NodeJs 第二十章 代理
发布时间:2024年01月21日
在计算机网络中,代理是一种中间服务,能够代理用户与网络资源之间的通信。代理服务器可以缓存网页内容、过滤网络流量或隐藏用户的真实IP地址等功能。
在日常开发中,我们接触最多的是客户端发送ajax到服务端。但是服务端并不是 node ,而是java或者go。
例如我们用 vue 开发应用。我们的感知是从客户端直接发送 ajax 到服务端。但是在浏览器发送ajax 到服务端,服务端响应到浏览器会出现跨域。这个时候就需要配置代理,node 此时就可以充当这个角色。
实际在开发环境 vue 就是利用 express 创建了一个开发服务,充当代理角色。这个代理服务主要是利用 http-proxy-middleware 中间件,实现代理服务器。
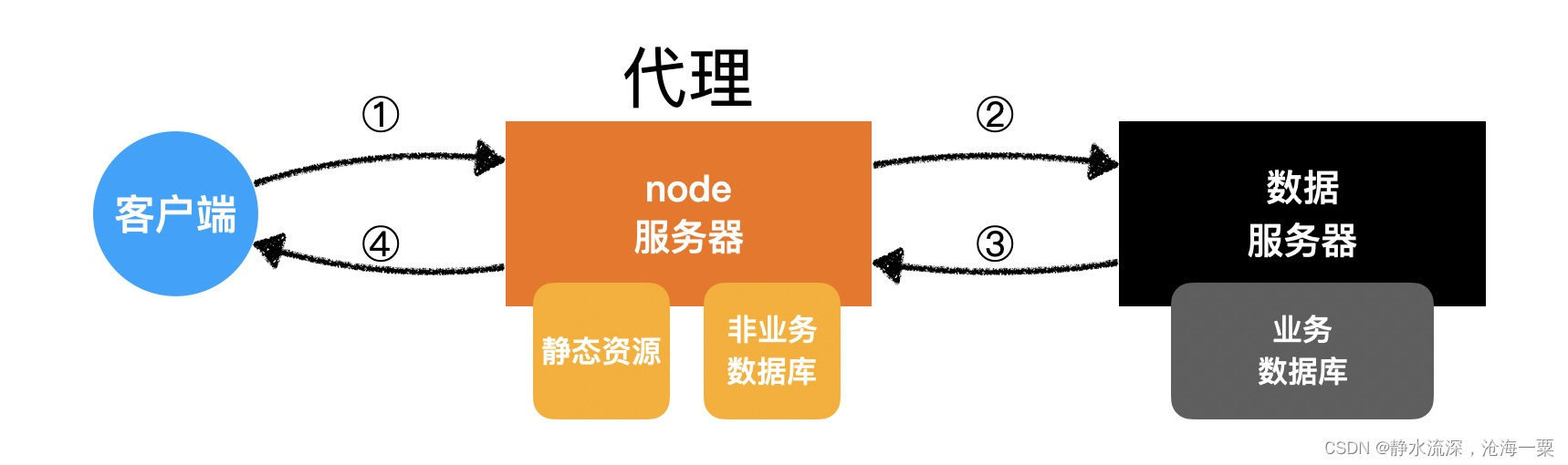
node 实现代理服务器原理
- 浏览器发送 ajax 请求到 node 服务
- node 服务将和 java 或者 go 服务约定好的 api转发给java 或者 go服务端
- java 服务或者 node 服务响应个 node 代理服务
- node 服务在响应给浏览器
简单示例
const http = require('http');
const proxyServer = http.createServer((request, response) => {
// 创建代理请求的选项
const options = {
hostname: '目标服务器的主机名',
port: 80, // 目标服务器的端口号
path: request.url,
method: request.method,
headers: request.headers
};
// 发起代理请求
const proxyRequest = http.request(options, (proxyResponse) => {
// 将代理服务器收到的响应转发给客户端
response.writeHead(proxyResponse.statusCode, proxyResponse.headers);
// 将代理服务器的响应通过管道传输给客户端,实现响应的转发。
proxyResponse.pipe(response);
});
// 将客户端发来的请求体转发给目标服务器
request.pipe(proxyRequest);
// 处理代理请求错误
proxyRequest.on('error', (error) => {
console.error('代理请求错误:', error);
response.statusCode = 500;
response.end();
});
});
// 启动代理服务器
const PORT = 3000;
proxyServer.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log('代理服务器已启动,监听端口', PORT);
});
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/aXin_li/article/details/135731893
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!