【MySQL表的增删改查】
目录:
前言
| 剑指offer:一年又6天 |
|---|
表的增删改查
CRUD:Create(创建), Retrieve(查找), Update(修改), Delete(删除).
Create(创建)
1.插入
语法:
INSERT [INTO] table_name
[(column [, column] ...)]
VALUES (value_list) [, (value_list)] ...
value_list: value, [, value] ...
插入测试
案例:
-- 建表
mysql> create table stu1(
-> id int unsigned primary key auto_increment,
-> name varchar(20) not null,
-> QQ varchar(10) unique key
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
mysql> desc stu1;
+-------+------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int(10) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | |
| QQ | varchar(10) | YES | UNI | NULL | |
+-------+------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
3 rows in set (0.01 sec)
-- 插入数据
mysql> insert into stu1 values(1, '陈平安', '1234456'); -- 全列插入 & 单行插入
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> insert stu1 values(2, '宁姚', '1234567'); -- 全列插入 & 单行插入
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into stu1(id, name, QQ) values(3, '裴钱', '422414'); -- 指定列插入 & 单行插入
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> insert into stu1(name, QQ) values('陈如初', '4224149'); -- 指定列插入 & 单行插入
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into stu1(name) values('小米粒'), ('老厨子'), ('周首席'); -- 指定列插入 & 多行插入
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from stu1;
+----+-----------+---------+
| id | name | QQ |
+----+-----------+---------+
| 1 | 陈平安 | 1234456 |
| 2 | 宁姚 | 1234567 |
| 3 | 裴钱 | 422414 |
| 4 | 陈如初 | 4224149 |
| 5 | 小米粒 | NULL | -- id自增长
| 6 | 老厨子 | NULL |
| 7 | 周首席 | NULL |
+----+-----------+---------+
7 rows in set (0.01 sec)
插入否则更新
假设现在数据量非常大,我们不知道之前有什么数据而且现在想要插入新的数据,如果和之前的数据冲突就使用现在的数据覆盖之前的数据。
mysql> insert into stu1 values(1, '陈好人', '6666666');
ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '1' for key 'PRIMARY' --- 主键冲突
语法:
INSERT ... ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE
column = value [, column = value] ...
案例:
mysql> insert into stu1 values(1, '陈好人', '6666666');
ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '1' for key 'PRIMARY'
mysql> insert into stu1 values(1, '陈好人', '6666666') on duplicate key update name='陈好人', QQ='666666'; -- 如果发生了键冲突就update更新数据
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from stu1;
+----+-----------+---------+
| id | name | QQ |
+----+-----------+---------+
| 1 | 陈好人 | 666666 | -- 更新
| 2 | 宁姚 | 1234567 |
| 3 | 裴钱 | 422414 |
| 4 | 陈如初 | 4224149 |
| 5 | 小米粒 | NULL |
| 6 | 老厨子 | NULL |
| 7 | 周首席 | NULL |
+----+-----------+---------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
受影响的行数
mysql> create table tb1( num int primary key); -- 测试表
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.06 sec)
mysql> insert into tb1(num) values(1) on duplicate key update num=1;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) -- 1
mysql> select * from tb1;
+-----+
| num |
+-----+
| 1 |
+-----+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into tb1(num) values(1) on duplicate key update num=1;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) -- 0
mysql> select * from tb1;
+-----+
| num |
+-----+
| 1 |
+-----+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into tb1(num) values(1) on duplicate key update num=100;
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.01 sec) -- 2
mysql> select * from tb1;
+-----+
| num |
+-----+
| 100 |
+-----+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-- 0 row affected: 表中有冲突数据,但冲突数据的值和 update 的值相等
-- 1 row affected: 表中没有冲突数据,数据被插入
-- 2 row affected: 表中有冲突数据,并且数据已经被更新
mysql> insert into tb1(num) values(2) on duplicate key update num=200;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
-- ROW_COUNT()函数查看受影响的行数
mysql> select row_count();
+-------------+
| row_count() |
+-------------+
| 1 |
+-------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
2.替换
语法:
REPLACE INTO tablename[(cloumn1, cloumn2...)] values (...);
案例:
mysql> replace into stu1(id, name) values(1, '陈迹');
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.00 sec) -- 2
mysql> replace into stu1(id, name) values(10, '陈灵均');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) -- 1
mysql> select * from stu1;
+----+-----------+---------+
| id | name | QQ |
+----+-----------+---------+
| 1 | 陈迹 | NULL | -- 替换:没有插入QQ则默认为null
| 2 | 宁姚 | 1234567 |
| 3 | 裴钱 | 422414 |
| 4 | 陈如初 | 4224149 |
| 5 | 小米粒 | NULL |
| 6 | 老厨子 | NULL |
| 7 | 周首席 | NULL |
| 10 | 陈灵均 | NULL |
+----+-----------+---------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 1 row affected: 表中没有冲突数据,数据被插入
-- 2 row affected: 表中有冲突数据,删除后重新插入
结论:replace功能上等同于上面insert的on duplicate key,不过字数更少。
Retrieve(查找)
SELECT
[DISTINCT] {* | {column [, column] ...}
FROM table_name
[WHERE ...]
[ORDER BY column [ASC | DESC], ...]
[LIMIT ...]
