算法通关村第一关——黄金挑战 | 环与双向链表
目录
1. 单链表中的环问题
1.1 确定链表中是否有环
给你一个链表的头节点?head?,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪?next?指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数?pos?来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。注意:pos?不作为参数进行传递?。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环?,则返回?true?。 否则,返回?false?。
示例 1:
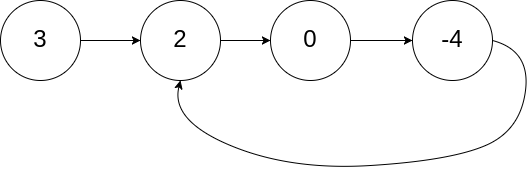
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 输出:true 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
解法一:利用hash。
遍历的时候将元素放入map中,如果有环就一定会发生碰撞,碰撞的位置就是环的入口
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode pos=head;
Set<ListNode> set=new HashSet<>();
while (pos!=null){
if (set.contains(pos)){
return true;
}else {
set.add(pos);
pos=pos.next;
}
}
return false;
}解法二:双指针
确认是否有环,最优解就是双指针,即快慢指针。没有环,快指针就会到达链表的表尾;有环,则一定会相遇。
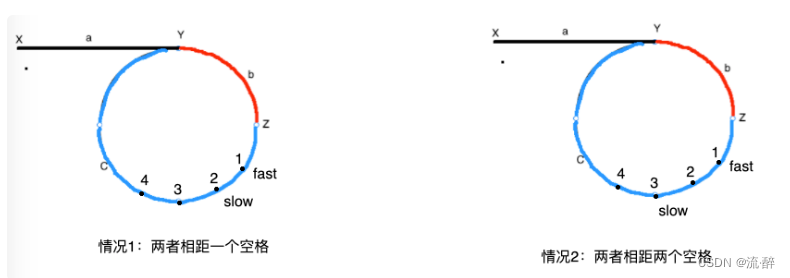
如上图,最近的两种情况就是两个指针相距一个空格和两个空格。
第一种情况:相距一个空格,slow走一步,fast走两步,则在三的位置相遇。
第二种情况:相距两个空格,slow走一步到达4,fast走两步到达3,此时又是第一种情况。
当fast在slow前面的时候,slow指针也就只能等着被套圈了。
/**
* 是否存在环,双指针
* @param head
* @return
*/
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head==null||head.next==null){
return false;
}
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
if (fast==slow){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}1.2 确定环的入口
给定一个链表的头节点 ?head?,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。?如果链表无环,则返回?null。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪?next?指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数?pos?来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果?pos?是?-1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos?不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
不允许修改?链表。
示例 1:
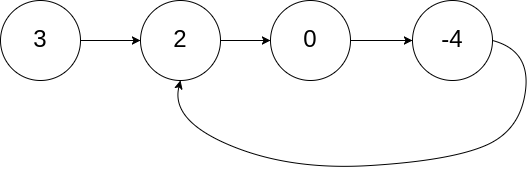
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
解法一:hash
在确定环的时候利用的hash也可以查找环形的入口,只是返回不是true和false了,返回的是结点
/**
* 确定环的入口
* @param head
* @return
*/
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode pos=head;
Set<ListNode> set=new HashSet<>();
while (pos!=null){
if (set.contains(pos)){
return pos;//此时pos结点就是环的入口
}else {
set.add(pos);
pos=pos.next;
}
}
return null;
}解法二:双指针
按照快慢的方式寻找到相遇的位置,然后将两指针分别放到链表的表头和相遇的位置,以相同的速度推进,即可找到环的入口。
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head==null||head.next==null){
return null;
}
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
while (fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){//先找到相遇的位置
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
if (fast==slow){
break;
}
}
if (fast==null||fast.next==null){//确定不是因为到达表尾而出的
return null;
}
slow=head;
while (fast!=slow){//寻找环形的入口
fast=fast.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return slow;
}或合并起来
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head==null||head.next==null){
return null;
}
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
while (fast!=null){
slow=slow.next;
if (fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
}else {
return null;
}
if (fast==slow){
slow=head;
while (fast!=slow){//寻找环形的入口
fast=fast.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
return null;
}2. 双向链表
增删改查
2.1 创建双向链表
/**
* 创建双向链表结点
*/
class DoubleNode {
public int data; //数据域
public DoubleNode next; //指向下一个结点
public DoubleNode prev;
public DoubleNode(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
//打印结点的数据域
public void displayNode() {
System.out.print("{" + data + "} ");
}
}2.2 插入节点
2.2.1 头插法
//头部插入,,first和last不是双向链表中的结点,类似于单链表中的虚拟结点,指向链表中的头尾结点
