链表 链表面试题
发布时间:2023年12月27日
一.??链表
1.1 链表的概念及结构
链表是一种
物理存储结构上非连续
存储结构,数据元素的
逻辑顺序
是通过链表中的
引用链接
次序实现的 。

注意:
1. 由上图可知, 链式结构在逻辑上是连续的, 但是在物理上不一定连续
2. 现实中的结点一般都是从堆上申请过来的
3. 从堆上申请的空间, 是按照一定的策略来分配的, 两次申请的空间可能连续, 也可能不连续
4. 一个结点node分为两个部分,? val存放数值,? next存放下一个节点的地址
?实际中链表的结构非常多样,以下情况组合起来就有8种链表结构:
1.
单向或者双向

2.
带头或者不带头
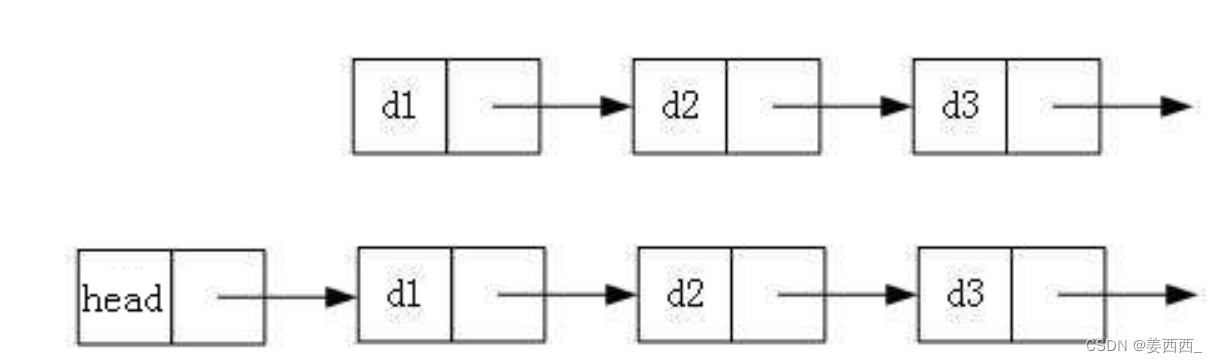
3. 循环或者非循环

虽然有这么多的链表的结构,但是我们重点掌握两种
:
无头单向非循环链表
:
结构简单
,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为
其他数据结构的子结构
,如哈希桶、图的邻接表等等。另外这种结构在笔试面试
中出现很多。
无头双向链表
:在
Java
的集合框架库中
LinkedList
底层实现就是无头双向循环链表。
?1.2 链表的简单实现
无头单项非循环链表的实现:
public class MySingleList implements IList{
static class ListNode{//定义一个结点
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
/*链表的头结点*/
public ListNode head;//这个head只是一个引用, 并不是代表这是个有头链表的意思
/*
public void createList(){
ListNode node1 = new ListNode(12);
ListNode node2 = new ListNode(155);
ListNode node3 = new ListNode(1234);
ListNode node4 = new ListNode(2);
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
node3.next = node4;
this.head = node1;
}
*/
/*头插法*/
@Override
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
}
//尾插法
@Override
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(head==null){
head = node;
}else{
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(cur.next != null){
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
}
}
//在指定位置插
@Override
public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
if(index < 0 ||index >size()){
throw new IndexException("index不合法"+index);
}
if(index == 0){
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if(index ==size()){
addLast(data);
return;
}
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
ListNode cur = searchPrevIndex(index);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
}
private ListNode searchPrevIndex(int index){
ListNode cur = head;
int count = 0;
while(count != index-1){
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
return cur;
}
//是否包含某个数
@Override
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val==key){
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
//删除结点
@Override
public void remove(int key) {
if(head ==null){
return;
}
if(head.val == key){
head = head.next;
return;
}
ListNode cur = findPrevKey(key);
if(cur == null){
throw new KeyException("找不到"+key);
}
ListNode del = cur.next;
cur.next = del.next;
}
private ListNode findPrevKey(int key){
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur.next != null){
if(cur.next.val == key){
return cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
//将所有的key结点都删掉
@Override
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
if(head ==null){
return;
}
ListNode prev = head;
ListNode cur = head.next;
while(cur !=null){
if(cur.val == key){
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}else{
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if(head.val == key){
head = head.next;
return;
}//最后删prev的key
}
//计算链表的长度
public int size() {
int count = 0;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
//清除链表
@Override
public void clear() {
head = null;
}
//打印链表
@Override
public void display() {
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
System.out.println(cur.val+" ");
cur=cur.next;//遍历所有节点
}
}
}注:
cue != null 表示遍历完整个链表
cur.next != null 表示遍历到了最后一个结点
1.3 链表面试题?