案例:
-- 创建表结构
mysql> create table grade(
-> id int unsigned primary key auto_increment,
-> name varchar(20) not null comment '同学姓名',
-> chinese float default 0.0 comment '语文成绩',
-> math float default 0.0 comment '数学成绩',
-> english float default 0.0 comment '英语成绩'
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
-- 插入数据
mysql> insert into grade(name, chinese, math, english) values
-> ('齐静春', 67, 98, 56),
-> ('陈平安', 87, 78, 77),
-> ('魏山君', 88, 98, 90),
-> ('陆沉', 82, 84, 67),
-> ('刘羡阳', 55, 85, 45),
-> ('陈迹', 70, 65, 30),
-> ('郑大风', 75, 65, 30);
Query OK, 7 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 7 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
1.SELECT 列
全列查找
-- 通常情况下不建议使用 * 进行全列查询
-- 1. 查询的列越多,意味着需要传输的数据量越大;
-- 2. 可能会影响到索引的使用。(索引待后面文章讲解)
mysql> select * from grade;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 1 | 齐静春 | 67 | 98 | 56 |
| 2 | 陈平安 | 87 | 78 | 77 |
| 3 | 魏山君 | 88 | 98 | 90 |
| 4 | 陆沉 | 82 | 84 | 67 |
| 5 | 刘羡阳 | 55 | 85 | 45 |
| 6 | 陈迹 | 70 | 65 | 30 |
| 7 | 郑大风 | 75 | 65 | 30 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
指定列查找
-- 指定列的顺序不必按定义表的顺序来
mysql> select name, math from grade; -- 查看学生的姓名与数学成绩
+-----------+------+
| name | math |
+-----------+------+
| 齐静春 | 98 |
| 陈平安 | 78 |
| 魏山君 | 98 |
| 陆沉 | 84 |
| 刘羡阳 | 85 |
| 陈迹 | 65 |
| 郑大风 | 65 |
+-----------+------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select chinese, math, english, name from grade;
+---------+------+---------+-----------+
| chinese | math | english | name |
+---------+------+---------+-----------+
| 67 | 98 | 56 | 齐静春 |
| 87 | 78 | 77 | 陈平安 |
| 88 | 98 | 90 | 魏山君 |
| 82 | 84 | 67 | 陆沉 |
| 55 | 85 | 45 | 刘羡阳 |
| 70 | 65 | 30 | 陈迹 |
| 75 | 65 | 30 | 郑大风 |
+---------+------+---------+-----------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
查询字段为表达式
-- 表达式不包含字段
mysql> select name, math, 1 from grade; -- 1, 1+1, 'hello'等带有结果导向的都是表达式
+-----------+------+---+
| name | math | 1 |
+-----------+------+---+
| 齐静春 | 98 | 1 |
| 陈平安 | 78 | 1 |
| 魏山君 | 98 | 1 |
| 陆沉 | 84 | 1 |
| 刘羡阳 | 85 | 1 |
| 陈迹 | 65 | 1 |
| 郑大风 | 65 | 1 |
+-----------+------+---+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 表达式包含一个字段
mysql> select name, math, math+10 from grade;
+-----------+------+---------+
| name | math | math+10 |
+-----------+------+---------+
| 齐静春 | 98 | 108 |
| 陈平安 | 78 | 88 |
| 魏山君 | 98 | 108 |
| 陆沉 | 84 | 94 |
| 刘羡阳 | 85 | 95 |
| 陈迹 | 65 | 75 |
| 郑大风 | 65 | 75 |
+-----------+------+---------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 表达式包含多个字段
mysql> select name, chinese+math+english from grade;
+-----------+----------------------+
| name | chinese+math+english |
+-----------+----------------------+
| 齐静春 | 221 |
| 陈平安 | 242 |
| 魏山君 | 276 |
| 陆沉 | 233 |
| 刘羡阳 | 185 |
| 陈迹 | 165 |
| 郑大风 | 170 |
+-----------+----------------------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
字段重命名
语法:
SELECT COLUMN [AS] alias_name FROM tablename;
案例:
mysql> select name, chinese+math+english as total from grade;
+-----------+-------+
| name | total |
+-----------+-------+
| 齐静春 | 221 |
| 陈平安 | 242 |
| 魏山君 | 276 |
| 陆沉 | 233 |
| 刘羡阳 | 185 |
| 陈迹 | 165 |
| 郑大风 | 170 |
+-----------+-------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select name, chinese+math+english total from grade;
+-----------+-------+
| name | total |
+-----------+-------+
| 齐静春 | 221 |
| 陈平安 | 242 |
| 魏山君 | 276 |
| 陆沉 | 233 |
| 刘羡阳 | 185 |
| 陈迹 | 165 |
| 郑大风 | 170 |
+-----------+-------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
结果去重
-- 去重前
mysql> select math from grade;
+------+
| math |
+------+
| 98 |
| 78 |
| 98 |
| 84 |
| 85 |
| 65 |
| 65 |
+------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 去重后
mysql> select distinct math from grade;
+------+
| math |
+------+
| 98 |
| 78 |
| 84 |
| 85 |
| 65 |
+------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
2.WHERE条件
比较运算符:
| 运算符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| >, >=, <, <= | 大于,大于等于,小于,小于等于 |
| = | 等于,NULL不安全, 比如 NULL=NULL 结果为NULL |
| <=> | 等于,NULL安全,比如NULL<=>NULL结果为TRUE(1) |
| != , <> | 不等于 |
| IS NULL | 为空值,NULL的比较时更推荐 |
| IS NOT NULL | 不为空值,NULL的比较时更推荐 |
| BETWEEN num1 AND num2 | 范围匹配:[num1, num2], 如果 num1<= value <= num2,返回 TRUE(1) |
| IN(option, …) | 在给定的值列表中 |
| LIKE | 模糊匹配,‘%’ 匹配任意多个字符(包括零个), '_'匹配一个字符 |
逻辑运算符:
| 运算符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| AND | 多个条件必须全部为TRUE(1) ,结果才为TRUE(1) |
| OR | 任意一个条件为TRUE(1),结果就为TRUE(1) |
| NOT | 条件为TRUE(1),结果为FALSE(1) |
这些运算符可以在SELECT语句的WHERE子句中使用,用于对表中的数据进行条件判断和过滤。
案例:
英语不及格的同学及英语成绩(<60)
mysql> select name, english from grade where english <= 60;
+-----------+---------+
| name | english |
+-----------+---------+
| 齐静春 | 56 |
| 刘羡阳 | 45 |
| 陈迹 | 30 |
| 郑大风 | 30 |
+-----------+---------+
4 rows in set (0.01 sec)
语文成绩在 [80, 90] 分的同学及语文成绩
-- 使用and连接
mysql> select name, chinese from grade where chinese>=80 and chinese<=90;
+-----------+---------+
| name | chinese |
+-----------+---------+
| 陈平安 | 87 |
| 魏山君 | 88 |
| 陆沉 | 82 |
+-----------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 使用 between ... and ... 条件
mysql> select name, chinese from grade where chinese between 80 and 90;
+-----------+---------+
| name | chinese |
+-----------+---------+
| 陈平安 | 87 |
| 魏山君 | 88 |
| 陆沉 | 82 |
+-----------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
数学成绩是 58 或者 59 或者 98 或者 99 分的同学及数学成绩
-- 使用 or 连接
mysql> select name, math from grade where math=58 or math=59 or math=98 or math=99;
+-----------+------+
| name | math |
+-----------+------+
| 齐静春 | 98 |
| 魏山君 | 98 |
+-----------+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 使用 in (option, ...) 条件
mysql> select name, math from grade where math in(58, 59, 98, 99);
+-----------+------+
| name | math |
+-----------+------+
| 齐静春 | 98 |
| 魏山君 | 98 |
+-----------+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
姓陈的同学 及 陈某同学
-- % 匹配任意多个(包括 0 个)任意字符
mysql> select name from grade where name like '陈%';
+-----------+
| name |
+-----------+
| 陈平安 |
| 陈迹 |
+-----------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- _ 匹配严格的一个任意字符
mysql> select name from grade where name like '陈_';
+--------+
| name |
+--------+
| 陈迹 |
+--------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
语文成绩好于英语成绩的同学
-- WHERE 条件中比较运算符两侧都是字段
mysql> select name, chinese, english from grade where chinese > english;
+-----------+---------+---------+
| name | chinese | english |
+-----------+---------+---------+
| 齐静春 | 67 | 56 |
| 陈平安 | 87 | 77 |
| 陆沉 | 82 | 67 |
| 刘羡阳 | 55 | 45 |
| 陈迹 | 70 | 30 |
| 郑大风 | 75 | 30 |
+-----------+---------+---------+
6 rows in set (0.01 sec)
总分在 200 分以下的同学
mysql> select name, chinese+math+english as total from grade where chinese+math+english<200;
+-----------+-------+
| name | total |
+-----------+-------+
| 刘羡阳 | 185 |
| 陈迹 | 165 |
| 郑大风 | 170 |
+-----------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
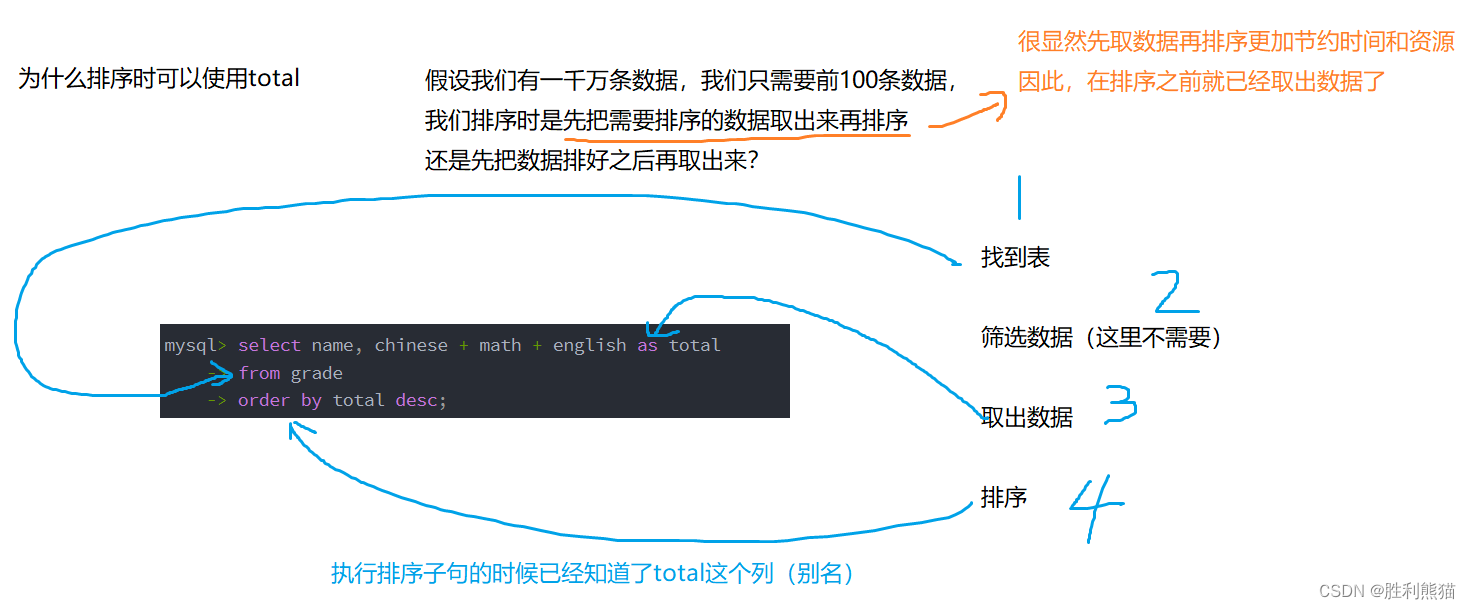
拓展1:语句的执行顺序(重要,下面还会涉及)
mysql> select name, chinese+math+english as total from grade where total <200;
ERROR 1054 (42S22): Unknown column 'total' in 'where clause'
-- 因此 WHERE 条件中使用表达式
-- 别名不能用在 WHERE 条件中
mysql> select name, chinese + math + english 总分
-> from grade
-> where chinese + math + english < 200;
+-----------+--------+
| name | 总分 |
+-----------+--------+
| 刘羡阳 | 185 |
| 陈迹 | 165 |
| 郑大风 | 170 |
+-----------+--------+
3 rows in set (0.01 sec)
拓展2:MySQL查询是:边查询边显示结果
类似于C语言的for循环遍历整张表,假设grade表中有一百万条数据,where子句就会执行一百万次,假设where判断成立十万次,则select执行十万次。
语文成绩 > 80 并且不姓陈的同学
-- 语文成绩 > 80
mysql> select name, chinese from grade where chinese > 80;
+-----------+---------+
| name | chinese |
+-----------+---------+
| 陈平安 | 87 |
| 魏山君 | 88 |
| 陆沉 | 82 |
+-----------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 姓陈的同学
mysql> select name, chinese from grade where name like '陈%';
+-----------+---------+
| name | chinese |
+-----------+---------+
| 陈平安 | 87 |
| 陈迹 | 70 |
+-----------+---------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 语文成绩 > 80 并且不姓陈的同学
mysql> select name, chinese from grade where chinese > 80 and name not like '陈%';
+-----------+---------+
| name | chinese |
+-----------+---------+
| 魏山君 | 88 |
| 陆沉 | 82 |
+-----------+---------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
陈某同学,否则要求总成绩 > 200 并且 语文成绩 < 数学成绩 并且 英语成绩 > 80
-- 陈某同学
mysql> select name, chinese, math, english from grade
-> where name like '陈_';
+--------+---------+------+---------+
| name | chinese | math | english |
+--------+---------+------+---------+
| 陈迹 | 70 | 65 | 30 |
+--------+---------+------+---------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-- 总成绩 > 200 并且 语文成绩 < 数学成绩 并且 英语成绩 > 80
mysql> select name, chinese, math, english from grade
