SpringBoot+FastJson 优雅的过滤 Response Body
Spring 源码系列
1、Spring 学习之扩展点总结之后置处理器(一)
2、Spring 学习之扩展点总结之后置处理器(二)
3、Spring 学习之扩展点总结之自定义事件(三)
4、Spring 学习之扩展点总结之内置事件(四)
5、Spring 学习之扩展点总结之@Import(五)
6、Spring 学习之AOP总结之基础介绍(六)
7、Spring 学习之AOP总结之实现代理(七)
8、SpringBoot 学习之自动配置基本原理(八)
9、SpringBoot 学习之启动原理(九)
10、ElasticSearch学习随笔之SpringBoot Starter 操作
11、图数据库 Neo4j 学习之SpringBoot整合
12、SpringBoot 学习之常用 Filter / Advice 总结
13、SpringBoot+FastJson 优雅的过滤 Response Body
文章目录
前言
还是那个问题,前两天在开发一个需求时遇到这么一个问题,就是对接口的返回体【Response Body】做一些处理,,猛然间居然还是手足无措,最后决定使用 ResponseBodyAdvice 通知来实现,所以总结了一下开发中常用的 Filter 和 Advice,也欢迎 码友 们指点一二,我也会在空闲时第一时间补充进去,博文见 《SpringBoot 学习之常用 Filter / Advice 总结》。
不过发现即便使用 Filter 或者 Advice 可以实现,但是不够优雅…
目前企业开发项目中基本上都是用 JSON 格式作为 API 响应体,我负责的项目亦是,并且使用的是 alibaba 的 fastjson,然后有前面大佬的杰作加上我的虚心学习之后,决定用 FastJson 扩展点【FastJsonHttpMessageConverter】来实现。
提示:只要按照思路简介的几步完成即可实现优雅的过滤消息体功能!
一、思路简介
在 Spring Boot 中,默认使用 Jackson 库来将返回体转换为 JSON 格式的数据。 Jackson 是一个流行的 JSON 处理库,Spring 框架中集成了它作为默认的 JSON 序列化和反序列化工具。
不过在我们的应用中也使用到了 FastJson 来对响应体或对象实体与 JSON 进行转换,既然使用到了了 FastJson,那我们就可以通过 FastJson 扩展来在转换 JSON 的过程中实现字段过滤,这样我觉得就优雅了许多。
FastJson 中有一个 FastJsonHttpMessageConverter 是 FastJson 中提供的消息【转换器】,我们就通过继承FastJsonHttpMessageConverter 并重写转换功能来实现返回体字段过滤。
具体有如下几点:
- 编写
@ResponseJSON和@Ignore注解,我们通过注解来配置每个接口返回的字段。- 自定义转换器【
JSONHttpMessageConverter】继承FastJsonHttpMessageConverter并且实现ApplicationContextAware接口(主要用于获取上下文)。- 自定义
HandlerHolder类实现接口HandlerInterceptor,主要用于获取到我们自己开发的请求处理器Handler(请求处理器)。- 自定义
EntityClassPropertyFilter过滤器实现FastJson提供的PropertyPreFilter过滤器并且 重写 apply(*) 方法 ,通过实现这个方法,可以自定义过滤规则,在序列化对象时,Fastjson将会根据实现了PropertyPreFilter接口的对象的apply方法来判断哪些属性需要被序列化,哪些属性需要被过滤掉。- 自定义
AppConfig配置类让返回体转换器生效。
二、FastJsonHttpMessageConverter 是什么?
