数据分析-Pandas如何整合多张数据表
数据分析-Pandas如何整合多张数据表
数据表,时间序列数据在数据分析建模中很常见,例如天气预报,空气状态监测,股票交易等金融场景。数据分析过程中重新调整,重塑数据表是很重要的技巧,此处选择Titanic数据,以及巴黎、伦敦欧洲城市空气质量监测 N O 2 NO_2 NO2?数据作为样例。
数据分析
本文用到的样例数据:
样例代码:
数据准备
拿到数据后,很多情况下数据分散在多张表格中,不能直接用,这就需要对数据进行加工处理。
比如在air_quality数据中,大多数情况下NO2和pm25数据是在两张表中的。NO2数据
In [1]: air_quality_no2 = air_quality_no2[["date.utc", "location",
...: "parameter", "value"]]
...:
In [2]: air_quality_no2.head()
Out[2]:
date.utc location parameter value
0 2019-06-21 00:00:00+00:00 FR04014 no2 20.0
1 2019-06-20 23:00:00+00:00 FR04014 no2 21.8
2 2019-06-20 22:00:00+00:00 FR04014 no2 26.5
3 2019-06-20 21:00:00+00:00 FR04014 no2 24.9
4 2019-06-20 20:00:00+00:00 FR04014 no2 21.4
PM25数据,如下所示:
In [3]: air_quality_pm25 = air_quality_pm25[["date.utc", "location",
...: "parameter", "value"]]
...:
In [4]: air_quality_pm25.head()
Out[4]:
date.utc location parameter value
0 2019-06-18 06:00:00+00:00 BETR801 pm25 18.0
1 2019-06-17 08:00:00+00:00 BETR801 pm25 6.5
2 2019-06-17 07:00:00+00:00 BETR801 pm25 18.5
3 2019-06-17 06:00:00+00:00 BETR801 pm25 16.0
4 2019-06-17 05:00:00+00:00 BETR801 pm25 7.5
那么,Boss的各种数据分析处理要求就来了。
表格拼接
Boss:我就想合并不同监测站的 N O 2 和 P M 25 NO_2 和 PM_{25} NO2?和PM25?监测值到一张相同结构的表中,表格结构相同,直接加到尾巴上。以下为图示

concat
concat函数提供多个表格拼接到一个维度上,DataFrame有两个axis,可以是沿着列拼接,也可以沿着行拼接。默认如下:是axis=0,沿着列方向拼接起来。
In [5]: air_quality = pd.concat([air_quality_pm25, air_quality_no2], axis=0)
In [6]: air_quality.head()
Out[6]:
date.utc location parameter value
0 2019-06-18 06:00:00+00:00 BETR801 pm25 18.0
1 2019-06-17 08:00:00+00:00 BETR801 pm25 6.5
2 2019-06-17 07:00:00+00:00 BETR801 pm25 18.5
3 2019-06-17 06:00:00+00:00 BETR801 pm25 16.0
4 2019-06-17 05:00:00+00:00 BETR801 pm25 7.5
拼接的变化,可以通过shape属性观察到。如 axis=0时,行数变化:3178 = 1110 + 2068 行。这样操作:
In [7]: print('Shape of the ``air_quality_pm25`` table: ', air_quality_pm25.shape)
Shape of the ``air_quality_pm25`` table: (1110, 4)
In [8]: print('Shape of the ``air_quality_no2`` table: ', air_quality_no2.shape)
Shape of the ``air_quality_no2`` table: (2068, 4)
In [9]: print('Shape of the resulting ``air_quality`` table: ', air_quality.shape)
Shape of the resulting ``air_quality`` table: (3178, 4)
