YOLOV5之提高模型评估和测试方法(Ensemble、TTA、WBF)
1、Model Ensembling Tutorial
1、Ensemble
集成建模是通过使用许多不同的建模算法或使用不同的训练数据集,创建多个不同的模型来预测结果的过程。然后,集成模型聚合每个基本模型的预测,并对未见数据进行一次最终预测。使用集成模型的动机是为了减少预测的泛化误差。只要基础模型具有多样性和独立性,采用集成方法时模型的预测误差减小。这种方法在进行预测时寻求群体的智慧。尽管集成模型在模型中具有多个基础模型,但它作为单个模型进行操作和执行。
1、Ensemble Test
python val.py --data data/tower.yaml --weights runs/train/exp1/weights/best.pt --img 1024 --half
在测试和推断时,只需将额外的模型附加到任何现有val.py或detect.py命令的weights参数中,就可以将多个预先训练的模型集成到一起。这个例子测试了两个模型的集成:
YOLOv5x
YOLOv5l6
python val.py --weights yolov5x.pt yolov5l6.pt --data coco.yaml --img 640 --half
代码位置:from models.experimental import attempt_download, attempt_load # scoped to avoid circular import
def attempt_load(weights, map_location=None, inplace=True, fuse=True):
from models.yolo import Detect, Model
# Loads an ensemble of models weights=[a,b,c] or a single model weights=[a] or weights=a
#加载模型权重=[a,b,c]或单个模型权重=[a]或权重=a的集合
model = Ensemble()
for w in weights if isinstance(weights, list) else [weights]:
ckpt = torch.load(attempt_download(w), map_location=map_location) # load
if fuse:
model.append(ckpt['ema' if ckpt.get('ema') else 'model'].float().fuse().eval()) # FP32 model
else:
model.append(ckpt['ema' if ckpt.get('ema') else 'model'].float().eval()) # without layer fuse
# Compatibility updates
for m in model.modules():
if type(m) in [nn.Hardswish, nn.LeakyReLU, nn.ReLU, nn.ReLU6, nn.SiLU, Detect, Model]:
m.inplace = inplace # pytorch 1.7.0 compatibility
if type(m) is Detect:
if not isinstance(m.anchor_grid, list): # new Detect Layer compatibility
delattr(m, 'anchor_grid')
setattr(m, 'anchor_grid', [torch.zeros(1)] * m.nl)
elif type(m) is Conv:
m._non_persistent_buffers_set = set() # pytorch 1.6.0 compatibility
if len(model) == 1:
return model[-1] # return model
else:
print(f'Ensemble created with {weights}\n')
for k in ['names']:
setattr(model, k, getattr(model[-1], k))
model.stride = model[torch.argmax(torch.tensor([m.stride.max() for m in model])).int()].stride # max stride
return model # return ensemble
Output:
val: data=./data/coco.yaml, weights=['yolov5x.pt', 'yolov5l6.pt'], batch_size=32, imgsz=640, conf_thres=0.001, iou_thres=0.6, task=val, device=, single_cls=False, augment=False, verbose=False, save_txt=False, save_hybrid=False, save_conf=False, save_json=True, project=runs/val, name=exp, exist_ok=False, half=True
YOLOv5 🚀 v5.0-267-g6a3ee7c torch 1.9.0+cu102 CUDA:0 (Tesla P100-PCIE-16GB, 16280.875MB)
Fusing layers...
Model Summary: 476 layers, 87730285 parameters, 0 gradients # Model 1
Fusing layers...
Model Summary: 501 layers, 77218620 parameters, 0 gradients # Model 2
Ensemble created with ['yolov5x.pt', 'yolov5l6.pt'] # Ensemble notice
val: Scanning '../datasets/coco/val2017.cache' images and labels... 4952 found, 48 missing, 0 empty, 0 corrupted: 100% 5000/5000 [00:00<00:00, 49695545.02it/s]
Class Images Labels P R mAP@.5 mAP@.5:.95: 100% 157/157 [03:58<00:00, 1.52s/it]
all 5000 36335 0.747 0.637 0.692 0.502
Speed: 0.1ms pre-process, 39.5ms inference, 2.0ms NMS per image at shape (32, 3, 640, 640) # <--- ensemble speed
Evaluating pycocotools mAP... saving runs/val/exp3/yolov5x_predictions.json...
