【Java】JDBC的使用
发布时间:2024年01月20日
JDBC
package jdbc_demo;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class jdbc {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
//1.注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获取连接
String url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test";
String username="root";
String password="123";
Connection conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
//3.定义sql
String sql ="update account set money = 3000 where id=1";
//4.获取执行sql的对象Statement
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
//5.执行sql
int count = stmt.executeUpdate(sql);//返回受影响的行数
//6.处理结果
System.out.println("受影响"+count+"行");
//7.释放资源
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
}


数据修改成功。
DriverManager
Driver Manager的作用:
注册驱动
获取数据库连接

静态代码块会进行注册驱动。
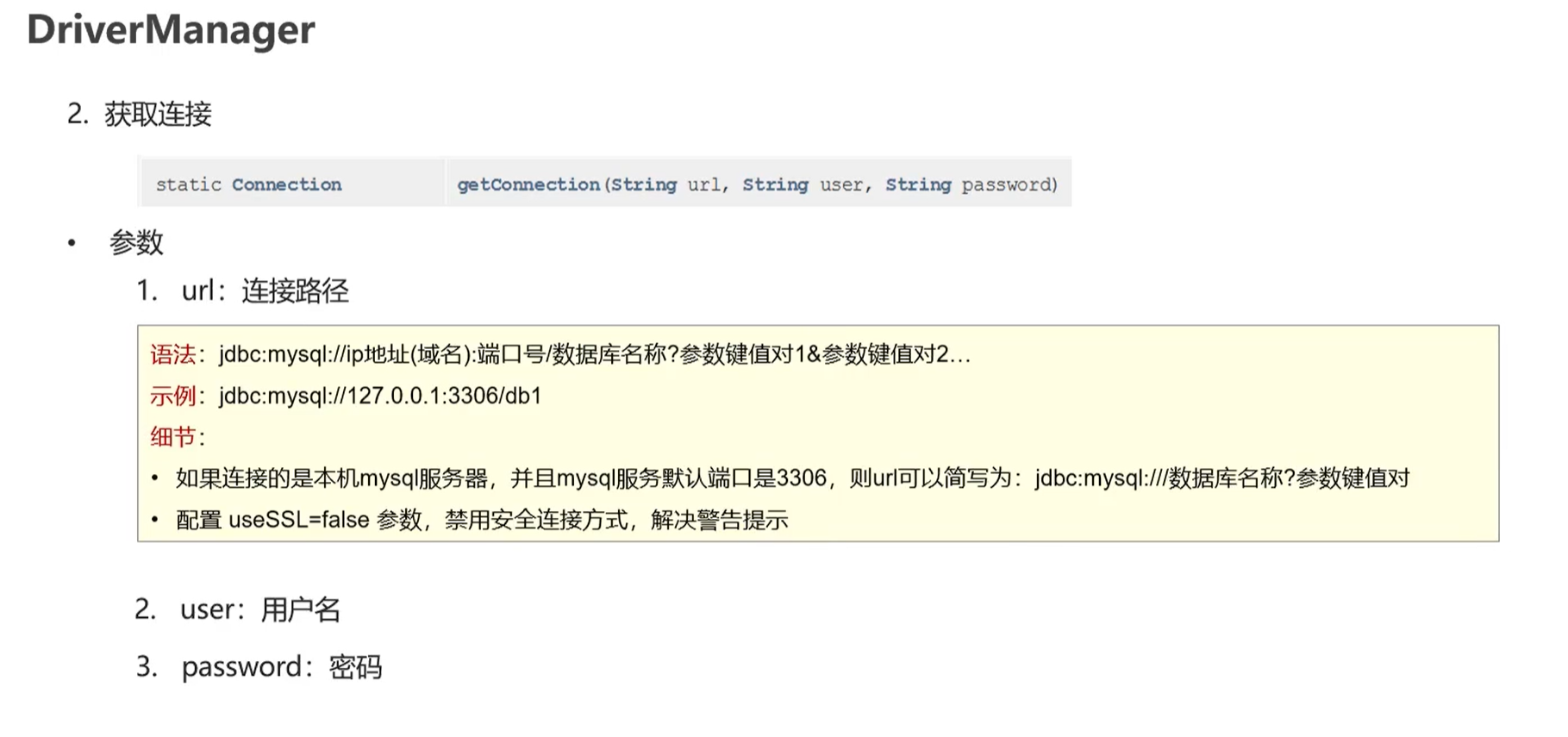
不使用SSL
jdbc:mysql:///db1?useSSL=false
Connection
Connection作用:
获取执行SQL的对象
管理事务
-
获取执行SQL的对象
- 普通执行SQL对象
Statement createStatement()- 预编译SQL的执行SQL对象:防止SQL注入
PreparedStatement prepareStatement(sql)- 执行存储过程的对象
CallableStatement prepareCall(sql) -
事务管理
- MySQL事务管理