-> where chinese + math + english > 200 and
-> chinese < math and
-> english > 80;
+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| name | chinese | math | english |
+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 魏山君 | 88 | 98 | 90 |
+-----------+---------+------+---------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
-- 陈某同学,否则要求总成绩 > 200 并且 语文成绩 < 数学成绩 并且 英语成绩 > 80
mysql> select name, chinese, math, english from grade
-> where name like '陈_' or -- 小陈父亲是校长(开玩笑)
-> (chinese + math + english > 200 and chinese < math and english > 80); -- 三个条件合在一起算一个,可以用括号括起来
+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| name | chinese | math | english |
+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 魏山君 | 88 | 98 | 90 |
| 陈迹 | 70 | 65 | 30 |
+-----------+---------+------+---------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
NULL 的查询
-- null使用 = 比较不安全
mysql> select null = null, null = 0, 0 = 0;
+-------------+----------+-------+
| null = null | null = 0 | 0 = 0 |
+-------------+----------+-------+
| NULL | NULL | 1 |
+-------------+----------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-- 使用 <=> 与 is null
mysql> select null <=> null, null is null, null <=> 0;
+---------------+--------------+------------+
| null <=> null | null is null | null <=> 0 |
+---------------+--------------+------------+
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
+---------------+--------------+------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-- 创建测试表
mysql> select * from test_null;
+------+--------+
| id | name |
+------+--------+
| 1 | 张三 |
| NULL | 李四 |
| 2 | NULL |
| NULL | NULL |
+------+--------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from test_null where id is null;
+------+--------+
| id | name |
+------+--------+
| NULL | 李四 |
| NULL | NULL |
+------+--------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from test_null where id is not null;
+------+--------+
| id | name |
+------+--------+
| 1 | 张三 |
| 2 | NULL |
+------+--------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from test_null where id is not null and name is not null;
+------+--------+
| id | name |
+------+--------+
| 1 | 张三 |
+------+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
3.结果排序
语法:
-- ASC 升序(ascending)
-- DESC 降序(descending)
SELECT ... FROM table_name [WHERE ...]
ORDER BY column [ASC|DESC], [...];
注意:没有 ORDER BY 子句的查询,返回的顺序是未定义的,永远不要依赖这个顺序
案例:
同学及数学成绩,按数学成绩升序显示
mysql> select name, math from grade order by math asc;
+-----------+------+
| name | math |
+-----------+------+
| 陈迹 | 65 |
| 郑大风 | 65 |
| 陈平安 | 78 |
| 陆沉 | 84 |
| 刘羡阳 | 85 |
| 齐静春 | 98 |
| 魏山君 | 98 |
+-----------+------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 默认升序排列,不过还是推荐显示写出来
mysql> select name, math from grade order by math;
+-----------+------+
| name | math |
+-----------+------+
| 陈迹 | 65 |
| 郑大风 | 65 |
| 陈平安 | 78 |
| 陆沉 | 84 |
| 刘羡阳 | 85 |
| 齐静春 | 98 |
| 魏山君 | 98 |
+-----------+------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
带有null的排序
-- NULL 视为比任何值都小,升序出现在最上面
mysql> select * from test_null order by id asc;
+------+--------+
| id | name |
+------+--------+
| NULL | 李四 |
| NULL | NULL |
| 1 | 张三 |
| 2 | NULL |
+------+--------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- NULL 视为比任何值都小,降序出现在最下面
mysql> select * from test_null order by id desc;
+------+--------+
| id | name |
+------+--------+
| 2 | NULL |
| 1 | 张三 |
| NULL | 李四 |
| NULL | NULL |
+------+--------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
查询同学各门成绩,依次按 数学降序,英语升序,语文升序的方式显示
-- 优先级逐次递减:先按数学降序排序,数学成绩相等的情况下按照英语升序排序,数学和英语都相等的情况下按照语文升序排序
mysql> select name, chinese, math, english from grade
-> order by math desc, english asc, chinese asc;
+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| name | chinese | math | english |
+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 齐静春 | 67 | 98 | 56 |
| 魏山君 | 88 | 98 | 90 |
| 刘羡阳 | 55 | 85 | 45 |
| 陆沉 | 82 | 84 | 67 |
| 陈平安 | 87 | 78 | 77 |
| 陈迹 | 70 | 65 | 30 |
| 郑大风 | 75 | 65 | 30 |
+-----------+---------+------+---------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
查询同学及总分,由高到低
mysql> select name, chinese + math + english as total
-> from grade
-> order by chinese + math + english desc;
+-----------+-------+
| name | total |
+-----------+-------+
| 魏山君 | 276 |
| 陈平安 | 242 |
| 陆沉 | 233 |
