数据结构从入门到入土——初识泛型
目录
一,包装类
1.基本数据类型和对应的包装类
| 基本数据类型 | 包装类 | 内存大小(单位:字节) |
| byte | Byte | 1 |
| short | Short | 2 |
| int | Integer | 4 |
| long | Long | 8 |
| float | Float | 4 |
| double | Double | 8 |
| char | Character | 2 |
| boolean | Boolean | 未定义 |
2.装箱和拆箱
int i = 10;
// 装箱操作,新建一个 Integer 类型对象,将 i 的值放入对象的某个属性中
Integer?i =?10;隐式装箱
Integer ii = Integer.valueOf(i);//显示装箱
Integer ij = new Integer(i);
// 拆箱操作,将 Integer 对象中的值取出,放到一个基本数据类型中
int j = ii.intValue();
3.自动装箱和自动拆箱
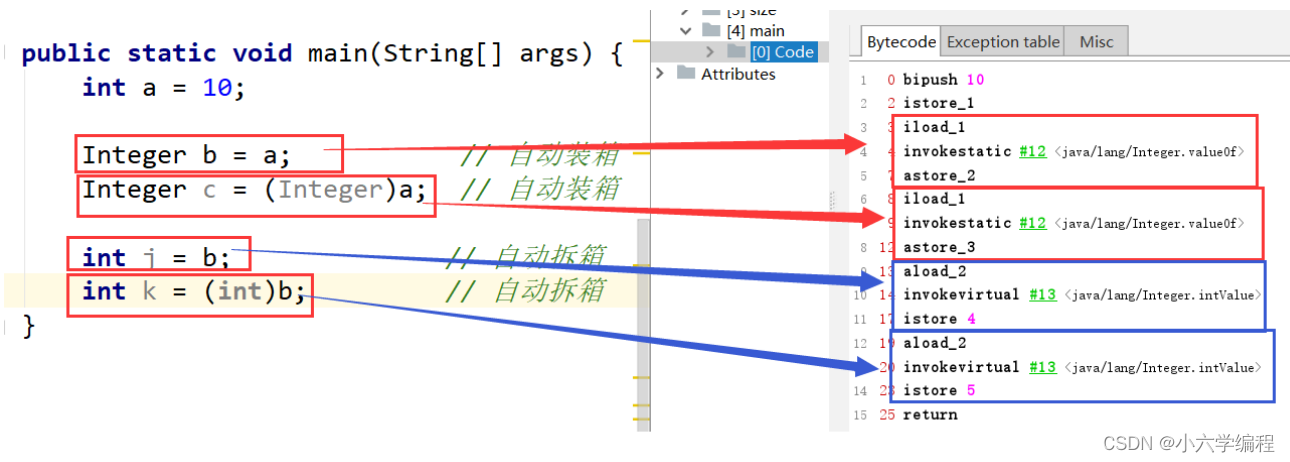
int i = 10;
Integer ii = i; // 自动装箱
Integer ij = (Integer)i; // 自动装箱
int j = ii; // 自动拆箱
int k = (int)ii; // 自动拆箱
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer a = 127;
Integer b = 127;
Integer c = 128;
Integer d = 128;
System.out.println(a == b);
System.out.println(c == d);
}
答案:true? ?false
解析:
这里我们需要先了解Integer的源码

我们发现定义的i的值满足一定范围,点进而这个low和high的范围正好满足[-128,127],所以这个数组则有下标[0,255]这256个下标,而返回的这个数组的下标则满足i+(-(-128)),也就是i+128下标对应的元素,当i+128>255时则会产生新的对象,所以上述代码中c和d的地址已不相同,所以输出的值才会是false。
二,什么是泛型?

三,引出泛型
class MyArray {
public Object[] array = new Object[10];
public Object getPos(int pos) {
return this.array[pos];
}
public void setVal(int pos,Object val) {
this.array[pos] = val;
}
}
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArray myArray = new MyArray();
myArray.setVal(0,10);
myArray.setVal(1,"hello");//字符串也可以存放
String ret = myArray.getPos(1);//编译报错
System.out.println(ret);
}
}
语法
class 泛型类名称<类型形参列表> {
// 这里可以使用类型参数
}
class ClassName<T1, T2, ..., Tn> {
}
class 泛型类名称<类型形参列表> extends 继承类/* 这里可以使用类型参数 */ {
// 这里可以使用类型参数
}
class ClassName<T1, T2, ..., Tn> extends ParentClass<T1> {
// 可以只使用部分类型参数
}
上述代码进行改写如下:
class MyArray<T> {
Object[] array = new Object[10];
public void setValue(int pos,T val) {
array[pos] = val;
}
public T getValue(int pos) {
return (T)array[pos];
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArray<Integer> myArray= new MyArray<Integer>();
myArray.setValue(1,1);
int i = myArray.getValue(1);
MyArray<String> myArray1 = new MyArray<String>();
myArray1.setValue(0,"hehe");
String str = myArray1.getValue(0);
}
}
???? E 表示 Element???? K 表示 Key???? V 表示 Value???? N 表示 Number???? T 表示 Type???? S, U, V 等等 - 第二、第三、第四个类型
T [] ts = new T [ 5 ]; // 是不对的
四,泛型类的使用
1.语法
泛型类 < 类型实参 > 变量名 ; // 定义一个泛型类引用new 泛型类 < 类型实参 > ( 构造方法实参 ); // 实例化一个泛型类对象
MyArray < Integer > list = new MyArray < Integer > ();
2.类型推导(Type Inference)
MyArray < Integer > list = new MyArray <> (); // 可以推导出实例化需要的类型实参为 Integer
五,裸类型(Raw Type)
说明:
MyArray list = new MyArray ();
六,泛型是如何编译的
1.擦除机制
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- (每日持续更新)jdk api之FileInputStream基础、应用、实战
- C# ManagementClass类
- PyQt5实现学生管理系统第三天(下)
- leetcode深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索总结 Python
- Linux之Iptables简易应用
- SpringBoot的启动器——spring-boot-starter介绍和常见启动器说明
- STM32 HAL库定时器触发DMA并口数据传输
- C++ 将引用用于类对象
- 将yolov8的检测框从正框修改为旋转框需要做那些修改?
- NodeJS报错Cannot access ‘xxx‘ before initialization排查解决