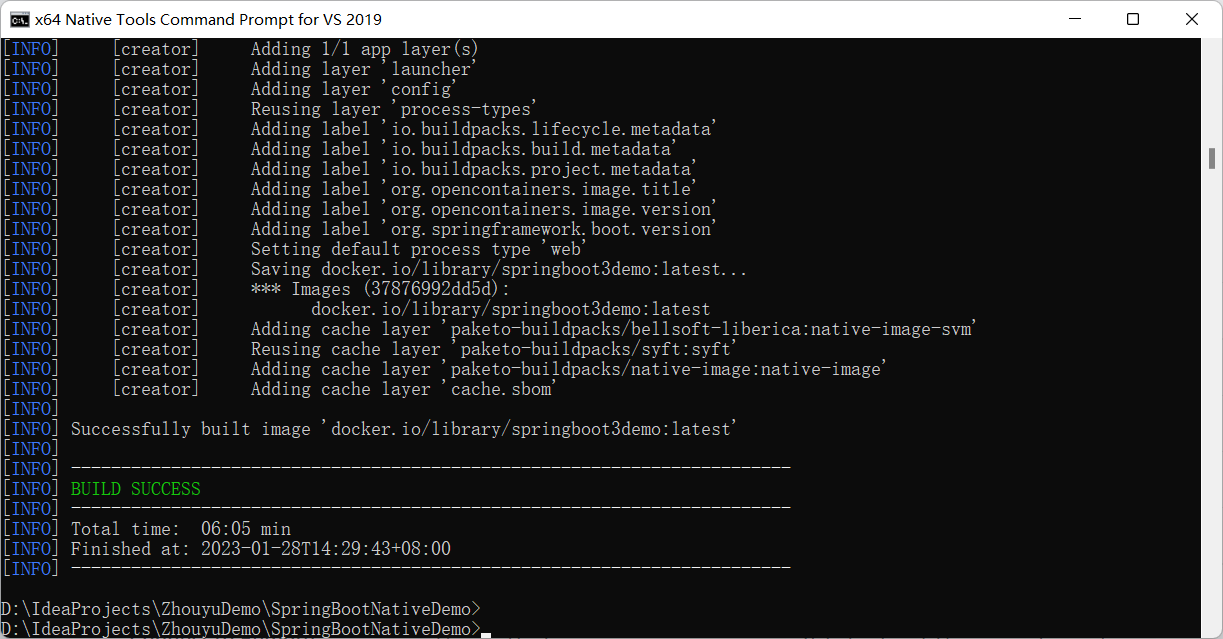
执行完之后,就能看到docker镜像了:
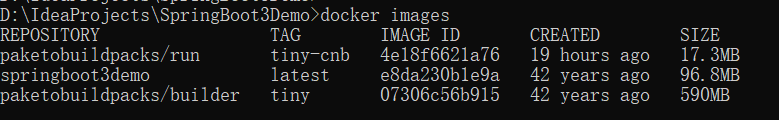
然后就可以运行容器了:
docker run --rm -p 8080:8080 springboot3demo
如果要传参数,可以通过-e
docker run --rm -p 8080:8080 -e methodName=test springboot3demo
不过代码中,得通过以下代码获取:
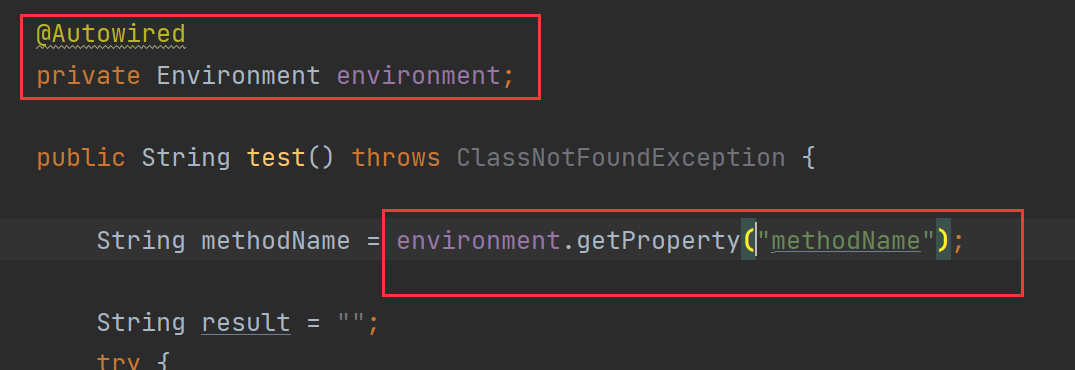
String methodName = System.getenv("methodName")
建议工作中直接使用Environment来获取参数:
RuntimeHints
假如应用中有如下代码:
public class ZhouyuService {
public String test(){
return "zhouyu";
}
}
@Component
public class UserService {
public String test(){
String result = "";
try {
Method test = ZhouyuService.class.getMethod("test", null);
result = (String) test.invoke(ZhouyuService.class.newInstance(), null);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return result;
}
}
在UserService中,通过反射的方式使用到了ZhouyuService的无参构造方法(ZhouyuService.class.newInstance()),如果我们不做任何处理,那么打成二进制可执行文件后是运行不了的,可执行文件中是没有ZhouyuService的无参构造方法的,会报如下错误:
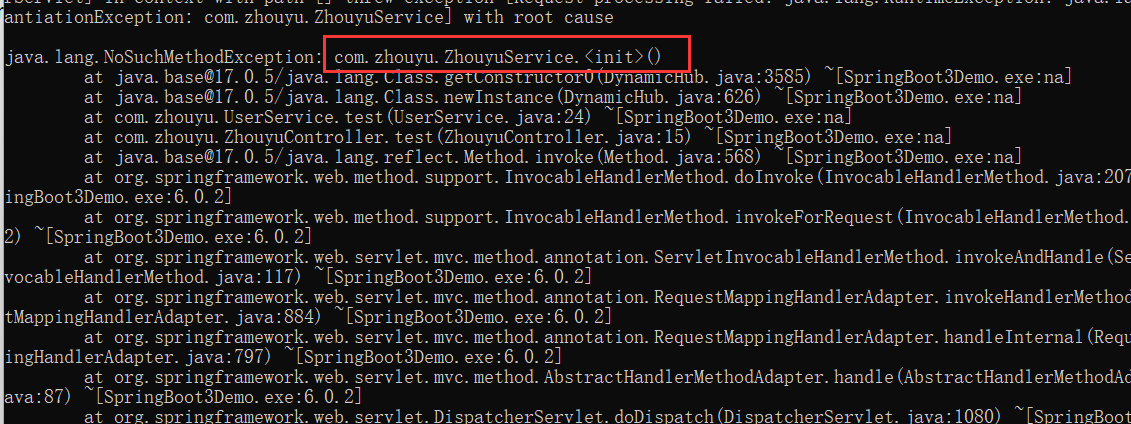
我们可以通过Spring提供的Runtime Hints机制来间接的配置reflect-config.json。
方式一:RuntimeHintsRegistrar
提供一个RuntimeHintsRegistrar接口的实现类,并导入到Spring容器中就可以了:
@Component
@ImportRuntimeHints(UserService.ZhouyuServiceRuntimeHints.class)
public class UserService {
public String test(){
String result = "";
try {
Method test = ZhouyuService.class.getMethod("test", null);
result = (String) test.invoke(ZhouyuService.class.newInstance(), null);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return result;
