数据结构之顺序表的增删查改
别丢了你的勇敢
前言:
自今日起,我们正式越过C语言的大山,走向了数据结构的深山,现如今摆在我们面前的第一个坎就是顺序表,我们需要了解顺序表的定义,并且知道,如何对其进行增删查改,之后我们需要在此处基础上写出一份通讯录代码,ok,顺序表,启动!
1.什么是顺序表
1.1线性表
1.2顺序表
顺序表是一种线性表的数据结构,它是由一组具有相同特性的数据元素按照一定的顺序排列而成的。顺序表的底层结构是数组,对数组的封装,实现了常?的增删改查等接口。?顺序表可以使用数组来实现,也可以使用动态数组来实现。
顺序表分为静态顺序表和动态顺序表
静态顺序表是使用固定长度的数组来存储元素,数组的长度在创建时就确定了,无法改变。静态顺序表的优点是访问元素的时间复杂度为O(1),缺点是插入和删除元素的时间复杂度较高。
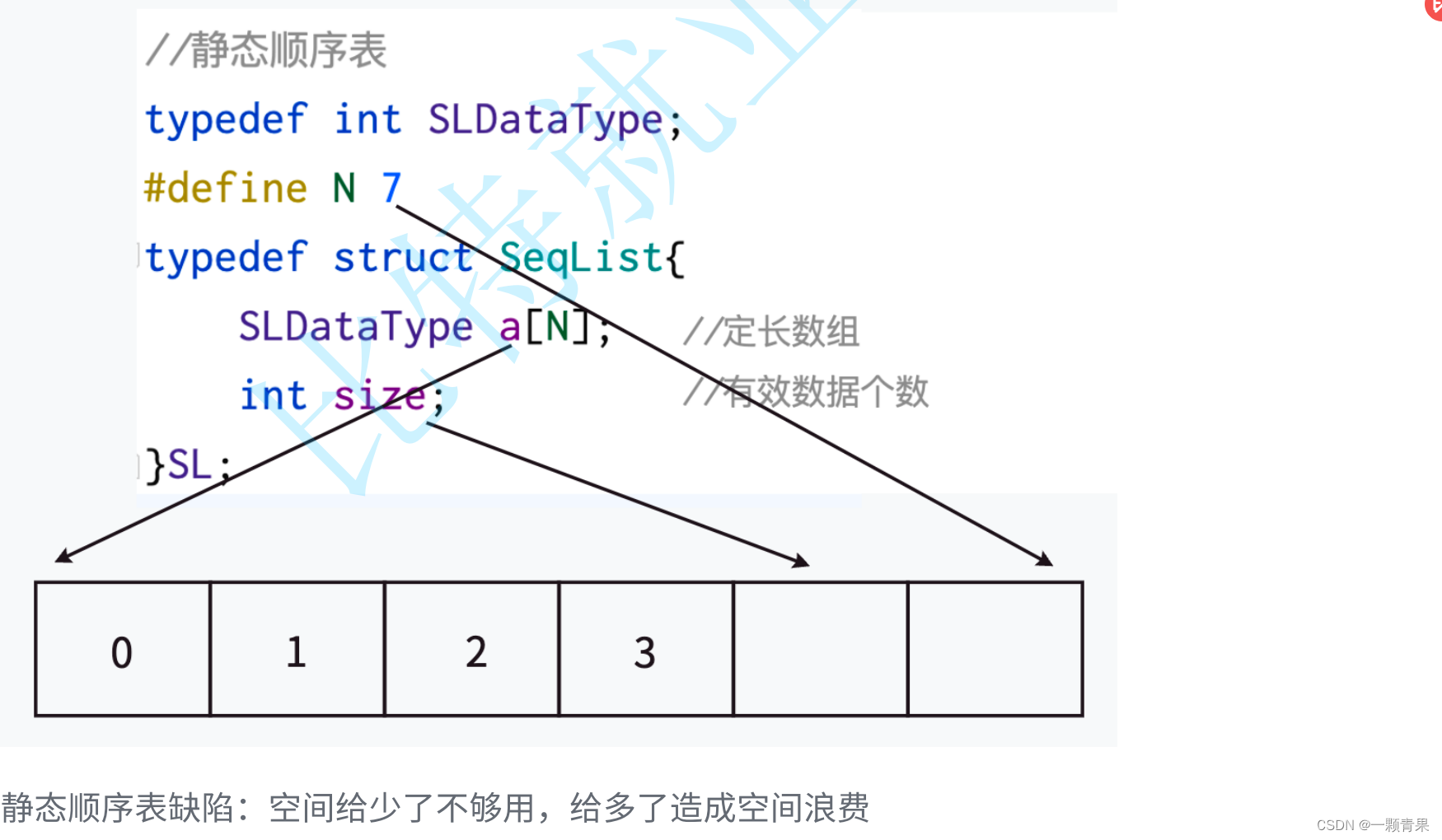
图片来自比特就业课官网链接:https://www.bitejiuyeke.com
动态顺序表是使用可以动态开辟的数组来存储元素,数组的长度可以根据需要进行动态调整。动态顺序表的优点是可以灵活地插入和删除元素,缺点是访问元素的时间复杂度为O(1)。
顺序表是一种常见的数据结构,它在实际中被广泛使用,常见的应用场景包括数组、字符串等。

图片来自比特就业课官网链接:https://www.bitejiuyeke.com
动态顺序表和静态顺序表的使用是极其相似的,只是静态的顺序表建立在栈区,动态顺序表通过动态内存分配建立于堆区,由于动态涉及了动态内存分配,难度会稍稍高一些,所以我们今天的增删查改直接是以动态顺序表为对象,如果你能明白了这个,那静态顺序表也是同样的原理,也是可以写出来的。
2、 动态顺序表的实现
2.1头文件
# define INIT_CAPACITY 4typedef int SLDataType;// 动态顺序表 -- 按需申请typedef struct SeqList{SLDataType* a;int size; // 有效数据个数int capacity; // 空间容量}SL;//初始化顺序表void SLInit (SL* ps);// 销毁顺序表void SLDestroy (SL* ps);// 打印顺序表内容void SLPrint (SL* ps);// 扩容void SLCheckCapacity (SL* ps);//尾 部插? 数据void SLPushBack (SL* ps, SLDataType x);//尾 部删除 数据void SLPopBack (SL* ps);// 头部插? 数据void SLPushFront (SL* ps, SLDataType x);// 头部删除 数据void SLPopFront (SL* ps);// 指定位置插? 数据void SLInsert (SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x);// 指定位置 删除数据void SLDelete(SL* ps, int pos);// 指定位置修改 数据void SLModify(SL* ps, int pos,SLDataType x);// 指定位置查找 数据void SLSearch(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x);
2.2具体分析