| 齐静春 | 221 |
| 刘羡阳 | 185 |
| 郑大风 | 170 |
| 陈迹 | 165 |
+-----------+-------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select name, chinese + math + english as total
-> from grade
-> order by total desc; -- 注意注意注意
+-----------+-------+
| name | total |
+-----------+-------+
| 魏山君 | 276 |
| 陈平安 | 242 |
| 陆沉 | 233 |
| 齐静春 | 221 |
| 刘羡阳 | 185 |
| 郑大风 | 170 |
| 陈迹 | 165 |
+-----------+-------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
查询姓陈的同学或者姓魏的同学数学成绩,结果按数学成绩由高到低显示
mysql> select name, math from grade
-> where name like '陈%' or name like '魏%'
-> order by math desc;
+-----------+------+
| name | math |
+-----------+------+
| 魏山君 | 98 |
| 陈平安 | 78 |
| 陈迹 | 65 |
+-----------+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
4.筛选分页结果
语法:
-- 起始下标为 0
-- 从 s 开始,筛选 n 条结果
SELECT ... FROM table_name [WHERE ...] [ORDER BY ...] LIMIT s, n;
-- 从 0 开始,筛选 n 条结果
SELECT ... FROM table_name [WHERE ...] [order by ...] limit n;
-- 从 s 开始,筛选 n 条结果,比第二种用法更明确,建议使用
SELECT ... FROM table_name [WHERE ...] [ORDER BY ...] LIMIT n OFFSET s;
建议:对未知表进行查询时,最好加一条 LIMIT 1,避免因为表中数据过大,查询全表数据导致数据库卡死
按 id 进行分页,每页 3 条记录,分别显示 第 1、2、3 页
-- 从 0 开始查询 3 行 (这个0你可以理解为下标也可以理解为相对于第一行的偏移量)
mysql> select * from grade limit 3;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 1 | 齐静春 | 67 | 98 | 56 |
| 2 | 陈平安 | 87 | 78 | 77 |
| 3 | 魏山君 | 88 | 98 | 90 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 从 3 开始查询 3 行
mysql> select * from grade limit 3,3;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 4 | 陆沉 | 82 | 84 | 67 |
| 5 | 刘羡阳 | 55 | 85 | 45 |
| 6 | 陈迹 | 70 | 65 | 30 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 从 6 开始查询 3 行
mysql> select * from grade limit 6,3;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 7 | 郑大风 | 75 | 65 | 30 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-- 从 0 开始 查询 5 行
mysql> select * from grade limit 5 offset 0;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 1 | 齐静春 | 67 | 98 | 56 |
| 2 | 陈平安 | 87 | 78 | 77 |
| 3 | 魏山君 | 88 | 98 | 90 |
| 4 | 陆沉 | 82 | 84 | 67 |
| 5 | 刘羡阳 | 55 | 85 | 45 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Update(修改)
语法:
UPDATE table_name SET column1= expr[, colun2=expr,...]
[WHERE ...] [ORDER BY ...] [LIMIT ...];
案例:
将陈平安同学的数学成绩变更为 80 分
-- 查看原数据
mysql> select name, math from grade where name = '陈平安';
+-----------+------+
| name | math |
+-----------+------+
| 陈平安 | 78 |
+-----------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-- 更新数据
mysql> update grade set math = 80 where name = '陈平安';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.02 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
-- 查看更新后的数据
mysql> select name, math from grade where name = '陈平安';
+-----------+------+
| name | math |
+-----------+------+
| 陈平安 | 80 |
+-----------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
将刘羡阳同学的数学成绩变更为 60 分,语文成绩变更为 70 分
mysql> select name, math, chinese from grade where name = '刘羡阳';
+-----------+------+---------+
| name | math | chinese |
+-----------+------+---------+
| 刘羡阳 | 85 | 55 |
+-----------+------+---------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-- 一次修改多列,逗号分割
mysql> update grade set math = 60, chinese = 70
-> where name = '刘羡阳';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
mysql> select name, math, chinese from grade where name = '刘羡阳';
+-----------+------+---------+
| name | math | chinese |
+-----------+------+---------+
| 刘羡阳 | 60 | 70 |
+-----------+------+---------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
将总成绩倒数前三的 3 位同学的数学成绩加上 30 分
mysql> select name, chinese + math + english as total from grade
-> order by total asc
-> limit 3 offset 0;
+-----------+-------+
| name | total |
+-----------+-------+
| 陈迹 | 165 |
| 郑大风 | 170 |
| 刘羡阳 | 175 |
+-----------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> update grade set math = math + 30
-> order by chinese + math + english asc
-> limit 3 offset 0;
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.01 sec)
Rows matched: 3 Changed: 3 Warnings: 0
mysql> select name, chinese + math + english as total from grade
-> order by total asc
-> limit 3 offset 0;
+-----------+-------+
| name | total |
+-----------+-------+
| 陈迹 | 195 | -- 成绩更新成功,不过他们仨还是后三名
| 郑大风 | 200 |
| 刘羡阳 | 205 |
+-----------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.01 sec)
将所有同学的语文成绩更新为原来的 2 倍
注意:更新全表的语句慎用!
