SpringBoot实用篇
SpringBoot实用篇
1、热部署
-
什么是热部署?
所谓热部署,就是在应用正在运行的时候升级软件,却不需要重新启动应用。对于Java应用程序来说,热部署就是在运行时更新Java类文件。
-
热部署有什么用?
- 节约时间,热部署只需要重新更新一下改动过的class文件,不需要全部再编译一遍
- 提高开发效率,热部署对于静态资源能够实现实时更新,不需要再重启项目
1.1 手动开启热部署
之前在SSM中我们热部署,是通过勾选两个选项就实现了:

而在SpringBoot首先我们需要通过热部署依赖实现热部署:(Step1)
<!--热部署依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 配置插件,让热部署依赖spring-boot-devtools生效 -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<!-- 设置为true,让热部署devtools生效 -->
<fork>true</fork>
<addResources>true</addResources>
</configuration>
</plugin>
然后每次当我们修改了代码(Step2)后,我们需要点击构建项目:(Step3)

这样就不需要重启项目了
知识拓展:重启和重载
- 重启(Restart):自定义开发代码,包含类、页面、配置文件等,加载位置restart类加载器
- 重载(ReLoad):jar包,加载位置base类加载器
重新运行项目也就是重启项目包括了Restart过程和ReLoad过程,而热部署只包含Restart过程
1.2 自动开启热部署
自动开启热部署,也是需要引入热部署依赖的
-
Step1:

-
Step2:
温馨提示:如果使用的是IDEA 2021.2之前版本的话还是使用快捷键
Shift+Ctrl+Alt+/,选择Registry...,将compiler.automake.allow.when.app.running选项勾上(这里我使用的是2022版的IDEA)
注意:汉化后的IDEA这个选项的位置发生了变化

-
Step3:
IDEA鼠标悬停5秒不动,IDEA就会自动开启热部署
1.3 热部署相关配置
通过修改项目中的文件,你可以发现其实并不是所有的文件修改都会激活热部署的,原因在于在开发者工具中有一组配置,当满足了配置中的条件后,才会启动热部署,配置中默认不参与热部署的目录信息如下:
/META-INF/maven/META-INF/resources/resources/static/public/templates
以上目录中的文件如果发生变化,是不参与热部署的。如果想修改配置,可以通过application.yml文件进行设定哪些文件不参与热部署操作,如果想添加不参与热部署的文件或文件夹,可以通过下面的配置:
spring:
devtools:
restart:
# 设置不参与热部署的文件或文件夹
exclude: static/**,public/**,config/application.yml
# 关闭或开启热部署(false表示关闭)
enable: false
/**表示文件夹
知识拓展:
在resource下的配置文件中选择关闭热部署,可以会在其它地方打开,比如在resource/config/下的配置文件中开启了热部署,又或者在file下的配置文件,又或者是file下config下的配置文件中开启了热部署,这是由于其它三个配置文件的优先级要高于resource下的配置文件,我们可以通过设置临时属性来提高优先级,也可以通过设置Java系统属性值,具体相关知识可以参考:SpringBoot运维篇学习笔记
2、高级配置
相关配置学习,在基础篇的学习了配置,在运维篇也学习了配置,现在实用篇还是接着学习配置。越往后相关配置就越接近开发,相关配置也是在开发中最常用的那些
2.1 属性绑定
所谓的属性绑定就是指“属性文件中的属性和配置类中字段之间形成一个映射关系”
2.1.1 @ConfigurationProperties
-
使用
@ConfigurationProperties实现属性绑定-
为自定义的Bean绑定属性
配置文件(application.yml):
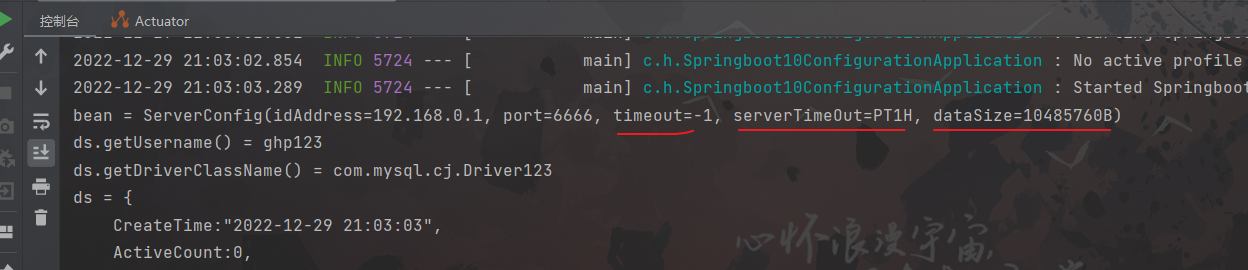
servers: idAddress: 192.168.0.1 port: 6666 timeout: -1配置类(ServerConfig):
package com.hhxy.config; import lombok.Data; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * @author ghp * @date 2022/12/29 * @title * @description */ @Component @Data @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "servers") public class ServerConfig { private String idAddress; private int port; private long timeout; }可能会报这个警告:
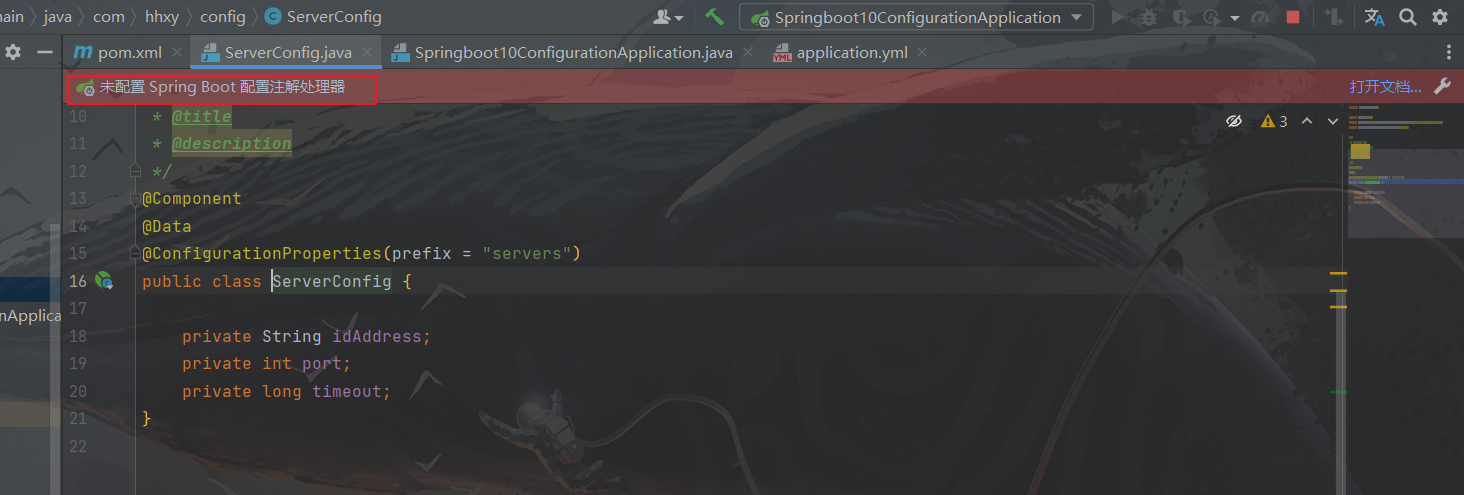
需要添加依赖:
<!--SpringBoot配置注解处理器的依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> </dependency>测试类(可以重新创建一个测试类,这里我是直接使用了启动类来测试):
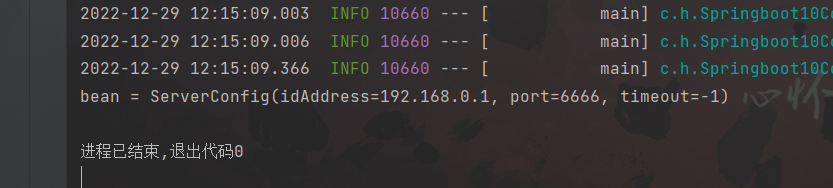
package com.hhxy; import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource; import com.hhxy.config.ServerConfig; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; @SpringBootApplication public class Springboot10ConfigurationApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { ConfigurableApplicationContext ctx = SpringApplication.run(Springboot10ConfigurationApplication.class, args); ServerConfig bean = ctx.getBean(ServerConfig.class); System.out.println("bean = " + bean); } }测试结果:
-
为第三方的Bean绑定属性
配置类(这里我是直接将测试代码和第三方Bean都写在了入口类,可以分开写,将第三方Bean写在一个单独的配置类中):
package com.hhxy; import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; @SpringBootApplication public class Springboot10ConfigurationApplication { @Bean //@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "datasource")//这里也可以使用这个注解与配置文件中的值进行属性绑定 public DruidDataSource dataSource(){ DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource(); ds.setUsername("ghp"); ds.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); return ds; } public static void main(String[] args) { ConfigurableApplicationContext ctx = SpringApplication.run(Springboot10ConfigurationApplication.class, args); DruidDataSource ds = ctx.getBean(DruidDataSource.class); System.out.println("ds.getUsername() = " + ds.getUsername()); System.out.println("ds.getDriverClassName() = " + ds.getDriverClassName()); System.out.println("ds = " + ds); } }测试结果:
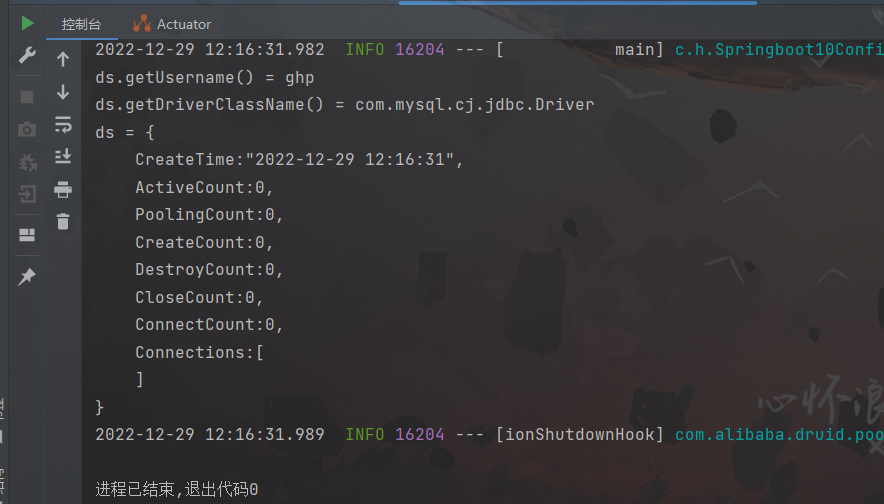
如果使用ConfigurationProperties进行属性绑定,但同时使用set设置属性值:
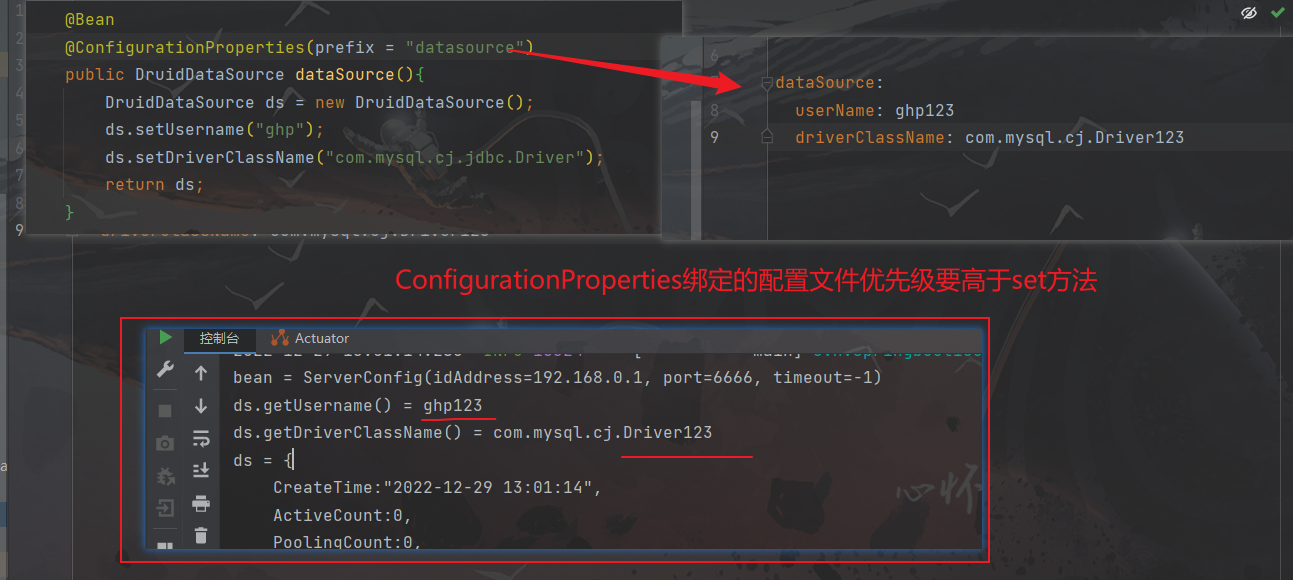
-
知识拓展:
@EnableConfigurationProperties(开启属性绑定,并确定属性绑定的目标是谁)使用@ConfigurationProperties注解可以为bean进行属性绑定,那在一个业务系统中,哪些bean通过注解@ConfigurationProperties去绑定属性了呢
目前我们定义Bean不是通过类注解
@Compent定义,就是通过@Bean定义。通过类注解定义的Bean,我们将@ConfigurationProperties注解写在类上,通过@Bean定义的,我们将@ConfigurationProperties注解写在方法上,那么我们该如何确定哪些Bean通过@ConfigurationProperties注解绑定了属性呢?因为这个注解不仅可以写在类上,还可以写在方法上,所以找起来就比较麻烦了。为了解决这个问题,SpringBoot给我们提供了一个全新的注解,专门标注使用@ConfigurationProperties注解绑定属性的Bean是哪些。
@EnableConfigurationProperties注解的主要作用是用来标记哪些Bean是使用@ConfigurationProperties去绑定了属性的,此外它不仅具有标记功能,还能帮我们把标记的类创建一个Bean(这个注解只能写在类上,方便查找)@SpringBootApplication // 告诉开发者ServerConfig配置类是使用@ConfigurationProperties去绑定属性的,同时为它创建一个Bean @EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerConfig.class) public class Springboot10ConfigurationApplication { ... }注意:此时ServerConfig不需要再去添加
@Component注解了(这个@ConfigurationProperties注解仍然需要),因为@EnableConfigurationProperties注解已经为他创建了一个Bean,如果同时存在会报一个NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException(没有定义唯一的Bean,说明此时重复定义了Bean)的异常PS:@EnableConfigurationProperties注解可以同时标注多个类
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ServerConfig.class,A.class,B.class,...})
2.1.2 宽松绑定/松散绑定
可以看到当我们的datasource编程dataSource时,就会报错:
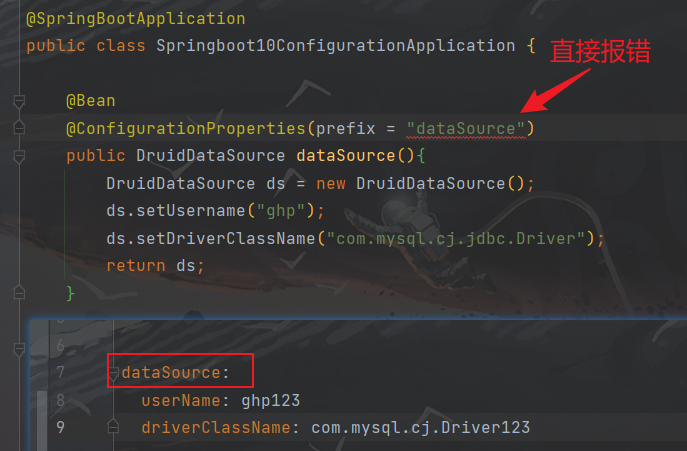
这是由于这里属于严格格式,必须按照特定的规则(纯小写)来进行书写,但是对于配置文件中的属性和配置类中的字段,却是使用宽松绑定(松散绑定)的
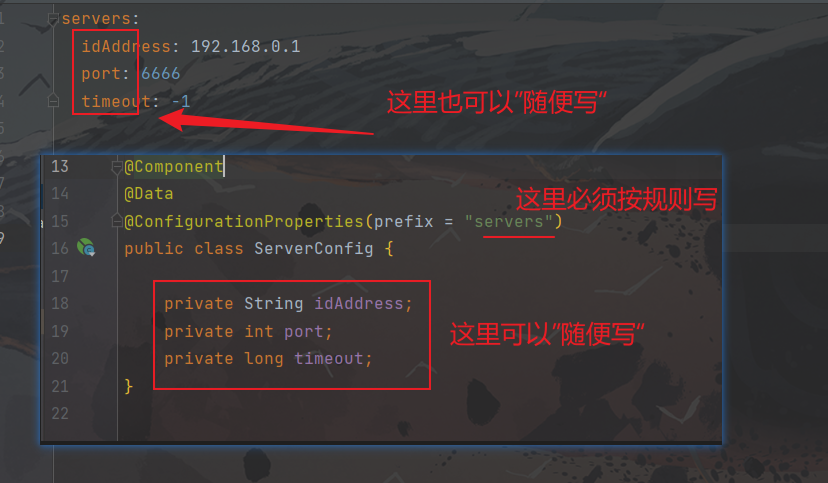
这里的随便写,意思就是可以忽略大小写、_、-,这三种东西可以随意组合,比如:idaddress,id-address,id_adress,Id-AddR_ess……这些最终都可以匹配到配置类中的idAdress,同理配置类中的idAddress也可以三种方式任意组合,常用的有三种形式:烤肉串模式,下滑行模式,小驼峰模式,常量模式
==注意:==必须是@ConfigurationProperties注解绑定的属性,才能随便写,如果使用@Value("${servers.idAddress}")注解获取配置文件中的属性值,则该属性只能使用 idAdress 这一种写法,否则就直接报错
2.2 常用计量单位
配置文件
servers:
idAddress: 192.168.0.1
port: 6666
timeout: -1
serverTimeOUt: 1
dataSize: 10 # 这里现在代表10MB,因为@DataSizeUnit设置的单位是MB
# dataSize: 10MB # 可以不使用注解,直接在这里使用MB,和上面使用注解的效果是一样的
配置类:
@Component
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "servers")
public class ServerConfig {
private String idAddress;
private int port;
private long timeout; // long的单位一般默认ms,但是它没有提示
@DurationUnit(ChronoUnit.HOURS)
private Duration serverTimeOut; // 使用Duration,可以让数字带单位(默认是ms),并且可以设置单位,比如年、月、日
@DataSizeUnit(DataUnit.MEGABYTES)
private DataSize dataSize; // 设置容量大小(默认单位是B),可以将单位改成MB、KB、GB
}
测试类:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext ctx = SpringApplication.run(Springboot10ConfigurationApplication.class, args);
ServerConfig bean = ctx.getBean(ServerConfig.class);
System.out.println("bean = " + bean);
DruidDataSource ds = ctx.getBean(DruidDataSource.class);
System.out.println("ds.getUsername() = " + ds.getUsername());
System.out.println("ds.getDriverClassName() = " + ds.getDriverClassName());
