Verilog刷题笔记15
题目:
An adder-subtractor can be built from an adder by optionally negating one of the inputs, which is equivalent to inverting the input then adding 1. The net result is a circuit that can do two operations: (a + b + 0) and (a + ~b + 1). See Wikipedia if you want a more detailed explanation of how this circuit works.
Build the adder-subtractor below.
You are provided with a 16-bit adder module, which you need to instantiate twice:
module add16 ( input[15:0] a, input[15:0] b, input cin, output[15:0] sum, output cout );
Use a 32-bit wide XOR gate to invert the b input whenever sub is 1. (This can also be viewed as b[31:0] XORed with sub replicated 32 times. See replication operator.). Also connect the sub input to the carry-in of the adder.

我的解法:
module top_module(
input [31:0] a,
input [31:0] b,
input sub,
output [31:0] sum
);
wire [15:0] sum1,sum2;
wire [31:0]b1;
wire cout;
assign b1={32{sub}}^b;
add16 add161(.a(a[15:0]),.b(b1[15:0]),.cin(sub),.cout(cout),.sum(sum1));
add16 add162(.a(a[31:16]),.b(b1[31:16]),.cin(cout),.cout(),.sum(sum2));
assign sum = {sum2,sum1};
endmodule
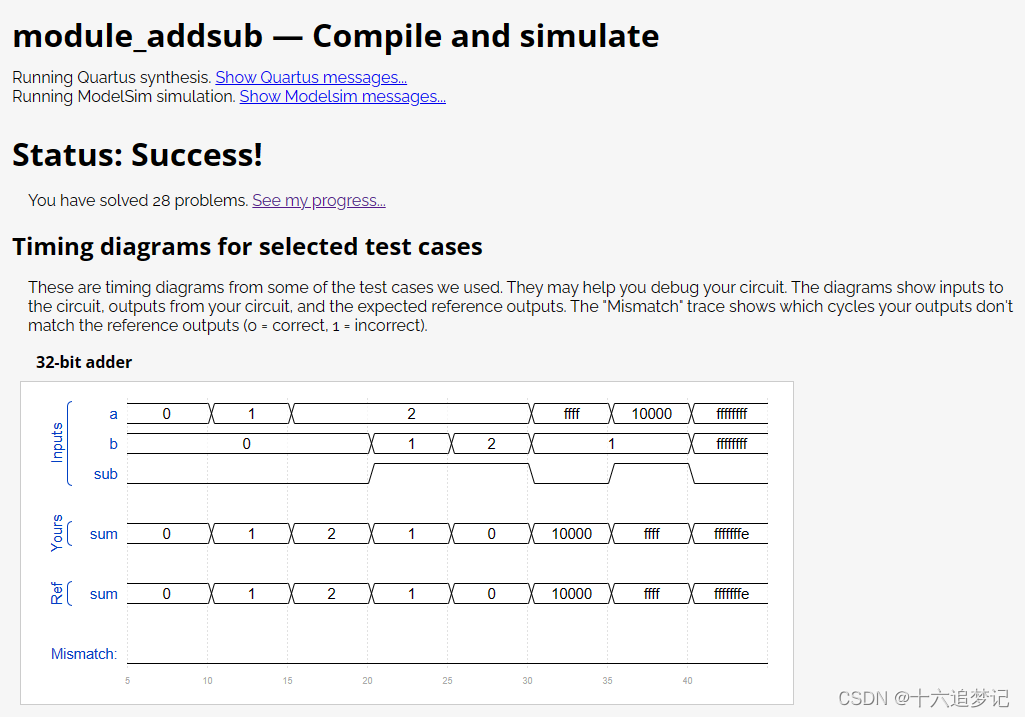
结果正确:
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 阿里云 SAE 2.0 正式商用:极简易用、百毫秒弹性效率,降本 40%
- 代码随想录算法训练营第二十四天| 77.组合
- 04-获取认证的用户身份信息
- springboot/java/php/node/python基于springboot的宿舍管理系统【计算机毕设】
- 谷歌地图搜索功能的bug
- vue3之echarts3D环柱图
- 设计模式篇---职责链模式
- Linux驱动学习—ioctl接口
- IP2326_NPD 支持15W快充的 2节/3节串联锂电池升压充电IC
- 宝塔nginx部署前端页面刷新报404