【LeetCode 热题 HOT 100】题解笔记 —— Day05
? 作者主页:欢迎来到我的技术博客😎
? 个人介绍:大家好,本人热衷于Java后端开发,欢迎来交流学习哦!( ̄▽ ̄)~*
🍊 如果文章对您有帮助,记得关注、点赞、收藏、评论??????
📣 您的支持将是我创作的动力,让我们一起加油进步吧!!!🎉🎉
文章目录
一、二叉树的层序遍历
1. 题目描述
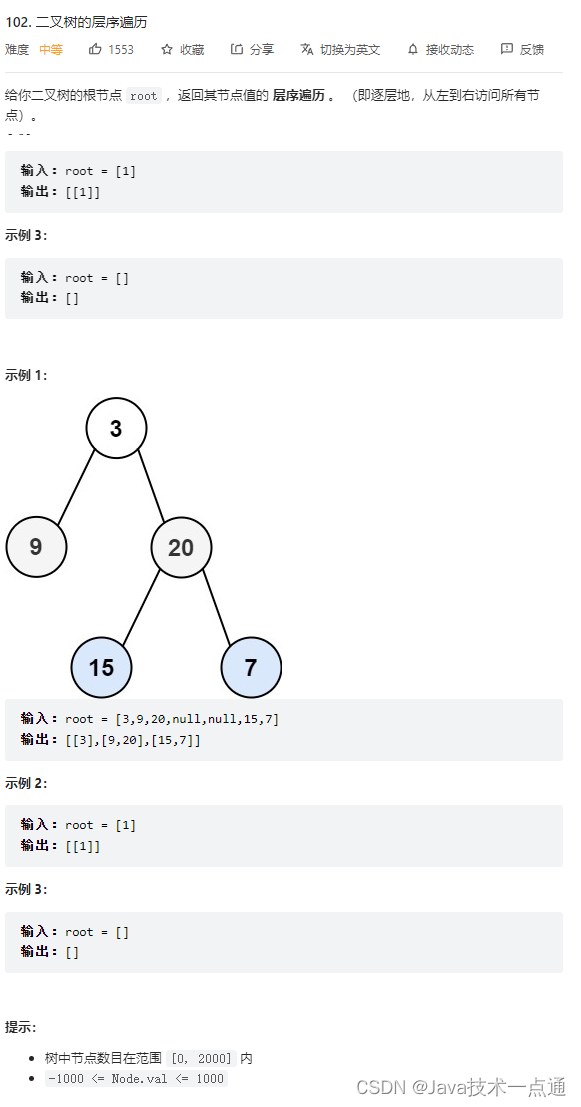
2. 思路分析
(bfs)
宽度优先遍历,一层一层来做。即:
- 将根节点插入队列中;
- 创建一个新队列,用来按顺序保存下一层的所有子节点;
- 对于当前队列中的所有节点,按顺序依此将儿子加入新队列,并将当前节点的值记录在答案中;
- 重复步骤2-3,直到队列为空为止。
3. 代码实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
if (root) q.push(root);
while (q.size()) {
vector<int> level;
int len = q.size();
while (len --) {
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
level.push_back(t->val);
if (t->left) q.push(t->left);
if (t->right) q.push(t->right);
}
res.push_back(level);
}
return res;
}
};
二、二叉树的最大深度
1. 题目描述
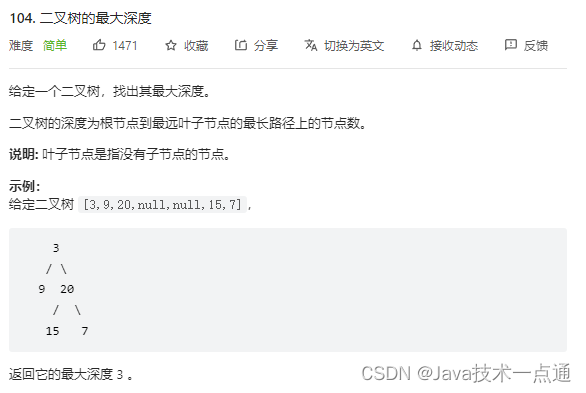
2. 思路分析
递归求解: 当前树的最大深度等于左右子树的最大深度加1。
3. 代码实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return 0;
return max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}
};
三、从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
1. 题目描述
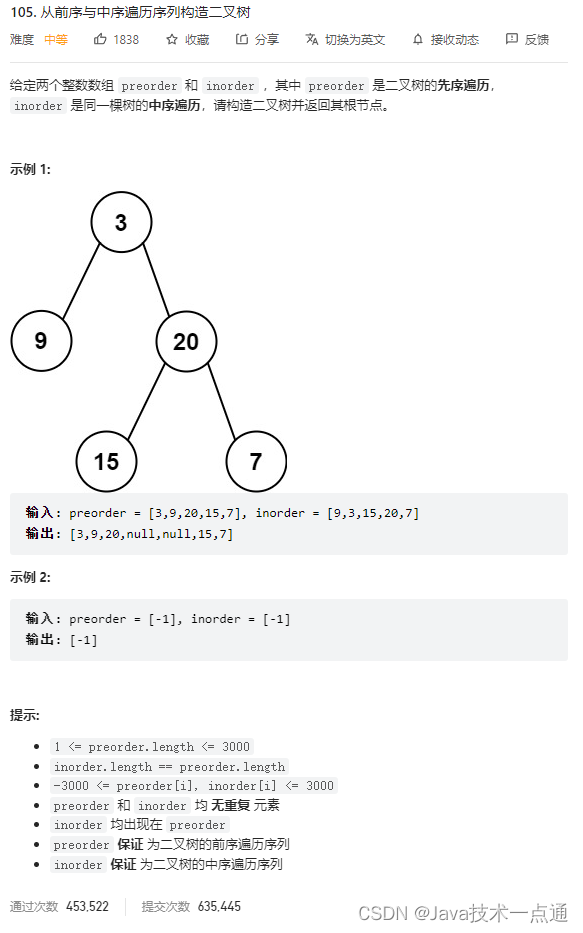
2. 代码实现
class Solution {