System.out.println("ds = " + ds);
}
PS:104857608 B / 1024 = 10240 KB / 1024 = 10MB
2.3 属性校验
??目前我们在进行属性绑定时可以通过松散绑定规则在书写时放飞自我了,但是在书写时由于无法感知模型类中的数据类型,就会出现类型不匹配的问题,比如代码中需要int类型,配置中给了非法的数值,例如写一个“a",这种数据肯定无法有效的绑定,还会引发错误。
??SpringBoot给出了强大的数据校验功能,可以有效的避免此类问题的发生。在JAVAEE的JSR303规范中给出了具体的数据校验标准,开发者可以根据自己的需要选择对应的校验框架,此处使用Hibernate提供的校验框架来作为实现进行数据校验。书写应用格式非常固定,话不多说,直接上步骤
-
Step1:导入依赖
这里需要两个依赖,一个是JSR303规范,一个是JSR303规范的实现类,它们就类似于JDBC和MySQL驱动的关系。
<!--属性校验依赖(JSR303规范)--> <dependency> <groupId>javax.validation</groupId> <artifactId>validation-api</artifactId> </dependency> <!--Hibernate校验器(JSR303规范的实现类)--> <dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate.validator</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId> </dependency> -
Step2:在需要开启校验功能的类上使用注解
@Validated开启校验功能 -
Step3:在开启了校验功能的类中的字段上添加校验规则
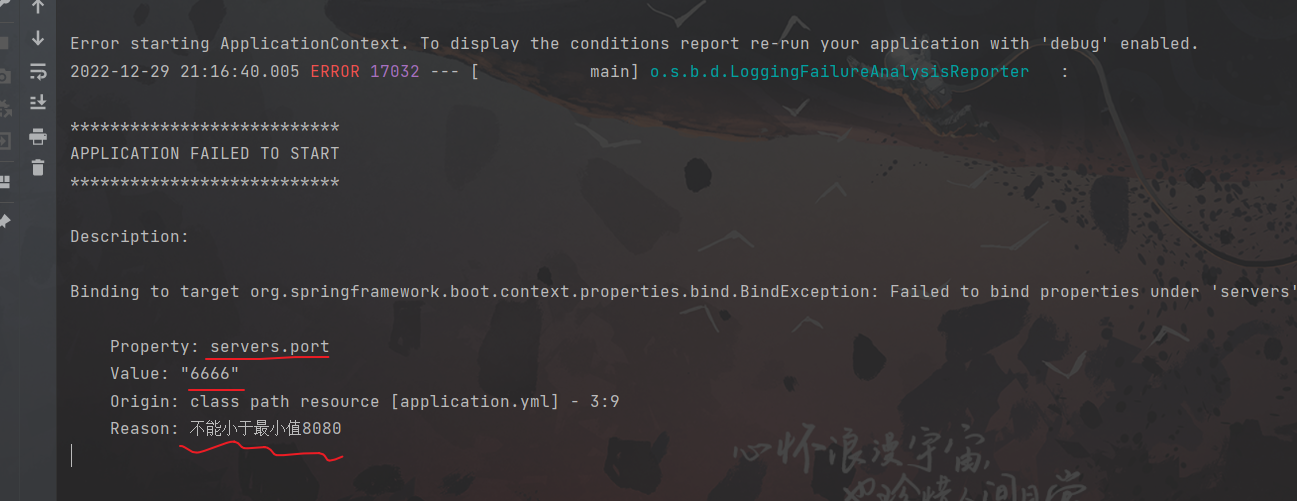
@Component @Data @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "servers") @Validated public class ServerConfig { private String idAddress; @Max(value = 8888, message = "不能大于最大值8888") @Min(value = 8080, message = "不能小于最小值8080") private int port; private long timeout; @DurationUnit(ChronoUnit.HOURS) private Duration serverTimeOut; @DataSizeUnit(DataUnit.MEGABYTES) private DataSize dataSize; } -
Step4:测试
测试类和2.2中的是一样的,略
知识拓展:类型转换的一个坑

在SpringBoot中,如果对于纯数字的字符串不使用引号包括,在解析时会将他转换成int类型!比如0127,它先会被默认当成8进制(8进制都是以0开始的,后面接0~7),0127转成int类型(默认是10进制)87,此时当我们获取配置属性中的值,就变成了87.
所以配置文件中书写纯数字的字符串时,一定要养成添加引号的习惯,说不定哪天就碰到这种错误了,让你看半天(习惯很重要)。
如果字符串是0x123也一样,会当成16进制来转换……
3、测试
3.1 加载测试属性
-
设置临时测试属性
配置文件:
test: prop: testValue测试类:
// properties用于添加临时属性 //@SpringBootTest(properties = {"test.prop=testValue1"}) // args同样可以添加临时属性 @SpringBootTest(args = {"--test.prop=testValue2"}) public class PropertiesAndArgsTest { @Value("${test.prop}") private String value; @Test public void testProperties(){ System.out.println(value); } }注意:当properties和args同时存在时,以args为主,三者的优先级是:
@Value < properties < args -
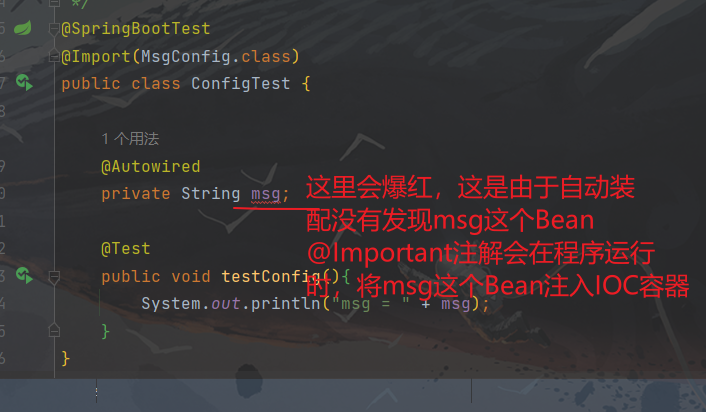
@Important:为测试类导入专属配置配置类:
package com.hhxy.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; /** * @author ghp * @date 2022/12/29 * @title * @description */ public class MsgConfig { @Bean public String msg(){ return "MsgConfig被加载了"; } }测试类:
package com.hhxy.test; import com.hhxy.config.MsgConfig; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import; /** * @author ghp * @date 2022/12/29 * @title * @description */ @SpringBootTest @Import(MsgConfig.class) public class ConfigTest { @Autowired private String msg; @Test public void testConfig(){ System.out.println("msg = " + msg); } }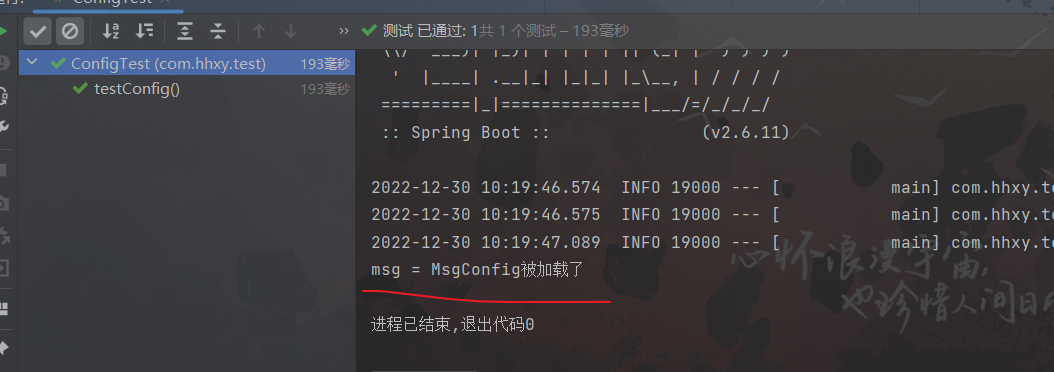
这样这个配置类就只能在这一个测试类中生效了,对其它测试类没有任何的影响
3.2 测试Controller
之前测试Controller都是使用postmain或者是RestfulTool插件进行测试的,而SpringBoot为我们提供了测试Controller的方式,只是默认是处于关闭状态的,我们需要手动开启
3.2.1 开启Controller测试
如果我们想要测试Controller(表现层),首先我们应该在测试的使用启动Web服务器
- 默认值:
SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.NONE,不启动Web服务器 SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.DEFINED_PORT:启动Web服务器,并使用自定义的端口(也就是你当前配置的端口,没有配置就默认是8080)SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT:启动Web服务器,并且使用随机端口
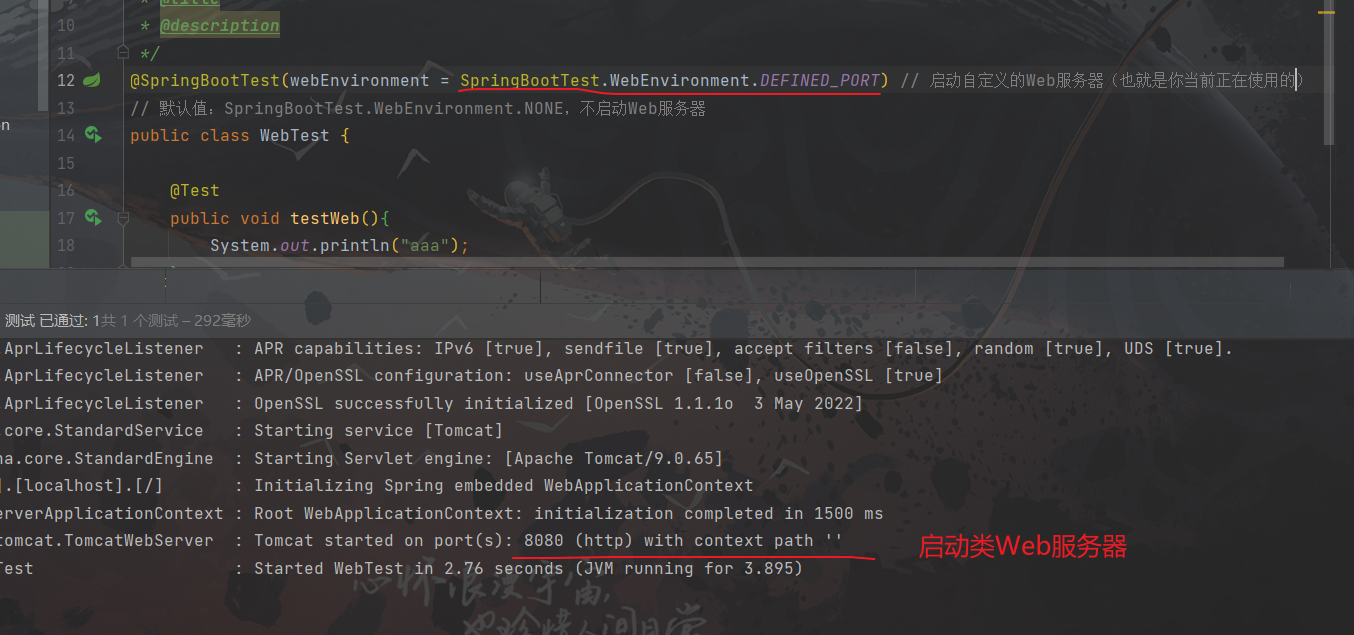
实例:
先准备一个Controller
package com.hhxy.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author ghp
* @date 2022/12/30
* @title
* @description
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@GetMapping("/test1")
public String test1(){
System.out.println("test1被访问了!");
return "test1被访问";
}
}
-
Step1:开启Web服务器
// 开启Web服务器,并使用自定义的端口 @SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.DEFINED_PORT) public class WebTest { } -
Step2:开启虚拟调用
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.DEFINED_PORT) // 开启虚拟MVC的调用 @AutoConfigureMockMvc public class WebTest { } -
Step3:创建请求
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder requestBuilder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/test/test1"); -
Step4:执行请求
package com.hhxy.test; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc; import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockHttpServletRequestBuilder; import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders; /** * @author ghp * @date 2022/12/30 * @title * @description */ @SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.DEFINED_PORT) @AutoConfigureMockMvc public class WebTest { @Test public void testWeb(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception { // 访问路径: http://localhost:8080/test/test1 // 创建一个虚拟的请求 MockHttpServletRequestBuilder requestBuilder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/test/test1"); // 执行请求 mvc.perform(requestBuilder); } }测试结果如下:
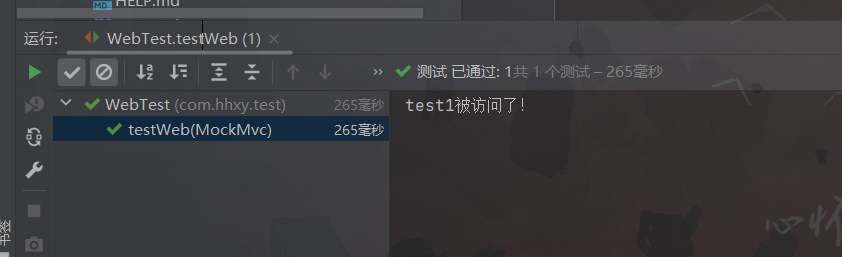
3.2.2 匹配响应数据
-
匹配响应状态
// 开启Web服务器,并使用自定义端口 @SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.DEFINED_PORT) // 开启虚拟MVC的调用 @AutoConfigureMockMvc public class WebTest { @Test public void testStatus(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception { // 创建一个虚拟的请求 MockHttpServletRequestBuilder requestBuilder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/test/test2"); // 执行请求 ResultActions actions = mvc.perform(requestBuilder); // 设置预期值,用于判断是否请求成功 StatusResultMatchers status = MockMvcResultMatchers.status(); ResultMatcher ok = status.isOk(); // status中的API封装了所有请求状态(这里我使用的状态是请求成功,状态码是200) // 将预期值与响应状态进行匹配 actions.andExpect(ok); } }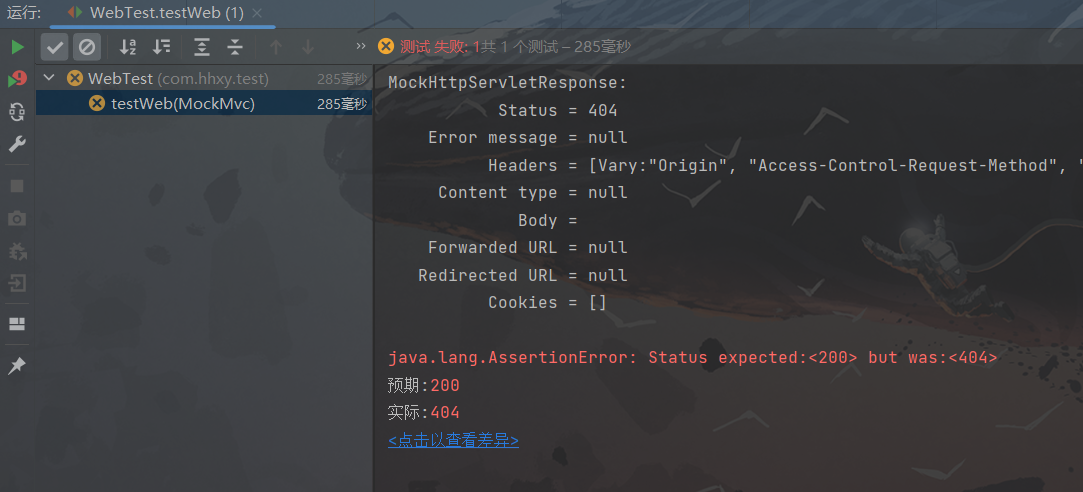
-
匹配响应体
@Test public void testResponseBody(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception { // 创建一个虚拟的请求 MockHttpServletRequestBuilder requestBuilder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/test/test1"); // 执行请求 ResultActions actions = mvc.perform(requestBuilder); // 设置预期值,用于判断是否请求成功 ContentResultMatchers content = MockMvcResultMatchers.content(); ResultMatcher result = content.string("springboot"); // ResultMatcher json = content.json(""); // 还可以匹配JSON字符串 // 添加预期值与响应值进行匹配 actions.andExpect(result); }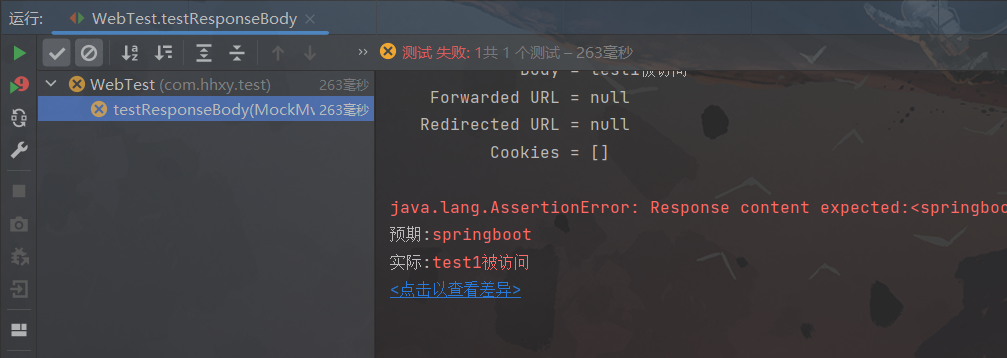
-
匹配响应头
// 创建并执行请求 // 设置预期值 HeaderResultMatchers header = MockMvcResultMatchers.header(); ResultMatcher contentType = header.string("Content-Type", "application/json"); // 添加预期值与响应值进行匹配 action.andExpect(contentType);
3.3 测试回滚
前面(运维篇1.1小节)我们遇到了,打包项目时test下所有的测试方法都被执行了一遍,这是由于Maven的生命周期决定的。所有的测试方法执行一遍后,会给我们的数据库添加一些没有用的测试数据,虽然当时我们可以通过IDEA设置跳过测试,但显然跳过测试会给项目带来极大的安全隐患,所以我们需要测试,但如果避免测试后数据无法持久化保存到数据库中呢?这就需要用到测试回滚了
主要实现是靠@Transactional注解,这个注解添加类上,可以让类中所有的方法变成一个个事物(在Spring篇学过),添加这个注解后,所有的方法就会被当成事物,众所周知事务必须提交才能生效,比提交的事物可以随时回滚,而在测试类中添加@Transactional注解,它的默认配置项@Rollback是true,并且测试类中的事务默认是不提交的,这样测试方法照样可以运行,但是数据是不能添加到数据库中的(如果想要数据添加到数据库中,可以设置@Rollback为false)
@SpringBootTest
@Transactional
@Rollback(true)
public class DaoTest {
@Autowired
private BookService bookService;
@Test
void testSave(){
Book book = new Book();
book.setName("test`");