思路:
1. 若链表为空, 直接返回null
2. 当我们移动cur指针, 指向值为val的结点时, 就无法找到上一个结点, 使上一个结点的next == cur.next, 所以我们再定义一个指针prev, 指向cur前面的结点, 所以我们将prev == head, cur == head.next
3. 循环判断cur.val是否等于val, 若等于, 删除此节点prev.next = cur.next,?并cur向后走cur = cur.next, prev保持不动; 若不等于, prev和cur都向后走prev = cur, cur = cur.next, 循环结束的条件为cur遍历完整个链表cur != null
4. 上面的步骤, 我们忽略了判断头结点, 在后面加上判断即可(若在前面判断头结点是否值为val, 如果相等的话, head = head.next, 那么将prev == head时, 后面还会忽略掉head结点, 除非放在循环里, 直到head.val != val)
代码如下:
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if(head ==null){
return null;
}
ListNode prev = head;
ListNode cur = head.next;
while(cur !=null){
if(cur.val == val){
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}else{
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if(head.val == val){
head = head.next;
return head;
}
return head;
2.
反转一个单链表。链接
思路:
1. 若链表为空, 则返回null2. 若链表只有一个结点, 则返回这个节点3. 创建cur引用指向head.next, 将head.next置为空, 需循环的将cur的结点进行头插到head结点前cur.next = head, 但为了找到后面的结点, 需先创建一个节点curNext = cur.next, 然后进行头插, 将head = cur, cur = curNext, 循环条件为cur遍历完整个链表cur != null
代码:
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null){
return head;
}
if(head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode cur =head.next;
head.next = null;
while(cur != null){
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = head;
head = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
return head;
}思路一:求出链表的长度/2, 但此方法效率不高思路二:1. 定义两个引用fast, slow, 分别指向head, 循环每次fast走两个结点? fast = fast.next.next, slow走一个结点? slow = slow.next2. 如果链表为偶数个结点, 那么当循环条件为fast != null时, slow正好指向两个中间结点的第二个节点;?如果链表为奇数个结点, 那么当循环条件为fast.next != null时, slow正好指向中间结点, 所以, 循环条件为 fast != null && fast.next != null , 注意, 不可以两个条件调换顺序, 若调换可能会发生空指针异常
代码:
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
if(head == null){
return head;
}
if(head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;思路一:找到(链表长度-k)的结点, 但此方法效率较低思路二:1. 如果k<0, 返回null;2. 定义两个引用fast, slow, 分别指向head, 将fast移动k-1步,定义一个count=0, 循环count++, 当 count != k-1时停止, 在循环中让 fast = fast.next, 如果 fast == null, 说明k的值过大, 不合法,返回null3. 然后fast和slow同时移动, 当fast移动到最后一个位置 fast.next == null, 此时slow指向的就是倒数第k个结点
代码:
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) {
if(k<0){
return null;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
int count = 0;
while(count != k-1){
if(fast.next == null){
return null;
}
fast = fast.next;
count++;
}
while(fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
5.
将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。链接
思路:
1. 创建一个新链表(其实是只有一个表头), 将有序的链表储存在新链表中, 并创建一个cur用来遍历新链表2. 循环着同时遍历两个链表, 并比较val的大小, 将val值较小的结点, 尾插到新的链表中, 并继续遍历下一个节点, 另一个链表的指针保持不动, cur向下遍历, 循环停下来的条件为 当有一方全部遍历完3. 如果list1遍历完成, 那么将list2剩余的直接尾插到新链表中即可, 同理,?如果list2遍历完成, 那么将list1剩余的直接尾插到新链表中即可.
