redis数据结构源码分析——跳表zset
文章目录
跳表的基本思想
Skip List(跳跃列表)这种随机的数据结构,可以看做是一个二叉树的变种,它在性能上与红黑树、AVL树很相近;但是Skip List(跳跃列表)的实现相比前两者要简单很多,目前Redis的zset实现采用了Skip List(跳跃列表)。
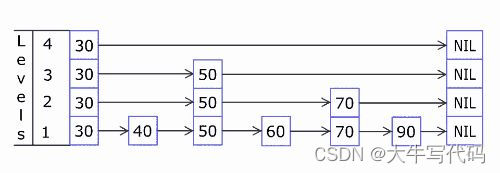
特点
1、分层,每层由有序链表构成
2、头节点在每层出现
3、某个节点如果在上层出现,那在下层也出现
4、节点的层数是随机的
节点与结构
跳跃表节点zskiplistNode
/* ZSETs use a specialized version of Skiplists */
typedef struct zskiplistNode {
sds ele;
double score;
struct zskiplistNode *backward;
struct zskiplistLevel {
struct zskiplistNode *forward;
unsigned long span;
} level[];
} zskiplistNode;
属性
ele:存储字符串数据
score:存储排序分值
*backward:指针,指向当前节点最底层的前一个节点
level[]:柔性数组,随机生成1-64的值
forward:指向本层下一个节点
span:本层下个节点到本节点的元素个数
跳跃表链表
typedef struct zskiplist {
struct zskiplistNode *header, *tail;
unsigned long length;
int level;
} zskiplist;
属性
header,tail:头节点和尾节点
length:跳跃表长度(不包括头节点)
tail:跳跃表高度
跳表的设计思想和优势
1、能够同时拥有链表和数优势的数据结构,既有链表插入快的特点又有数组查询快的特点
2、随机跨越层数
3、最底层的链表是双向链表,包含所有元素
4、对于有序链表查询优化,相比较于平衡数来说,更好实现
5、内存占用上来看,相比较于平衡数会更少
API解析
Tip:以下的zsl为zskiplist
zslCreate(创建跳跃表)
/* Create a new skiplist. */
zskiplist *zslCreate(void) {
int j;
zskiplist *zsl;
zsl = zmalloc(sizeof(*zsl));
zsl->level = 1;
zsl->length = 0;
zsl->header = zslCreateNode(ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL,0,NULL);
for (j = 0; j < ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL; j++) {
zsl->header->level[j].forward = NULL;
zsl->header->level[j].span = 0;
}
zsl->header->backward = NULL;
zsl->tail = NULL;
return zsl;
}
大致流程:
1、定义一个zsl,申请内存,赋初始值
2、调用zslCreateNode创建出头节点
3、每层头节点赋初始值
4、尾节点赋null值
zslCreateNode(创建节点)
/* Create a skiplist node with the specified number of levels.
* The SDS string 'ele' is referenced by the node after the call. */
zskiplistNode *zslCreateNode(int level, double score, sds ele) {
zskiplistNode *zn =
zmalloc(sizeof(*zn)+level*sizeof(struct zskiplistLevel));
zn->score = score;
zn->ele = ele;
return zn;
}
大致流程:
1、申请内存(节点内存和柔性数组的内存)
2、属性赋值
zslGetRank(查找排位)
排位就是累积跨越的节点数量
unsigned long zslGetRank(zskiplist *zsl, double score, sds ele) {
zskiplistNode *x;
unsigned long rank = 0;
int i;
x = zsl->header;
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (x->level[i].forward &&
(x->level[i].forward->score < score ||
(x->level[i].forward->score == score &&
sdscmp(x->level[i].forward->ele,ele) <= 0))) {
rank += x->level[i].span;
x = x->level[i].forward;
}
/* x might be equal to zsl->header, so test if obj is non-NULL */
if (x->ele && x->score == score && sdscmp(x->ele,ele) == 0) {
return rank;
}
}
return 0;
}
大致流程:
1、从最上层开始遍历节点并对比元素,对比score
2、如果当前分值大雨下一个分值,则累加span(比对分值,如果分值一样就比对ele)
3、指向本层的下一个节点
4、如果找到了,也就是ele相同,则返回
zslDelete(删除节点)
int zslDelete(zskiplist *zsl, double score, sds ele, zskiplistNode **node) {
zskiplistNode *update[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL], *x;
int i;
x = zsl->header;
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (x->level[i].forward &&
(x->level[i].forward->score < score ||
(x->level[i].forward->score == score &&
sdscmp(x->level[i].forward->ele,ele) < 0)))
{
x = x->level[i].forward;
}
update[i] = x;
}
/* We may have multiple elements with the same score, what we need
* is to find the element with both the right score and object. */
x = x->level[0].forward;
if (x && score == x->score && sdscmp(x->ele,ele) == 0) {
zslDeleteNode(zsl, x, update);
if (!node)
zslFreeNode(x);
else
*node = x;
return 1;
}
return 0; /* not found */
}
大致流程:
1、遍历跳表
2、比对分值,比对ele
3、如分值小于或等于当前值,并且ele不相等,继续下一个并记录节点
4、如分值和ele都相同,调用zslDeleteNode删除该节点
跳表是在很多排名以及分数相关的场景中使用频率极高的数据结构,也是设计的极其巧妙的一种结构,希望本篇文章能帮助各位更加深入的理解这种结构。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- this.baseMapper.getRoleNameByUserId 会调用什么
- C++ 实现游戏(例如MC)键位显示
- 06 HAL库驱动PWM常见的外设
- 网络编程day1
- DevC++ easyx实现地图拖动,超过屏幕大小的巨大地图的局部显示在屏幕的方法——用悬浮窗的原理来的实现一个视口
- BeanUtils工具类简介
- 静态网页设计——校园官网(HTML+CSS+JavaScript)
- Jmeter 压测 —— 性能调优5大注意!
- Open CASCADE 建模:瓶子教程
- 电脑开启虚拟化如何查看自己的主机主板型号