算法训练营Day21(二叉树)
发布时间:2023年12月20日
530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差?
需要领悟一下二叉树遍历上双指针操作,优先掌握递归
530. 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差 - 力扣(LeetCode)
虽然说递归的返回值为int一般是不需要遍历整个树,之间返回的,但是对于这道题完全可以把提供的二叉树当作递归函数,因为root为null直接返回,什么时候为null? 无非就是第一个根节点为null
才会直接返回,比如这样二叉树,这个左孩子为null的时候,return一个-1,是对整体没什么作用的,也就是说,这里retrun -1既可以排除为null的情况,递归使用也不回带来什么影响。因为没对返回值做什么处理,仅仅是排除二叉树为null的时候。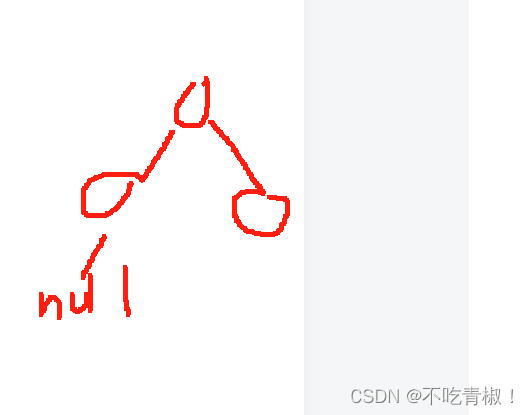
class Solution {
private int minValue=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
private TreeNode pre;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return -1;
getMinimumDifference(root.left);
if(pre!=null){
minValue = Math.min(minValue,Math.abs(root.val-pre.val));
}
pre = root;
getMinimumDifference(root.right);
return minValue;
}
}?501.二叉搜索树中的众数?
?
和?530差不多双指针思路,不过?这里涉及到一个很巧妙的代码技巧。
class Solution {
private TreeNode pre;
private int count = 0;
private int maxCount = 0;
private List<Integer> result= new ArrayList<>();
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
travel(root);
int [] res = new int[result.size()];
for(int i = 0;i<result.size();i++){
res[i] = result.get(i);
}
return res;
}
void travel(TreeNode root){
if(root==null) return;
travel(root.left);
//根
//count统计
if(pre==null){
count = 1;
}else if(root.val==pre.val){
count++;
}else{
count = 1;
}
pre = root;
//结果收集
if(count==maxCount){
result.add(root.val);
}else if(count>maxCount){
maxCount = count;
result.clear();
result.add(root.val);
}
travel(root.right);
}
}236.?二叉树的最近公共祖先?
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先 - 力扣(LeetCode)
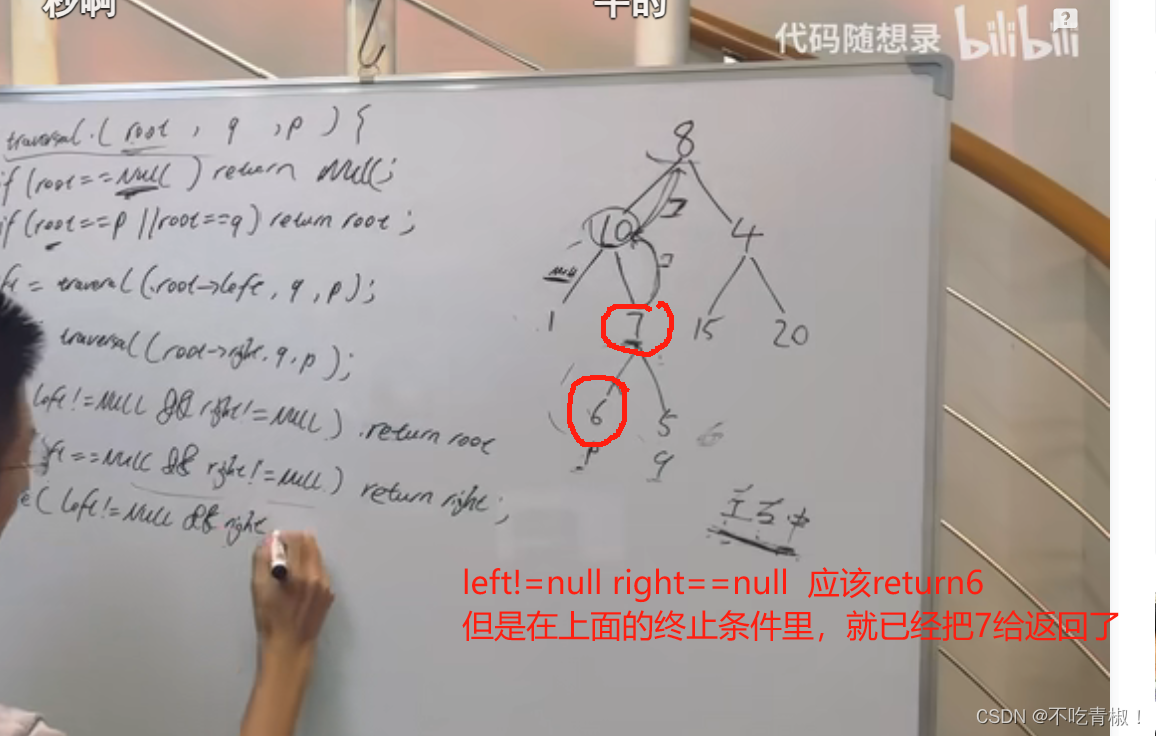
注意终止条件,是3个,
再注意一下后续遍历进行判断,左孩子有p或者q 有孩子有p或q 才是祖先
还得注意一下情况2
写题的时候,先按照后续遍历写出来,再在脑子里回想一遍递归过程,就很好理解了,代码虽然简洁,还是需要认真的思考一下。
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
//终止条件,遇到p q null的时候终止
if(root==null||root==p || root==q) return root;
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(left==null&&right==null) return null;
else if(left==null&&right!=null) return right;
else if(left!=null&&right==null) return left;
else return root;
}
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_65728526/article/details/135076227
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!