代码:
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode newList = new ListNode();
ListNode cur = newList;
while(list1 !=null && list2 !=null){
if(list1.val > list2.val){
cur.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
cur = cur.next;
}else{
cur.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if(list1 == null){
cur.next = list2;
}else{
cur.next = list1;
}
return newList.next;
}
思路:
1. 创建一个指针cur用来遍历链表, 将小于x的数, 放在一个链表中, 并用bs, be来记录链表的表头和表尾, 将大于等于x的数, 放在一个链表中, 并用as, ae来记录链表的表头和表尾2. 循环遍历链表, 停下的的条件为全部遍历完, 即cur != null, 如果此时的cur.val小于x, 则将cur给bs,但是我们要考虑, 如果bs为空时, 将cur给bs,此时be也为cur, 如果bs不为空, 那么只需将be.next = cur, 并且be = be.next, 同理, cur.val大于x也是一样的3. 最后将两个链表连接起来, 即 be.next = as, 将 ae.next 置为null, 返回bs即可完善代码:4. 若链表为空, 则返回null5. 若给出的值x都小于或大于链表中的数, 即可能小于x的这个链表为空, 那么我们访问 be.next 就会造成空指针异常, 所以需判断, 如果bs?== null, 直接返回as, 如果大于等于x的这个链表为空, 那么我们直接返回bs无影响6. 如果ae为空, 则访问 ae.next 时会空指针异常, 则需判断
代码:
public ListNode partition(ListNode pHead, int x) {
if (pHead == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode cur = pHead;
ListNode bs = null;
ListNode be = null;
ListNode as = null;
ListNode ae = null;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val < x) {
if (bs == null) {
bs = cur;
be = cur;
} else {
be.next = cur;
be = be.next;
}
} else {
if (as == null) {
as = cur;
ae = cur;
} else {
ae.next = cur;
ae = ae.next;
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if (bs == null) {
return as;
}
be.next = as;
if (as != null) {
ae.next = null;
}
return bs;
}
7.
链表的回文结构。链接
思路:
1. 找到中间结点(同第三题)2. 将中间结点以后的链表逆序(同第二题)3. 两头分别向中间同时前进, 并判断val值是否相等
代码:
public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode A) {
if (A == null) {
return true;
}
//找到中间值slow
ListNode fast = A;
ListNode slow = A;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
//将后面的链表逆序
ListNode cur = slow.next;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = slow;
slow = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
//判断是否是回文
while (A != slow) {
if (A.val == slow.val) {
A = A.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (A.next == slow) {
return true;
}
} else {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
8.
输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点。链接
思路:
1. 求出两链表的长度, 如果headA比headB长len, 就让headA先走len步, 剩下的headA和headB一起走, 如果headA == headB且不为空, 那么就相交, 反之, 如果headB比headA长len, 就让headB先走len步, 剩下的headA和headB一起走, 如果headA == headB且不为空, 那么就相交.2. 但是上述方法过于冗杂, 总的来说就是让长的那个链表先走len步, 那么我们可以定义 一个pLong指针永远指向长的那个链表,??一个Short 指针永远指向短的那个链表 , 先让 pLong = headA, pShort = headB, 暂且认为headA长, 然后让len=lenA-lenB, 如果len<0, 那么说明headB长, 那么让pLong = headB, pShort = headA, len =lenB - lenA, 如果len<=0, 那么让pLong = headA, pShort = headB, 回到链头(因为计算长度时pLong和pShort已经指到链表尾)
代码:
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode pLong = headA;
ListNode pShort = headB;
int lenA = 0;
while(pLong != null){
lenA++;
pLong = pLong.next;
}
int lenB = 0;
while(pShort != null){
lenB++;
pShort = pShort.next;
}
int len = lenA - lenB;
if(len < 0){
pLong = headB;
pShort = headA;
len = lenB - lenA;
}else{
pLong = headA;
pShort = headB;
}
while(len != 0){
pLong = pLong.next;
len--;
}
while(pLong != pShort && pLong != null){
pLong = pLong.next;
pShort = pShort.next;
}
if(pLong == null){
return null;
}
return pLong;
}
}
9.
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。链接
结论:
判断是否有环, 实际上就是判断两个指针, 一个每次走两步, 一个每次走一步, 两个指针是否会相遇, 即指向同一个结点.
(为什么一个走两步, 一个走一步呢?