}
static class ZhouyuServiceRuntimeHints implements RuntimeHintsRegistrar {
@Override
public void registerHints(RuntimeHints hints, ClassLoader classLoader) {
try {
hints.reflection().registerConstructor(ZhouyuService.class.getConstructor(), ExecutableMode.INVOKE);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
方式二:@RegisterReflectionForBinding
@RegisterReflectionForBinding(ZhouyuService.class)
public String test(){
String result = "";
try {
Method test = ZhouyuService.class.getMethod("test", null);
result = (String) test.invoke(ZhouyuService.class.newInstance(), null);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return result;
}
注意
如果代码中的methodName是通过参数获取的,那么GraalVM在编译时就不能知道到底会使用到哪个方法,那么test方法也要利用RuntimeHints来进行配置。
@Component
@ImportRuntimeHints(UserService.ZhouyuServiceRuntimeHints.class)
public class UserService {
public String test(){
String methodName = System.getProperty("methodName");
String result = "";
try {
Method test = ZhouyuService.class.getMethod(methodName, null);
result = (String) test.invoke(ZhouyuService.class.newInstance(), null);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return result;
}
static class ZhouyuServiceRuntimeHints implements RuntimeHintsRegistrar {
@Override
public void registerHints(RuntimeHints hints, ClassLoader classLoader) {
try {