private:
unordered_map<int, int> inMap;
public:
TreeNode* myBuildTree(vector<int>& preorder, int preStart, int preEnd, vector<int>& inorder, int inStart, int inEnd)
{
if(preStart > preEnd) return nullptr;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(preorder[preStart]);
int inRoot = inMap[preorder[preStart]];
int numsLeft = inRoot - inStart;
root->left = myBuildTree(preorder, preStart + 1, preStart + numsLeft, inorder, inStart, inRoot - 1);
root->right = myBuildTree(preorder, preStart + numsLeft + 1, preEnd, inorder, inRoot + 1, inEnd);
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
int n = preorder.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
{
inMap[inorder[i]] = i;
}
return myBuildTree(preorder, 0, n - 1, inorder, 0, n - 1);
}
};
四、二叉树展开为链表
1. 题目描述
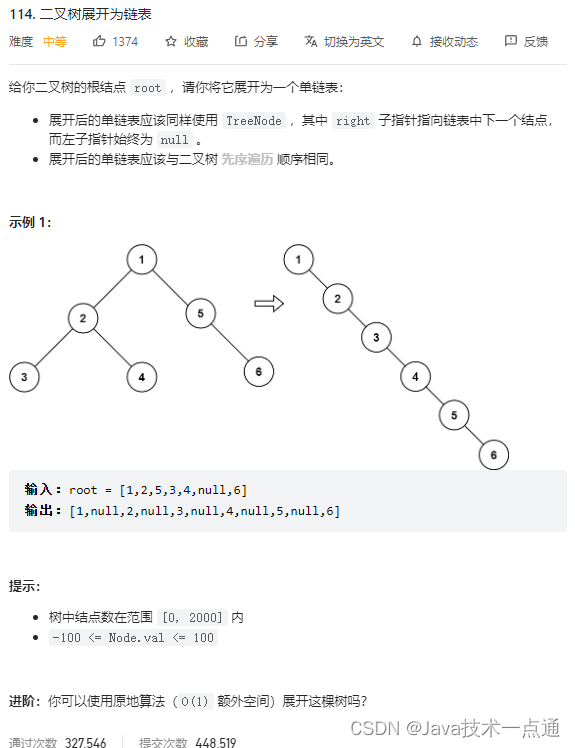
2. 思路分析
算法流程:
- 将左子树插入到右子树的地方;
- 将原来的右子树接到左子树的最右节点;
- 考虑新的右子树的根节点,一直重复上面的过程,知道新的右子树为空。
可以看一下图解理解上述的过程:
1
/ \
2 5
/ \ \
3 4 6
//将 1 的左子树插入到右子树的地方
1
\
2 5
/ \ \
3 4 6
//将原来的右子树接到左子树的最右边节点
1
\
2
/ \
3 4
\
5
\
6
//将 2 的左子树插入到右子树的地方