事实上,对日期重排后,不同表格源数据的行排序也发生变化。
merge
In [10]: air_quality = air_quality.sort_values("date.utc")
In [11]: air_quality.head()
Out[11]:
date.utc location parameter value
2067 2019-05-07 01:00:00+00:00 London Westminster no2 23.0
1003 2019-05-07 01:00:00+00:00 FR04014 no2 25.0
100 2019-05-07 01:00:00+00:00 BETR801 pm25 12.5
1098 2019-05-07 01:00:00+00:00 BETR801 no2 50.5
1109 2019-05-07 01:00:00+00:00 London Westminster pm25 8.0
用共同信息整合表格
如何依据某列属性,合并2个表格数据。比如学生身高,体重等体能信息表,和数理化等学科成绩表合并,住建是学生的ID。如下图所示:
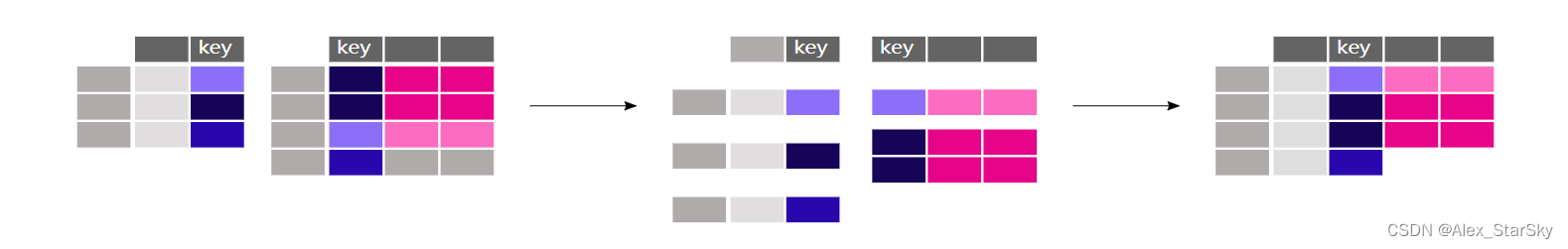
如果需要把每个监测站地理坐标,和实时的 N O 2 NO_2 NO2?监测值和 P M 2.5 PM_{2.5} PM2.5?监测值合并。关键是两点:地理坐标和监测值是不同的属性,表格大小不一致,需要扩充。此处用merge()函数,提供拼接函数的功能。
In [12]: stations_coord.head()
Out[12]:
location coordinates.latitude coordinates.longitude
0 BELAL01 51.23619 4.38522
1 BELHB23 51.17030 4.34100
2 BELLD01 51.10998 5.00486
3 BELLD02 51.12038 5.02155
4 BELR833 51.32766 4.36226
In [13]: air_quality = pd.merge(air_quality, stations_coord, how="left", on="location")
In [14]: air_quality.head()
Out[14]:
date.utc ... coordinates.longitude
0 2019-05-07 01:00:00+00:00 ... -0.13193
1 2019-05-07 01:00:00+00:00 ... 2.39390
2 2019-05-07 01:00:00+00:00 ... 2.39390
3 2019-05-07 01:00:00+00:00 ... 4.43182
4 2019-05-07 01:00:00+00:00 ... 4.43182
[5 rows x 6 columns]
对于air_quality 的每一行,对应的坐标会从stations_coord中,拼到每行中,其中它们有共同的列:location,作为拼接的key。而使用left拼接,主要是air_quality放在左边的缘故。
In [24]: air_quality = pd.merge(air_quality, air_quality_parameters,
....: how='left', left_on='parameter', right_on='id')
....:
In [25]: air_quality.head()
Out[25]:
date.utc ... name
0 2019-05-07 01:00:00+00:00 ... NO2
1 2019-05-07 01:00:00+00:00 ... NO2
2 2019-05-07 01:00:00+00:00 ... NO2
3 2019-05-07 01:00:00+00:00 ... PM2.5
4 2019-05-07 01:00:00+00:00 ... NO2
[5 rows x 9 columns]
以上代码只是一个简单示例,示例代码中的表达式可以根据实际问题进行修改。
觉得有用 收藏 收藏 收藏
点个赞 点个赞 点个赞
End
数据分析
经典算法
GPT专栏文章:
GPT实战系列-ChatGLM3本地部署CUDA11+1080Ti+显卡24G实战方案
GPT实战系列-LangChain + ChatGLM3构建天气查询助手
GPT实战系列-大模型为我所用之借用ChatGLM3构建查询助手
GPT实战系列-P-Tuning本地化训练ChatGLM2等LLM模型,到底做了什么?(二)
GPT实战系列-P-Tuning本地化训练ChatGLM2等LLM模型,到底做了什么?(一)
GPT实战系列-ChatGLM2部署Ubuntu+Cuda11+显存24G实战方案
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!