因为最小单位就是一步, 即一个结点, 每走一次, 快指针就快慢指针一步, , 那么最多快指针就比慢指针快一圈, 此时两个指针相遇, 如果按照3:1 或4:1等方法走, 可能会绕很多圈才能相遇, 还可能会永远错过)
代码:
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return false;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
思路:
1. 判断是否有环(第九题)2. 结论:当按照第九题的方法, 快的走两步, 慢的走一步, 那么一定会在环的某个位置相遇,这时, 我们将慢的重新放回头结点, 快的在相遇点不动, 再按照每次都走一步的速度前进, 那么当两个指针再次相遇时, 这个位置就是链表入环的第一个节点.
为什么是这样呢?
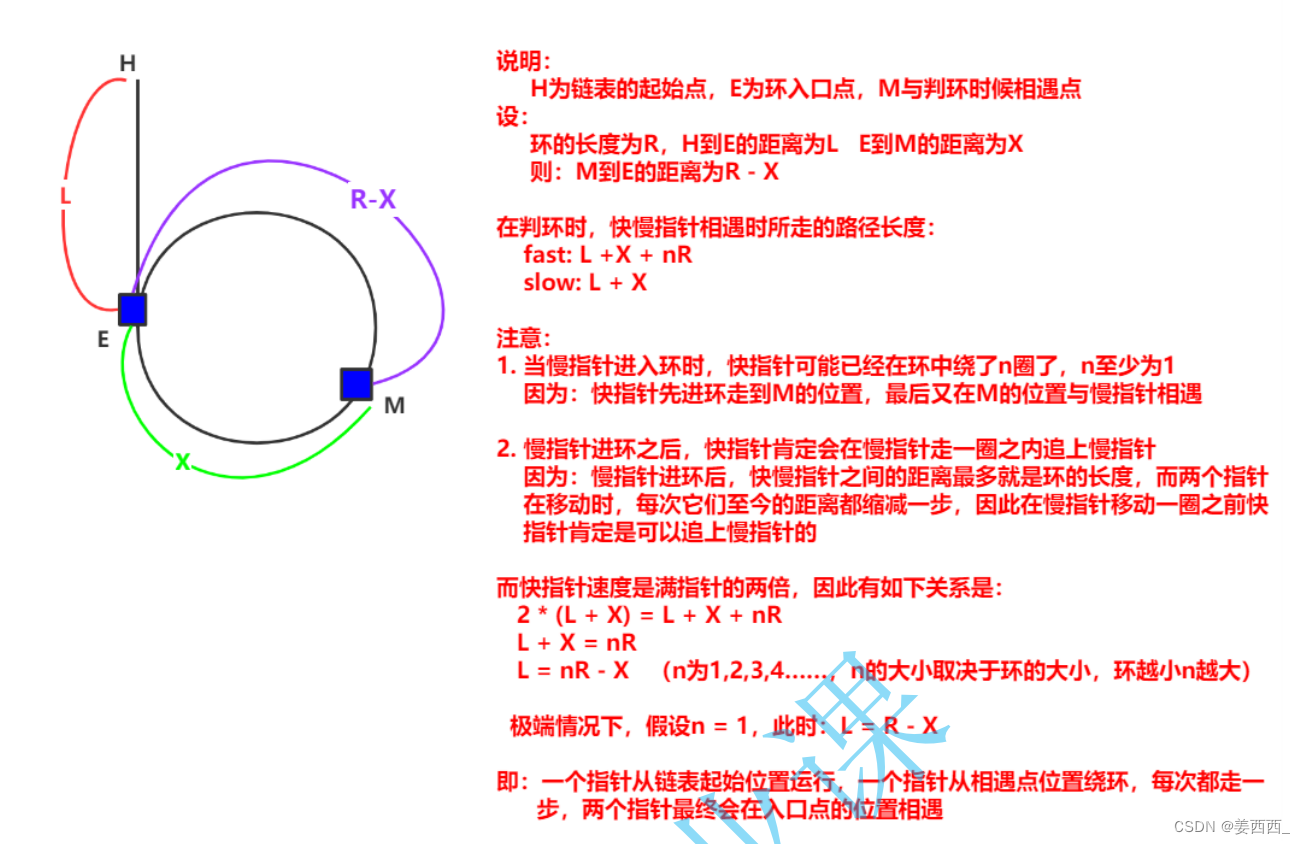
代码:
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (true) {
if (fast == null) {
return null;
}
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow) {
break;
}
}
slow = head;
while (slow != fast) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_73992740/article/details/135170739
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!