- JDBC事务管理
开启事务:
setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit):true;true为自动提交事务,false为手动提交事务,也就是开启事务提交事务:
commit()回滚事务:
rollback()package jdbc_demo; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.Statement; public class jdbc { public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { //1.注册驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); //2.获取连接 String url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test"; String username="root"; String password="123"; Connection conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password); conn.setAutoCommit(false); //3.定义sql String sql1 ="update account set money = 3000 where id=1"; String sql2 ="update account set money = 3000 where id=2"; //4.获取执行sql的对象Statement Statement stmt = conn.createStatement(); //5.执行sql int count1 = 0;//返回受影响的行数 int count2 = 0; try { count1 = stmt.executeUpdate(sql1); count2 = stmt.executeUpdate(sql2); //都执行完毕了,就提交事务 conn.commit(); } catch (Exception e) { conn.rollback(); throw new RuntimeException(e); } //6.处理结果 System.out.println("受影响"+count1+"行"); System.out.println("受影响"+count2+"行"); //7.释放资源 stmt.close(); conn.close(); } }
Statement

ResultSet

while(rs.next())//光标移动到下一行,并且判断当前行数据是否有效
{
//获取数据
rs.getXxx(参数);
}
package jdbc_demo;
import java.sql.*;
public class jdbc {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
//1.注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获取连接
String url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test";
String username="root";
String password="123";
Connection conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
//3.定义sql
String sql="select * from account";
//4.获取Statement对象
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
//执行sql语句
ResultSet rs=stmt.executeQuery(sql);
while(rs.next()){
int id=rs.getInt(1);
String name=rs.getString(2);
double money =rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id);
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(money);
System.out.println("--------------------");
}
//7.释放资源
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
}
需求:查询account账户表数据,封装为Account对象中,并且存储到ArrayList集合当中。
package jdbc_demo;
import pojo.Account;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class jdbc {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
//1.注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获取连接
String url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test";
String username="root";
String password="123";
Connection conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
//3.定义sql
String sql="select * from account";
//4.获取Statement对象
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