ok,然后咱们,从上到下,挨个分析
🍎2.2.1
#define INIT_CAPACITY 4
这是一个宏定义,也是我们初始化默认通讯录的初始容量,即四个单位空间
🍏2.2.2
typedef int SLDataType;
这是用typedef给int换了个名字,这时候肯定有人会问了,为啥不直接用int,
?? 原因如下:
我们的顺序表是对数组的封装,但我们不能确实是什么类型的数组,如果我直接用int,那后面代码里也都是int,可假如我后来想给这个数组换成char类型呢,那我就要把所有int都改为char,于是乎我们直接用typedef创建一个类型名,之后代码也都用这个类型名,这样我之后想修改就只需要把
typedef?int? SLDataType改为typedef char? SLDataType就ok了
这点在我们之后写通讯录时会体现出来
🍐 2.2.3
typedef struct SeqList{SLDataType* a;int size; // 有效数据个数int capacity; // 空间容量}SL;
🍊 2.2.4
void SLInit (SL* ps);
void SLInit(SL* ps)
{
?? ??? ?ps->a = (SLDataType*)malloc(CAPACITY * sizeof(SLDataType));
?? ??? ?ps->size = 0;
?? ??? ?ps->capacity = 4;
}
🍋2.2.5
void SLDestroy (SL* ps);
void SLDestroy(SL* ps)
{
?? ?free(ps->a);
?? ?ps->a = NULL;
?? ?ps->size = 0;
?? ?ps->capacity = 0;
}
🍌 2.2.6
void SLPrint (SL* ps);
void SLPrint(SL* ps)
{
?? ?for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
?? ??? ?printf("%d ?", ps->a[i]);
}
🍉 2.2.7
void SLCheckCapacity (SL* ps);
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{
?? ?SLDataType* p = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->a, 2 * ps->capacity * sizeof(SLDataType));
?? ?if (p == NULL)
?? ?{
?? ??? ?perror("realloc fail");
?? ??? ?exit(1);
?? ?}
?? ?ps->a = p;
?? ?ps->capacity *= 2;
}
🍇 2.2.8
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x); ?