1
\
2
\
3 4
\
5
\
6
//将原来的右子树接到左子树的最右边节点
1
\
2
\
3
\
4
\
5
\
6
3. 代码实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void flatten(TreeNode* root) {
while (root) {
auto p = root->left;
if (p) {
while (p->right) p = p->right;
p->right = root->right;
root->right = root->left;
root->left = nullptr;
}
root = root->right;
}
}
};
五、买卖股票的最佳时机
1. 题目描述

2. 思路分析
我们只需要遍历价格数组一遍,记录历史最低点,然后在每一天考虑一个问题:如果我们是在历史最低点买进的,那么我今天卖出能赚多少钱?当考虑完所有的天数之时,我们就得到了最佳的答案。
3. 代码实现
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0, minp = INT_MAX; i < prices.size(); i ++) {
res = max(res, prices[i] - minp);
minp = min(minp, prices[i]);
}
return res;
}
};
六、二叉树中的最大路径和
1. 题目描述
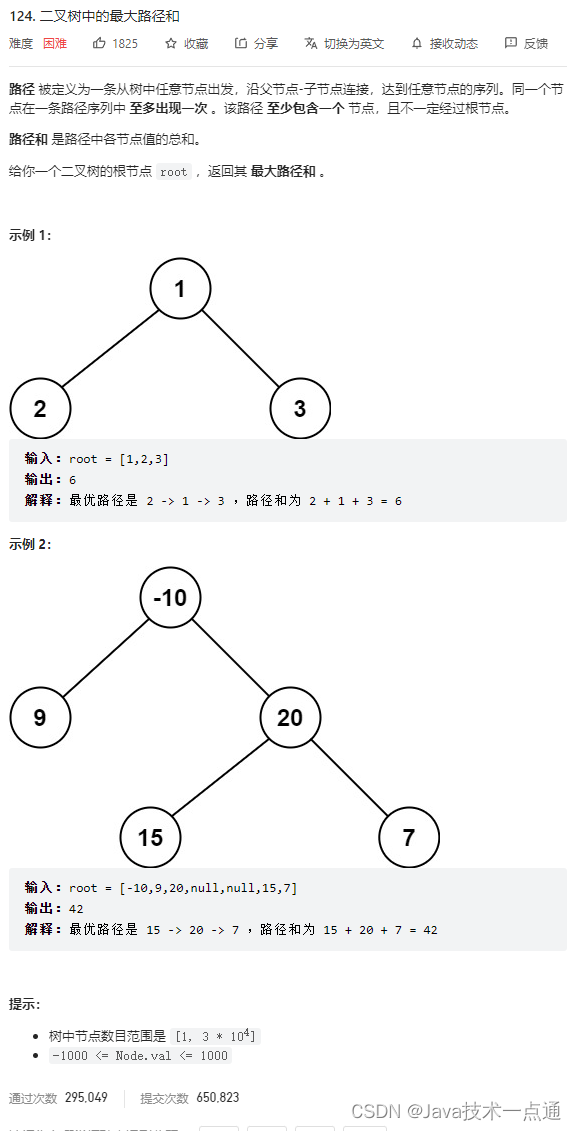
2. 代码实现
class Solution {
public:
//动态规划、递归
/*思路:
*对于每一个根节点,选择一个能够使路径和最大的左右子树根作为连接结点,对于每个子树都是如此;
*每个结点只能链接一次在路径中
*递归思想和分治思想类似,以此向下递归遍历左右子树
*/
int maxPathSum(TreeNode* root) {
int maxSum=INT_MIN;
getMax(root,maxSum);
return maxSum;
}
int getMax(TreeNode* root,int &maxSum){
//深度遍历到叶结点停止
if(root==nullptr){
return 0;
}
//记录根节点左右子树的最大路径和,如果左子树或右子树的路径小于0,则就是0;
