jdk 线程池与 tomcat 线程池对比
一、线程池的作用
1. 提高性能:线程的创建需要开辟虚拟机栈、本地方法栈、程序计数器等线程私有空间,同时也会一比一的创建一个内核线程,在线程销毁时需要回收这些系统资源。频繁地创建和销毁线程会大大浪费系统资源,这时候就需要线程池来管理线程,提高线程的复用
2. 控制并发度:限制同时执行的线程数量,通过控制并发度来避免资源过度占用和系统过载。
3. 任务排队:提供任务队列,可以将所有待执行的任务进行排队,保证任务按照一定的顺序执行,避免因为线程不足而导致任务丢失
二、java 自带线程池?ThreadPoolExecutor
Java JUC下提供了一套 Executor 框架,主要支持以下几种线程池的创建
a. FixedThreadPool(固定大小线程池):维护固定数量的线程,任务提交后会立即执行。如果所有线程都被占用,新任务会被放入任务队列中等待。适用于并发任务数固定且较小的情况。
b. CachedThreadPool(缓存线程池):线程池大小不固定,根据任务量动态创建和回收线程。如果当前有空闲线程,则会直接使用,如果没有则会创建新的线程。适用于并发任务数较大或者任务执行时间较短的情况。
c. SingleThreadPool(单线程池):线程池中只有一个线程,所有的任务按照顺序执行。适用于保证任务执行顺序的场景,如任务间有依赖关系或需要按照提交顺序执行。
d. ScheduledThreadPool(定时线程池):用于定时执行任务和周期性执行任务。可以设置线程数量和延迟时间来执行任务
不推荐使用 Executors 工厂模式创建上述四种线程池,缺少很多线程池的参数设置且默认参数并不合理,容易出现性能问题或者资源浪费。推荐使用?ThreadPoolExecutor类 (类结构图如下) 手动创建线程池,可以自定义线程池的大小、任务队列、拒绝策略以及其他参数。这样可以根据具体的业务需求和系统资源状况来优化线程池的性能和稳定性。
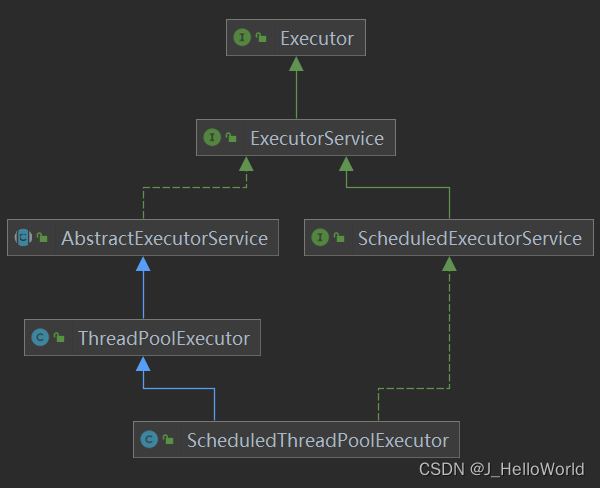
ThreadPoolExecutor 核心参数
- corePoolSize(核心线程数):表示线程池中保持活动状态的线程数量。在没有任务执行时,核心线程也会一直存在。当有新任务提交时,线程池会优先创建核心线程来处理任务。
- maximumPoolSize(最大线程数):表示线程池中允许存在的最大线程数。当线程池中的线程数达到最大线程数并且任务队列已满时,新提交的任务会触发拒绝策略。
- keepAliveTime(线程空闲时间):表示当线程池中的线程数量超过核心线程数时,空闲线程在被终止之前要等待新任务的时间。线程空闲时间的单位由TimeUnit参数指定。
- unit(时间单位):用于指定keepAliveTime的时间单位,可以是秒、毫秒、微秒等。
- workQueue(任务队列):用于存储待执行的任务的队列。线程池中的线程会从任务队列中取出任务进行执行。
- ThreadPoolExecutor提供了多种实现供选择,如ArrayBlockingQueue、LinkedBlockingQueue、SynchronousQueue等。
- threadFactory(线程工厂):用于创建新线程的工厂,默认使用Executors.defaultThreadFactory()。 handler(拒绝策略):当线程池无法处理新提交的任
? ? ? 如果 corePoolSize 长时间无效占用线程数量,可通过 allowCoreThreadTimeOut 设置项要求线程池:将包括“核心线程”在内的,没有任务分配的所有线程,在等待 keepAliveTime 时间后全部回收掉。
线程池的线程分配流程

三、tomcat 线程池 StandardThreadExecutor?