hints.reflection().registerConstructor(ZhouyuService.class.getConstructor(), ExecutableMode.INVOKE);
hints.reflection().registerMethod(ZhouyuService.class.getMethod("test"), ExecutableMode.INVOKE);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
或者使用了JDK动态代理:
public String test() throws ClassNotFoundException {
String className = System.getProperty("className");
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(className);
Object o = Proxy.newProxyInstance(UserService.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{aClass}, new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
return method.getName();
}
});
return o.toString();
}
那么也可以利用RuntimeHints来进行配置要代理的接口:
public void registerHints(RuntimeHints hints, ClassLoader classLoader) {
hints.proxies().registerJdkProxy(UserInterface.class);
}
方式三:@Reflective
对于反射用到的地方,我们可以直接加一个@Reflective,前提是ZhouyuService得是一个Bean:
@Component
public class ZhouyuService {
@Reflective
public ZhouyuService() {
}
@Reflective
public String test(){
return "zhouyu";
}
}
以上Spring6提供的RuntimeHints机制,我们可以使用该机制更方便的告诉GraalVM我们额外用到了哪些类、接口、方法等信息,最终Spring会生成对应的reflect-config.json、proxy-config.json中的内容,GraalVM就知道了。
Spring AOT的源码实现
流程图:https://www.processon.com/view/link/63edeea8440e433d3d6a88b2
SpringBoot 3.0插件实现原理
上面的SpringBoot3.0实战过程中,我们在利用image-native编译的时候,target目录下会生成一个spring-aot文件夹:
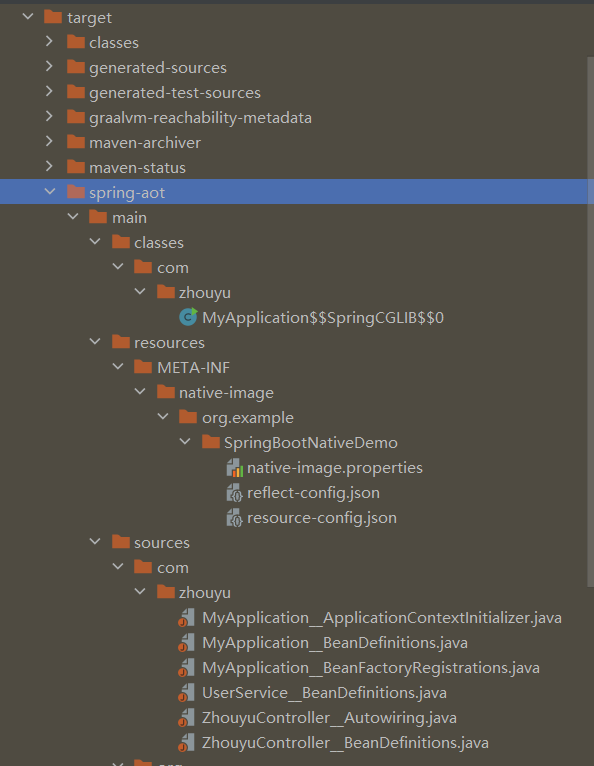