FastJsonHttpMessageConverter 是 FastJson 中提供的消息转换器,在 Spring Boot 中可以用来将对象转换为 JSON 格式的数据,用于处理接口返回体的数据,具体作用如下:
- JSON 转换,
FastJsonHttpMessageConverter实现了 Spring 框架中的HttpMessageConverter接口,能够将 JAVA 对象转换成 JSON 格式数据,以便通过 HTTP 返回给客户端。- FastJson 配置,该转换器对 FastJson 进行配置,比如设置序列化特性、日期格式化等。
- 可以替代 Spring Boot 默认的 Jackson 转换器。
三、@*** 注解编写
按照思路简介 第 1 步,编写注解类,直接上代码。
3.1 @ResponseJSON 注解
package com.selftest.web.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface ResponseJSON {
Ignore[] ignore() default {};
boolean enable() default true;
}
3.2 @Ignore 注解
package com.selftest.web.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Ignore {
Class<?> declaringClass();
String[] propNames();
boolean inverse() default false;
}
四、JSONHttpMessageConverter 消息体处理实现
按照思路简介第 2 步,编写 JSONHttpMessageConverter 类,代码中都有注释,直接上代码。
这个类是实现响应体的主要部分,主要是实现消息体转换和配置,代码比较多,分开一段一段看。
4.1 JSONHttpMessageConverter 类及依赖
package com.selftest.web.http;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.PropertyPreFilter;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializeFilter;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.support.config.FastJsonConfig;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.support.spring.FastJsonHttpMessageConverter;
import com.selftest.web.RequestHandlerHolder;
import com.selftest.web.annotation.Ignore;
import com.selftest.web.annotation.ResponseJSON;
import com.selftest.web.filter.EntityClassPropertyFilter;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.core.MethodParameter;
import org.springframework.http.HttpOutputMessage;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageNotWritableException;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.*;
/**
* JSON 数据转换,实现返回体字段过滤
*/
public class JSONHttpMessageConverter extends FastJsonHttpMessageConverter implements ApplicationContextAware {
/**
* 应用上下文
*/
private ApplicationContext ctx;
/**
* 请求处理器 Handler 持有者
*/
@Resource
private RequestHandlerHolder requestHandlerHolder;
private FastJsonConfig fastJsonConfig = new FastJsonConfig();
此处代码下面依次呈现
3.2 writeInternal() 方法
3.3 toJSONString() 方法
3.4 getSerializeFilter() 方法
3.5 setApplicationContext() 方法
}
4.2 writeInternal() 处理消息体
/**
* 返回体处理
* @param obj the object to write to the output message
* @param outputMessage the HTTP output message to write to
* @throws IOException
* @throws HttpMessageNotWritableException
*/
@Override
protected void writeInternal(Object obj, HttpOutputMessage outputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotWritableException {
//获取到返回流
OutputStream out = outputMessage.getBody();
String jsonString = toJSONString(obj);
out.write(jsonString.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
4.3 toJSONString() 对象转换 JSON
/**
* 将对象转换为JSON字符串
* @return
*/
private String toJSONString(Object obj){
//获取到处理请求的 Handler
if(Objects.isNull(requestHandlerHolder)){
return JSON.toJSONString(obj);
}
Object handler = requestHandlerHolder.getHandler();
//如果 handler 为空或者 handler 不为空但是返回类型不是 entity 的
if(Objects.isNull(handler)
|| (Objects.nonNull(requestHandlerHolder.getHandlerMethod().getReturnType())
&& requestHandlerHolder.getHandlerMethod().getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(ResponseEntity.class))){
return JSON.toJSONString(obj);
}
//如果是处理方法,则获取到返回类型 ReturnType、annotation
ResponseJSON annotation = null;
if (handler instanceof HandlerMethod) {
HandlerMethod method = (HandlerMethod) handler;
MethodParameter returnType = method.getReturnType();
annotation = returnType.getMethodAnnotation(ResponseJSON.class);
if (Objects.isNull(annotation)) {
annotation = method.getMethodAnnotation(ResponseJSON.class);
}
}