book.setName("test`");
book.setName("test`");
// 将测试数据添加到数据库中
bookService.save(book);
}
}
3.4 随机生成测试用例
前面我们一直都是使用硬编码,将测试数据写死的,但是写死的数据是很难成功测出bug的,所以我们需要随机生成测试数据
配置文件:
testCase:
book:
id: ${random.int}
id2: ${random.int(10)} # [0,10)的整数
id3: ${random.int(5,10)} # [5,10)的整数
id4: ${random.int?5,10!}
# [5,10)的整数,数字前后可以是任意的符号,非敏感字符除外,比如-号,这里了解即可,一般都默认使用括号
name: ${random.value} # 随机生成一个MD5加密的32位字符串
uuid: ${random.uuid} # 随机生成一个uuid
publishTime: ${random.long} # 随机生成long范围内的整数
配置类:
@Component
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "testcase.book")
public class BookCase {
private int id;
private int id2;
private int id3;
private int id4;
private String name;
private String uuid;
private long publishTime;
}
测试类:
@SpringBootTest
public class BookCaseTest {
@Autowired
BookCase bookCase;
@Test
public void testBookCase(){
System.out.println("bookCase = " + bookCase);
}
}
4、数据访问层解决方案
4.1 SQL
4.1.1 数据源技术
当我们引入Druid对应的starter后,即使在配置文件中不配置Druid,SpringBoot也会默认使用Druid。当我们不引入Druid对应的starter,SpringBoot会默认使用HikariCP数据源,他是SpringBoot内嵌的数据源,SpringBoot内部共配置了三种数据源:
- HikariCP(号称轻量级数据源中最快的):默认使用
- Tomcat提供的DataSource:当HiKariCP不可用时,且在Web环境,将使用Tomcat内置的数据源
- Commons DBCP:HikariCP不可用,Tomcat数据源不可用,将使用DBCP数据源
这就是SpringBoot为开发者提供的数据源解决方案
Hikari配置方式:
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm_db?serverTimezone=UTC
hikari:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: root
druid配置方式:
spring:
datasource:
druid:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm_db?serverTimezone=UTC
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: root
4.1.2 持久化技术
springboot充分发挥其最强辅助的特征,给开发者提供了一套现成的数据层技术,叫做JdbcTemplate。其实这个技术不能说是springboot提供的,因为不使用springboot技术,一样能使用它,谁提供的呢?spring技术提供的,所以在springboot技术范畴中,这个技术也是存在的,毕竟springboot技术是加速spring程序开发而创建的。
实例:
导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
测试
@SpringBootTest
public class JdbcTemplateTest {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Test
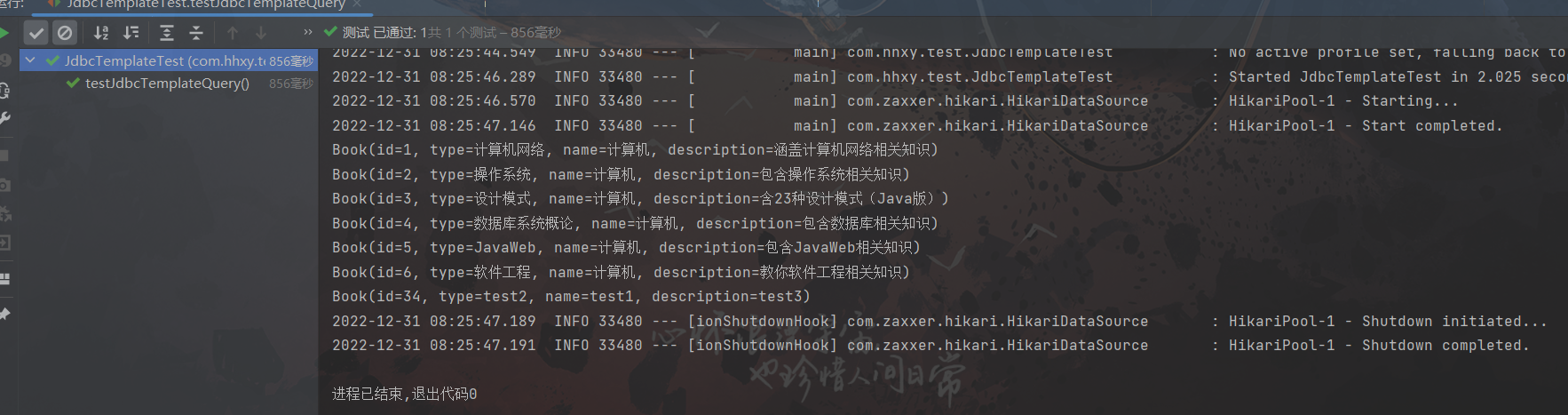
public void testJdbcTemplateQuery() {
String sql = "select * from tb_book";
/*
这种方式查询出来是一个Map集合,Map集合用起来比较麻烦
List<Map<String, Object>> books = jdbcTemplate.queryForList(sql);
books.forEach(System.out::println);
*/
// 标准化查询
RowMapper<Book> rm = new RowMapper<Book>() {
@Override
public Book mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
Book book = new Book(rs.getInt("id"), rs.getString("name"),
rs.getString("type"), rs.getString("description"));
return book;
}
};
List<Book> books = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, rm);
books.forEach(System.out::println);
}
@Test
public void testJdbcTemplateSave(){
String sql = "insert into tb_book values (null, 'test1', 'test2', 'test3')";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql);
}
}
知识拓展:JdbcTemplate相关配置
spring: # jdbc相关配置 jdbc: template: query-timeout: 10s # 最大查询时间,超过这个时间就终止查询(不带单位默认是ms) max-rows: 100 # 一次能够查询到的最大记录条数,这里设置的一次最大能查100条记录 fetch-size: 50 # 一次查询给你的记录条数,超过50条就会重新执行查询操作(因为不可能将所有的记录一次性全部给你,内存有限)
4.1.3 数据库技术
截止到目前,springboot给开发者提供了内置的数据源解决方案和持久化解决方案,在数据层解决方案三件套中还剩下一个数据库,莫非springboot也提供有内置的解决方案?还真有,还不是一个,三个,这一节就来说说内置的数据库解决方案。
springboot提供了3款内置的数据库,分别是:
- H2:内存数据库,是由Java编写的,支持在内存中创建表和数据库
- HSQL:HSQLDB(HyperSQL DataBase)是一个开放源代码的JAVA数据库,其具有标准的SQL语法和JAVA接口,它可以自由使用和分发,非常简洁和快速的
- Derby:是一个完全用java编写的数据库,它非常小巧,核心部分derby.jar只有2M,所以既可以做为单独的数据库服务器使用,也可以内嵌在应用程序中使用
它们都很轻巧,都能在内存中运行,都是使用Java编写的,一般用来测试
-
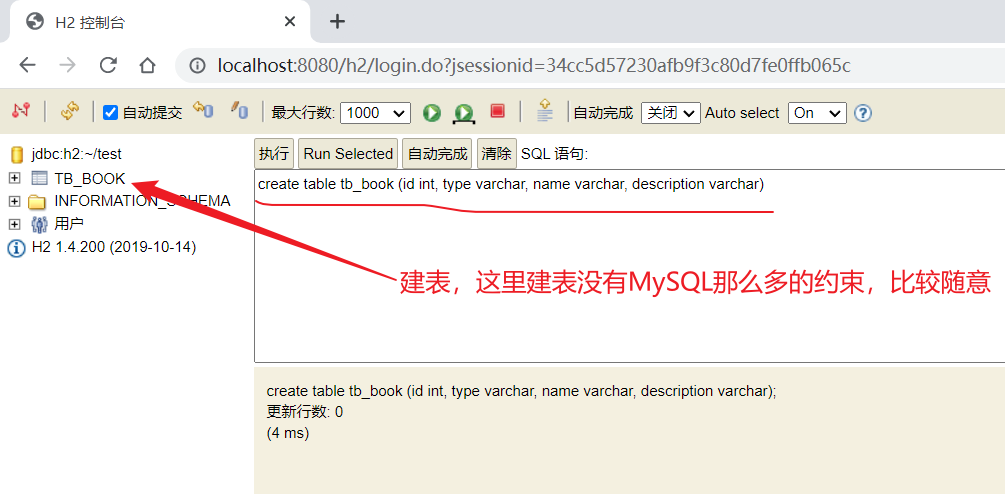
配置H2DB
-
Step1:导入依赖
<!--h2依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>com.h2database</groupId> <artifactId>h2</artifactId> </dependency> <!--jpa对应的starter--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> </dependency> <!--JdbcTemplate对应的starter--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId> </dependency>备注:此外还需要SpringMVC对应的Starter(这不是H2DB所必须的,只是为了测试需要)
-
Step2:编写配置文件
# 配置端口 server: port: 8080 # Spring相关配置 spring: # h2数据库相关配置 h2: console: path: /h2 # 启动路径 enabled: true # 是否启用h2数据库(true表示是) # 这个是数据源配置是用来初始化h2的一些信息,初始化后,就可以不需要了 datasource: url: jdbc:h2:~/test hikari: driver-class-name: org.h2.Driver # 这一行可以省略 username: sa password: 123456 -
Step3:启动
运行SpringBoot程序的启动类,运行成功后,在浏览器中访问
http://localhost:8080/h2这个链接,就能够来到H2DB的控制台了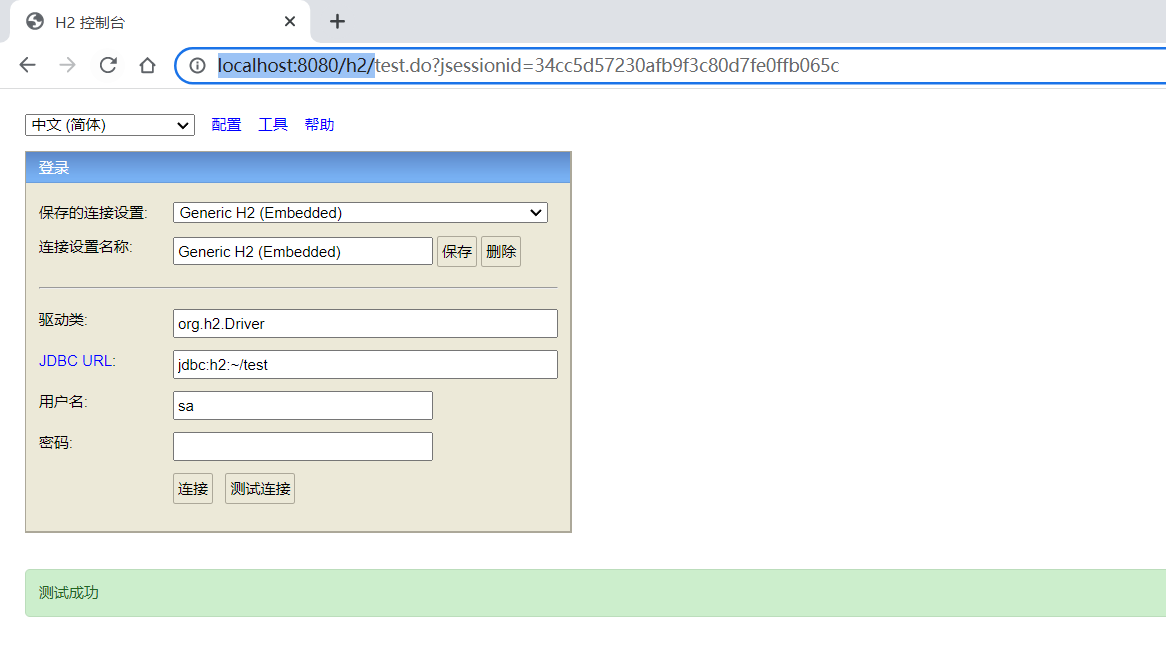
备注:该数据库在C盘的user目录下
-
-
Step4:测试
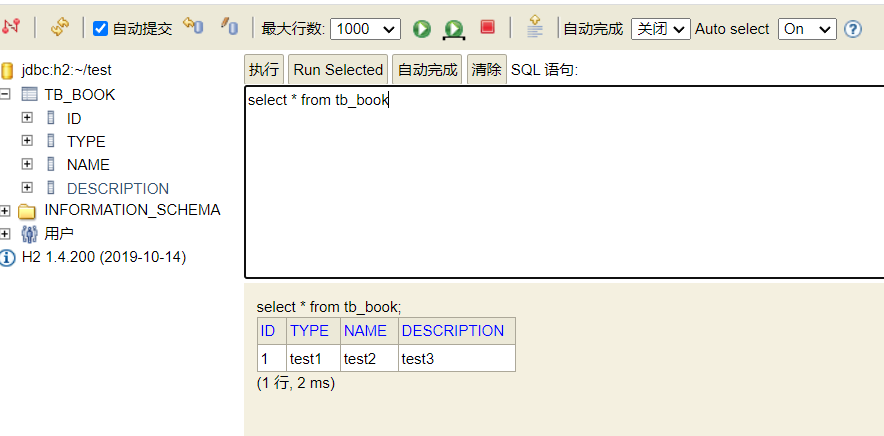
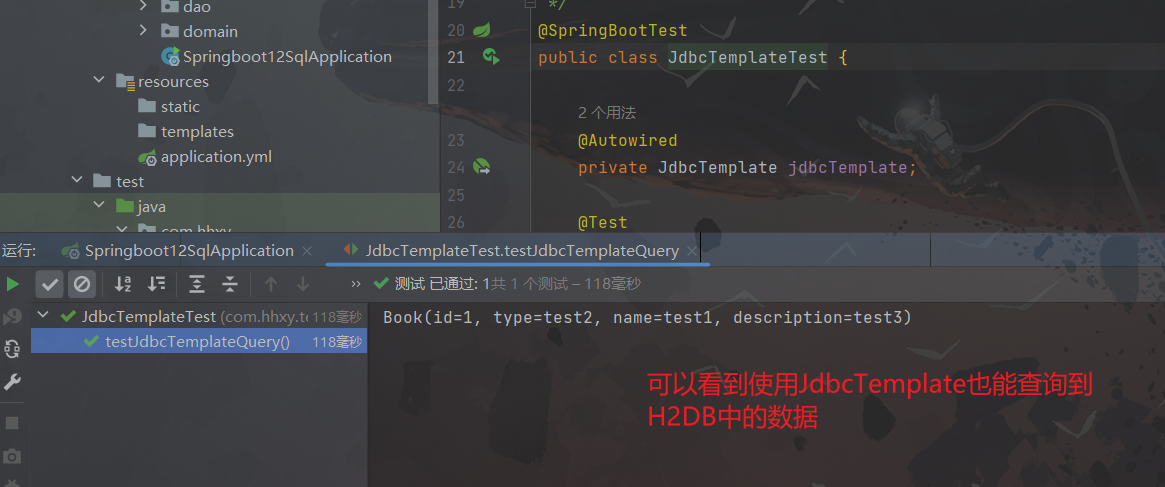
总结
- 数据源技术:Druid、Hikari、tomcat DataSource、DBCP
- 持久化技术:MyBatisPlus、MyBatis、JdbcTemplate
- 数据库技术:MySQL、H2、HSQL、Derby
这些东西可以任意搭配,总共有4*3*4种方案
4.2 NoSQL
4.2.1 整合Redis
Redis安装教程请参考:Redis基础篇学习笔记
-
Step1:导入依赖
<!--Redis对应的starter--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> </dependency> -
Step2:编写配置文件
# 配置端口 server: port: 8080 # spring相关配置 spring: redis: host: 192.168.88.130 port: 6379 password: 32345678 -
Step3:测试
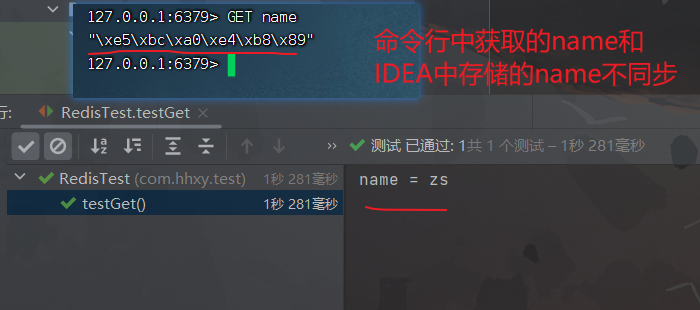
package com.hhxy.test; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations; /** * @author ghp * @date 2022/12/31 * @title * @description */ @SpringBootTest public class RedisTest { @Autowired private RedisTemplate redisTemplate; @Test public void testSet(){ // 获取操作String类型的对象 ValueOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue(); // 将String类型的数据添加到Redis中 ops.set("name", "zs"); } @Test public void testGet(){ ValueOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue(); Object name = ops.get("name"); System.out.println("name = " + name); } }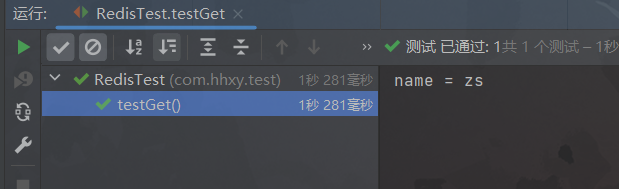
知识拓展:RedisTemplate&StringRedisTemplate
这是由于Redis内部不提供Java对象的存储格式,因此当操作的数据以对象的形式存在时,会进行转码,转换成字符串格式后进行操作。为了方便开发者使用基于字符串为数据的操作,SpringBoot整合Redis时提供了专用的API接口StringRedisTemplate(这在Redis基础篇学习笔记中有更加详细的说明,也提供了解决方案)
PS:其实StringReidsTemplate是RedisTemplate的一个指定了泛型的API,
StringRedisTemplate就是RedisTemplate<String, String>
4.2.2 整合MongoDB
??使用Redis技术可以有效的提高数据访问速度,但是由于Redis的数据格式单一性,无法操作结构化数据,当操作对象型的数据时,Redis就显得捉襟见肘了。在保障访问速度的情况下,如果想操作结构化数据,看来Redis无法满足要求了,此时需要使用全新的数据存储结束来解决此问题,本节讲解SpringBoot如何整合MongoDB技术。
??MongoDB是一个基于分布式文件存储的数据库,是一个开源、高性能、无模式1的文档型2数据库。由C++语言编写。旨在为WEB应用提供可扩展的高性能数据存储解决方案。MongoDB是一个介于关系数据库和非关系数据库之间的产品,是非关系数据库当中功能最丰富,最像关系数据库的。它支持的数据结构非常松散,是类似 json 的 bson 格式,因此可以存储比较复杂的数据类型。Mongo最大的特点是它支持的查询语言非常强大,其语法有点类似于面向对象的查询语言,几乎可以实现类似关系数据库单表查询的绝大部分功能,而且还支持对数据建立索引。
MongoDB的安装可以参考:MongoDB学习笔记
-
Step1:启动MongoDB
-
Step2:创建SpringBoot程序,导入依赖
<!--MongoDB对应的starter--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId> </dependency> -
Step3:编写配置文件
spring: data: mongodb: uri: mongodb://localhost/test -
Step4:编码测试
@SpringBootTest public class MongoTemplateTest { @Autowired private MongoTemplate mongoTemplate; @Test public void testSave(){ Book book = new Book(1, "test1", "test2","test3"); // 添加数据 mongoTemplate.save(book); } @Test public void testFind(){ List<Book> books = mongoTemplate.findAll(Book.class); books.forEach(System.out::println); } }
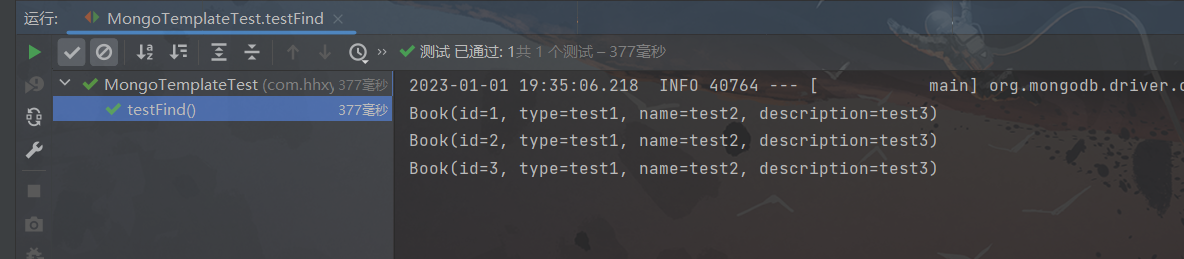