...
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.515 # <--- ensemble mAP
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.699
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.75 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.557
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=100 ] = 0.356
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=100 ] = 0.563
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=100 ] = 0.668
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets= 1 ] = 0.387
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets= 10 ] = 0.638
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.689 # <--- ensemble mAR
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=100 ] = 0.526
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=100 ] = 0.743
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=100 ] = 0.844
2、Ensemble Inference
python detect.py --weights yolov5x.pt yolov5l6.pt --img 640 --source data/images
Output:
detect: weights=['yolov5x.pt', 'yolov5l6.pt'], source=data/images, imgsz=640, conf_thres=0.25, iou_thres=0.45, max_det=1000, device=, view_img=False, save_txt=False, save_conf=False, save_crop=False, nosave=False, classes=None, agnostic_nms=False, augment=False, update=False, project=runs/detect, name=exp, exist_ok=False, line_thickness=3, hide_labels=False, hide_conf=False, half=False
YOLOv5 🚀 v5.0-267-g6a3ee7c torch 1.9.0+cu102 CUDA:0 (Tesla P100-PCIE-16GB, 16280.875MB)
Fusing layers...
Model Summary: 476 layers, 87730285 parameters, 0 gradients
Fusing layers...
Model Summary: 501 layers, 77218620 parameters, 0 gradients
Ensemble created with ['yolov5x.pt', 'yolov5l6.pt']
image 1/2 /content/yolov5/data/images/bus.jpg: 640x512 4 persons, 1 bus, 1 tie, Done. (0.063s)
image 2/2 /content/yolov5/data/images/zidane.jpg: 384x640 3 persons, 2 ties, Done. (0.056s)
Results saved to runs/detect/exp2
Done. (0.223s)

3、Ensemble and TTA
模型集成和TTA不是相互排斥的。你可以TTA一个模型,你也可以集成一组有或没有TTA的模型:
集成运行多个模型,而TTA用不同的扩充测试单个模型。通常情况下,我看到的最佳结果是直接合并输出网格(即集成YOLOv5l和YOLOv5x),而不是简单地从多个模型中附加框以供NMS进行排序。这并不总是可能的,但是,例如用YOLOv5x集成一个efficiency entdet模型,你不能合并网格,你必须使用NMS或WBF(或merge NMS)来得到最终的结果
python detect.py --weights yolov5x.pt yolov5l6.pt --img 640 --source data/images
python detect.py --weights model1.pt model2.pt --augment
2、Test-Time Augmentation (TTA) Tutorial
本指南解释了如何在测试和推断过程中使用测试时间增强(TTA),以改进YOLOv5的mAP和召回。2022年9月25日更新。
1、TTA
TTA的基本流程是通过对原图做增强操作,获得很多份增强后的样本与原图组成一个数据组,然后用这些样本获取推理结果,最后把多份的推理结果按一定方法合成得到最后的推理结果再进行精度指标计算。流程图如下:
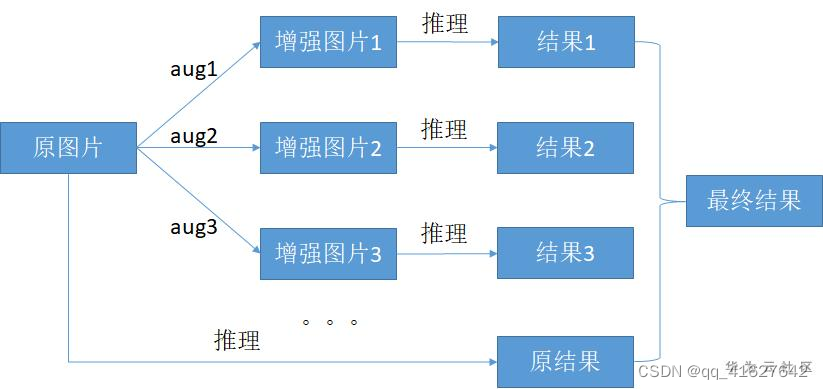
通常,只执行一个简单的测试时间扩展,比如移位、裁剪或图像翻转。
我们还通过图像的水平翻转来增加测试集;对原始图像和翻转后的图像进行软最大类后验平均,得到图像的最终得分。
