鸿蒙开发-UI-布局-层叠布局
前言
上文详细学习了线性布局,学习了线性容器内子元素在主轴以及交叉轴上的排列方式,子元素自适应相关的知识点,本文继续学习层叠布局。
一、基本概念
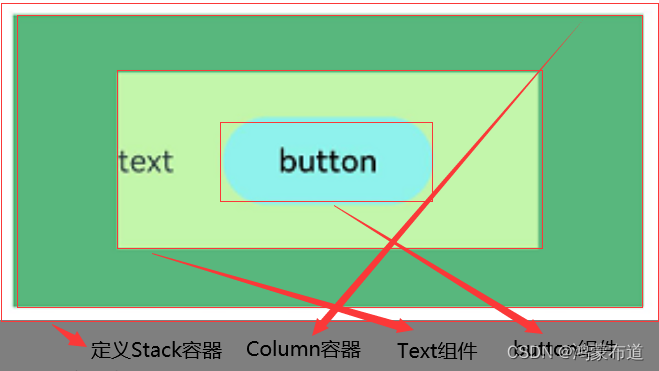
层叠布局(StackLayout)用于在屏幕上预留一块区域来显示组件中的元素,提供元素可以重叠的布局,层叠布局通过Stack容器组件实现位置的固定定位与层叠。
Stack组件为容器组件,容器内可包含各种子组件。其中子组件默认进行居中堆叠。子元素被约束在Stack下,进行自己的样式定义以及排列
Column(){
Stack() {
Column(){}.width('90%').height('100%').backgroundColor('#ff58b87c')
Text('text').width('60%').height('60%').backgroundColor('#ffc3f6aa')
Button('button').width('30%').height('30%').backgroundColor('#ff8ff3eb').fontColor('#000')
}.width('100%').height(150).margin({ top: 50 })
}Stack容器中定义三个子组件Column、Text、Button,子组件默认是居中堆叠,兄弟组件堆叠次序默认根据组件定义顺序,后面定义组件堆叠在前面定义的组件上。如果要控制兄弟组件堆叠次序可以通过Z序控制。
二、对齐方式
Stack组件通过alignContent参数实现位置的相对移动,支持九种对齐方式

三、Z序控制
Stack容器中兄弟组件显示层级关系可以通过Z序控制的zIndex属性改变。zIndex值越大,显示层级越高,即zIndex值大的组件会覆盖在zIndex值小的组件上方,如果后面子元素尺寸大于前面子元素尺寸,则前面子元素完全隐藏。
堆叠实例1:
Stack({ alignContent: Alignment.BottomStart }) {
Column() {
Text('Stack子元素1').textAlign(TextAlign.End).fontSize(20)
}.width(100).height(100).backgroundColor(0xffd306)
Column() {
Text('Stack子元素2').fontSize(20)
}.width(150).height(150).backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
Column() {
Text('Stack子元素3').fontSize(20)
}.width(200).height(200).backgroundColor(Color.Grey)
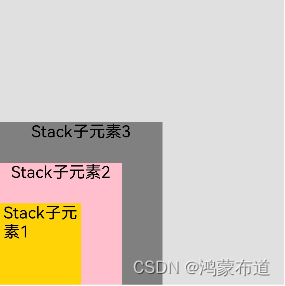
}.margin({ top: 100 }).width(350).height(350).backgroundColor(0xe0e0e0)?Alignment.BottomStart 设置对齐方式左下,Text('Stack子元素3')子元素位置最后,根据默认堆叠次序规则,会覆盖前面定义的兄弟组件,其定义的width(200).height(200),大于兄弟组件,所以呈现出来下图效果,其前面定义的兄弟组件完全被覆盖

堆叠实例2:
Stack({ alignContent: Alignment.BottomStart }) {
? Column() {
? ? Text('Stack子元素1').fontSize(20)
? }.width(100).height(100).backgroundColor(0xffd306).zIndex(2)