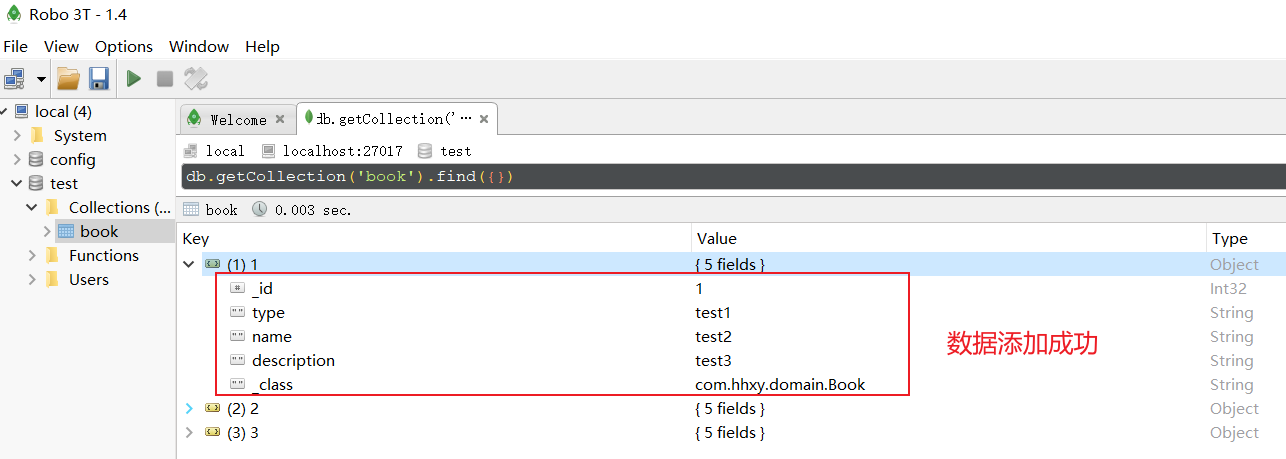
我们可以在robo3t中查看到,数据已经添加成功:
4.2.3 整合ES
??NoSQL解决方案已经讲完了两种技术的整合了,Redis可以使用内存加载数据并实现数据快速访问,MongoDB可以在内存中存储类似对象的数据并实现数据的快速访问,在企业级开发中对于速度的追求是永无止境的。下面要讲的内容也是一款NoSQL解决方案,只不过他的作用不是为了直接加速数据的读写,而是加速数据的查询的,叫做ES技术
??ES(Elasticsearch )是一个分布式、高扩展、高实时的搜索与数据分析引擎。主要特点能够实现全文搜索3,它能很方便的使大量数据具有搜索、分析和探索的能力。充分利用Elasticsearch的水平伸缩性,能使数据在生产环境变得更有价值。
PS:浏览器的搜索提示功能就是使用了ES
Elasticsearch 详细使用方法可以参考:ES学习笔记
-
Step1:启动ES
启动成功后,可以访问
localhost:9200,如果出现下面这个页面就说明启动成功了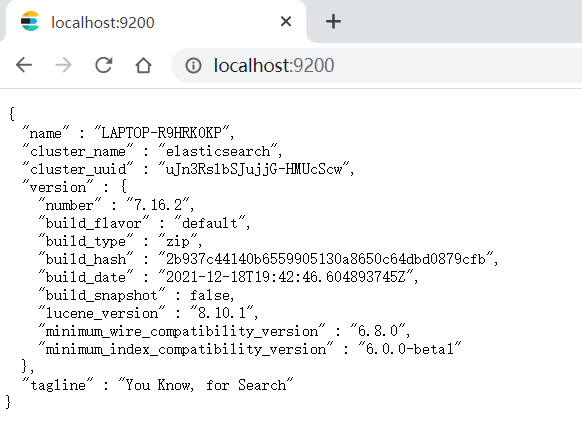
-
Step2:创建SpringBoot程序,导入依赖
-
Step3:
5、整合第三方技术
5.1 缓存
5.1.1 快速体验缓存
体验一:使用HashMap模拟一个缓存,减少数据库的查询操作
-
Step1:搭建环境
1)导入依赖
<!--lombok依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> </dependency> <!--mysql驱动--> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> </dependency> <!--druid对应的starter--> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.2.6</version> </dependency> <!--MybatisPlus对应的starter--> <dependency> <groupId>com.baomidou</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>3.4.3.4</version> </dependency> <!--SpringMVC对应的starter--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <!--Junit对应的starter--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency>2)编写配置文件
# 端口配置 server: port: 8080 # Spring相关配置 spring: datasource: druid: driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot_study?serverTimezone=UTC username: root password: 32345678 # MybatisPlus相关配置 mybatis-plus: global-config: db-config: table-prefix: tb_ # MyBatisPlus会自动将数据库中所有表的前缀给去掉,所以需要加上前缀 id-type: auto # MyBatisPlus默认有自己设置Id的策略(雪花算法),如果想要使用数据库的Id自增,需要在这里进行设置 # 开启MyBatisPlus的日志 configuration: log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl -
Step2:编码
BookService:
@Service public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService { @Autowired private BookDao bookDao; // 使用HashMap模拟缓存 private HashMap<Integer, Book> cache = new HashMap(); @Override public Book getById(Integer id) { // return bookDao.selectById(id); // 当“缓存”中有数据就不用再去查数据库库了 Book book = cache.get(id); if (book == null) { Book queryBook = bookDao.selectById(id); cache.put(id, queryBook); } return cache.get(id); } }其它,略……详情请参考Gitee或Github仓库
-
Step3:测试
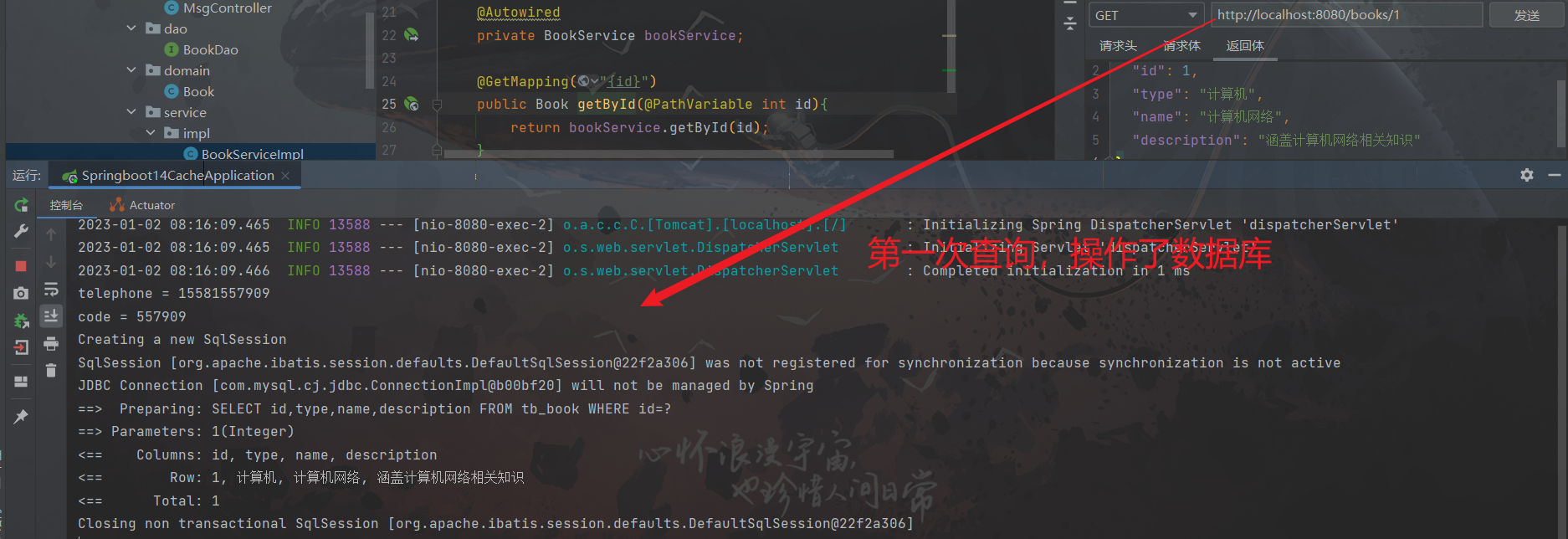
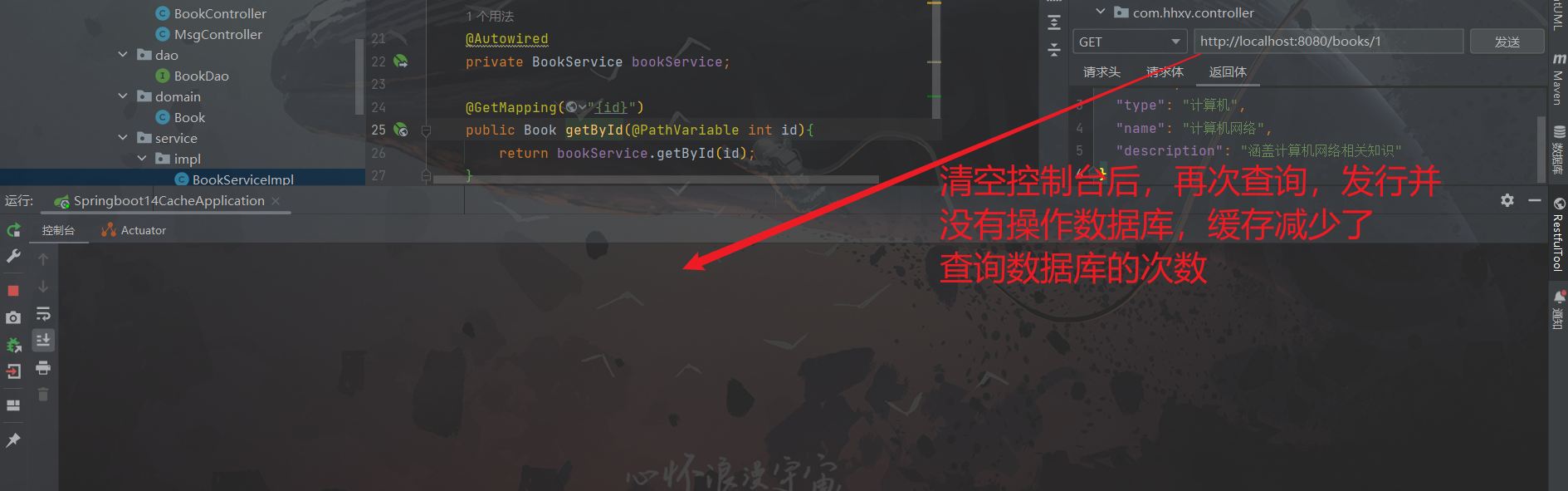
体验二:使用SpringBoot内置的缓存,临时存储手机验证码
-
Step1:搭建环境
上同,略……
-
Step2:编码
1)SmCodeServiceImpl:
@Service public class MsgServiceImpl implements MsgService { private HashMap<String, String> cache = new HashMap<>(); @Override public String get(String telephone) { // 取电话号码后六位,作为验证码 String code = telephone.substring(telephone.length() - 6); cache.put(telephone, code); return code; } @Override public boolean check(String telephone, String code) { String queryCode = cache.get(telephone); // 判断用户输入的验证码和之前得到的验证码是否相同 return code.equals(queryCode); } }2)MsgController:
package com.hhxy.controller; import com.hhxy.domain.SMCode; import com.hhxy.service.SMCodeService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; /** * @author ghp * @date 2023/1/2 * @title * @description */ @RestController @RequestMapping("/sms") public class SMCodeController { @Autowired private SMCodeService smCodeService; @GetMapping("{tel}") public String getCode(@PathVariable("tel") String telephone){ String code = smCodeService.sendCodeToSM(telephone); return code; } @PostMapping public boolean checkCode(SMCode smCode){ return smCodeService.checkCode(smCode); } } -
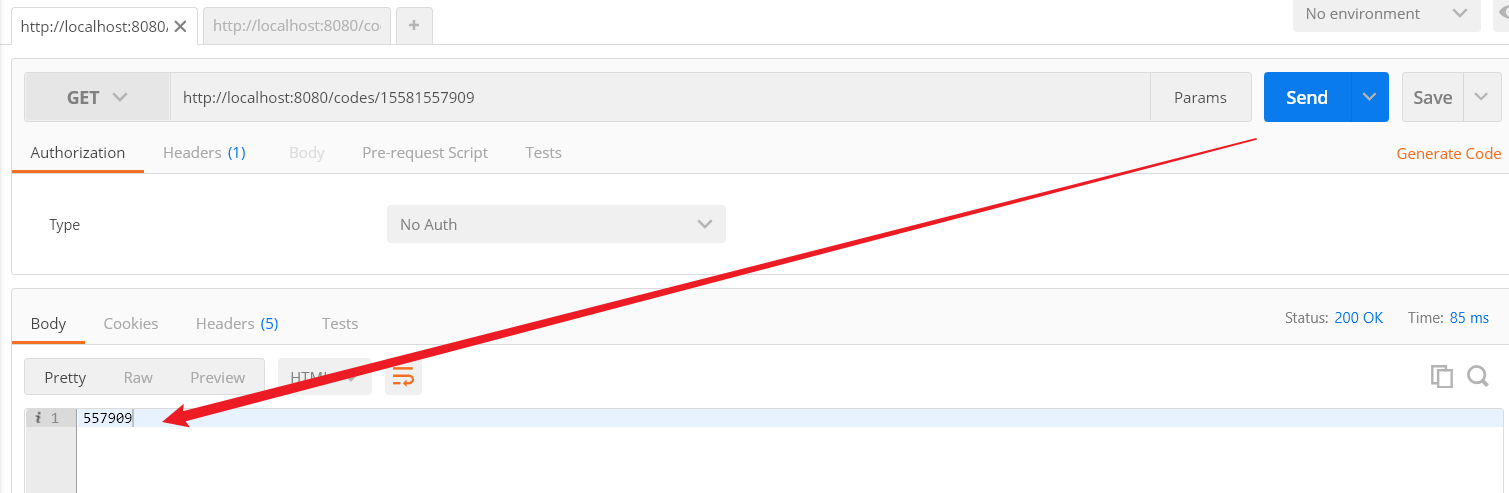
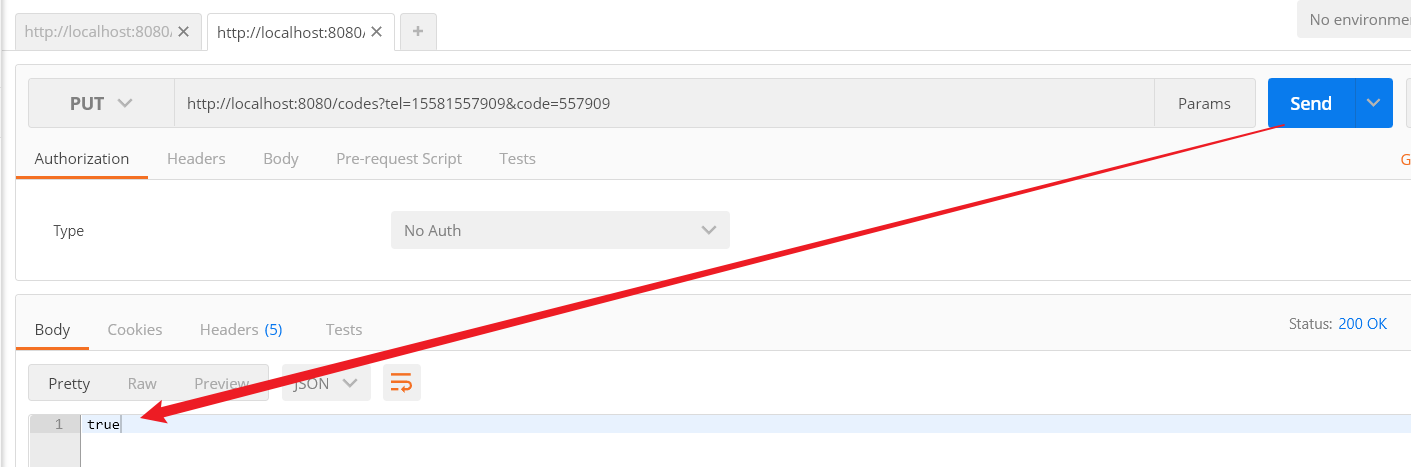
Step3:测试
5.1.2 内置缓存解决方案
SpringBoot技术提供有内置的缓存解决方案,可以帮助开发者快速开启缓存技术,并使用缓存技术进行数据的快速操作,例如读取缓存数据和写入数据到缓存。
| 注解 | 说明 |
|---|---|
@EnableCaching | 开启缓存注解功能 |
@Cacheable | 在方法中执行前,Spring先查看缓存中是否有数据,如果有数据,则直接返回缓存数据;如果没有数据,则将方法返回值存储到缓存中 |
@CachePut | 将方法的返回值放到缓存中 |
@CacheEvict | 将一条或多条数据从缓存中删除 |
- condition:用于设置条件,满足条件时才缓存数据(没有result对象)
- unless:满足条件,不缓存
实例:
使用5.1.1中体验一的例子,将它改造成使用SpringBoot内置的缓存技术
-
Step1:搭建环境
1)导入依赖
<!--cache对应的starter--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId> </dependency>2)编写配置文件……
-
Step2:开启缓存
在SpringBoot程序的入口类上加上一个
@EnableCaching注解,告诉SpringBoot开启缓存 -
Step3:编写
@Service public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService { @Autowired private BookDao bookDao; // 使用SpringBoot内置的缓存策略 @Override @Cacheable(value = "cacheSpace", key="#id") // SpEL表达式,或者写#p0,表示第1个参数 public Book getById(Integer id) { return bookDao.selectById(id); } }添加
@Cacheable注解以后,vlaue用于设置缓存空间,缓存数据以key-value的形式存储到缓存空间中,而通过key可以设置key,这里我将key设置为查询数据的id(设置的key要保障唯一性,一般都是以id为key),这样后面查询重复数据时,就不需要再去查询数据库了,大大节约了时间、资源
5.1.3 整合Ehcache
常见的缓存技术:Generic、JCacheEhcache、Hazelcast、Infinispan、Couchbase、Redis、Caffeine、Simple(默认)、Memcached……共9种,前8种都有SpringBoot官方提供的整合策略,而最后一种SpringBoot官方没有提供整合策略,但是也很常见,而Simple是SpringBoot默认提供的缓存策略,5.1.2中使用的就是就是Simple
-
Step1:导入依赖
<!--Ehcache的依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId> <artifactId>ehcache</artifactId> </dependency>PS:相较于使用SpringBoot内置的缓存,我们使用Ehcache就是多加一个配置文件
-
Step2:开启缓存
在SpringBoot程序的入口类上加上一个
@EnableCaching注解,告诉SpringBoot开启缓存 -
Step3:添加Ehcache的配置文件
1)application.yml
# Spring相关配置 spring: datasource: druid: driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot_study?serverTimezone=UTC username: root password: 32345678 # 告诉SpringBoot使用ehcache cache: type: ehcache注意:当你的ehcache配置文件不是ehcache.xml,则需要使用对应的文件名,比如你改成my-ehcache.xml,那么你的就需要设置成
cache: type: ehcache ehcache: config: my-ehcache.xml2)ehcache.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd" updateCheck="false"> <diskStore path="D:\ehcache" /> <!--默认缓存策略 --> <!-- external:是否永久存在,设置为true则不会被清除,此时与timeout冲突,通常设置为false--> <!-- diskPersistent:是否启用磁盘持久化--> <!-- maxElementsInMemory:最大缓存数量--> <!-- overflowToDisk:超过最大缓存数量是否持久化到磁盘--> <!-- timeToIdleSeconds:最大不活动间隔,设置过长缓存容易溢出,设置过短无效果,可用于记录时效性数据,例如验证码--> <!-- timeToLiveSeconds:最大存活时间--> <!-- memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:缓存清除策略--> <defaultCache eternal="false" diskPersistent="false" maxElementsInMemory="1000" overflowToDisk="false" timeToIdleSeconds="60" timeToLiveSeconds="60" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU" /> <!--注意:在service层中cache注解配置的缓存空间要和这里的name保持一致--> <cache name="smCode" eternal="false" diskPersistent="false" maxElementsInMemory="1000" overflowToDisk="false" timeToIdleSeconds="10" timeToLiveSeconds="10" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU" /> </ehcache> -
Step4:测试
和内置的缓存使用方式一样,主要通过:
@Cacheable和@CachePut两个注解
5.1.4 整合Redis(缓存)
-
Step1:导入依赖
<!--redis缓存的依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> </dependency> -
Step2:编写配置文件
# redis相关配置 cache: type: redis redis: user-key-prifix: false key-prifix: sms_ cache-null-values: false time-to-live: 10s redis: host: 192.168.88.130 port: 6379 password: 32345678 -
Step3:编码测试
略……,和前面的一模一样,这足以说明SpringBoot的厉害之处,它将各种各样的缓存都实现了一个同一的接口,换一个缓存只需要修改一下配置文件的参数,导入对应缓存的依赖就可以了