1、Test Normally
在尝试TTA之前,我们想要建立一个基准性能来进行比较
python val.py --weights yolov5x.pt --data coco.yaml --img 640 --half
Output:
val: data=./data/coco.yaml, weights=['yolov5x.pt'], batch_size=32, imgsz=640, conf_thres=0.001, iou_thres=0.65, task=val, device=, single_cls=False, augment=False, verbose=False, save_txt=False, save_hybrid=False, save_conf=False, save_json=True, project=runs/val, name=exp, exist_ok=False, half=True
YOLOv5 🚀 v5.0-267-g6a3ee7c torch 1.9.0+cu102 CUDA:0 (Tesla P100-PCIE-16GB, 16280.875MB)
Fusing layers...
Model Summary: 476 layers, 87730285 parameters, 0 gradients
val: Scanning '../datasets/coco/val2017' images and labels...4952 found, 48 missing, 0 empty, 0 corrupted: 100% 5000/5000 [00:01<00:00, 2846.03it/s]
val: New cache created: ../datasets/coco/val2017.cache
Class Images Labels P R mAP@.5 mAP@.5:.95: 100% 157/157 [02:30<00:00, 1.05it/s]
all 5000 36335 0.746 0.626 0.68 0.49
Speed: 0.1ms pre-process, 22.4ms inference, 1.4ms NMS per image at shape (32, 3, 640, 640) # <--- baseline speed
Evaluating pycocotools mAP... saving runs/val/exp/yolov5x_predictions.json...
...
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.504 # <--- baseline mAP
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.688
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.75 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.546
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=100 ] = 0.351
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=100 ] = 0.551
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=100 ] = 0.644
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets= 1 ] = 0.382
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets= 10 ] = 0.628
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.681 # <--- baseline mAR
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=100 ] = 0.524
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=100 ] = 0.735
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=100 ] = 0.826
2、Test with TTA
向任何现有的val.py命令添加——augment以启用TTA,并将图像大小增加约30%以改善结果。注意,启用TTA的推断通常需要正常推断的2-3倍时间,因为图像被左右翻转并以3种不同的分辨率处理,输出在NMS之前合并。部分速度下降是由于更大的图像尺寸(832 vs 640),而另一部分是由于实际的TTA操作。
python val.py --weights yolov5x.pt --data coco.yaml --img 832 --augment --half
Output:
val: data=./data/coco.yaml, weights=['yolov5x.pt'], batch_size=32, imgsz=832, conf_thres=0.001, iou_thres=0.6, task=val, device=, single_cls=False, augment=True, verbose=False, save_txt=False, save_hybrid=False, save_conf=False, save_json=True, project=runs/val, name=exp, exist_ok=False, half=True
YOLOv5 🚀 v5.0-267-g6a3ee7c torch 1.9.0+cu102 CUDA:0 (Tesla P100-PCIE-16GB, 16280.875MB)
Fusing layers...
