数据结构与算法—哈希表
发布时间:2023年12月18日
哈希表
1. 问题引出
??看一个实际需求,google公司的一个上机题:有一个公司,当有新的员工来报道时,要求将该员工的信息加入(id,性别,年龄等),当输入该员工的id时,要求查到该员工的所有信息。要求: 不使用数据库,尽量节省内存,速度越快越好=>哈希表(散列)。
2. 基本介绍
??散列表 (Hash table,也叫哈希表),是根据关键码值(Key value)而直接进行访问的数据结构。也就是说,它通过把关键码值映射到表中一个位置来访问记录,以加快查找的速度。这个映射函数叫做散列函数,存放记录的数据叫做散列表。
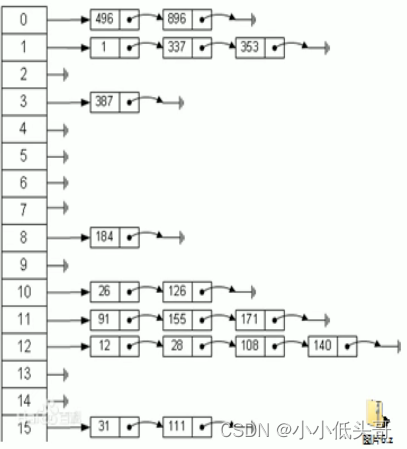
3. 应用实例
题目:有一个公司,当有新元哦概念股来报道时,就将该员工的信息加入(id,name),当输入该员工的id时,要求找到该员工的所有信息
要求:不使用数据库,速度越快越好 => 哈希表
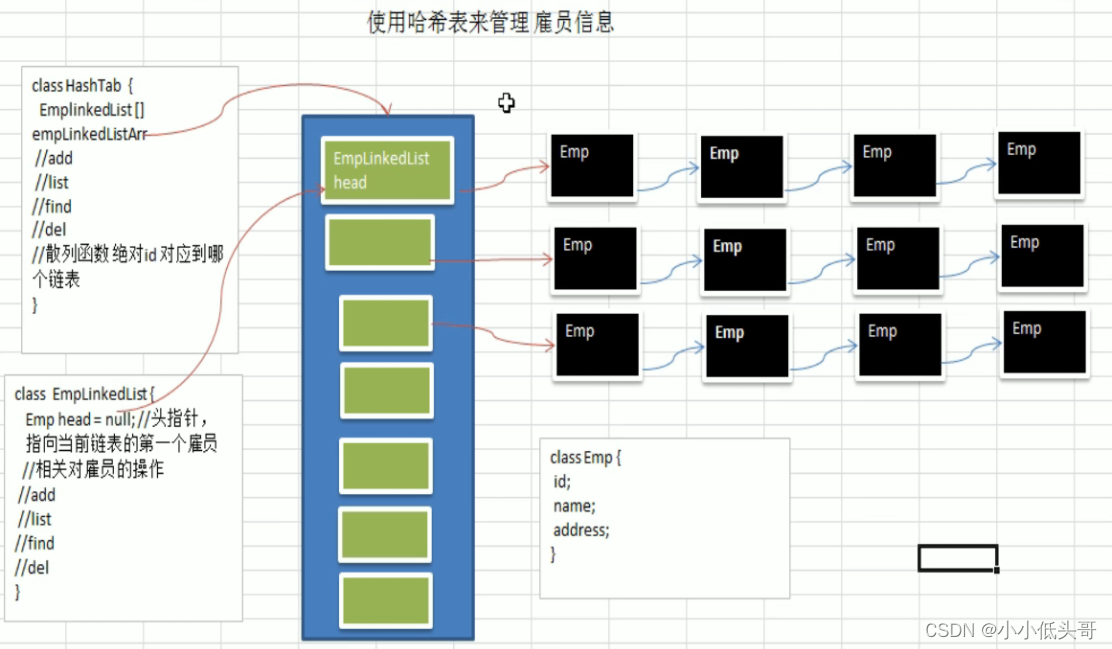
代码如下[包含 增 删 查]
class HashTab { //哈希表
//定义大小为size的EmpLinkedList数组
private int size;
private EmpLinkedList[] empLinkedLists;
public HashTab(int size) {
this.size = size;
//设置大小
empLinkedLists = new EmpLinkedList[size];
//但是注意!!!