5.1.5 整合Memcached
这一节,我就直接跳过了,等以后要用的时候再来学习一下,就算现在学了,很久不用也很容易就忘了
-
Step1:下载
windows版安装包下载地址:https://www.runoob.com/memcached/window-install-memcached.html
-
Step2:安装
自行脑补,略……
5.1.6 整合JetCache
??目前我们使用的缓存都是要么A要么B,能不能AB一起用呢?这一节就解决这个问题。springboot针对缓存的整合仅仅停留在用缓存上面,如果缓存自身不支持同时支持AB一起用,springboot也没办法,所以要想解决AB缓存一起用的问题,就必须找一款缓存能够支持AB两种缓存一起用,有这种缓存吗?还真有,阿里出品,jetcache。
??jetcache严格意义上来说,并不是一个缓存解决方案,只能说他算是一个缓存框架,然后把别的缓存放到jetcache中管理,这样就可以支持AB缓存一起用了。并且jetcache参考了springboot整合缓存的思想,整体技术使用方式和springboot的缓存解决方案思想非常类似。下面咱们就先把jetcache用起来,然后再说它里面的一些小的功能。JetCache对SpringCache进行了封装,在原有功能的基础上实现了多级缓存、缓存统计、自动刷新、异步调用、数据报表等功能。
??做之前要先明确一下,jetcache并不是随便拿两个缓存都能拼到一起去的。目前jetcache支持的缓存方案本地缓存支持两种,远程缓存支持两种,分别如下:
- 本地缓存(Local)
- LinkedHashMap
- Caffeine
- 远程缓存(Remote)
- Redis
- Tair
其实也有人问我,为什么jetcache只支持2+2这么4款缓存呢?阿里研发这个技术其实主要是为了满足自身的使用需要。最初肯定只有1+1种,逐步变化成2+2种。下面就以LinkedHashMap+Redis的方案实现本地与远程缓存方案同时使用。
5.1.6.1 远程方案
-
Step1:导入依赖
<!--lombok依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> </dependency> <!--mysql驱动--> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> </dependency> <!--druid对应的starter--> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.2.6</version> </dependency> <!--MybatisPlus对应的starter--> <dependency> <groupId>com.baomidou</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>3.4.3.4</version> </dependency> <!--SpringMVC对应的starter--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <!--Junit对应的starter--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!--JetCache对应的starter--> <dependency> <groupId>com.alicp.jetcache</groupId> <artifactId>jetcache-starter-redis</artifactId> <version>2.6.2</version> </dependency> <!--热部署依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId> </dependency> -
Step2:启用JetCache
在SpringBoot的启动类上加上
@EnableCreateCacheAnnotation注解,告诉SpringBoot使用JetCache -
Step3:编写配置文件
jetcache: remote: default: type: redis host: 192.168.88.130 port: 6379 password: 32345678 poolConfig: maxTotal: 50 -
Step4:编码
@Service public class SMCodeServiceImpl implements SMCodeService { @Autowired private CodeUtil codeUtil; // 创建JetCache对象 @CreateCache(area = "default", name="jetCacheSpace_", expire = 3, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS) // area用于设置缓存空间,默认是default,这个要与yml配置文件对应上, // expire用于设置缓存有效期,默认单位是秒,timeUnit设置expire的单位 private Cache<String, String> jetCache; /** * 发送验证码 */ @Override public String sendCodeToSM(String telephone) { String code = CodeUtil.generator(telephone); jetCache.put(telephone, code); return code; } /** * 检查验证码 */ @Override public boolean checkCode(SMCode smCode) { String code = smCode.getCode(); String cacheCode = jetCache.get(smCode.getTelephone()); return cacheCode.equals(code); } }Controller的代码参考5.1.1
-
Step5:测试

可以在redis中查看刚刚存进去的值,它是:
area_namevlaue的形式:(一般name都是字符串加上下划线或者冒号,用于区分value)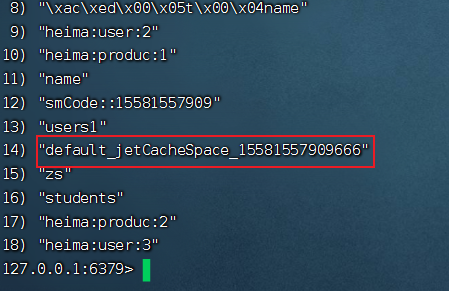
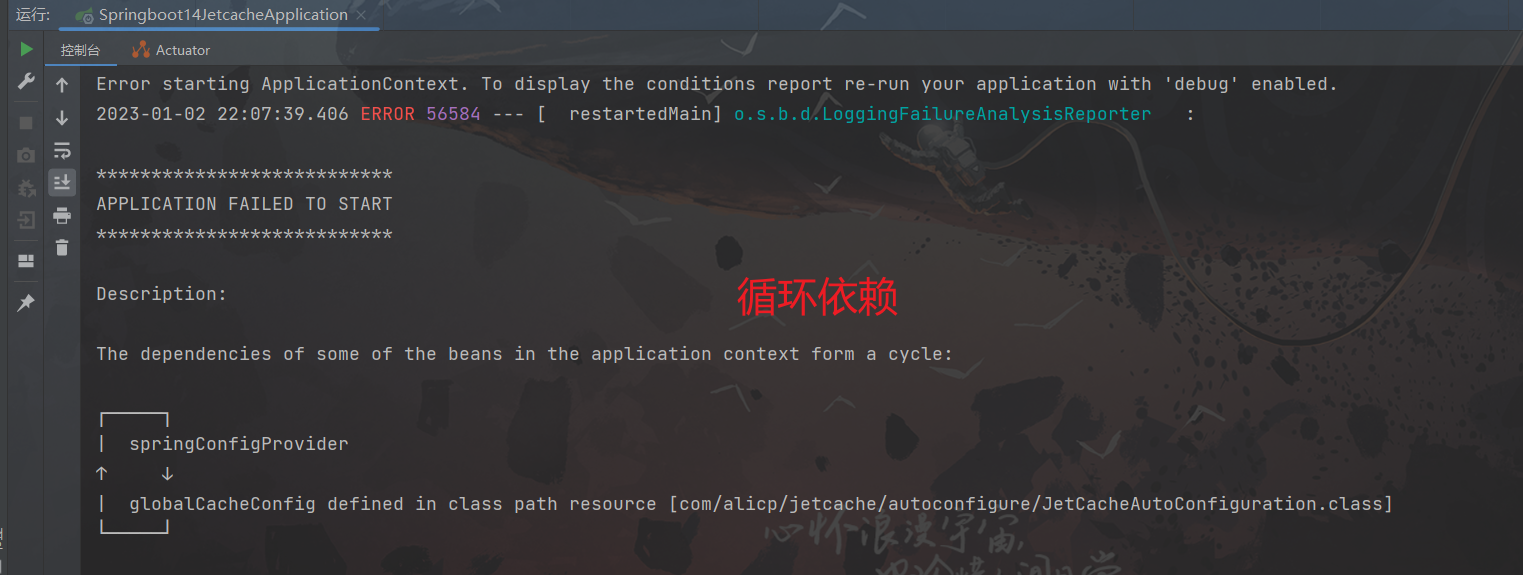
温馨提示:SprintBoot版本使用5.4.2或者更低的版本,高版本已经禁止了循环依赖
5.1.6.2 本地方案
-
Step1:导入依赖
上同,略……
-
Step2:启动jetcache
-
Step3:编写配置文件
jetcache: local: localDefault: type: linkedhashmap keyConvertor: fastjson -
Step4:编码
@CreateCache(area = "localDefault", name="jetCacheSpace_", expire = 10, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS, cacheType = CacheType.LOCAL) private Cache<String, String> jetCache;cacheType用于指定使用本地缓存还是使用远程缓存,默认是使用远程缓存
-
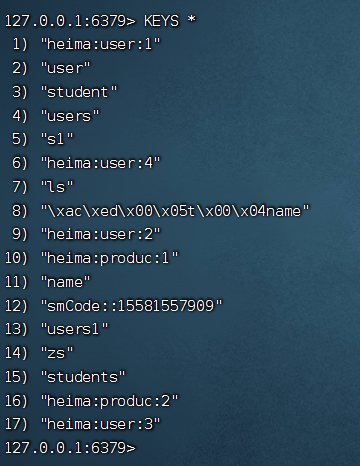
Step5:测试
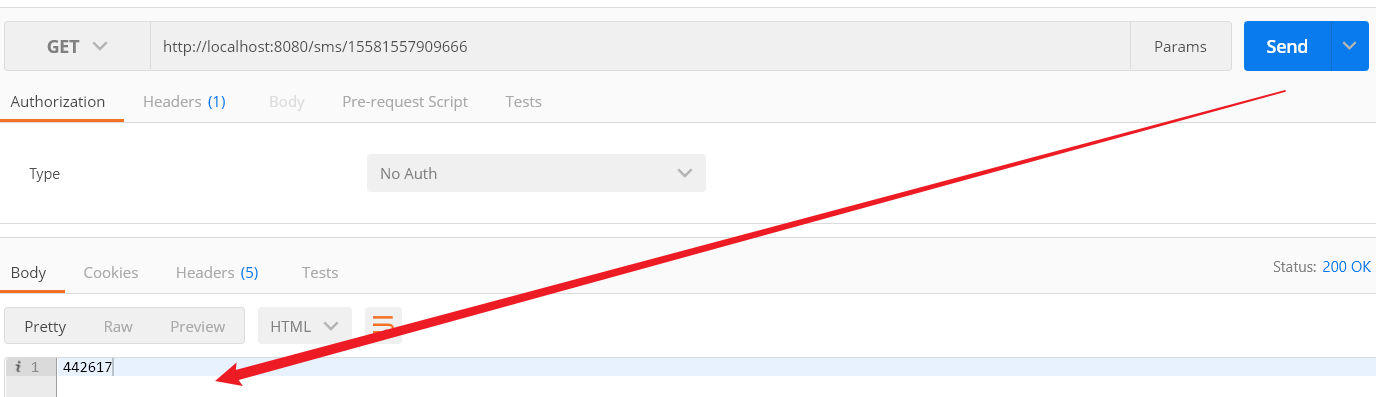
可以发现程序运行了,但是在redis中并没有找到与之对应的值,这是由于使用了本地缓存,数据存储在LinkedHashMap中
5.1.6.3 远程+本地
jetcache:
local:
default:
type: linkedhashmap
keyConvertor: fastjson
remote:
default:
type: redis
host: localhost
port: 6379
poolConfig:
maxTotal: 50
sms:
type: redis
host: localhost
port: 6379
poolConfig:
maxTotal: 50
配置cacheType为BOTH即则本地缓存与远程缓存同时使用
@Service
public class SMSCodeServiceImpl implements SMSCodeService {
@CreateCache(name="jetCache_",expire = 1000,timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS,cacheType = CacheType.BOTH)
private Cache<String ,String> jetCache;
}
JetCache相关配置
| 属性 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
jetcache.statIntervalMinutes | 0 | 统计间隔,0表示不统计 |
jetcache.hiddenPackages | 无 | 自动生成name时,隐藏指定的包名前缀 |
| `jetcache.[local | remote].${area}.type` | 无 |
| `jetcache.[local | remote].${area}.keyConvertor` | 无 |
| `jetcache.[local | remote].${area}.valueEncoder` | java |
| `jetcache.[local | remote].${area}.valueDecoder` | java |
| `jetcache.[local | remote].${area}.limit` | 100 |
| `jetcache.[local | remote].${area}.expireAfterWriteInMillis` | 无穷大 |
jetcache.local.${area}.expireAfterAccessInMillis | 0 | 仅local类型的缓存有效,毫秒单位,最大不活动间隔 |
5.1.6.4 方法缓存
所谓的方法缓存,就是将方法返回的数据保存到缓存中,然后下次调用方法,会先从缓存中查询
-
Step1:导入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>com.alicp.jetcache</groupId> <artifactId>jetcache-starter-redis</artifactId> <version>2.6.2</version> </dependency> -
Step2:开启方法缓存
@SpringBootApplication // 启用jetcache @EnableCreateCacheAnnotation // 开启方法缓存 @EnableMethodCache(basePackages = "com.hhxy") public class Springboot14JetcacheApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Springboot14JetcacheApplication.class, args); } } -
Step3:编写配置文件
jetcache: remote: default: type: redis host: 192.168.88.130 port: 6379 password: 32345678 poolConfig: maxTotal: 50 #最大连接数 local: localDefault: type: linkedhashmap keyConvertor: fastjson==注意:==这里一定要记得给remote方案配
keyConvertor: fastjson,否则会报空指针异常,这是由于Redis是不支持保存Object -
Step4:编码
??由于redis缓存中不支持保存对象,因此需要对redis设置当Object类型数据进入到redis中时如何进行类型转换。需要配置keyConvertor表示key的类型转换方式,同时标注value的转换类型方式,值进入redis时是java类型,标注valueEncode为java,值从redis中读取时转换成java,标注valueDecode为java。
注意:为了实现Object类型的值进出redis,需要保障进出redis的Object类型的数据必须实现序列化接口,否则会报
NotSerializableException。1)BookService:
@Override @Cached(name="book_",key="#id",expire = 3600,cacheType = CacheType.REMOTE) public Book getById(Integer id) { return bookDao.selectById(id); }2)BookController:
@RestController @RequestMapping("/books") public class BookController { @Autowired private BookService bookService; @GetMapping("{id}") @Cached(name = "book", key = "#id", expire = 10) public Book getById(@PathVariable int id){ return bookService.getById(id); } @Override // 更新缓存中的数据 @CacheUpdate(name = "book_", key = "#book.id", value = "#book") public boolean update(Book book) { return bookDao.updateById(book) > 0; } @Override // 删除缓存中的数据 @CacheInvalidate(name = "book_", key = "#id") public boolean delete(Integer id) { return bookDao.deleteById(id) > 0; } } -
Step5:测试
略……
5.1.7 整合J2Cache
jetcache可以在限定范围内构建多级缓存,但是灵活性不足,不能随意搭配缓存,本节介绍一种可以随意搭配缓存解决方案的缓存整合框架,j2cache
实例:
使用J2Cache来创建EhCache+Redis的搭配
-
Step1:导入依赖