? Column() {
? ? Text('Stack子元素2').fontSize(20)
? }.width(150).height(150).backgroundColor(Color.Pink).zIndex(1)
? Column() {
? ? Text('Stack子元素3').fontSize(20)
? }.width(200).height(200).backgroundColor(Color.Grey)
}.margin({ top: 100 }).width(350).height(350).backgroundColor(0xe0e0e0)?Alignment.BottomStart 设置对齐方式左下,通过zIndex控制兄弟组件层叠顺序,zIndex默认0,设置越大显示层级越高,Text('Stack子元素1') > Text('Stack子元素2') >?Text('Stack子元素3')。显示顺序,Text('Stack子元素3')在最下,Text('Stack子元素1')在最上。
四、使用场景
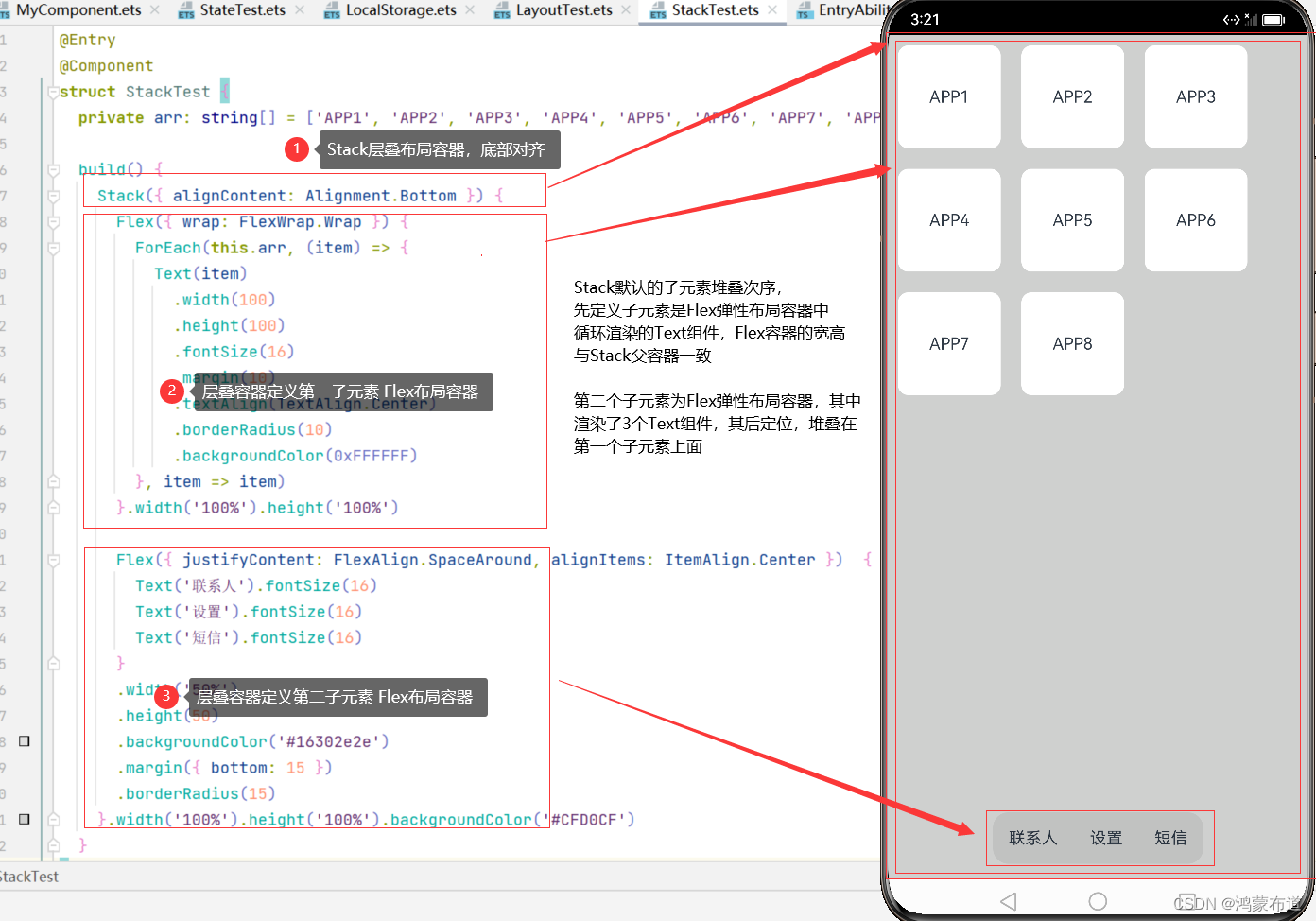
使用层叠布局快速搭建手机页面显示模型
@Entry
@Component
struct StackTest {
private arr: string[] = ['APP1', 'APP2', 'APP3', 'APP4', 'APP5', 'APP6', 'APP7', 'APP8'];
build() {
Stack({ alignContent: Alignment.Bottom }) {
Flex({ wrap: FlexWrap.Wrap }) {
ForEach(this.arr, (item) => {
Text(item)
.width(100)
.height(100)
.fontSize(16)
.margin(10)
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
.borderRadius(10)
.backgroundColor(0xFFFFFF)
}, item => item)
}.width('100%').height('100%')
Flex({ justifyContent: FlexAlign.SpaceAround, alignItems: ItemAlign.Center }) {
Text('联系人').fontSize(16)
Text('设置').fontSize(16)
Text('短信').fontSize(16)
}
.width('50%')
.height(50)
.backgroundColor('#16302e2e')
.margin({ bottom: 15 })
.borderRadius(15)
}.width('100%').height('100%').backgroundColor('#CFD0CF')
}
}
总结
本文详细学习常见布局方式-层叠布局,学习如何控制层叠布局中子元素的堆叠顺序,后面继续学习弹性布局。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 小程序 模板语法和事件绑定
- Android基于Gradle8.2的海外包框架
- Linux中禁用SELinux
- git命令删除本地和远程分支
- 一键在线获取APP公钥、包名、签名及备案信息方法介绍
- typeorm联表查询:副表json格式放到主表字段下或多个副表字段并列主表字段
- 第5章-第2节-Java里的匿名对象和构造方法
- 《整机柜服务器通用规范》由OCTC正式发布!浪潮信息牵头编制
- 神经网络实战分类与回归任务
- 教材订书季丨马上订新书,开学即迎新教材!