//数组大小虽然决定了 但是数组里的元素默认初始化为null
//即每个EmpLinkedList = null;
//需要初始化
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
empLinkedLists[i] = new EmpLinkedList();//初始化每个元素链表
}
}
public void findEmpById(int no) { //通过Id找对象
//empLinkedLists[hashFun(no)] 找到对应的链表
//.find(no) 在对应的链表中找相应的节点
empLinkedLists[hashFun(no)].find(no);
}
public void delete(int no){ //根据编号删除对应元素
//empLinkedLists[hashFun(emp.getId())] 找到对应的链表
//.delete在对应的链表中删除节点
empLinkedLists[hashFun(no)].delete(no);
}
public void add(Emp emp) { //添加元素到哈希表中
//empLinkedLists[hashFun(emp.getId())] 找到对应的链表
//.add添加对象到对应的链表中
empLinkedLists[hashFun(emp.getId())].add(emp);
}
public void list() { //显示哈希表中的数据
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
empLinkedLists[i].list(i); //依次显示每一条链表的数据
}
}
public int hashFun(int no) { //散列函数 用来决定数据放哪一个链表
return no % size; //返回编号对size的取模
}
}
class EmpLinkedList { //定义Emp链表
private Emp head = null; //定义头节点
public void add(Emp emp) { //添加新员工 直接添加到最后一个位置
if (head == null) { //如果头节点是空的
head = emp; //直接把头节点指向次员工
return;
}
Emp temp = head;
while (temp.getNext() != null) {//遍历到最后一个节点退出循环
temp = temp.getNext(); //继续下一个节点
}
//退出循环后 此节点指向最后一个节点
temp.setNext(emp); //将最后一个节点next指向新的节点
}
public void delete(int no) { //根据no号删除对应的节点
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("此处无垠三变量");
return;
} else if (head.getId() == no) { //如果头节点就是要删除的对象
head = head.getNext(); //则直接头节点后移就行了
return;
}
Emp temp = head;
while (temp.getNext() != null) {
if (temp.getNext().getId() == no) { //如果下一个节点是删除的节点
temp.setNext(temp.getNext().getNext()); //将temp的next指向后面第二位
break;
}
temp = temp.getNext(); //否则后移 继续判断下一位
}
}
public void find(int no) { //查找对应no是否存在
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("目标不存在");
return;
}
Emp temp = head;
while (temp != null) {//遍历每一个节点
if (temp.getId() == no) { //说明找到了对应的目标
System.out.println(temp); //输出对应的信息
return;
}
temp = temp.getNext(); //继续下一个节点
}
//正常退出循环后 说明目标不存在
System.out.println("目标不存在");
}
public void list(int no) { //显示链表
if (head == null) { //说明为空
System.out.println("第" + (no + 1) + "条链表为空");
return;
}
Emp temp = head;
System.out.print("第" + (no + 1) + "条链表:");
while (temp != null) {//遍历每一个节点
System.out.print(temp + " ");
temp = temp.getNext(); //继续下一个节点
}
System.out.println();
}
}
class Emp { //定义Emp节点
private int Id; //编号
private String name; //名字
private Emp next; //指向下一个节点 默认为null
public Emp(int id, String name) { //构造器
Id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public Emp getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Emp next) {
this.next = next;
}
public int getId() {
return Id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
Id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "{" +
"Id=" + Id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", next=" + (next == null ? null : next.hashCode()) +
'}';
}
}
其实整个代码不难理解,就是在链表的基础上,创建了多个链表进行管理。看韩老师敲一遍代码,自己就能敲出来了。
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_49429082/article/details/135051628
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 数模学习day08-拟合算法
- C++ //练习 2.5 指出下述字面值的数据类型并说明每一组内几种字面值的区别:
- [NOIP2006 提高组] 作业调度方案(待修改)
- 如何进行继电器负载测试
- C++项目之酒店客房管理系统架构——设计模式应用场景详解(上)
- 非父子组件通信的方法
- linux信号量封装
- 万店时代新茶饮“封场围猎”,古茗赴港IPO以备战?
- Armv8-M的TrustZone技术之内存属性单元
- LC 2807. 在链表中插入最大公约数