<!--j2cache核心实现包--> <dependency> <groupId>net.oschina.j2cache</groupId> <artifactId>j2cache-core</artifactId> <version>2.8.4-release</version> </dependency> <!--j2cache对应的starter(包含了redis)--> <dependency> <groupId>net.oschina.j2cache</groupId> <artifactId>j2cache-spring-boot2-starter</artifactId> <version>2.8.0-release</version> </dependency> <!--Ehcache依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId> <artifactId>ehcache</artifactId> </dependency> -
Step2:编写配置文件
ehcache.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd" updateCheck="false"> <diskStore path="D:\ehcache" /> <!--默认缓存策略 --> <!-- external:是否永久存在,设置为true则不会被清除,此时与timeout冲突,通常设置为false--> <!-- diskPersistent:是否启用磁盘持久化--> <!-- maxElementsInMemory:最大缓存数量--> <!-- overflowToDisk:超过最大缓存数量是否持久化到磁盘--> <!-- timeToIdleSeconds:最大不活动间隔,设置过长缓存容易溢出,设置过短无效果,可用于记录时效性数据,例如验证码--> <!-- timeToLiveSeconds:最大存活时间--> <!-- memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:缓存清除策略--> <defaultCache eternal="false" diskPersistent="false" maxElementsInMemory="1000" overflowToDisk="false" timeToIdleSeconds="10" timeToLiveSeconds="10" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU" /> </ehcache>j2cache.properties:
# 1级缓存 j2cache.L1.provider_class = ehcache ehcache.configXml = ehcache.xml # 2级缓存 j2cache.L2.provider_class = net.oschina.j2cache.cache.support.redis.SpringRedisProvider j2cache.L2.config_section = redis redis.hosts = 192.168.88.130:6379 redis.password = 32345678 redis.mode = single # 1级缓存中的数据如何到达二级缓存 j2cache.broadcast = net.oschina.j2cache.cache.support.redis.SpringRedisPubSubPolicyapplication.yml:
server: port: 8080 j2cache: config-location: j2cache.properties -
Step3:编码测试
SMSCodeServiceImpl:
@Service public class SMSCodeServiceImpl implements SMSCodeService { @Autowired private CodeUtils codeUtils; @Autowired private CacheChannel cacheChannel; @Override public String sendCodeToSMS(String tele) { String code = codeUtils.generator(tele); cacheChannel.set("sms",tele,code); return code; } @Override public boolean checkCode(SMSCode smsCode) { String code = cacheChannel.get("sms",smsCode.getTele()).asString(); return smsCode.getCode().equals(code); } } -
Step4:测试
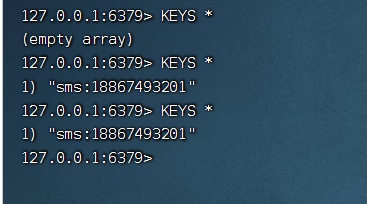
5.2 任务
SpringBoot整合第三方技术第二部分我们来说说任务系统,其实这里说的任务系统指的是定时任务。定时任务是企业级开发中必不可少的组成部分,诸如长周期业务数据的计算,例如年度报表,诸如系统脏数据的处理,再比如系统性能监控报告,还有抢购类活动的商品上架,这些都离不开定时任务。本节将介绍两种不同的定时任务技术。
5.2.1 整合Quartz
Quartz是一个定时任务框架,它的配置比较复杂, SpringBoot对Quartz进行了整合,通过设置默认配置,一定程度降低了Quartz的配置。关于Quartz具体可以参考:Quartz官方文档_w3cschool
Quartz基础概念:
- 工作(Job):用于定义具体执行的工作
- 工作明细(JobDetail):用于描述定时工作相关的信息
- 触发器(Trigger):描述了工作明细与调度器的对应关系
- 调度器(Scheduler):用于描述触发工作的执行规则,通常使用cron表达式定义规则
单说就是你定时干什么事情,这就是工作,工作不可能就是一个简单的方法,还要设置一些明细信息。工作啥时候执行,设置一个调度器,可以简单理解成设置一个工作执行的时间。工作和调度都是独立定义的,它们两个怎么配合到一起呢?用触发器。完了,就这么多。下面开始springboot整合Quartz。
示例:
-
Step1:导入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-quartz</artifactId> </dependency> -
Step2:创建工作
public class MyQuartz extends QuartzJobBean { @Override protected void executeInternal(JobExecutionContext context) throws JobExecutionException { System.out.println("任务开始执行..."); } } -
Step3:编写配置类,主要是编写工作明细,绑定触发器
@Configuration public class QuartzConfig { /** * 设置工作明细 */ @Bean public JobDetail printJobDetail(){ // 绑定具体的工作(storeDurably持久化,防止工作被清理) return JobBuilder.newJob(MyQuartz.class).storeDurably().build(); } /** * 设置触发器 */ @Bean public Trigger printJobTrigger(){ //0点0分0秒,0日0月0星期 ScheduleBuilder<? extends Trigger> scheduleBuilder = CronScheduleBuilder.cronSchedule("0/2 * * * * ?");//5秒执行一次 // 绑定对应的工作明细 return TriggerBuilder.newTrigger().forJob(printJobDetail()).withSchedule(scheduleBuilder).build(); } }
5.2.2 Spring Task
前面我们使用了SpringBoot整合Quartz,但是发现Quartz还是比较复杂,于是Spring Boot就提供了Spring Task来用来解决定时任务(不得不说,SpringBoot真的太香了)
-
Step1:开启定时任务
在SpringBoot程序的启动类上加上
@EnableScheduling注解 -
Step2:编写定时任务
@Component public class MyJob { @Scheduled(cron = "0/2 * * * * ?") public void printJob(){ System.out.println("使用spring task执行定时任务"); } }
Spring Task相关配置:
spring:
task:
scheduling:
pool:
size: 1 # 任务调度线程池大小 默认 1
thread-name-prefix: ssm_ # 调度线程名称前缀 默认 scheduling-
shutdown:
await-termination: false # 线程池关闭时等待所有任务完成
await-termination-period: 10s # 调度线程关闭前最大等待时间,确保最后一定关闭
5.3 邮件
邮件相关基础概念:
- SMTP(Simple Mail Transfer Protocol):简单邮件传输协议,用于发送电子邮件的传输协议
- POP3(Post Office Protocol - Version 3):用于接收电子邮件的标准协议
- IMAP(Internet Mail Access Protocol):互联网消息协议,是POP3的替代协议
简单说就是SMPT是发邮件的标准,POP3是收邮件的标准,IMAP是对POP3的升级
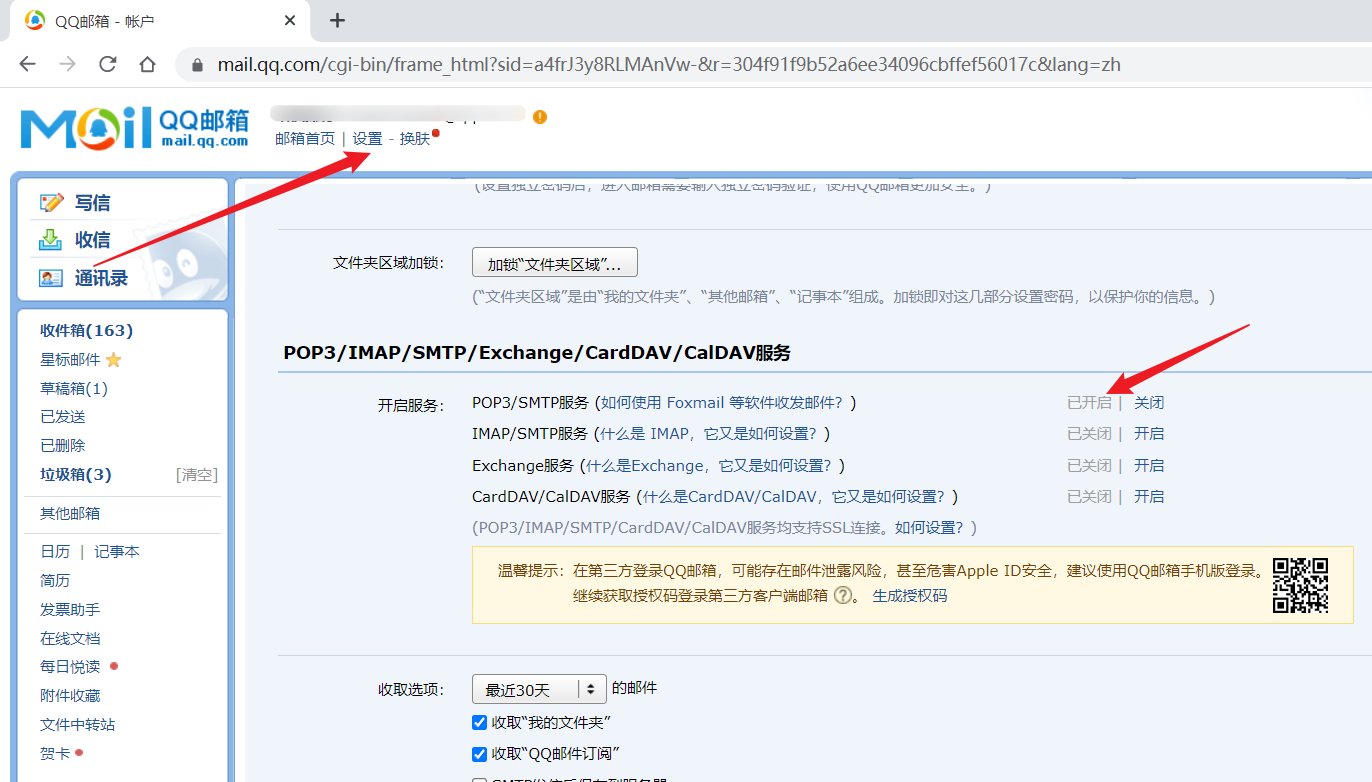
备注:下面的示例使用qq邮箱,需要先开启smtp服务
示例一:
-
Step1:导入依赖
<!--javamail对应的starter--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-mail</artifactId> </dependency> -
Step2:编写配置文件
application.yml
spring: mail: host: smtp.qq.com username: 3254213612@qq.com password: hnvluolizjmsdahi -
Ste3:发送邮件
@Service public class SendMailServiceImpl implements SendMailService { @Autowired private JavaMailSender javaMailSender; // 发送人 private String from = "3254213612@qq.com"; // 接收人 private String to = "3254213612@qq.com"; // 标题 private String subject = "测试邮件"; // 正文 private String context = "测试使用Java发送邮件"; @Override public void sendMail() { SimpleMailMessage msg = new SimpleMailMessage(); msg.setFrom(from+"(ghp)"); msg.setTo(to); msg.setSubject(subject); msg.setText(context); javaMailSender.send(msg); } } -
Step4:测试
@SpringBootTest public class SendMailServiceTest { @Autowired private SendMailService sendMailService; @Test public void testSendMail(){ sendMailService.sendMail(); } }
示例二:发送复杂邮件
package com.hhxy.service.impl;
import com.hhxy.service.SendMailService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.mail.javamail.JavaMailSender;
import org.springframework.mail.javamail.MimeMessageHelper;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.mail.MessagingException;
import javax.mail.internet.MimeMessage;
import java.io.File;
/**
* @author ghp
* @date 2023/1/3
* @title
* @description
*/
@Service
public class SendMailServiceImpl implements SendMailService {
@Autowired
private JavaMailSender javaMailSender;
// 发送人
private String from = "3254213612@qq.com";
// 接收人
private String to = "3254213612@qq.com";
// 标题
private String subject = "测试邮件";
// 正文
private String context = "<a href='https://www.baidu.com'>点击跳转到百度</a>" +
"<img src='https://tse2-mm.cn.bing.net/th/id/OIP-C.0DHXK9N4Ogrz2MWvzNOJfAHaNL?w=182&h=324&c=7&r=0&o=5&dpr=1.3&pid=1.7'/>";
@Override
public void sendMail() {
// 发送复杂(多部件)邮件
MimeMessage msg = javaMailSender.createMimeMessage();
try {
// true表示要发送附件
MimeMessageHelper helper = new MimeMessageHelper(msg, true);
helper.setFrom(from+"(ghp)");
helper.setTo(to);
helper.setSubject(subject);
//true表示要解析html
helper.setText(context, true);
// 添加附件
File file = new File("E:\\project\\SpringBoot\\springboot_15_email\\target\\springboot_15_email-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar");
helper.addAttachment(file.getName(), file);
} catch (MessagingException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
javaMailSender.send(msg);
}
}
5.4 消息
5.4.1 消息基础概念
-
什么是消息?