????????不同于 jdk 自带的线程池,tomcat 应用的场景基本都是IO密集型请求,即系统请求非常消耗CPU的占比比较低,所以tomcat在设计线程池的时候,重新设计了线程池分配原则,请求进来时会优先创建并分配线程而不是进入等待队列
设计点1: 增加继承 LinkedBlockingQueue 的 TaskQueue
private transient volatile ThreadPoolExecutor parent = null;
@Override
public boolean offer(Runnable o) {
// 如果线程池为空,直接入队列
if (parent==null) return super.offer(o);
// 当前线程池线程数 = 最大线程池数,进入队列等待
if (parent.getPoolSize() == parent.getMaximumPoolSize()) return super.offer(o);
// 已提交并执行中的任务数 <= 当前线程池线程数,进入队列等待
if (parent.getSubmittedCount()<=(parent.getPoolSize())) return super.offer(o);
// 当前线程池线程数 < 最大线程数,返回false (即创建新线程)
if (parent.getPoolSize()<parent.getMaximumPoolSize()) return false;
// 其他条件进去等待队列
return super.offer(o);
}你是不是会疑惑,已提交并执行中的任务数 <= 当前线程池线程数,为什么是进入队列等待 ?
首先看下?submittedCount 是干什么用的,跟踪代码发现 tomcat 自己也写了一个? org.apache.tomcat.util.threads.ThreadPoolExecutor ,submittedCount 的主要职责是记录已提交的任务数,调用?execute 时 +1 ,afterExecute?执行结束时 - 1, 即该条件成立下进入队列的任务很快就会被执行,举个具体的栗子看下,即在线程运行资源不紧张的情况下,可以有效地控制线程池的负载,避免过多的线程创建和销毁,提高线程池的性能和资源利用率
| 任务 | 线程数 |
| a (即将结束) | 1 |
| b(进行中) | 2 |
| c (新进入) | 队列中等待 |
| d (新进入) | 进入下一个条件继续创建线程 |
设计点2: 提供自己的?org.apache.tomcat.util.threads.ThreadPoolExecutor?
public class ThreadPoolExecutor extends java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor {
/**
* The number of tasks submitted but not yet finished. This includes tasks
* in the queue and tasks that have been handed to a worker thread but the
* latter did not start executing the task yet.
* This number is always greater or equal to {@link #getActiveCount()}.
*/
private final AtomicInteger submittedCount = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Override
protected void afterExecute(Runnable r, Throwable t) {
submittedCount.decrementAndGet();
if (t == null) {
stopCurrentThreadIfNeeded();
}
}
public int getSubmittedCount() {
return submittedCount.get();
}
/**
* Executes the given command at some time in the future. The command
* may execute in a new thread, in a pooled thread, or in the calling
* thread, at the discretion of the <code>Executor</code> implementation.
* If no threads are available, it will be added to the work queue.
* If the work queue is full, the system will wait for the specified
* time and it throw a RejectedExecutionException if the queue is still
* full after that.
*
* @param command the runnable task
* @param timeout A timeout for the completion of the task
* @param unit The timeout time unit
* @throws RejectedExecutionException if this task cannot be
* accepted for execution - the queue is full
* @throws NullPointerException if command or unit is null
*/
public void execute(Runnable command, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
submittedCount.incrementAndGet();
try {
super.execute(command);
} catch (RejectedExecutionException rx) {
if (super.getQueue() instanceof TaskQueue) {
final TaskQueue queue = (TaskQueue)super.getQueue();
try {
if (!queue.force(command, timeout, unit)) {
submittedCount.decrementAndGet();
throw new RejectedExecutionException(sm.getString("threadPoolExecutor.queueFull"));
}
} catch (InterruptedException x) {
submittedCount.decrementAndGet();
throw new RejectedExecutionException(x);
}
} else {
submittedCount.decrementAndGet();
throw rx;
}
}
}
private static class RejectHandler implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r,
java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
throw new RejectedExecutionException();
}
}
}TaskQueue 与?ThreadPoolExecutor 配合,修改线程分配策略
public class ThreadPoolExecutor extends AbstractExecutorService {
public void execute(Runnable command) {
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
// ctl 控制线程池的状态和活动线程的数量(低29位:线程池数量、高3位:线程池状态)
int c = ctl.get();
// 活动线程数 < 核心线程数, 创建线程
if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) {
// 尝试添加一个新的工作线程来执行任务
if (addWorker(command, true))
return;
c = ctl.get();
}
// 线程池处于运行状态,并且任务成功添加到工作队列中
if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) {
int recheck = ctl.get();
// 线程池非运行状态并且移除任务成功,走拒绝策略
if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command))
reject(command);
// 没有活动线程,添加一个新的工作线程
else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0)
addWorker(null, false);
}
// 线程池处于运行状态或入队不成功(taskQueue返回false),尝试创建新线程
else if (!addWorker(command, false))
// 创建线程失败走拒绝策略
reject(command);
}
}四、总结
对比 Tomcat? 线程池和 JDK 线程池,一个是线程数未达到最大线程数之前,优先创建线程执行任务,另一个是队列未满,优先让任务排队,总体而言tomcat线程池更适用于 IO 密集型应用场景,而对于CPU密集型任务,
ThreadPoolExecutor?是更通用和灵活性更高一些
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!