这个spring-aot文件夹是编译的时候spring boot3.0的插件生成的,resources/META-INF/native-image文件夹中的存放的就是graalvm的配置文件。
当我们执行mvn -Pnative native:compile时,实际上执行的是插件native-maven-plugin的逻辑。
我们可以执行
mvn help:describe -Dplugin=org.graalvm.buildtools:native-maven-plugin -Ddetail
来查看这个插件的详细信息。

发现native:compile命令对应的实现类为NativeCompileMojo,并且会先执行package这个命令,从而会执行process-aot命令,因为spring-boot-maven-plugin插件中有如下配置:
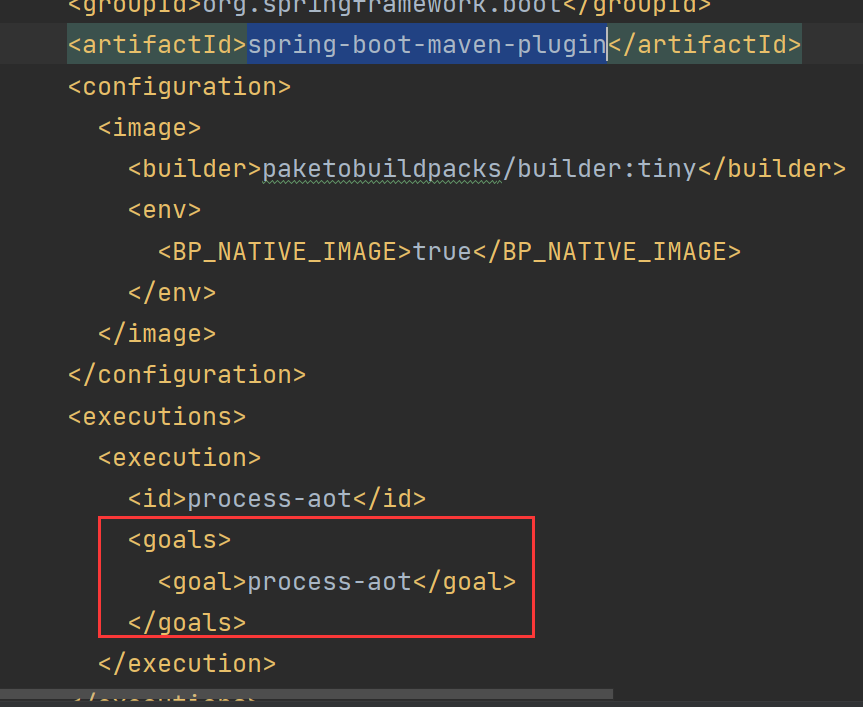
我们可以执行
mvn help:describe -Dplugin=org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-maven-plugin -Ddetail
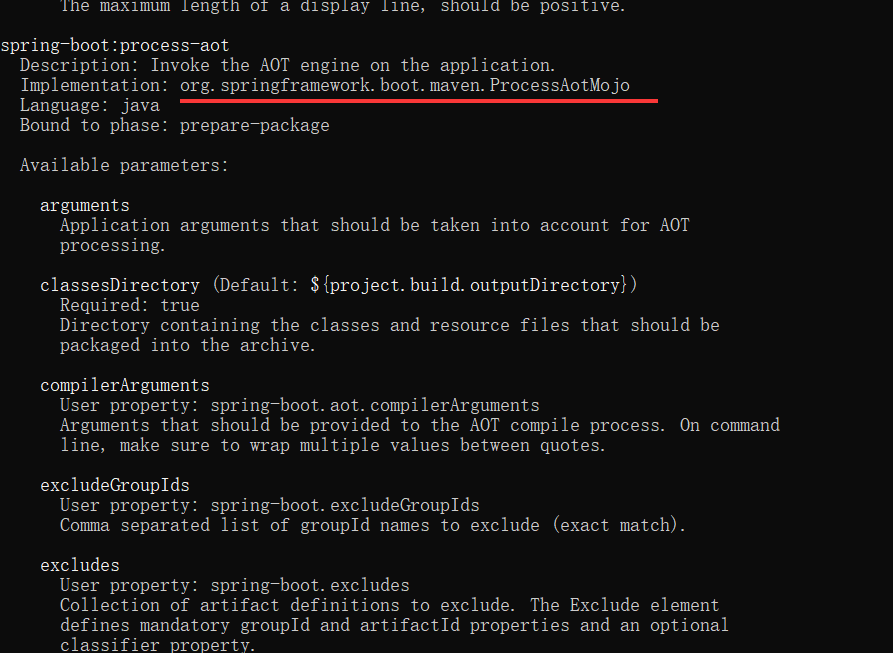
发现对应的phase为:prepare-package,所以会在打包之前执行ProcessAotMojo。
所以,我们在运行mvn -Pnative native:compile时,会先编译我们自己的java代码,然后执行executeAot()方法(会生成一些Java文件并编译成class文件,以及GraalVM的配置文件),然后才执行利用GraalVM打包出二进制可执行文件。
对应的源码实现:
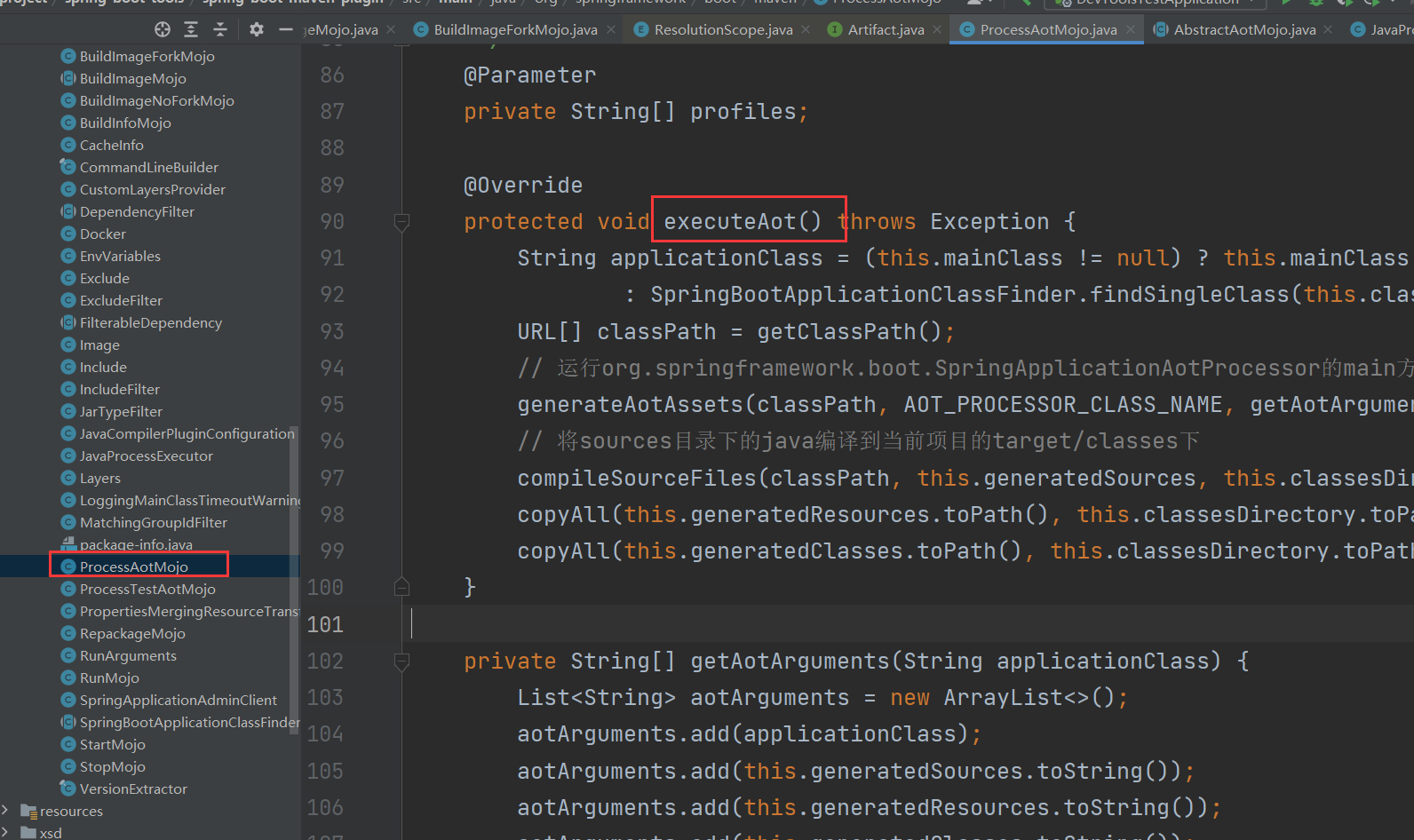
maven插件在编译的时候,就会调用到executeAot()这个方法,这个方法会:
- 先执行org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationAotProcessor的main方法
- 从而执行SpringApplicationAotProcessor的process()
- 从而执行ContextAotProcessor的doProcess(),从而会生成一些Java类并放在spring-aot/main/sources目录下,详情看后文
- 然后把生成在spring-aot/main/sources目录下的Java类进行编译,并把对应class文件放在项目的编译目录下target/classes
- 然后把spring-aot/main/resources目录下的graalvm配置文件复制到target/classes
- 然后把spring-aot/main/classes目录下生成的class文件复制到target/classes
Spring AOT核心原理
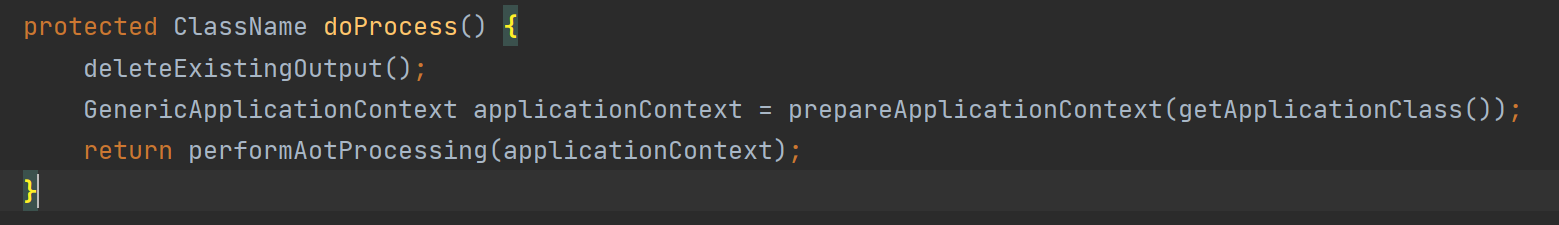