消息可以理解为一组带有信息的数据,比如:对象、数字、字符等都可以是消息
-
消息的分类
- 同步消息:发送的消息需要等待接收方作出响应,然后才能接着发送消息
- 异步消息:发送的消息不需要接收方作出响应,可以继续发送消息
其实这个在AJAX中就有所了解了,所谓的同步请求和异步请求
-
Java处理消息的三种异步消息传递技术
-
JMS:即Java消息服务(Java Message Service)应用程序接口,是一个Java平台中关于面向消息中间件(MOM)的API,用于在两个应用程序之间,或分布式系统中发送消息,进行异步通信。
JMS规范中规范了消息有两种模型。分别是点对点模型和发布订阅模型
- 点对点模型:peer-2-peer,生产者会将消息发送到一个保存消息的容器中,通常使用队列模型,使用队列保存消息。一个队列的消息只能被一个消费者消费,或未被及时消费导致超时。这种模型下,生产者和消费者是一对一绑定的
- 发布订阅模型:publish-subscribe,生产者将消息发送到一个保存消息的容器中,也是使用队列模型来保存。但是消息可以被多个消费者消费,生产者和消费者完全独立,相互不需要感知对方的存在
JMS中消息共有6种::TextMessage、MapMessage、BytesMessage、StreamMessage、ObjectMessage、Message (只有消息头和属性)。JMS实现有:ActiveMQ、Redis、HornetMQ、RabbitMQ、RocketMQ(没有完全遵守JMS规范)
备注:JMS只规范了Java语言的消息实现。JMS规范了消息开发的API
-
AMQP:即Advanced Message Queuing Protocol,一个提供统一消息服务的应用层标准高级消息队列协议,是应用层协议的一个开放标准,为面向消息的中间件设计。AMQP规范了网络交换的数据格式,兼容JMS。
备注:弥补了JMS的缺点,能够规范各种语言的消息实现,具有跨平台性。AMQP规范了消息的传递格式
AMQP相较于JMS有跟多的消息模型,灵活性非常高:
- direct exchange
- fanout exchange
- topic exchange
- headers exchange
- system exchange
AMQP统一了消息格式,消息种类只有一种:字节数组(byte[])
AMQP的实现:RabbitMQ、StormMQ、RocketMQ
-
MQTT:MQTT(Message Queueing Telemetry Transport)是一个基于客户端-服务器的消息发布/订阅传输协议。MQTT协议是轻量、简单、开放和易于实现的,这些特点使它适用范围非常广泛,主要应用于物联网……
-
5.4.2 整合ActiveMQ
略……跳过了😆
5.4.3 整合RabbitMQ
5.4.4 整合RocketMQ
5.4.5 整合Kafka
6、监控
6.1 监控概述
-
什么是监控?
就是通过软件的方式展示另一个软件的运行情况,运行的情况则通过各种各样的指标数据反馈给监控人员。例如网络是否顺畅、服务器是否在运行、程序的功能是否能够整百分百运行成功,内存是否够用,等等等等。
-
监控的作用:
- 监控服务是否处于宕机状态
- 监控服务的运行指标
- 监控程序的运行日志
- 管理服务的状态
-
监控的实现步骤
- Step1:显示监控信息的程序,用于获取服务信息(主动或被动拉去监控信息),并显示对应的信息
- Step2:运行的服务,启动时主动上报,同时需要告诉监控程序自己需要被监控,被监控的数据有哪些
如果监控程序被动拉去监控信息,而是由被监控的程序主动去上报监控信息,则不是实时监控(不推荐);如果监控程序是主动去获取程序的监控信息,则是实时监控(推荐)。如果被监控程序不主动上报自己要被监控,则监控程序无法知道谁要被监控;如果被监控程序不明确告诉监控的数据有哪些,则监控程序会监控到机密数据,这是存在安全隐患的
-
监控的分类(基于SpringBoot):
HTTP方式:通过编写一个服务端程序来监控应用(6.2的案例就是使用这种方式)JMX(Java Management Extensions)方式:通过原生Java官方提供的技术,JMX是一个为应用程序、设备、系统等植入管理功能的框架。JMX可以跨越一系列异构操作系统平台、系统体系结构和网络传输协议,灵活的开发无缝集成的系统、网络和服务管理应用(通过jconsole指令可以进入JMX窗口)
6.2 可视化监控平台
??SpringBoot抽取了大部分监控系统的常用指标,提出了监控的总思想。然后就有好心的同志根据监控的总思想,制作了一个通用性很强的监控系统,因为是基于springboot监控的核心思想制作的,所以这个程序被命名为Spring Boot Admin。
??Spring Boot Admin,这是一个开源社区项目,用于管理和监控SpringBoot应用程序。这个项目中包含有客户端和服务端两部分,而监控平台指的就是服务端。我们做的程序如果需要被监控,将我们做的程序制作成客户端,然后配置服务端地址后,服务端就可以通过HTTP请求的方式从客户端获取对应的信息,并通过UI界面展示对应信息。
主要的功能点有:
- 显示应用程序的监控状态
- 应用程序上下线监控
- 查看 JVM,线程信息
- 可视化的查看日志以及下载日志文件
- 动态切换日志级别
- Http 请求信息跟踪
- 其他功能点……
6.2.1 开发服务端程序
-
Step1:导入依赖
<properties> <java.version>1.8</java.version> <spring-boot-admin.version>2.5.4</spring-boot-admin.version> </properties> <!--SpringBoot监控服务的依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>de.codecentric</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-server</artifactId> </dependency> <!--版本依赖管理器--> <dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>de.codecentric</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-admin-dependencies</artifactId> <version>${spring-boot-admin.version}</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement> -
Step2:开启监控服务
在SpringBoot的启动类上添加
@EnableAdminServer注解 -
Step3:配置端口
server: port: 8080 -
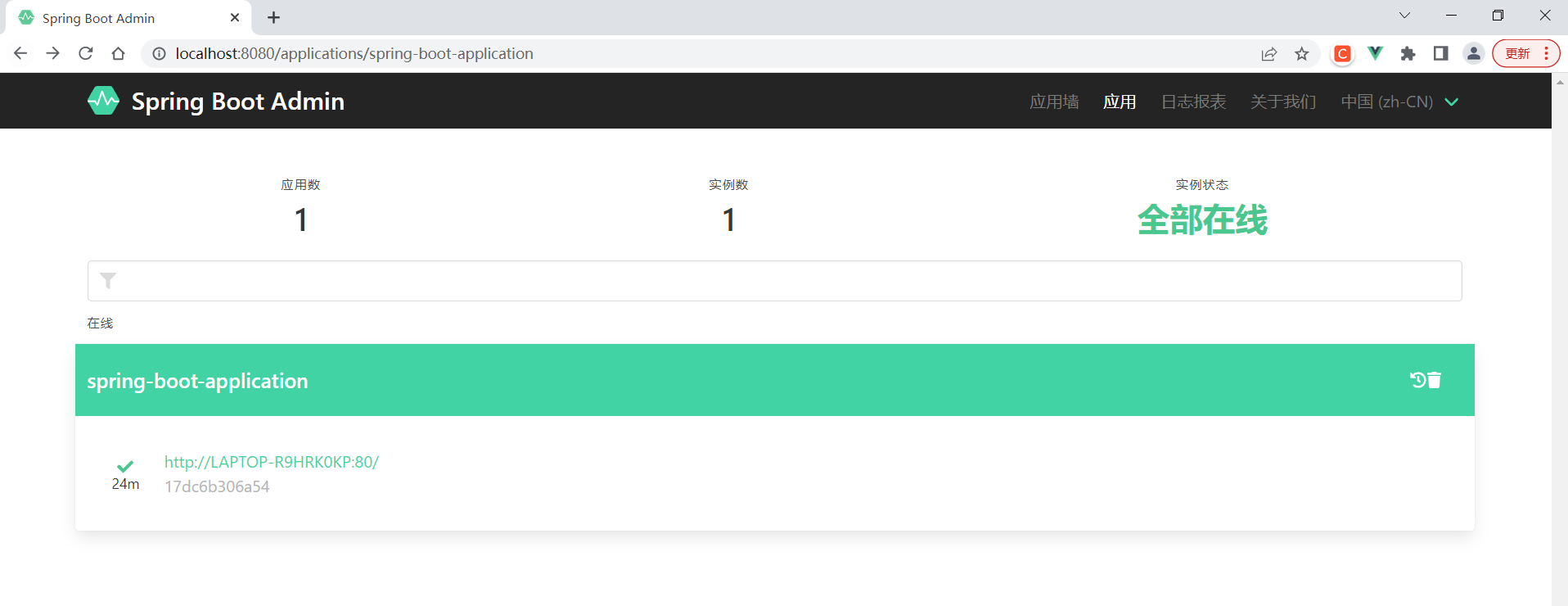
Step4:启动程序
6.2.2 开发客户端程序
-
Step1:导入依赖
<properties> <java.version>1.8</java.version> <spring-boot-admin.version>2.5.4</spring-boot-admin.version> </properties> <!--SpringBoot监控服务的依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>de.codecentric</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-client</artifactId> </dependency> <!--版本依赖管理器--> <dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>de.codecentric</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-admin-dependencies</artifactId> <version>${spring-boot-admin.version}</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement> -
Step2:编写配置文件
server: port: 80 spring: boot: admin: client: url: http://localhost:8080 management: endpoint: health: show-details: always # 允许监控服务器查看健康相关的所有信息(默认是never,不监控) endpoints: web: exposure: include: "*" # 允许监控服务器监控所有信息(默认是health,只能看健康信息) -
Step3:启动程序
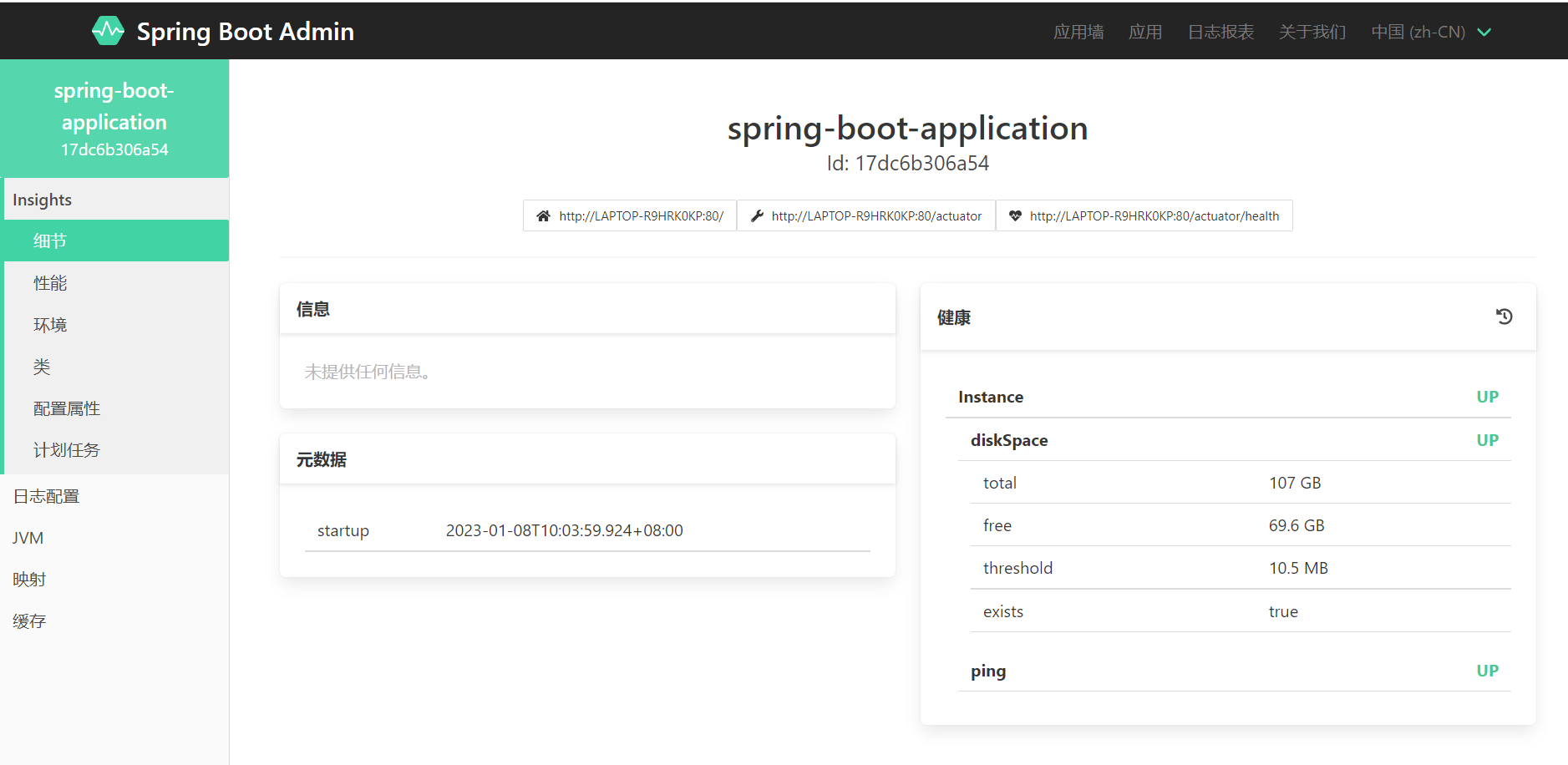
6.3 监控原理(端点映射)
前面可以可以通过SpringBoot Amin查看到被监控程序的很多数据,包括当前健康状态、程序线程相关数据、JVM相关数据、日志项数据……那么这些数据是怎么得到的,这就需要去查看映射了,在映射那个页面我们可以看到会有很多连接,这些连接就是监控服务器发送给客户端的请求,这些请求会被客户端响应,客户端会将相关信息发送给服务端,然后服务端会将这些数据进行展示