if(Objects.isNull(annotation) || (Objects.nonNull(annotation) && !annotation.enable())){
return Objects.nonNull(obj) ? JSON.toJSONString(obj) : null;
}
// 获取到真正实现返回体过滤的序列化 filter
SerializeFilter filter = getSerializeFilter(annotation);
// 封装自定义 filter, 传入上面的 filter 和 自定义注解
EntityClassPropertyFilter propertyFilter = new EntityClassPropertyFilter(filter, annotation);
return JSON.toJSONString(obj, propertyFilter, this.fastJsonConfig.getSerializerFeatures());
}
4.4 getSerializeFilter() 序列化Filter实现
/**
* 获取序列化 filter
* @param annotation
* @return
*/
private SerializeFilter getSerializeFilter(ResponseJSON annotation) {
if(Objects.nonNull(annotation)){
Ignore[] ignoreFields = annotation.ignore();
if(ignoreFields.length == 0){
return null;
}
Map<Class<?>, Map<Boolean, Set<String>>> ignoreMap = new HashMap<>();
for (Ignore ignore : ignoreFields) {
Class<?> declaringClass = ignore.declaringClass();
Map<Boolean, Set<String>> propNameMap = ignoreMap.get(declaringClass);
if(Objects.isNull(propNameMap)) {
propNameMap = new HashMap<>();
ignoreMap.put(declaringClass, propNameMap);
}
boolean inverse = ignore.inverse();
Set<String> propNameSet = propNameMap.get(inverse);
if(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(propNameSet)){
propNameSet = new HashSet<>();
propNameMap.put(inverse, propNameSet);
}
for (String propName : ignore.propNames()) {
propNameSet.add(propName);
}
}
// 返回 属性预处理 Filter 实例,真正实现返回体字段过滤
return (PropertyPreFilter) (jsonSerializer, object, name) -> {
for (Map.Entry<Class<?>, Map<Boolean, Set<String>>> ignoreEntry : ignoreMap.entrySet()) {
if (ignoreEntry.getKey().isAssignableFrom(object.getClass())) {
Set<String> ignorePropNames = ignoreEntry.getValue().get(false);
if (Objects.nonNull(ignorePropNames) && ignorePropNames.contains(name)) {
return false;
}
ignorePropNames = ignoreEntry.getValue().get(true);
if (Objects.nonNull(ignorePropNames) && !ignorePropNames.contains(name)) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
};
}
return null;
}
4.5 setApplicationContext() 设置上下文
/**
* 获取应用上下文
* @param applicationContext the ApplicationContext object to be used by this object
* @throws BeansException
*/
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.ctx = applicationContext;
}
五、HandlerHolder 获取请求处理器 Handler 实现
按照思路简介 第 3 步,编写 HandlerHolder 类,代码中都有注释,直接上代码。
这个类主要是为了能在处理消息体处理的时候能获取到 Handler,因为我们的消息体处理是通过 Handler 方法上的 @ResponseJSON 和 @Ignore 注解配置来实现的。
package com.selftest.web.interceptor;
import com.selftest.web.RequestHandlerHolder;
import org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* 请求处理拦截器,主要获取 Handler
* 通过 ThreadLocal 获取
*/
public class HandlerHolder implements HandlerInterceptor, RequestHandlerHolder {
/**
* 通过 ThreadLocal 来暂存和获取 Handler
*/
private final ThreadLocal<Object> HANDLERS = new ThreadLocal<>();
/**
* 在请求是获取到 Handler 并存入 ThreadLocal
* @param request current HTTP request
* @param response current HTTP response
* @param handler chosen handler to execute, for type and/or instance evaluation
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
HANDLERS.set(handler);
return true;
}
/**
* 从 ThreadLocal 获取 Handler
* @return
* @param <T>
*/
@Override
public <T> T getHandler(){
return (T) HANDLERS.get();
}
/**
* 获取 Handler 的方法
* @return
*/
@Override
public Method getHandlerMethod() {
Object handler = getHandler();
if (handler instanceof HandlerMethod) {
return ((HandlerMethod) handler).getMethod();
} else if (handler instanceof Method) {
return (Method) handler;
}
return null;
}
}
接口 RequestHandlerHolder 实现:
package com.selftest.web;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public interface RequestHandlerHolder {