-- 查看原数据
mysql> select name, chinese from grade;
+-----------+---------+
| name | chinese |
+-----------+---------+
| 齐静春 | 67 |
| 陈平安 | 87 |
| 魏山君 | 88 |
| 陆沉 | 82 |
| 刘羡阳 | 70 |
| 陈迹 | 70 |
| 郑大风 | 75 |
+-----------+---------+
7 rows in set (0.01 sec)
-- 更新数据
mysql> update grade set chinese = chinese * 2;
Query OK, 7 rows affected (0.01 sec)
Rows matched: 7 Changed: 7 Warnings: 0
-- 查看更新后数据
mysql> select name, chinese from grade;
+-----------+---------+
| name | chinese |
+-----------+---------+
| 齐静春 | 134 |
| 陈平安 | 174 |
| 魏山君 | 176 |
| 陆沉 | 164 |
| 刘羡阳 | 140 |
| 陈迹 | 140 |
| 郑大风 | 150 |
+-----------+---------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Delete(删除)
1.删除数据
语法:
DELETE FROM table_name [WHERE ...] [ORDER BY ...] [LIMIT ...];
案例:
删除陆沉同学的考试成绩
-- 查看陆沉同学的信息
mysql> select name, chinese from grade where name = '陆沉';
+--------+---------+
| name | chinese |
+--------+---------+
| 陆沉 | 164 |
+--------+---------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-- 删除陆沉同学的信息
mysql> delete from grade where name = '陆沉';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
-- 查看陆沉同学的信息是否还存在
mysql> select name, chinese from grade where name = '陆沉';
Empty set (0.00 sec)
删除整张表
-- 准备测试表
mysql> CREATE TABLE for_delete (
-> id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
-> name VARCHAR(20)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
-- 插入数据
mysql> INSERT INTO for_delete (name) VALUES ('A'), ('B'), ('C');
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.01 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
-- 查看数据
mysql> SELECT * FROM for_delete;
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 1 | A |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | C |
+----+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 删除整张表
mysql> DELETE FROM for_delete;
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> SELECT * FROM for_delete;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
-- 再次插入数据
mysql> INSERT INTO for_delete (name) VALUES ('D');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> SELECT * FROM for_delete;
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 4 | D |
+----+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-- 查看一下表结构,会有 AUTO_INCREMENT=n 项
mysql> SHOW CREATE TABLE for_delete\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: for_delete
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `for_delete` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=5 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 -- n = 5
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
删除操作只会删除表中的数据,并不会影响表的结构,并且delete删除时并不会重置auto_increment计数。
2.截断数据
语法:
TRUNCATE [TABLE] table_name;
注意:该语法慎用
- truncate只能对整表操作,不想delete可以删除部分数据;
- truncate实际上不对数据进行操作,因此比delete速度更快,但是truncate不经过事物,因此无法回滚(以后的文章会讲);
- truncate会重置auto_increment计数。
案例:
-- 创建测试表
mysql> CREATE TABLE for_truncate (
-> id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
-> name VARCHAR(20)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
-- 插入数据
mysql> INSERT INTO for_truncate (name) VALUES ('A'), ('B'), ('C');
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.01 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> SELECT * FROM for_truncate;
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 1 | A |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | C |
+----+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 截断测试表
mysql> TRUNCATE for_truncate;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
mysql> SELECT * FROM for_truncate;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
-- 再次插入数据
mysql> INSERT INTO for_truncate (name) VALUES ('D');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> SELECT * FROM for_truncate;
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 1 | D | -- AUTO_INCREMENT项被重置
+----+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-- 查看表结构
mysql> SHOW CREATE TABLE for_truncate\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: for_truncate
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `for_truncate` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=2 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
插入查询结果
语法:
INSERT INTO table_name[column...] SELECT ... ;
案例:对表中的数据进行去重(修改实际数据);
实现:将原表去重后的结果保存到新表中,使用新表替换原表。
-- 创建测试表
mysql> create table if not exists tb2(
-> id int,
-> name varchar(20)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec)
-- tb2中插入数据
mysql> insert into tb2(id, name) values(1, '张三'), (2, '李四'), (3, '王五');
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.02 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> insert into tb2(id, name) values(2, '李四'), (3, '王五');
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.01 sec)
Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from tb2;
+------+--------+
| id | name |
+------+--------+
| 1 | 张三 |
| 2 | 李四 |
| 3 | 王五 |
| 2 | 李四 |
| 3 | 王五 |
+------+--------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 创建与tb2一样的表结构(也可以show一下tb2的创建语句手动create)
mysql> create table tb3 like tb2;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec)
-- 显示结果去重
mysql> select distinct * from tb2;
+------+--------+
| id | name |
+------+--------+
| 1 | 张三 |
| 2 | 李四 |
| 3 | 王五 |
+------+--------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 插入查询结果
mysql> insert into tb3 select distinct * from tb2;
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.01 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
