面试算法119:最长连续序列
发布时间:2024年01月12日
题目
输入一个无序的整数数组,请计算最长的连续数值序列的长度。例如,输入数组[10,5,9,2,4,3],则最长的连续数值序列是[2,3,4,5],因此输出4。
分析
这个题目是关于整数的连续性的。如果将每个整数看成图中的一个节点,相邻的(数值大小相差1)两个整数有一条边相连,那么这些整数将形成若干子图,每个连续数值序列对应一个子图。计算最长连续序列的长度就转变成求最大子图的大小。
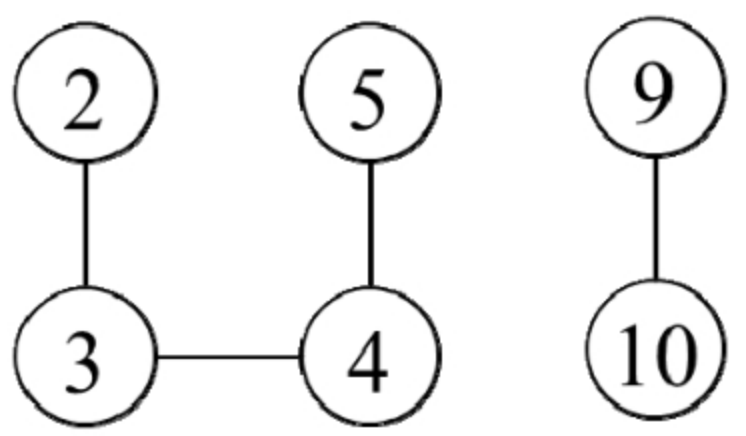
解
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {10, 5, 9, 2, 4, 3};
int result = longestConsecutive(nums);
System.out.println(result);
}
public static int longestConsecutive(int[] nums) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int num : nums) {
set.add(num);
}
int longest = 0;
while (!set.isEmpty()) {
Iterator<Integer> iter = set.iterator();
longest = Math.max(longest, bfs(set, iter.next()));
}
return longest;
}
private static int bfs(Set<Integer> set, int num) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(num);
set.remove(num);
int length = 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int i = queue.poll();
int[] neighbors = new int[] {i - 1, i + 1};
for (int neighbor : neighbors) {
if (set.contains(neighbor)) {
queue.offer(neighbor);
set.remove(neighbor);
length++;
}
}
}
return length;
}
}
分析
用哈希表fathers记录每个整数所在子集的父节点,哈希表counts用来记录以某个整数为根节点的子集中整数的数目。初始化并查集的时候每个整数的父节点都指向自己,也就是每个子集中只包含一个数字,所以哈希表counts的每个整数对应的值都被初始化为1。
接下来对于每个整数num,如果存在num-1和num+1,当它们在不同的子图中时将它们所在的子图用函数union合并,并更新合并后子集中元素的数目。
解
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {10, 5, 9, 2, 4, 3};
int result = longestConsecutive(nums);
System.out.println(result);
}
public static int longestConsecutive(int[] nums) {
Map<Integer, Integer> fathers = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> counts = new HashMap<>();
Set<Integer> all = new HashSet<>();
for (int num : nums) {
fathers.put(num, num);
counts.put(num, 1);
all.add(num);
}
for (int num : nums) {
if (all.contains(num + 1)) {
union(fathers, counts, num, num + 1);
}
if (all.contains(num - 1)) {
union(fathers, counts, num, num - 1);
}
}
int longest = 0;
for (int length : counts.values()) {
longest = Math.max(longest, length);
}
return longest;
}
private static void union(Map<Integer, Integer> fathers, Map<Integer, Integer> counts, int i, int j) {
int fatherOfI = findFather(fathers, i);
int fatherOfJ = findFather(fathers, j);
if (fatherOfI != fatherOfJ) {
fathers.put(fatherOfI, fatherOfJ);
int countOfI = counts.get(fatherOfI);
int countOfJ = counts.get(fatherOfJ);
counts.put(fatherOfJ, countOfI + countOfJ);
}
}
private static int findFather(Map<Integer, Integer> fathers, int i) {
if (fathers.get(i) != i) {
fathers.put(i, findFather(fathers, fathers.get(i)));
}
return fathers.get(i);
}
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/GoGleTech/article/details/135559630
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- C++轮子 · STL 序列容器
- 从Scroll怒喷社区用户事件,看L2龙头ZKFair的做事格局
- HANA:存储过程(Procedures) DBUG
- [NCTF 2023] web题解
- 什么是遗留系统?以及如何将它与现代应用程序集成
- RHCE【shell脚本(使用gzip、bzip2或者xz进行目录文件的压缩处理)】
- 灰度共生矩阵各参数说明
- 『新年首版』JeecgBoot v3.6.2 版本发布,企业级低代码开发平台
- 代码随想录训练营第二十四天打卡| 77. 组合
- 基于GPT-3、ChatGPT、GPT-4等Transformer架构的自然语言处理