【Leetcode 程序员面试金典 02.08】 —— 环路检测 |双指针
面试题02.08. 环路检测
给定一个链表,如果它是有环链表,实现一个算法返回环路的开头节点。若环不存在,请返回null。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪next指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数pos来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果pos是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
题目分析
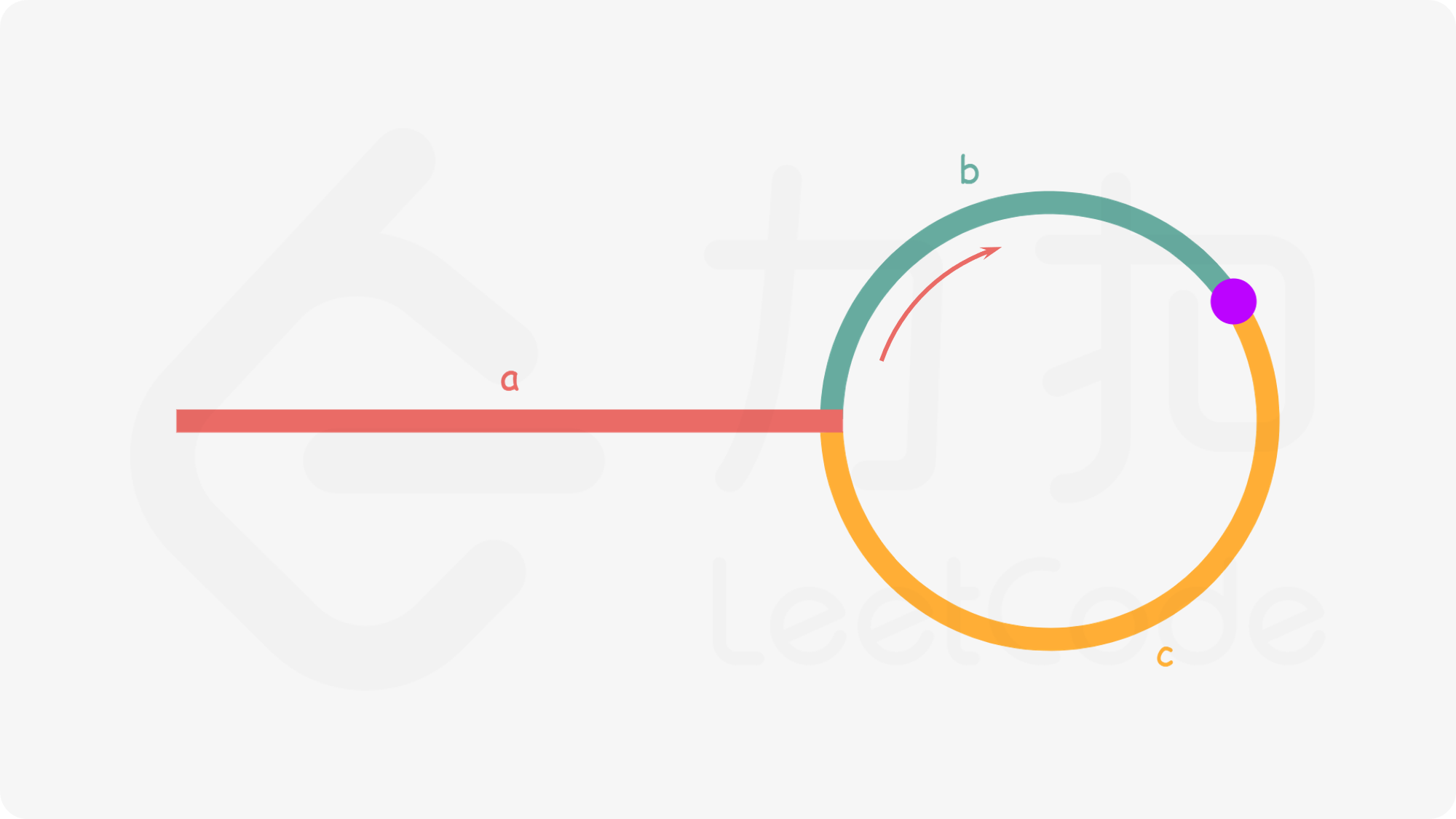
我们可以使用双指针解决本题
快指针走了:
a
+
(
b
+
c
)
m
+
b
a + (b+c)m + b
a+(b+c)m+b
慢指针走了:
a
+
(
b
+
c
)
n
+
b
a + (b+c)n + b
a+(b+c)n+b
根据快走的是慢的两倍,
a
+
(
b
+
c
)
m
+
b
=
2
(
a
+
(
b
+
c
)
n
+
b
)
a + (b+c)m + b = 2(a + (b+c)n + b)
a+(b+c)m+b=2(a+(b+c)n+b) =>
a
=
(
b
+
c
)
(
m
?
2
n
)
?
b
a = (b+c)(m-2n) - b
a=(b+c)(m?2n)?b
得 a 的距离为(环长度的倍数 - b),即 tmp 指针从头节点走到环开头节点等于 slow 指针走到环开头节点的距离
双指针顾名思义,就是同时使用两个指针,在序列、链表结构上指向的是位置,在树、图结构中指向的是节点,通过或同向移动,或相向移动来维护、统计信息
经典双指针的数组遍历,更多案例可见 Leetcode 双指针详解
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head == null){
return null;
}
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
while(fast != null){
slow = slow.next;
if(fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
} else {
return null;
}
if(slow == fast){
ListNode tmp = head;
while(tmp != slow){
tmp = tmp.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return tmp;
}
}
return null;
}
}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 【虹科分享】利用ProfiShark 构建便携式网络取证工具包
- matlab appdesigner系列-常用12-日期选择器
- “双十一、二” 业务高峰如何扛住?韵达快递选择 TDengine
- Jetbrains ai assistant激活成功了
- trino-435:dynamic catalog
- C++设计模式 #5 装饰模式(Decorator)
- Leetcode 416 分割等和子集
- 随机数的实现——rand函数、srand函数和time函数
- MYSQL的SWITCH语句和循环语句
- 【【UART 传输数据实验】】