-- 查看tb3
mysql> select * from tb3;
+------+--------+
| id | name |
+------+--------+
| 1 | 张三 |
| 2 | 李四 |
| 3 | 王五 |
+------+--------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 修改原表表名(确定不需要可以删除)
mysql> rename table tb2 to old_tb;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
-- 使用tb3替换tb2
mysql> rename table tb3 to tb2;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
-- 去重后的tb2
mysql> select * from tb2;
+------+--------+
| id | name |
+------+--------+
| 1 | 张三 |
| 2 | 李四 |
| 3 | 王五 |
+------+--------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
聚合函数
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| COUNT([DISTINCT] expr) | 返回查询到的数据的 数量 |
| SUM([DISTINCT] expr) | 返回查询到的数据的 总和,不是数字没有意义 |
| AVG([DISTINCT] expr) | 返回查询到的数据的 平均值,不是数字没有意义 |
| MAX([DISTINCT] expr) | 返回查询到的数据的 最大值,不是数字没有意义 |
| MIN([DISTINCT] expr) | 返回查询到的数据的 最小值,不是数字没有意义 |
案例:
统计班级共有多少同学
mysql> select * from tb2;
+------+--------+
| id | name |
+------+--------+
| 1 | 张三 |
| 2 | 李四 |
| 3 | 王五 |
| NULL | 赵六 |
| NULL | 赵六 |
| NULL | 赵六 |
+------+--------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 使用 * 做统计,不受 NULL 影响
mysql> select count(*) from tb2;
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 6 |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-- 使用列作统计,null不会进行统计
mysql> select count(id) from tb2;
+-----------+
| count(id) |
+-----------+
| 3 |
+-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-- 使用任意表达式也能进行统计
mysql> select count(1) from tb2;
+----------+
| count(1) |
+----------+
| 6 |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select count(2) from tb2;
+----------+
| count(2) |
+----------+
| 6 |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-- 因为表中有多少行数据就会打印多少行表达式
mysql> select 1 from tb2;
+---+
| 1 |
+---+
| 1 |
| 1 |
| 1 |
| 1 |
| 1 |
| 1 |
+---+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
统计本次考试的数学成绩分数个数
mysql> select name, math from grade;
+-----------+------+
| name | math |
+-----------+------+
| 齐静春 | 98 |
| 陈平安 | 80 |
| 魏山君 | 98 |
| 刘羡阳 | 90 |
| 陈迹 | 95 |
| 郑大风 | 95 |
+-----------+------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select count(math) from grade;
+-------------+
| count(math) |
+-------------+
| 6 |
+-------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-- distinct :去重后统计
mysql> select count(distinct math) from grade;
+----------------------+
| count(distinct math) |
+----------------------+
| 4 |
+----------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
统计数学成绩总分
mysql> select sum(math) from grade;
+-----------+
| sum(math) |
+-----------+
| 556 |
+-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
统计平均总分
mysql> select avg(chinese + math + english) as avg_total from grade;
+-------------------+
| avg_total |
+-------------------+
| 299.6666666666667 |
+-------------------+
1 row in set (0.02 sec)
返回英语最高分
mysql> select max(english) from grade;
+--------------+
| max(english) |
+--------------+
| 90 |
+--------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
返回 > 70 分以上的数学最低分
mysql> select min(math) from grade where math > 70;
+-----------+
| min(math) |
+-----------+
| 80 |
+-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
group by子句的使用
在select中使用group by 子句可以对指定列进行分组查询
select column1, column2, .. from table group by column;
所谓分组查询就是把一张表分为不同的组,在各个组内再进行查询;
或者说是把一张表分成多张子表,在各个子表内进行查询。
-- 添加性别列
mysql> alter table grade add gander enum('男', '女') default '男' after name;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.08 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> insert into grade(name, gander, chinese, math, english) values
-> ('宁姚', '女', 99, 99, 99),
-> ('陈暖树', '女', 90, 89, 80);
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.01 sec)
Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from grade;
+----+-----------+--------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | gander | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+--------+---------+------+---------+
| 1 | 齐静春 | 男 | 134 | 98 | 56 |
| 2 | 陈平安 | 男 | 174 | 80 | 77 |
| 3 | 魏山君 | 男 | 176 | 98 | 90 |
| 5 | 刘羡阳 | 男 | 140 | 90 | 45 |
| 6 | 陈迹 | 男 | 140 | 95 | 30 |
| 7 | 郑大风 | 男 | 150 | 95 | 30 |
| 8 | 宁姚 | 女 | 99 | 99 | 99 |
| 9 | 陈暖树 | 女 | 90 | 89 | 80 |
+----+-----------+--------+---------+------+---------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
统计男生数学平均分
mysql> select avg(math) from grade where gander = '男';
+-------------------+
| avg(math) |
+-------------------+
| 92.66666666666667 |
+-------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
统计男女数学平均分
-- where子句分别查找统计
mysql> select avg(math) from grade where gander = '男';
+-------------------+
| avg(math) |
+-------------------+
| 92.66666666666667 |
+-------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select avg(math) from grade where gander = '女';
+-----------+
| avg(math) |
+-----------+
| 94 |
+-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-- 使用 group 按照性别分组进行统计
mysql> select avg(math) from grade group by gander;
+-------------------+
| avg(math) |
+-------------------+
| 92.66666666666667 |
| 94 |
+-------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 可以带上性别
mysql> select gander, avg(math) as myavg from grade group by gander;
+--------+-------------------+
| gander | myavg |
+--------+-------------------+
| 男 | 92.66666666666667 |
| 女 | 94 |
+--------+-------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 为什么不可以再带上id?