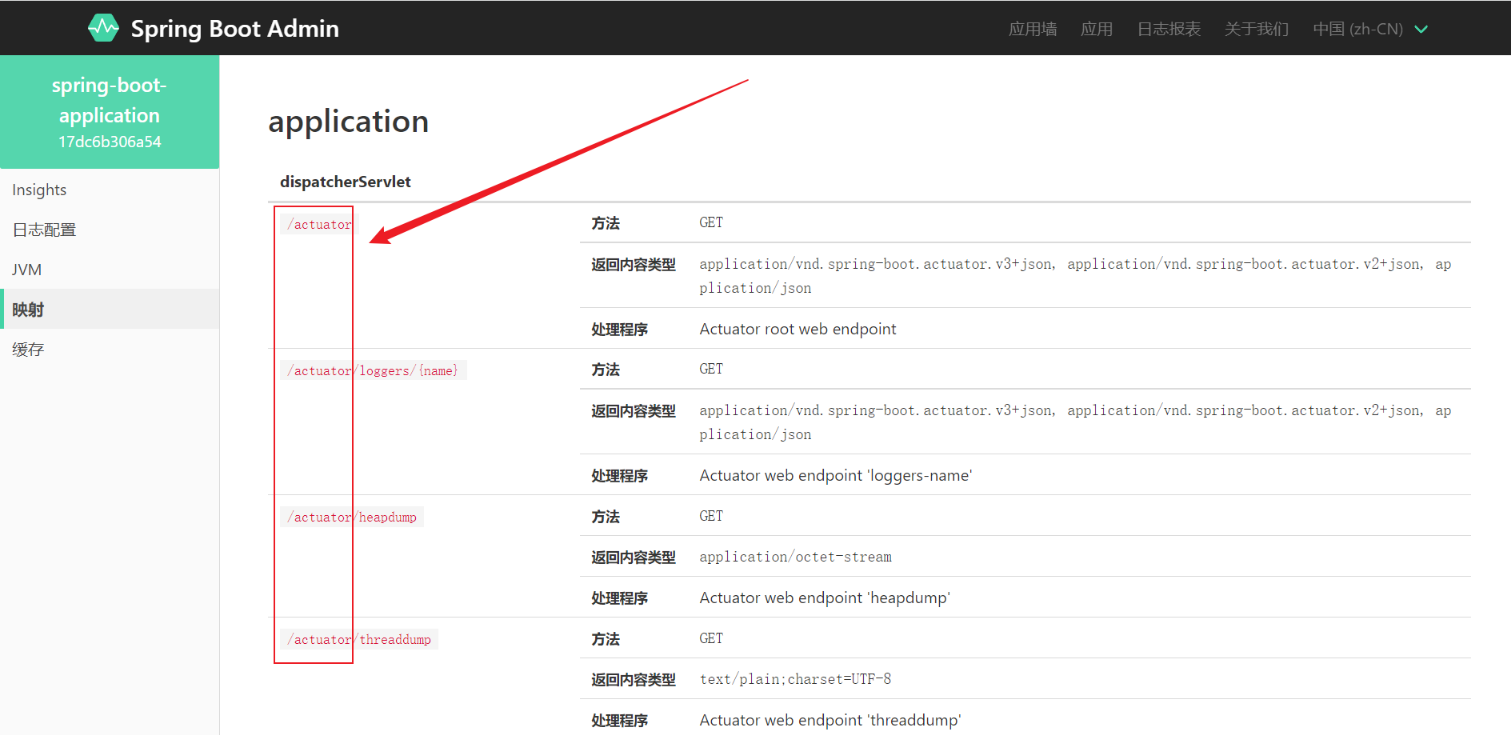
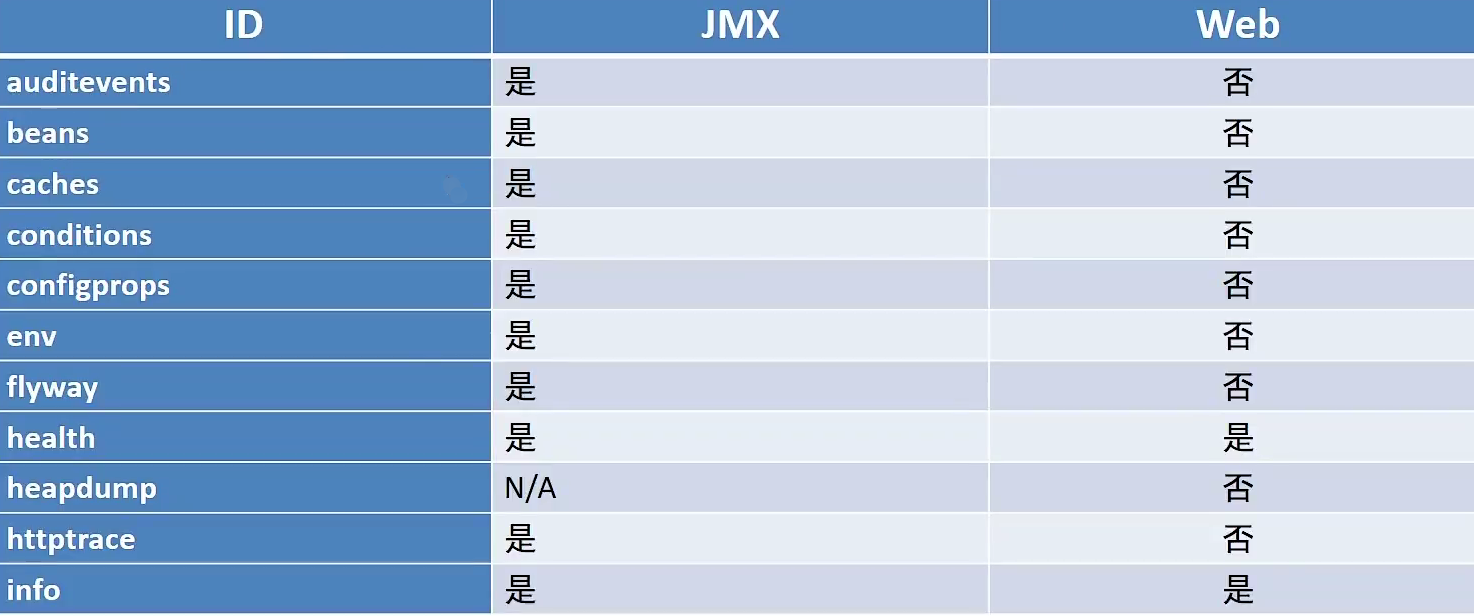
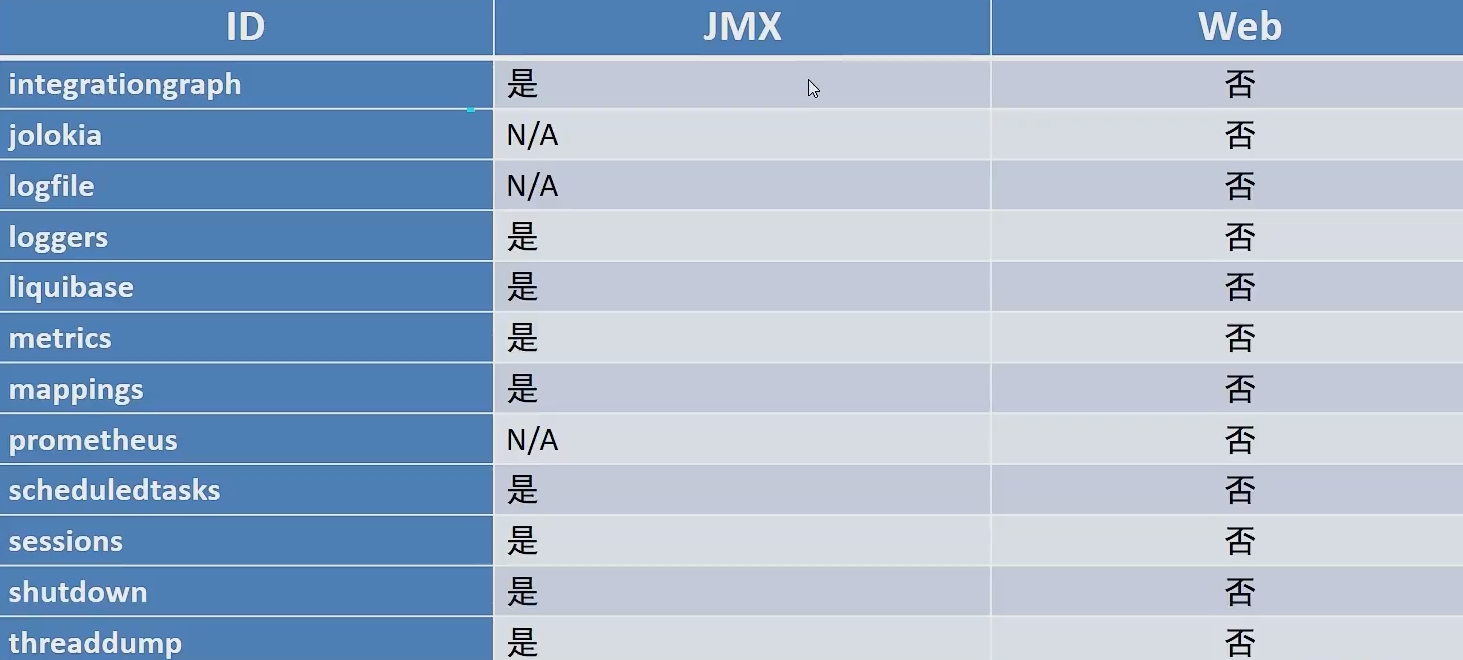
可以看到这里都是以/autuator开头的,autuatory可以称为端点,描述了一组监控信息,SpringBootAdmin提供了多个内置端点,通过访问端点就可以获取对应的监控信息,也可以根据需要自定义端点信息。通过发送请求路劲/actuator可以访问应用所有端点信息,如果端点中还有明细信息可以发送请求/actuator/端点名称来获取详细信息。以下列出了所有端点信息说明:
| ID | 描述 | 默认启用 |
|---|---|---|
auditevents | 暴露当前应用程序的审计事件信息。 | 是 |
beans | 显示应用程序中所有 Spring bean 的完整列表。 | 是 |
caches | 暴露可用的缓存。 | 是 |
conditions | 显示在配置和自动配置类上评估的条件以及它们匹配或不匹配的原因。 | 是 |
configprops | 显示所有 @ConfigurationProperties 的校对清单。 | 是 |
env | 暴露 Spring ConfigurableEnvironment 中的属性。 | 是 |
flyway | 显示已应用的 Flyway 数据库迁移。 | 是 |
health | 显示应用程序健康信息 | 是 |
httptrace | 显示 HTTP 追踪信息(默认情况下,最后 100 个 HTTP 请求/响应交换)。 | 是 |
info | 显示应用程序信息。 | 是 |
integrationgraph | 显示 Spring Integration 图。 | 是 |
loggers | 显示和修改应用程序中日志记录器的配置。 | 是 |
liquibase | 显示已应用的 Liquibase 数据库迁移。 | 是 |
metrics | 显示当前应用程序的指标度量信息。 | 是 |
mappings | 显示所有 @RequestMapping 路径的整理清单。 | 是 |
scheduledtasks | 显示应用程序中的调度任务。 | 是 |
sessions | 允许从 Spring Session 支持的会话存储中检索和删除用户会话。当使用 Spring Session 的响应式 Web 应用程序支持时不可用。 | 是 |
shutdown | 正常关闭应用程序。 | 否 |
threaddump | 执行线程 dump。 | 是 |
heapdump | 返回一个 hprof 堆 dump 文件。 | 是 |
jolokia | 通过 HTTP 暴露 JMX bean(当 Jolokia 在 classpath 上时,不适用于 WebFlux)。 | 是 |
logfile | 返回日志文件的内容(如果已设置 logging.file 或 logging.path 属性)。支持使用 HTTP Range 头来检索部分日志文件的内容。 | 是 |
prometheus | 以可以由 Prometheus 服务器抓取的格式暴露指标。 | 是 |
虽然说这里的大部分端点都是默认开启的,但是默认暴露(允许对外访问)的只有 health 和 info 端点,所以如果需要允许端点对外暴露,可以通过如下配置(如果想要暴露所有的端点,则可以直接配置 "*" ,前面设置过了):
management:
endpoint: # 单一端点的配置
# 允许监控服务器查看健康相关的所有信息包括接入的第三方服务信息(默认是never,只监控当前应用的健康信息,不会将恐第三方应用信息)
health:
show-details: always
endpoints: # 全部端点的配置
web:
exposure:
# 允许监控服务器监控所有信息(默认是对外开发health、info端点)
include: "*"
# include: [health, info, ...] # 这里也可以配置对外开发多个端点
6.4 常用端点
6.4.1 info端点
前面我们了解了所有的信息都是通过autuator这个端点的请求获取的,但是我们可以发现在信息这里是没有显示数据,这是因为
管理信息数据的是info端点,而info端点需要开发者自己去配置,才能显示数据,具体配置如下:
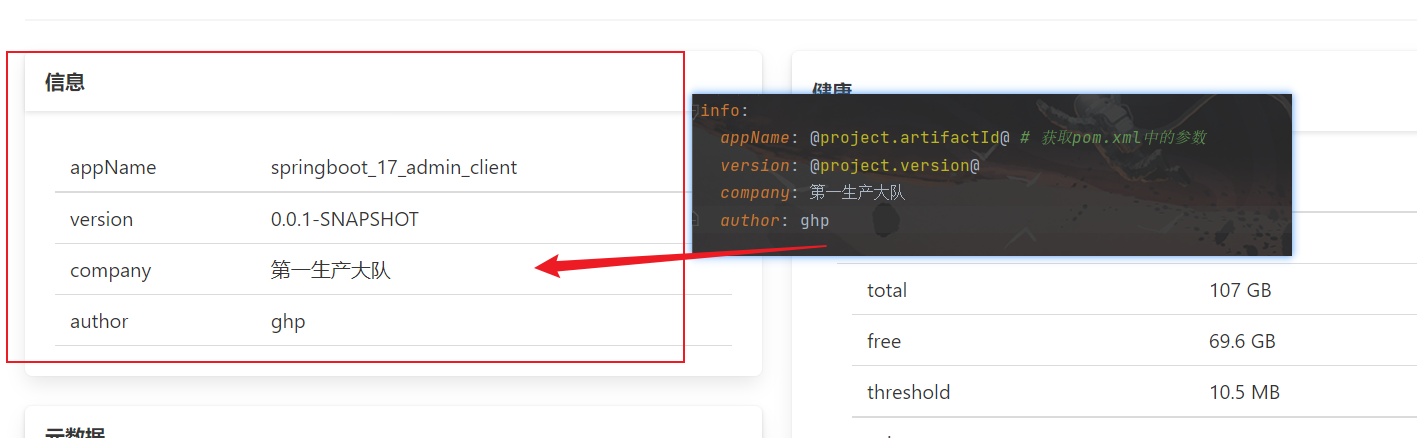
上面那种方式是通过配置文件来控制info端点的数据显示,下面我们将通过编程形式来控制info端点的数据显示
@Component
public class InfoConfig implements InfoContributor {
@Override
public void contribute(Info.Builder builder) {
builder.withDetail("runTime",System.currentTimeMillis()); //添加单个信息
Map infoMap = new HashMap();
infoMap.put("buildTime","2006");
builder.withDetails(infoMap); //添加一组信息
}
}
6.4.2 health端点
@Component
public class HealthConfig extends AbstractHealthIndicator {
@Override
protected void doHealthCheck(Health.Builder builder) throws Exception {
boolean condition = true;
if(condition) {
builder.status(Status.UP); //设置运行状态为启动状态
builder.withDetail("runTime", System.currentTimeMillis());
Map infoMap = new HashMap();
infoMap.put("buildTime", "2006");
builder.withDetails(infoMap);
// builder.up();
}else{
builder.status(Status.OUT_OF_SERVICE); //设置运行状态为不在服务状态
builder.withDetail("上线了吗?","你做梦");
// builder.down();
}
}
}
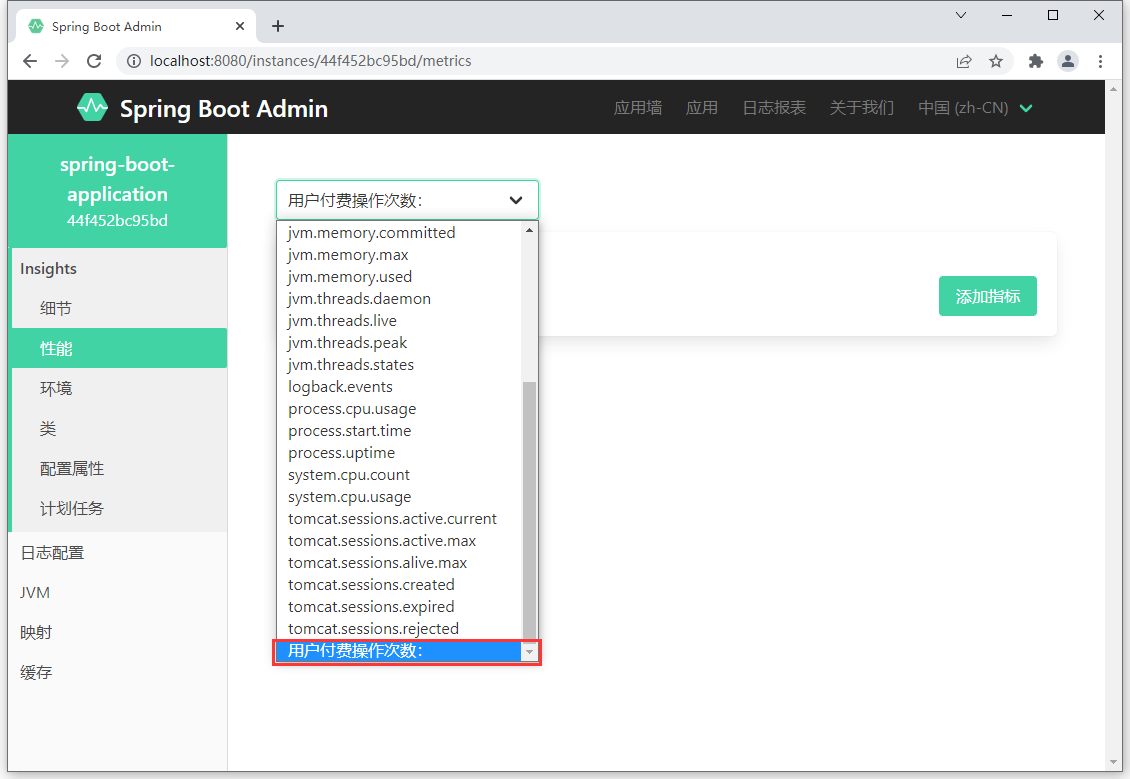
6.4.3 Metrics端点
metrics端点描述了性能指标,除了系统自带的监控性能指标,还可以自定义性能指标
@Service
public class BookServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<BookDao, Book> implements IBookService {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
private Counter counter;
public BookServiceImpl(MeterRegistry meterRegistry){
counter = meterRegistry.counter("用户付费操作次数:");
}
@Override
public boolean delete(Integer id) {
//每次执行删除业务等同于执行了付费业务
counter.increment();
return bookDao.deleteById(id) > 0;
}
}
6.5 自定义端点
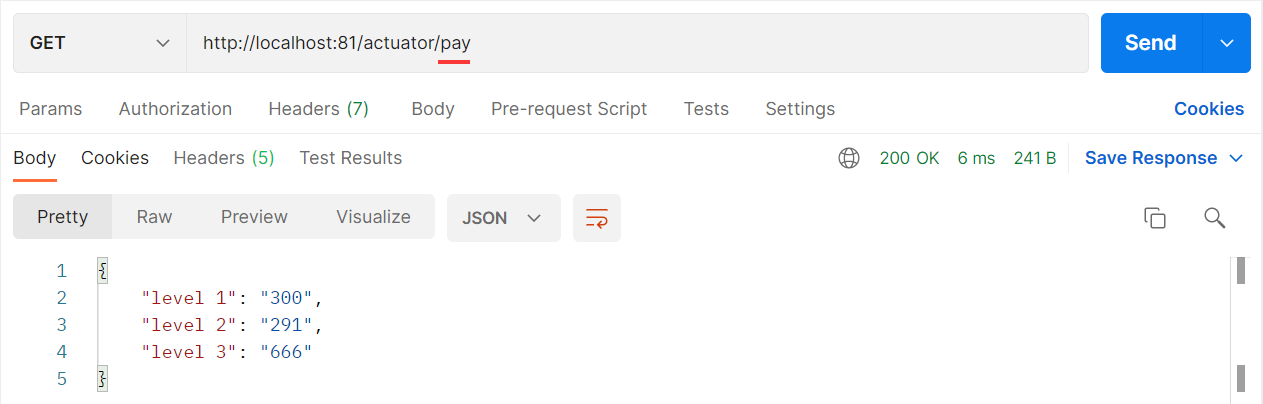
虽然SpringBoot Admin中已经提供了很多比较实用的端点,但是对于一些特殊的业务,我们需要通过自定义一个端点来解决完成这些业务
@Component
// 自定义端点,enableByDefault表示开启端点(默认就是true)
@Endpoint(id="pay",enableByDefault = true)
public class PayEndpoint {
// 访问这个端点就执行这个方法
@ReadOperation
public Object getPay(){
Map payMap = new HashMap();
payMap.put("level 1","300");
payMap.put("level 2","291");
payMap.put("level 3","666");
return payMap; // 将数据返回给访问方
}
}
参考资料:
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 我不是学霸,如何拿下软考高项(级)信息系统管理师证书?
- 知识付费saas租户平台的核心功能设计:打造高效、个性化的学习体验
- 鸿蒙OS应用开发之文本选择
- 函数栈帧的创建与销毁(这里使用vs2022进行演示)(未完)
- 微服务架构的服务注册和发现究竟采用Nacos还是Eureka ?
- nginx限流
- Mstar开发OSD菜单的步骤《一》
- TK美区洞察|聚焦定价走势,抓住市场新风向
- 实现将信息作为txt,pdf,图片的形式保存到电脑~
- fastadmin想自定义表格的样式,可以使用模板渲染并在模板中调用自定义的方法