<T> T getHandler();
Method getHandlerMethod();
}
六、EntityClassPropertyFilter 序列化对象属性过滤器
按照思路简介 第 4 步,编写 EntityClassPropertyFilter 类,代码中都有注释,直接上代码。
package com.selftest.web.filter;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.JSONSerializer;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.PropertyPreFilter;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializeFilter;
import com.selftest.web.annotation.ResponseJSON;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* 实现对象属性序列化 filter
*/
public class EntityClassPropertyFilter implements PropertyPreFilter {
private SerializeFilter filter;
private ResponseJSON annotation;
/**
* 实例化
* @param filter
* @param annotation
*/
public EntityClassPropertyFilter(SerializeFilter filter, ResponseJSON annotation) {
this.filter = filter;
this.annotation = annotation;
}
/**
* 自定义过滤规则, 判断哪些属性需要被序列化,哪些属性需要被过滤掉
* @param jsonSerializer
* @param object
* @param name
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean apply(JSONSerializer jsonSerializer, Object object, String name) {
Class<?> elementType = object.getClass();
if (Objects.nonNull(elementType)) {
while (!elementType.equals(Object.class)) {
if (Objects.nonNull(filter) && filter instanceof PropertyPreFilter) {
// 这里调用的是 JSONHttpMessageConverter 中 getSerializeFilter() 提供的 SerializeFilter
if (!((PropertyPreFilter)filter).apply(jsonSerializer, object, name)) {
return false;
}
}
elementType = elementType.getSuperclass();
}
}
return true;
}
}
七、AppConfig 配置类让转换器生效
按照思路简介 第 5 步,编写 HandlerHolder 类,代码中都有注释,直接上代码。
package com.selftest.config;
import com.selftest.web.http.JSONHttpMessageConverter;
import com.selftest.web.interceptor.HandlerHolder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
/**
* 配置类
*/
@Configuration
public class AppConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
/**
* 实例化请求 handler
* @return
*/
@Bean(name = "requestHandlerHolder")
public HandlerHolder requestHandlerHolder(){
return new HandlerHolder();
}
/**
* 返回体消息过滤 Bean
* @return
*/
@Bean
public JSONHttpMessageConverter jsonHttpMessageConverter(){
return new JSONHttpMessageConverter();
}
/**
* 注册请求拦截器
* @param registry
*/
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(requestHandlerHolder());
}
}
八、测试结果
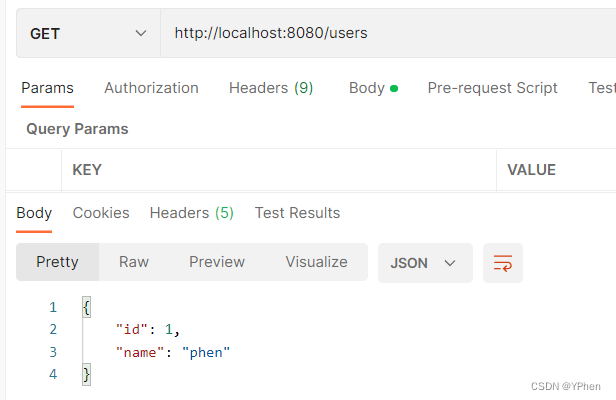
8.1 测试接口
@ResponseJSON(ignore = {
@Ignore(declaringClass = User.class, propNames = {"age"})
})
@GetMapping("users")
public User getUser(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setName("phen");
user.setAge(30);
return user;
}
8.2 请求测试
八、小结
在 Spring Boot 中,默认使用 Jackson 库来将返回体转换为 JSON 格式的数据。 Jackson 是一个流行的 JSON 处理库,Spring 框架中集成了它作为默认的 JSON 序列化和反序列化工具。
那在 FastJson 中提供的 FastJsonHttpMessageConverter 消息转换器,我们则可以通过对此转换器的重写来实现对请求体字段的过滤,在 FastJsonHttpMessageConverter 中的 getSerializeFilter() 方法返回了 PropertyPreFilter 实体则真正的实现了返回体字段的过滤,在 自定义类 JSONHttpMessageConverter 中的 toJSONString() 方法中我们可以看到这几句代码:
SerializeFilter filter = getSerializeFilter(annotation);
EntityClassPropertyFilter propertyFilter = new EntityClassPropertyFilter(filter, annotation);
return JSON.toJSONString(obj, propertyFilter, this.fastJsonConfig.getSerializerFeatures())
第二个参数 propertyFilter 则是我们自己定义的 Filter,并且实现了 FastJson 提供的序列化过滤器 PropertyPreFilter,EntityClassPropertyFilter 重写了 apply() 并且回调了 getSerializeFilter() 获取到的 filter,通过 JSON.toJSONString() 并且传入三个参数,第一个参数是我们自己实现的请求处理器返回的实体对象 User,第二个参数则是我们自己实现的序列化 Filter,第三个参数就是 FastJson 的默认的 SerializerFeature。
到这里,Spring Boot + FastJson 优雅的实现消息体字段的过滤就基本完成了,可以通过 debug 方式来看一下具体请求过滤是如何执行的,调用逻辑是什么。
江湖必有大佬藏,如有指点可别藏!
本文示例亲自手敲代码并且执行通过。
如有问题,还请指教。 评论区告诉我!!!一起学习一起进步!!!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!