prepareApplicationContext会直接启动我们的SpringBoot,并在触发contextLoaded事件后,返回所创建的Spring对象,注意此时还没有扫描Bean。
protected ClassName performAotProcessing(GenericApplicationContext applicationContext) {
FileSystemGeneratedFiles generatedFiles = createFileSystemGeneratedFiles();
DefaultGenerationContext generationContext = new DefaultGenerationContext(createClassNameGenerator(), generatedFiles);
ApplicationContextAotGenerator generator = new ApplicationContextAotGenerator();
// 会进行扫描,并且根据扫描得到的BeanDefinition生成对应的Xx_BeanDefinitions.java文件
// 并返回com.zhouyu.MyApplication__ApplicationContextInitializer
ClassName generatedInitializerClassName = generator.processAheadOfTime(applicationContext, generationContext);
// 因为后续要通过反射调用com.zhouyu.MyApplication__ApplicationContextInitializer的构造方法
// 所以将相关信息添加到reflect-config.json对应的RuntimeHints中去
registerEntryPointHint(generationContext, generatedInitializerClassName);
// 生成source目录下的Java文件
generationContext.writeGeneratedContent();
// 将RuntimeHints中的内容写入resource目录下的Graalvm的各个配置文件中
writeHints(generationContext.getRuntimeHints());
writeNativeImageProperties(getDefaultNativeImageArguments(getApplicationClass().getName()));
return generatedInitializerClassName;
}
public ClassName processAheadOfTime(GenericApplicationContext applicationContext,
GenerationContext generationContext) {
return withCglibClassHandler(new CglibClassHandler(generationContext), () -> {
// 会进行扫描,并找到beanType是代理类的请求,把代理类信息设置到RuntimeHints中
