过拟合与欠拟合
一、模型选择
1、问题导入


2、训练误差与泛化误差

3、验证数据集和测试数据集

4、K-折交叉验证
???????一般在没有足够多数据时使用。

二、过拟合与欠拟合

1、过拟合
过拟合的定义:
???????当学习器把训练样本学的“太好”了的时候,很可能已经把训练样本自身的一些特点当作了所有潜在样本都会具有的一般性质,这样就会导致泛化性能下降,这种现象称为过拟合。具体表现就是最终模型在训练集上效果好;在测试集上效果差。模型泛化能力弱。
过拟合的原因:
- 训练数据中噪音干扰过大,使得学习器认为部分噪音是特征从而扰乱学习规则。
- 建模样本选取有误,例如训练数据太少,抽样方法错误,样本label错误等,导致样本不能代表整体。
- 模型不合理,或假设成立的条件与实际不符。
- 特征维度/参数太多,导致模型复杂度太高。
2、欠拟合
欠拟合的定义:
???????欠拟合是指对训练样本的一般性质尚未学好。在训练集及测试集上的表现都不好。
欠拟合的原因:
- 模型复杂度过低
- 特征量过少
3、模型容量

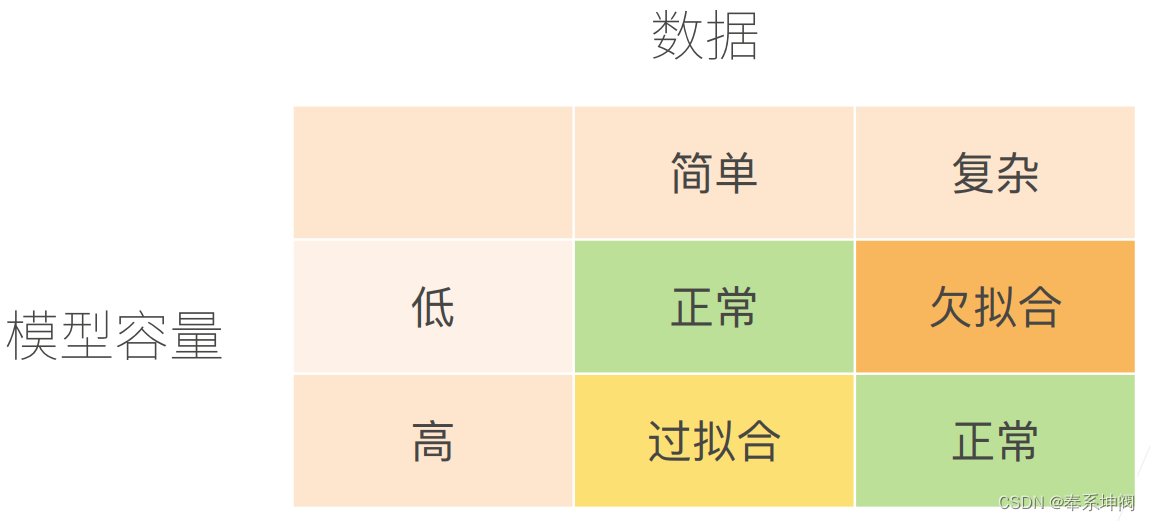
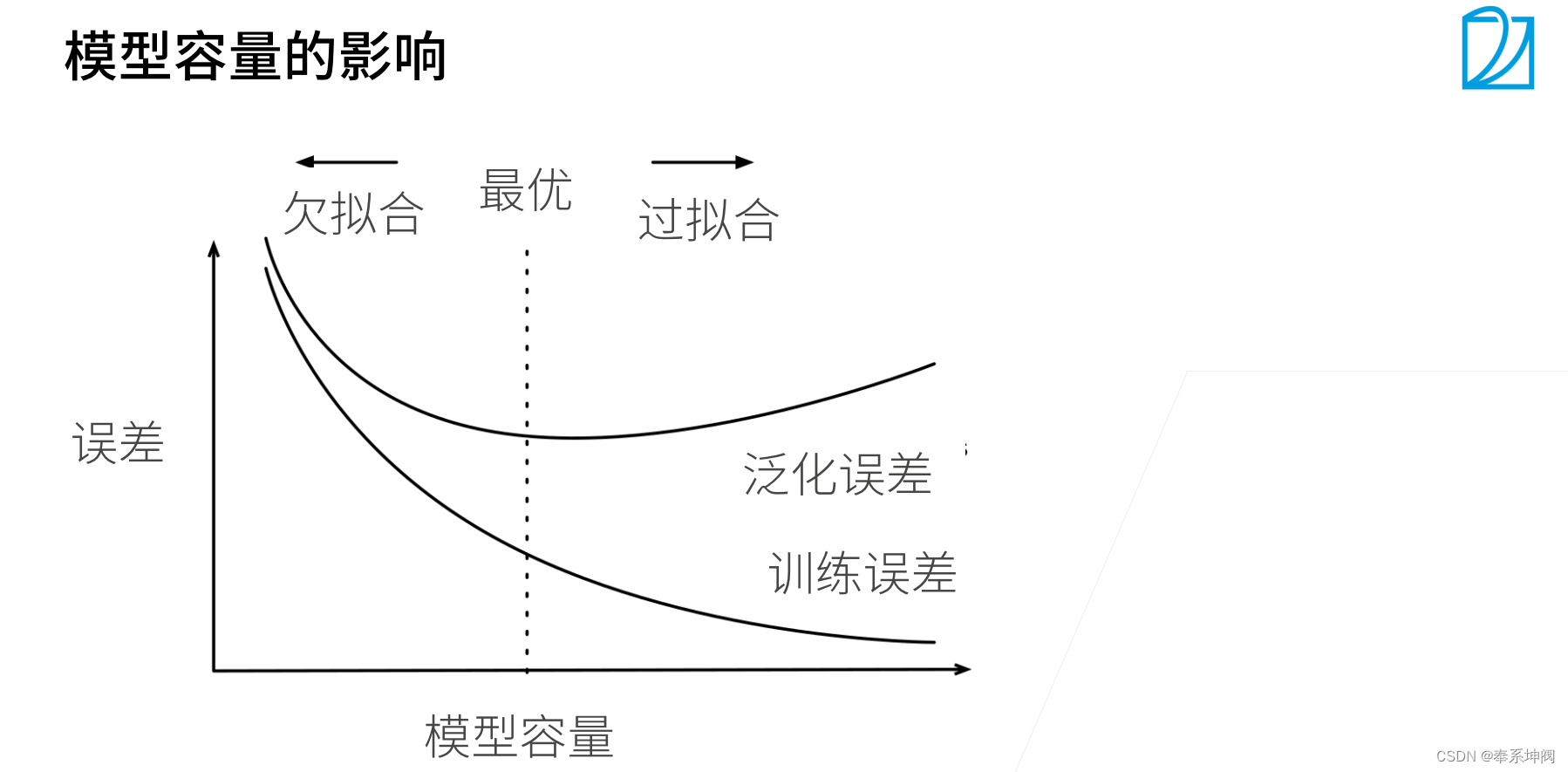
4、数据复杂度