/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/torch/nn/functional.py:718: UserWarning: Named tensors and all their associated APIs are an experimental feature and subject to change. Please do not use them for anything important until they are released as stable. (Triggered internally at /pytorch/c10/core/TensorImpl.h:1156.)
return torch.max_pool2d(input, kernel_size, stride, padding, dilation, ceil_mode)
Model Summary: 476 layers, 87730285 parameters, 0 gradients
val: Scanning '../datasets/coco/val2017' images and labels...4952 found, 48 missing, 0 empty, 0 corrupted: 100% 5000/5000 [00:01<00:00, 2885.61it/s]
val: New cache created: ../datasets/coco/val2017.cache
Class Images Labels P R mAP@.5 mAP@.5:.95: 100% 157/157 [07:29<00:00, 2.86s/it]
all 5000 36335 0.718 0.656 0.695 0.503
Speed: 0.2ms pre-process, 80.6ms inference, 2.7ms NMS per image at shape (32, 3, 832, 832) # <--- TTA speed
Evaluating pycocotools mAP... saving runs/val/exp2/yolov5x_predictions.json...
...
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.516 # <--- TTA mAP
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.701
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.75 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.562
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=100 ] = 0.361
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=100 ] = 0.564
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=100 ] = 0.656
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets= 1 ] = 0.388
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets= 10 ] = 0.640
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.696 # <--- TTA mAR
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=100 ] = 0.553
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=100 ] = 0.744
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=100 ] = 0.833
3、Inference with TTA
python detect.py --weights yolov5s.pt --img 832 --source data/images --augment
4、PyTorch Hub TTA
TTA被自动集成到所有YOLOv5 PyTorch Hub模型中,并可以通过在推理时传递augment=True来访问。
import torch
# Model
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s') # or yolov5m, yolov5x, custom
# Images
img = 'https://ultralytics.com/images/zidane.jpg' # or file, PIL, OpenCV, numpy, multiple
# Inference
results = model(img, augment=True) # <--- TTA inference
# Results
results.print() # or .show(), .save(), .crop(), .pandas(), etc.
5、Customize TTA
You can customize the TTA ops applied in the YOLOv5 forward_augment() method here:
yolov5/models/yolo.py
Lines 125 to 137 in 8c6f9e1
def forward_augment(self, x):
img_size = x.shape[-2:] # height, width
s = [1, 0.83, 0.67] # scales
f = [None, 3, None] # flips (2-ud, 3-lr)
y = [] # outputs
for si, fi in zip(s, f):
xi = scale_img(x.flip(fi) if fi else x, si, gs=int(self.stride.max()))
yi = self.forward_once(xi)[0] # forward
# cv2.imwrite(f'img_{si}.jpg', 255 * xi[0].cpu().numpy().transpose((1, 2, 0))[:, :, ::-1]) # save
yi = self._descale_pred(yi, fi, si, img_size)
y.append(yi)
return torch.cat(y, 1), None # augmented inference, train
3、WBF加权框融合
实验
1、TTA在模型评估实验
python val.py --data data/tower.yaml --weights runs/train/exp1/weights/best.pt --img 1024 --half
all 526 1409 0.97 0.93 0.962 0.838
Speed: 0.5ms pre-process, 7.2ms inference, 1.6ms NMS per image at shape (32, 3, 1024, 1024)
Results saved to runs/val/exp14
python val.py --data data/tower.yaml --weights runs/train/exp1/weights/best.pt --img 1024 --half --augment
all 526 1409 0.968 0.946 0.969 0.839
Speed: 0.4ms pre-process, 20.3ms inference, 1.5ms NMS per image at shape (32, 3, 1024, 1024)
Results saved to runs/val/exp15
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Tomcat部署及优化
- linux 内核proc 文件系统与seq接口
- 穿越时空的创新:解析云原生与Web3.0的奇妙渊源
- Cython(将Python编译为so)
- 基于大数据的校园一卡通数据分析与可视化平台-计算机毕业设计
- 如何自学python编程,掌握这10个要点让你事半功倍!
- 威锋二手手机收售管理系统(JSP+java+springmvc+mysql+MyBatis)
- 家庭自动化初学者完整指南
- 基于SpringBoot的宠物领养系统
- 设计模式--组合模式