applicationContext.refreshForAotProcessing(generationContext.getRuntimeHints());
// 拿出Bean工厂,扫描得到的BeanDefinition对象在里面
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = applicationContext.getDefaultListableBeanFactory();
ApplicationContextInitializationCodeGenerator codeGenerator =
new ApplicationContextInitializationCodeGenerator(generationContext);
// 核心
new BeanFactoryInitializationAotContributions(beanFactory).applyTo(generationContext, codeGenerator);
return codeGenerator.getGeneratedClass().getName();
});
}
BeanFactoryInitializationAotContributions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 把aot.factories文件的加载器以及BeanFactory,封装成为一个Loader对象,然后传入
this(beanFactory, AotServices.factoriesAndBeans(beanFactory));
}
BeanFactoryInitializationAotContributions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory,
AotServices.Loader loader) {
// getProcessors()中会从aot.factories以及beanfactory中拿出BeanFactoryInitializationAotProcessor类型的Bean对象
// 同时还会添加一个RuntimeHintsBeanFactoryInitializationAotProcessor
this.contributions = getContributions(beanFactory, getProcessors(loader));
}
return Collections.unmodifiableList(contributions);
}
总结一下,在SpringBoot项目编译时,最终会通过BeanFactoryInitializationAotProcessor来生成Java文件,或者设置RuntimeHints,后续会把写入Java文件到磁盘,将RuntimeHints中的内容写入GraalVM的配置文件,再后面会编译Java文件,再后面就会基于生成出来的GraalVM配置文件打包出二进制可执行文件了。