三、代码解释
???????我们可以通过多项式拟合来探索这些概念。
import math
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l1、生成数据集
???????给定,我们将使用以下三阶多项式来生成训练和测试数据的标签:
???????噪声项服从均值为0且标准差为0.1的正态分布。在优化的过程中,我们通常希望避免非常大的梯度值或损失值。这就是我们将特征从
调整为
的原因,这样可以避免很大的
带来的特别大的指数值。我们将为训练集和测试集各生成100个样本。
max_degree = 20 # 多项式的最大阶数
n_train, n_test = 100, 100 # 训练和测试数据集大小
true_w = np.zeros(max_degree) # 分配大量的空间
true_w[0:4] = np.array([5, 1.2, -3.4, 5.6]) # 注意true_w.shape = (max_degree,),只是后面16个都为0
features = np.random.normal(size=(n_train + n_test, 1))
np.random.shuffle(features) # features.shape = (n_train + n_test, 1)
# 使用 numpy.power 函数将 features 的每个元素分别与 np.arange(max_degree)(从0到max_degree-1的数组)进行幂运算。
poly_features = np.power(features, np.arange(max_degree).reshape(1, -1)) # ploy_feature.shape = (n_train + n_test, max_degree)
for i in range(max_degree):
poly_features[:, i] /= math.gamma(i + 1) # gamma(n)=(n-1)! 第i列数据除以i的阶乘
# labels的维度:(n_train+n_test,)
labels = np.dot(poly_features, true_w) # labels.shape = (n_train + n_test,) 通过将多项式特征 poly_features 与真实系数 true_w 相乘得到标签。
labels += np.random.normal(scale=0.1, size=labels.shape) # 向标签数据添加服从正态分布的噪声# 下面4个分别对应: w x x^n/n! y=w*(x^n/n!)
true_w, features, poly_features, labels = [torch.tensor(x, dtype= # 多项式:"polynomial"
torch.float32) for x in [true_w, features, poly_features, labels]] # for训练遍历列表[true_w, features, poly_features, labels]中的4个元素,将NumPy ndarray转换为tensor2、对模型进行训练和测试
???????首先让我们实现一个函数来评估模型在给定数据集上的损失。
def evaluate_loss(net, data_iter, loss):
"""评估给定数据集上模型的损失"""
metric = d2l.Accumulator(2) # 损失的总和,样本数量
for X, y in data_iter:
out = net(X)
y = y.reshape(out.shape)
l = loss(out, y)
metric.add(l.sum(), l.numel())
return metric[0] / metric[1]现在定义训练函数。
def train(train_features, test_features, train_labels, test_labels,
num_epochs=400):
loss = nn.MSELoss(reduction='none') # 使用均方根损失
input_shape = train_features.shape[-1] # input_shape=20
# 不设置偏置,因为我们已经在多项式中实现了它
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(input_shape, 1, bias=False))
batch_size = min(10, train_labels.shape[0])
train_iter = d2l.load_array((train_features, train_labels.reshape(-1,1)),
batch_size)
test_iter = d2l.load_array((test_features, test_labels.reshape(-1,1)),
batch_size, is_train=False)
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.01)
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', ylabel='loss', yscale='log',
xlim=[1, num_epochs], ylim=[1e-3, 1e2],
legend=['train', 'test'])
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
d2l.train_epoch_ch3(net, train_iter, loss, trainer)
if epoch == 0 or (epoch + 1) % 20 == 0:
animator.add(epoch + 1, (evaluate_loss(net, train_iter, loss),
evaluate_loss(net, test_iter, loss)))
print('weight:', net[0].weight.data.numpy())3、拟合结果分析
(1)三阶多项式函数拟合(正常)
???????我们将首先使用三阶多项式函数,它与数据生成函数的阶数相同。结果表明,该模型能有效降低训练损失和测试损失。学习到的模型参数也接近真实值。
# 从多项式特征中选择前4个维度,即1,x,x^2/2!,x^3/3!
# poly_features每行的前4个值是线性相关的,因为此时已经进行了幂运算、阶乘运算,就差乘true_w了,也正因如此前面才能使用单线性层nn.Linear拟合
train(poly_features[:n_train, :4], poly_features[n_train:, :4],
labels[:n_train], labels[n_train:])
(2)线性函数拟合(欠拟合)
???????让我们再看看线性函数拟合,减少该模型的训练损失相对困难。在最后一个迭代周期完成后,训练损失仍然很高。当用来拟合非线性模式(如这里的三阶多项式函数)时,线性模型容易欠拟合。不过这里的欠拟合是因为数据没给全(因为数据没给全而导致特征不明显),前4项weight的后面2项模型学不到,人为强制使模型欠拟合了,而不是模型容量不够。
# 从多项式特征中选择前2个维度,即1和x
train(poly_features[:n_train, :2], poly_features[n_train:, :2],
labels[:n_train], labels[n_train:])
(3)高阶多项式函数拟合(过拟合)?
???????现在,让我们尝试使用一个阶数过高的多项式来训练模型。在这种情况下,没有足够的数据用于学到高阶系数应该具有接近于零的值。因此,这个过于复杂的模型会轻易受到训练数据中噪声的影响。虽然训练损失可以有效地降低,但测试损失仍然很高。结果表明,复杂模型对数据造成了过拟合。其实就是给的数据太多(后面16项多余了),模型把不该学的(后面16项的weight)给学到了,于是就造成了过拟合。
# 从多项式特征中选取所有维度
train(poly_features[:n_train, :], poly_features[n_train:, :],
labels[:n_train], labels[n_train:], num_epochs=1500)
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 帝伯朗×实在RPA丨私域管理提效10倍,实现客户体验和渠道销量双提升
- Kubernetes 100个常用命令
- 最常见的SQL报错注入函数(floor、updatexml、extractvalue)及payload总结
- 民安智库(第三方市场调查公司)-如何提升医院体检中心客户满意度?
- tamarin manual总结笔记5(使用流程的模型规格)
- 用数据结构python写大数计算器
- 【操作系统】快速做题向 如果在限制为两道的多道批处理系统,有N个作业进入系统,作业调度采用XXX算法,进程调度采用XXX算法 题型解法
- 多次降价背后,良品铺子在进行怎样的“大转身”?
- Ubuntu server 22.04 LTS下安装ERPNEXT V15
- 微信小程序中音频播放