mysql> select id, gander, avg(math) as myavg from grade group by gander;
ERROR 1055 (42000): Expression #1 of SELECT list is not in GROUP BY clause and contains nonaggregated column 'db2.grade.id' which is not functionally dependent on columns in GROUP BY clause; this is incompatible with sql_mode=only_full_group_by
在MySQL中,当使用GROUP BY子句对结果进行分组时,SELECT语句中的列可以包含两种类型:聚合函数和分组列。
- 聚合函数:例如AVG、SUM、COUNT等,用于对分组后的数据进行计算,返回一个单一的结果值。
- 分组列:用于指定分组的条件,这些列的值相同的记录会被归为一组。
根据SQL的标准规定,在SELECT语句中,如果包含了分组列,那么SELECT列表中的非聚合列必须是分组列或者通过聚合函数进行计算的列。这是为了保证查询结果是明确的,每个分组只有一行结果。
显然,id列既不是分组列也不是聚合函数。
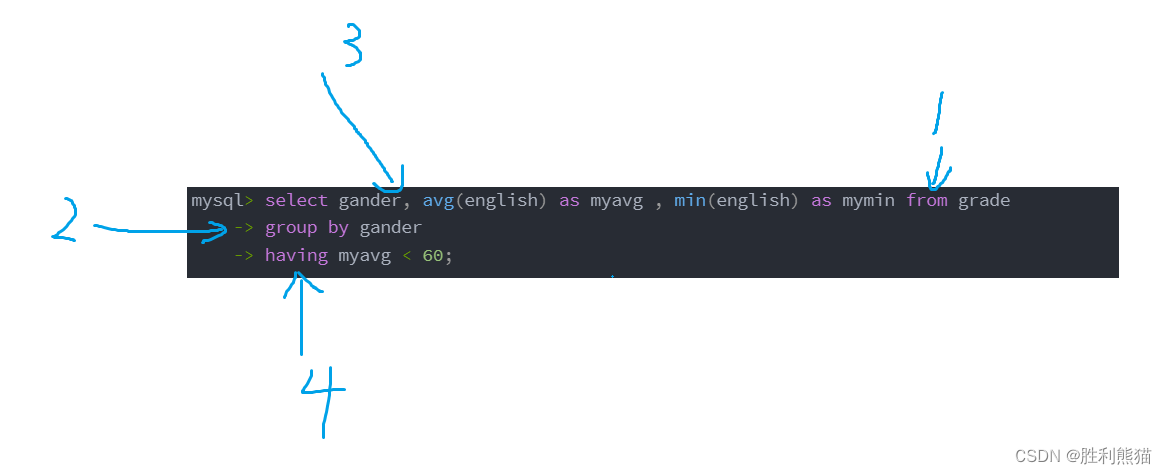
统计男女英语成绩的平均分,平均分 < 60 则显示平均分和最低分
-- 男女英语成绩的avg和min
mysql> select gander, avg(english) as myavg , min(english) as mymin from grade
-> group by gander;
+--------+--------------------+-------+
| gander | myavg | mymin |
+--------+--------------------+-------+
| 男 | 54.666666666666664 | 30 |
| 女 | 89.5 | 80 |
+--------+--------------------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- having 子句判断均值 < 60
mysql> select gander, avg(english) as myavg , min(english) as mymin from grade
-> group by gander
-> having myavg < 60;
+--------+--------------------+-------+
| gander | myavg | mymin |
+--------+--------------------+-------+
| 男 | 54.666666666666664 | 30 |
+--------+--------------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
having子句的执行顺序
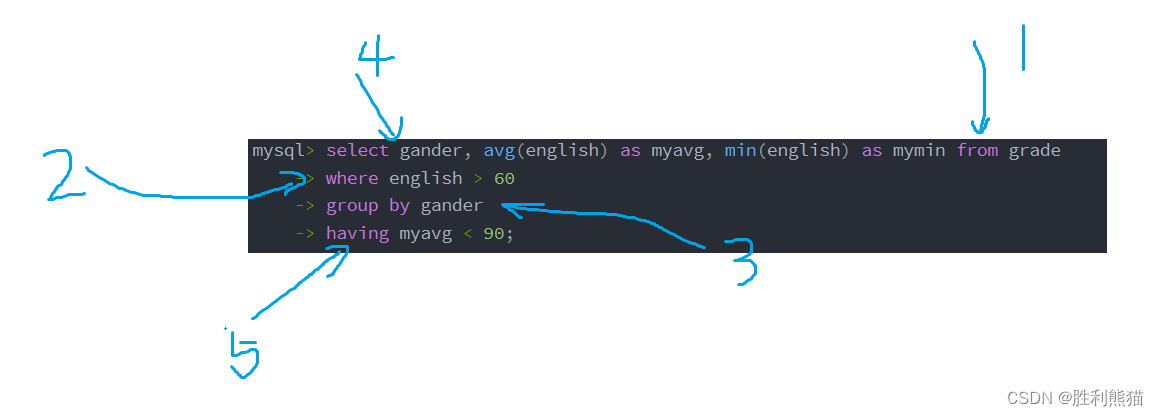
男女英语成绩 > 60 的 同学的平均值,低于90时输出他们的均值和最小值
-- 男女英语成绩 > 60 的 同学的均值和最小值
mysql> select gander, avg(english) as myavg, min(english) as mymin from grade
-> where english > 60
-> group by gander;
+--------+-------+-------+
| gander | myavg | mymin |
+--------+-------+-------+
| 男 | 83.5 | 77 |
| 女 | 89.5 | 80 |
+--------+-------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- having判断
mysql> select gander, avg(english) as myavg, min(english) as mymin from grade
-> where english > 60
-> group by gander
-> having myavg < 90;
+--------+-------+-------+
| gander | myavg | mymin |
+--------+-------+-------+
| 男 | 83.5 | 77 |
| 女 | 89.5 | 80 |
+--------+-------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
where与having都是用来筛选结果的,但是它们的应用范围和执行顺序并不相同:
上方例子中,查询的操作顺序如下:
- 通过WHERE子句筛选出满足条件(英语成绩大于60)的行。
- 根据gander列进行分组。
- 计算每个分组中英语成绩的平均值和最小值。
- 通过HAVING子句筛选出满足条件(平均值小于90)的分组。
-
WHERE子句:
- WHERE子句用于在执行SELECT语句时对表中的行进行筛选。
- WHERE子句通常出现在FROM子句之后,且在GROUP BY子句之前。
- WHERE子句可以包含任意的条件表达式,用于过滤满足条件的行。
- WHERE子句过滤的是表中的原始数据,即在进行分组之前进行过滤。
-
HAVING子句:
- HAVING子句用于在执行SELECT语句后对分组后的结果进行筛选。
- HAVING子句通常出现在GROUP BY子句之后。
- HAVING子句可以包含任意的条件表达式,用于过滤满足条件的分组。
- HAVING子句过滤的是分组后的结果,即在进行分组之后进行过滤。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!