??这个是尾插
- 在增加之前判断一下顺序表是不是满了,如果满了就调用扩容函数
- 再来一个尾插,也就是在数组最后面加入元素
- 之后直接在末尾加上该元素即可
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
?? ?if (ps->size + 1 > ps->capacity)
?? ??? ?SLCheckCapacity(ps);
?? ?ps->a[ps->size] = x;
?? ?(ps->size)++;
}
🍓 ?2.2.9
void SLPopBack (SL* ps);
- 尾删之前要判断一下顺序表是不是空的,
- 如果是就打印提示信息,若不是就把最后一个元素设置其值为0,
- 然后把顺序表的当前数据数量减一
void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{
?? ?if (ps->size - 1 < 0)
?? ?{
?? ??? ?printf("顺序表空了,无法删除\n");
?? ??? ?//perror("SLPopFront Fail");
?? ??? ?return ;
?? ?}
?? ?ps->a[ps->size - 1]=0;
?? ?(ps->size)--;
}
🍈2.2.10
void SLPushFront (SL* ps, SLDataType x);
- 第一步还是检验顺序表是不是满了
- 第二步我们要通过循环把所有元素集体向后移动一个单位,然后在空出来的第一个位置插入我们要插的值。
- 记得ps->size++
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType a)
{
?? ?if (ps->size + 1 > ps->capacity)
?? ??? ?SLCheckCapacity(ps);
?? ?for (int i = 1; i <= ps->size; i++)
?? ?{
?? ??? ?ps->a[i] = ps->a[i - 1];
?? ?}
?? ?(ps->size)++;
?? ?ps->a[0] = a;
}
🍒 2.2.11
void SLPopFront (SL* ps);
- 第一步检验顺序表是不是为空
- 第二步通过循环把元素集体向前移动一个单位,从而覆盖掉第一个元素
- 第三步ps->size--
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{
?? ?if (ps->size - 1 < 0)
?? ??? ?perror("SLPopFront Fail");
?? ?for (int i = 0; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
?? ?{
?? ??? ?ps->a[i] = ps->a[i + 1];
?? ?}
?? ?ps->a[ps->size - 1] = 0;
?? ?(ps->size)--;
}
🍑2.2.12
void SLInsert (SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x);
- 第一步检查是否需要扩容
- 第二步通过循环让下标pos及pos之后的元素集体后移一个单位,
- 第三步把数据放入下标为pos的地方
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)
{
?? ?if (ps->size + 1 < ps->capacity)
?? ??? ?SLCheckCapacity(ps);
?? ?for (int i = ps->size; i > pos; i--)
?? ??? ?ps->a[i] = ps->a[i - 1];
?? ?ps->a[pos] = x;ps->size++;
}
🥭2.2.13
void SLDelete(SL* ps, int pos);
- 第一步检查顺序表是否为空
- 第二步通过循环把下标pos之后的元素向前移动一个单位,从而覆盖掉pos对位空间的值
- 第三步ps->size--
void SLDelete(SL* ps, int pos)
{
?? ?if (ps->size - 1 < 0)
?? ?{
?? ??? ?printf("顺序表空了\n");
?? ??? ?//perror("SLPopFront Fail");
?? ??? ?return;
?? ?}
?? ?for (int i = pos; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
?? ??? ?ps->a[i] = ps->a[i + 1];
?? ?ps->size--;
}
🍍 2.2.14
void SLModify(SL* ps, int pos,SLDataType x);
void SLModify(SL* ps, int pos,SLDataType x)
{
?? ?if (pos >= ps->size)
?? ??? ?printf("要修改的元素不存在\n");
?? ?else
?? ??? ?ps->a[pos] = x;
}
🍍 2.2.15
void SLSearch(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x);
{
?? ?if (pos >= ps->size)
?? ??? ?printf("要查找的元素不存在\n");
?? ?else
?? ??? ?printf("%d\n",ps->a[pos]);
}
. 基于动态顺序表实现通讯录C语?基础要求:结构体、动态内存管理、顺序表、?件操作1、功能要求1)?少能够存储100个?的通讯信息2)能够保存??信息:名字、性别、年龄、电话、地址等3)增加联系?信息4)删除指定联系?5)查找制定联系?6)修改指定联系?7)显?联系?信息

本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 电脑文件msvcp140_1.dll丢失的解决方法,2分钟修复msvcp140_1.dll
- 算法实战(一)
- 抖音达人筛选需要注意什么,投放总结
- WorkPlus AI助理私有化部署,助力企业降本增效
- LLM之RAG理论(七)| 高提升RAG检索的四种方法
- 一种简单实用的电压电平转换器1V~3.6V FXLP34P5X
- 代理IP的计费方式有哪些?
- Python大数据之PySpark(六)RDD的操作
- Shell三剑客:awk(格式化输出)
- linux指令:grep