//执行sql语句
ResultSet rs=stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//创建集合
List<Account> list=new ArrayList<>();
while(rs.next()){
Account account=new Account();
int id=rs.getInt(1);
String name=rs.getString(2);
double money =rs.getDouble(3);
account.setId(id);
account.setName(name);
account.setMoney(money);
list.add(account);
}
System.out.println(list);
//7.释放资源
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
}
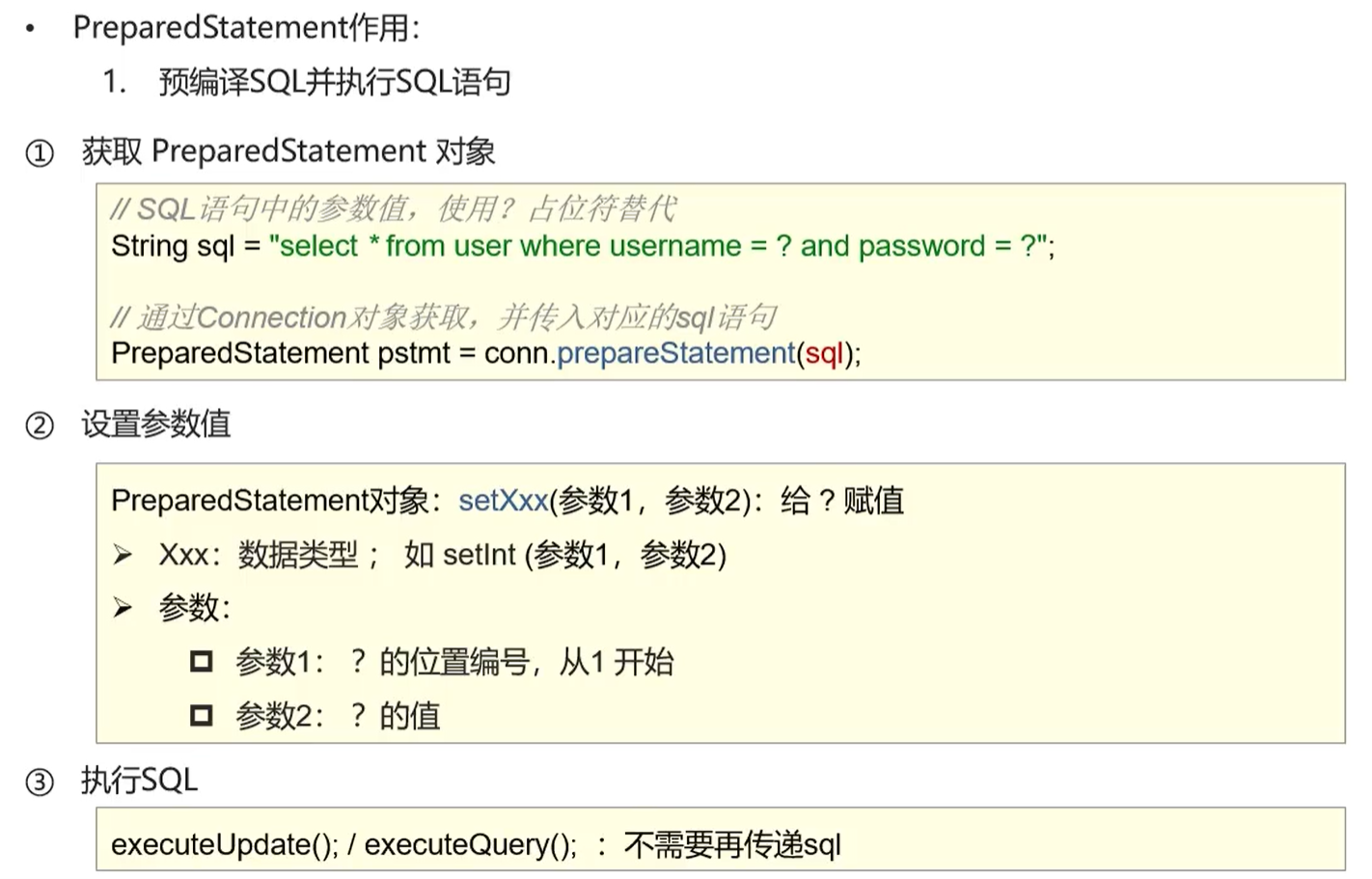
PreparedStatement
PreparedStatement可以在预编译阶段预防SQL注入问题。
public void testLogin_Inject() throws SQLException {
String url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test";
String username="root";
String password="123";
Connection conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
//接收用户输入 用户名和密码
String name="张三";
String pwd="123456";
String sql ="select * from user where username='"+name+"'and password='"+pwd+"'";
Statement stmt=conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs=stmt.executeQuery(sql);
if(rs.next()){
System.out.println("登录成功");
}else{
System.out.println("登录失败");
}
}
public void testLogin_Inject() throws SQLException {
String url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test";
String username="root";
String password="123";
Connection conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
//接收用户输入 用户名和密码
String name="张三";
String pwd="'or'1'='1";
String sql ="select * from user where username='"+name+"'and password='"+pwd+"'";
Statement stmt=conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs=stmt.executeQuery(sql);
if(rs.next()){
System.out.println("登录成功");
}else{
System.out.println("登录失败");
}
}

为什么可以登录成功?分析一下sql语句
select * from user where username='张三'and password=''or'1'='1'
前半段无论正确与否,后半段的1=1永远成立,又是or连接符,自然查询成功了。
如何解决?
package jdbc_demo;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
public class PreparedStatement {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
String url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test";
String username="root";
String password="123456";
String name="张三";
String pwd="'or'1'='1";
Connection conn= DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
// 修复了 SQL 语句中的问题
String sql ="select * from user where username=? and password=?";
java.sql.PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1,name);
pstmt.setString(2,pwd);
//执行sql
ResultSet rst=pstmt.executeQuery();
if(rst.next()){
System.out.println("登录成功");
}else{
System.out.println("登录失败");
}
}
}

文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/2301_79516932/article/details/135709105
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!