所以我们要看Java文件怎么生成的,RuntimeHints如何收集的就看具体的BeanFactoryInitializationAotProcessor就行了。
比如:
- 有一个BeanRegistrationsAotProcessor,它就会负责生成Xx_BeanDefinition.java以及Xx__ApplicationContextInitializer.java、Xx__BeanFactoryRegistrations.java中的内容
- 还有一个RuntimeHintsBeanFactoryInitializationAotProcessor,它负责从aot.factories文件以及BeanFactory中获取RuntimeHintsRegistrar类型的对象,以及会找到@ImportRuntimeHints所导入的RuntimeHintsRegistrar对象,最终就是从这些RuntimeHintsRegistrar中设置RuntimeHints。
Spring Boot3.0启动流程
在run()方法中,SpringBoot会创建一个Spring容器,但是SpringBoot3.0中创建容器逻辑为:
private ConfigurableApplicationContext createContext() {
if (!AotDetector.useGeneratedArtifacts()) {
return new AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext();
}
return new ServletWebServerApplicationContext();
}
如果没有使用AOT,那么就会创建AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext,它里面会添加ConfigurationClassPostProcessor,从而会解析配置类,从而会扫描。
而如果使用了AOT,则会创建ServletWebServerApplicationContext,它就是一个空容器,它里面没有ConfigurationClassPostProcessor,所以后续不会触发扫描了。
创建完容器后,就会找到MyApplication__ApplicationContextInitializer,开始向容器中注册BeanDefinition。
后续就是创建Bean对象了。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 全国(山东、安徽)职业技能大赛--信息安全管理与评估——XSC3-Windows应急响应题目+WP+环境
- Apisix常见问题
- 【计算机毕业设计】SSM电器商城系统
- ArgoCD
- E/E架构升级是汽车智能化发展关键
- 机器视觉——cv2窗口
- 17.5K Star,一款简洁美观的简历生成器,跳槽神器
- 【我的RUST库】get_local_info 0.2.0发布
- opencv和gdal的读写图片波段顺序问题
- ELK之Grafana读取ES-Nginx数据后地图不展示的问题