使用jackson对java类中包含泛型属性的bean进行序列化和反序列化
发布时间:2024年01月18日
最近在做项目时,需要对java的bean对象进行序列化转换为string字符串后,存入redis,然后再从redis中读取该string对象,反序列化为bean对象。正常的简单类型的对象使用jackson可以非常方便进行互为转换操作,但我们操作的对象有点复杂,造成存入redis的数据是对的,但反序列化时,一直没有正常将值反序列化成功,主要是由于类属性有一个Pair<double,double>的对象,该对象是一个abstract class对象,有相应的子类生成对应的实例对象。bean对象类似于下面的定义:

BoardcastRsp类中有一个Action的类,定义类似于如下:
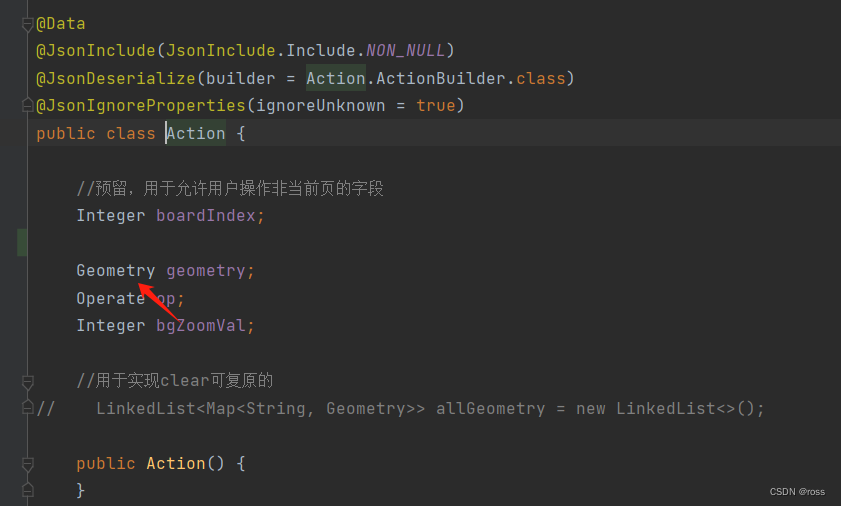 action类中的geometry对象的定义如下所示:
action类中的geometry对象的定义如下所示:
 对于Pair<Double,Double>类型,直接进行writeValueAsString和readValue则,从string中转换后的BoardcastRsp中的定义为Pair<Double,Double>类型的相关属性均无法正常反序列化。这种场景中,只能针对Pair类型的进行自定义的序列化和反序列化操作。相关的操作核心代码如下:
对于Pair<Double,Double>类型,直接进行writeValueAsString和readValue则,从string中转换后的BoardcastRsp中的定义为Pair<Double,Double>类型的相关属性均无法正常反序列化。这种场景中,只能针对Pair类型的进行自定义的序列化和反序列化操作。相关的操作核心代码如下:
//自定义序列化方法
class PairSerializer extends JsonSerializer<Pair> {
@Override
public void serialize(Pair pair, JsonGenerator jsonGenerator, SerializerProvider serializerProvider) throws IOException {
jsonGenerator.writeStartArray();
jsonGenerator.writeNumber((Double) pair.getKey());
jsonGenerator.writeNumber((Double) pair.getValue());
jsonGenerator.writeEndArray();
}
}
//自定义反序列化方法
class PairDeserializer extends JsonDeserializer<Pair> {
@Override
public Pair deserialize(JsonParser jsonParser, DeserializationContext deserializationContext) throws IOException {
ObjectCodec codec = jsonParser.getCodec();
JsonNode node = codec.readTree(jsonParser);
double key = node.get(0).asDouble();
double value = node.get(1).asDouble();
return Pair.of(key, value);
}
}
public class TestSDClass {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Action action = new Action();
action.setGeometry(new Polyline("1", "#dddd", 1,
MutablePair.of(0.0, 0.0), 222l,
MutablePair.of(0.0, 0.0), 2, "L22323",
MutablePair.of(0.0, 0.0),
MutablePair.of(0.0, 0.0),
"L1111"));
action.setOp(Action.Operate.DRAW);
BoardcastRsp boardcastRsp = new BoardcastRsp();
boardcastRsp.setAction(action);
boardcastRsp.setMediaId("1");
boardcastRsp.setLevel(Level.FIVE);
boardcastRsp.setCategory(BoardcastRsp.Category.ACTION);
// 创建 ObjectMapper 对象
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
// 创建自定义模块
SimpleModule module = new SimpleModule();
module.addSerializer(Pair.class, new PairSerializer());
module.addDeserializer(Pair.class, new PairDeserializer());
objectMapper.registerModule(module);
try {
// 序列化为 JSON 字符串
String jsonString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(boardcastRsp);
System.out.println(jsonString);
// 反序列化为 Java 对象
BoardcastRsp myClass2 = objectMapper.readValue(jsonString, BoardcastRsp.class);
System.out.println(myClass2.getLevel());
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
通过自定义的序列化和反序列化即可以将Pair<Double,Double>泛型相关的属性进行正常的操作了。上面的代码中,序列化时,将泛型对象设置为数组。反序列化时,从数组中取到两个double值,然后生成一个新的Pair对象,完成反序列化操作。
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/fycghy0803/article/details/135673997
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 虹科技术 | IO-Link Wireless如何赋能工厂车间迈向无线自动化?
- 聚观早报 | 一加Ace 3海外版;OpenAI发布安全指南
- MyTinySTL 简单分析(六)--vector.h
- RK3568开发笔记(十一):开发版buildroot固件移植一个ffmpeg播放rtsp的播放器Demo
- 什么是好的FPGA编码风格?(2)--多参考设计软件的语言模板(Language Templates)
- Mysql数据库备份还原
- 苹果手机数据恢复工具推荐,这款值得一试!
- Android安卓组件——Service1.
- Java毕业设计 SSM SpringBoot 在线学习系统
- 设置代码模板创建sql映射文件、Mybatis主配置文件