算法第十三天-组合总和Ⅱ
组合总和Ⅱ
题目要求

解题思路
按顺序搜索,设置合理的变量,在搜索的过程中判断是否会出现重复集结果。重点理解对输入数组排序的作用和参考代码中 大剪枝和小剪枝 的意思
这道题域上一问的区别在于:
- 第39题:candidates中的数字可以无限制重复被选取;
- 第40题:candidates中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次;
相同点在于:相同数字列表的不同排列被视为一个结果。
如何去掉重复的集合(重点)
为了使得解集不包含重复的组合。可以从以下两种方案思考:
- 使用 hash 天然去重功能,但是编码相对复杂;
- 使用和第39题和第15题相似的思路:不重复就不需要按顺序搜索,**在搜索过程中检测分支是否会出现重复结果。**注意:在这里的顺序不仅仅指数组candidates有序,还指按照一定顺序搜索结果。
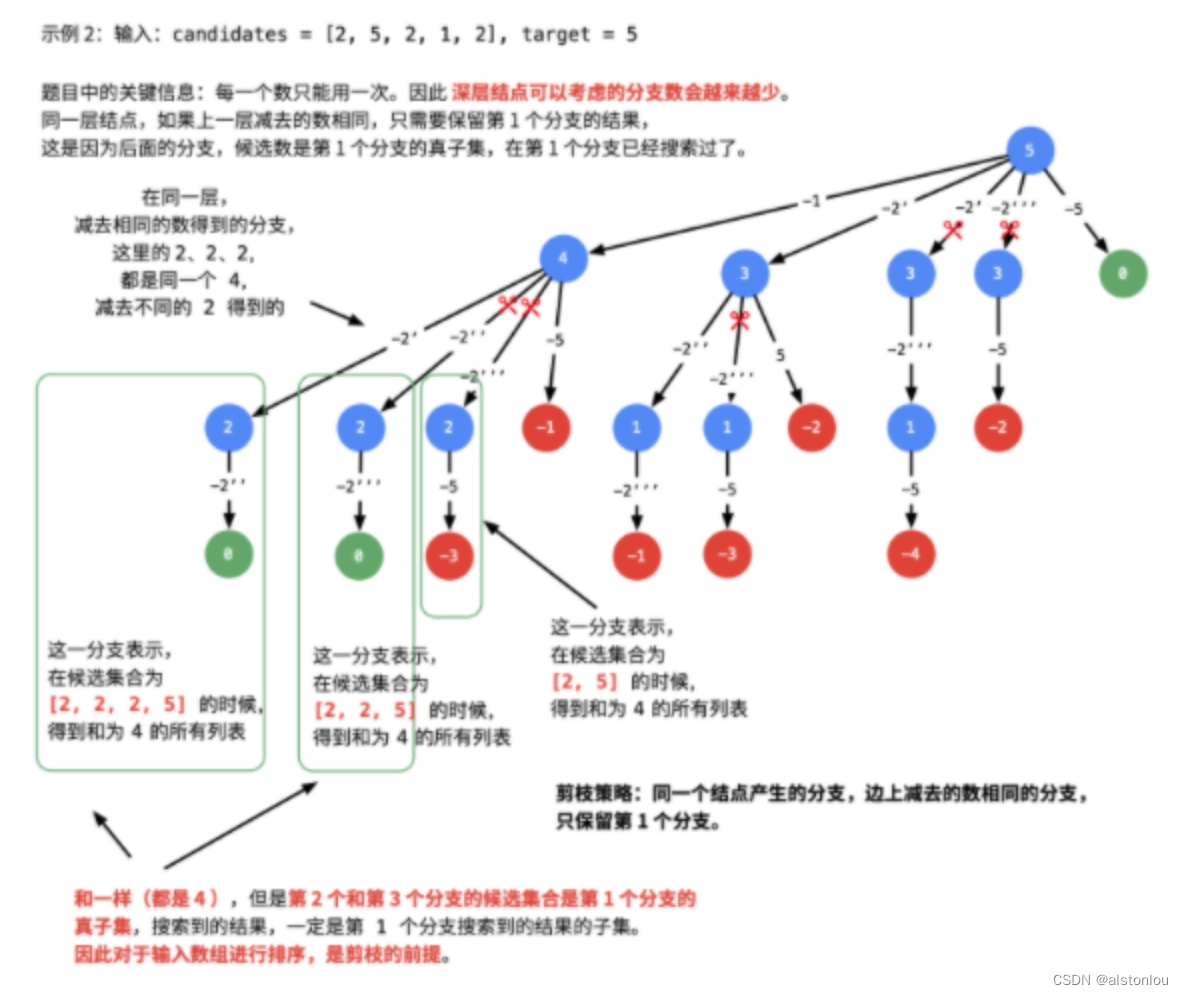

由39题我们知道,数组candidates有序,也是DFS 过程中实现[剪枝]的前提。
将数组先排序的思路来自于这个问题:去掉一个数组中重复的元素。很容易想到的方案是:先对数组升序排列,重复的元素一定不是排好序以后相同的连续数组区域的第1个元素。也就是说,剪枝发生在:**同一层数值相同的节点第2,3,…个节点,因为数值相同的第1个节点已经搜索出了包含了这个数值的全部结果,**同一层的其他节点,候选数的个数更少,搜索出的结果一定不会比第1个节点更多,并且是第一个节点的子集。
代码
from typing import List
class Solution:
def combinationSum2(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
def dfs(begin, path, residue):
if residue == 0:
res.append(path[:])
return
for index in range(begin, size):
if candidates[index] > residue:
break
if index > begin and candidates[index - 1] == candidates[index]:
continue
path.append(candidates[index])
dfs(index + 1, path, residue - candidates[index])
path.pop()
size = len(candidates)
if size == 0:
return []
candidates.sort()
res = []
dfs(0, [], target)
return res
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:
O
(
2
n
?
n
)
O(2^n * n)
O(2n?n),其中n为candidates的长度。在大多数的递归+回溯的题目中我们无法给出一个严格的渐近界限,故这里只分析一个较为宽松的渐近上界。
空间复杂度:
O
(
n
)
O(n)
O(n)
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 六、K8S-DaemonSet(DS)
- java数据结构与算法刷题-----LeetCode766. 托普利茨矩阵
- 基于JavaWeb+SSM+Vue基于微信小程序生鲜云订单零售系统的设计和实现
- 【后端】深入浅出Node.js
- 第十七章 多线程基础
- 自媒体实战篇:剪辑软件应用与实操
- AcWing 851. spfa求最短路&&AcWing 852. spfa判断负环—spfa算法
- ai智能写作软件有分享吗?分享4款解放双手的软件!
- 生物信息学及其研究方向与应用
- pytest - Getting Start