public void insertFirst(int data) {
DoubleNode newDoubleNode = new DoubleNode(data);
if (first==null) {
last = newDoubleNode;
} else {//如果不是第一个结点的情况
//将还没插入新结点之前链表的第一个结点的previous指向newNode
first.prev = newDoubleNode;
}
newDoubleNode.next = first; //将新结点的next指向first
first = newDoubleNode; //将新结点赋给first(链接)成为第一个结点
}2.2.2?尾插法
public void insertLast(int data) {
DoubleNode newDoubleNode = new DoubleNode(data);
if (first==null) {
first = newDoubleNode; //若链表为空,则将first指向新的结点(newNode)
} else {
newDoubleNode.prev = last;//将last的previous指向last(last永远指向的是最后一个结点)【此时还没有插入新的结点newNode,所以last指向的是当前链表的最后一个结点】
last.next = newDoubleNode; //将last.next(当前链表最后一个结点的next域)指向新的结点newNode
}
last = newDoubleNode; //由于插入了一个新的结点,又因为是尾部插入,所以将last指向newNode
}2.2.3?中间插入
//某个结点的后部插入
public void insertAfter(int key, int data) {
DoubleNode newDoubleNode = new DoubleNode(data);
DoubleNode current = first;
while ((current != null) && (current.data != key)) {
current = current.next;
}
//若当前结点current为空
if (current == null) { //current为null有两种情况 一种是链表为空,一种是找不到key值
if (isEmpty()) { //1、链表为空
first = newDoubleNode; //则插入第一个结点(其实可以调用其它的Insert方法)
last = newDoubleNode; //first和last均指向该结点(第一个结点)
} else {
last.next = newDoubleNode; //2、找不到key值
newDoubleNode.prev = last; //则在链表尾部插入一个新的结点
last = newDoubleNode;
}
} else {
if (current == last) { //第三种情况,找到了key值,分两种情况
newDoubleNode.next = null; //1、key值与最后结点的data相等
last = newDoubleNode; //由于newNode将是最后一个结点,则将last指向newNode
} else {
newDoubleNode.next = current.next; //2、两结点中间插入 四
current.next.prev = newDoubleNode; //将current当前结点的下一个结点赋给newNode.next
} //将current下一个结点即current.next的previous域指向current
current.next = newDoubleNode; //将当前结点的next域指向newNode
newDoubleNode.prev = current; //将新结点的previous域指向current(current在newNode前面一个位置)
}
}2.3 删除结点
2.3.1 删除头结点
//从头部删除结点
public DoubleNode deleteFirst() {
DoubleNode temp = first;
if (first.next == null) { //若链表只有一个结点,删除后链表为空,将last指向null
last = null;
} else {
first.next.prev = null; //若链表有两个(包括两个)以上的结点 ,因为是头部插入,则first.next将变成第一个结点,其previous将变成null
}
first = first.next; //将first.next赋给first
return temp; //返回删除的结点
}2.3.2?删除尾结点
//从尾部删除结点
public DoubleNode deleteLast() {
DoubleNode temp = last;
if (first.next == null) { //如果链表只有一个结点,则删除以后为空表,last指向null
first = null;
} else {
last.prev.next = null; //将上一个结点的next域指向null
}
last = last.prev; //上一个结点称为最后一个结点,last指向它
return temp; //返回删除的结点
}2.3.3 删除中间结点
//按值删除
public DoubleNode deleteKey(int key) {
DoubleNode current = first;
while (current != null && current.data != key) { //遍历链表寻找该值所在的结点
current = current.next;
}
if (current == null) { //若当前结点指向null则返回null,
return null; //两种情况当前结点指向null,一是该链表为空链表,而是找不到该值
} else {
if (current == first) { //如果current是第一个结点
first = current.next; //则将first指向它,将该结点的previous指向null,其余不变
current.next.prev = null;
} else if (current == last) { //如果current是最后一个结点
last = current.prev; //将last指向当前结点的上一个结点(我们将当前结点除名了以后它便不再是最后一个了)
current.prev.next = null; //相应的要删除结点的上一个结点的next域应指向null
} else {
current.prev.next = current.next; //当前结点的上一个结点的next域应指向当前的下一个结点
current.next.prev = current.prev; //当前结点的下一个结点的previous域应指向当前结点的上一个结点
}
}
return current; //返回
}本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- ChatGLM基于LangChain应用开发实践(二)
- 独立站新手卖家:Facebook营销工具汇总大全!
- 单电阻FOC算法实现永磁同步电机的调整步骤和设置
- SAP PO平台配置
- KaiOS OTA APN 方案
- 微信小程序vanUI组件模拟器没问题,真机调试样式错乱
- LLM之RAG实战(十四)| 利用LongContextRetriver克服RAG中的中间丢失现象
- String转JSON Object
- 059:vue中使用 AJAX来读取来自XML文件的信息
- Node.js基础知识点(二)