int leftMax=max(getMax(root->left,maxSum),0);
int rightMax=max(getMax(root->right,maxSum),0);
//每个子树的根节点都会遍历;根结点值加上左右子树的最大路径就是这个根节点的最大路经,用maxsum来存储
int temp=root->val+leftMax+rightMax;
//一个根节点加上左右子树的中的最大路径。
maxSum=max(maxSum,temp);
//max()代表一个根节点只能选择左右子树的其一作为路径的一部分才能满足作为路径一部分的条件。
return root->val+max(leftMax,rightMax);
}
};
七、最长连续序列
1. 题目描述

2. 思路分析
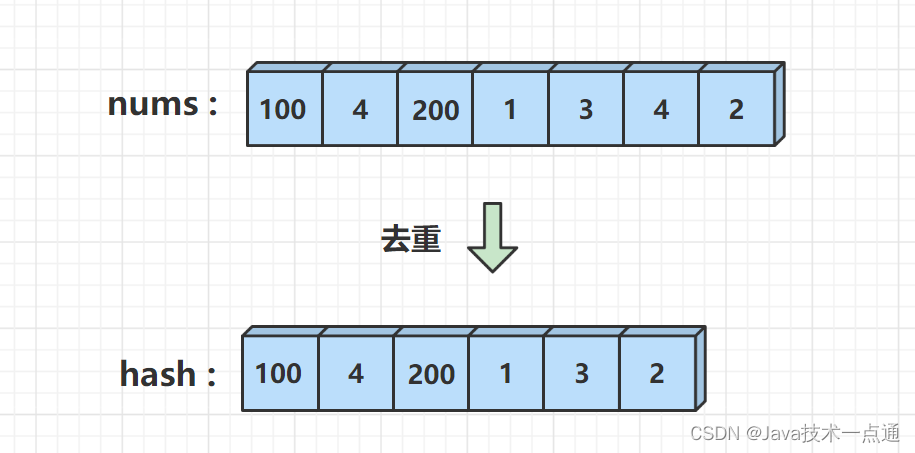
数组去重
一个数字连续序列是不包含重复的数字的,所以直接枚举去重过后的
h
a
s
h
hash
hash 数组是不会影响最后的结果的,但去重过的数组长度会更短,因此运行效率也会变得更高。
为了保证
O
(
n
)
O(n)
O(n) 的时间复杂度,避免重复枚举一段序列,我们要从序列的起始数字向后枚举。也就是说如果有一个
x
x
x,
x
+
1
x+1
x+1,
x
+
2
x+2
x+2,…,
x
+
y
x+y
x+y 的连续序列,我们只会以
x
x
x 为起点向后枚举,而不会从
x
+
1
x+1
x+1,
x
+
2
x+2
x+2 ,…,向后枚举。
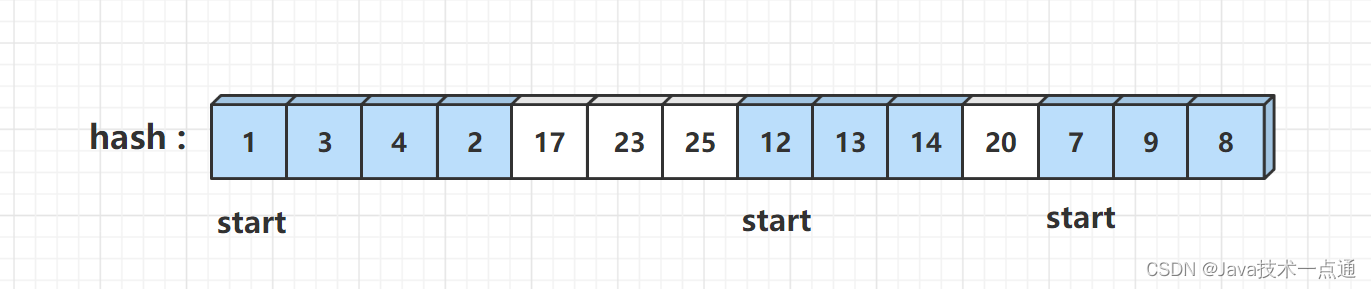
如何每次只枚举连续序列的起始数字
x
x
x?
其实只需要每次在哈希表中检查是否存在
x
?
1
x - 1
x?1 即可。如果
x
?
1
x - 1
x?1 存在,说明当前数
x
x
x 不是连续序列的起始数字,我们跳过这个数。
具体的流程如下:
- 定义一个哈希表 h a s h hash hash,将 n u m s nums nums 数组中的数都放入到哈希表中;
- 遍历哈希表 h a s h hash hash,如果当前数 x x x 的前驱 x ? 1 x - 1 x?1 不存在,我们就以当前数 x x x 为起点向后枚举;
- 假设最长枚举到数 y y y,那么连续序列长度即为 y ? x + 1 y - x + 1 y?x+1;
- 不断枚举更显答案。
3. 代码实现
class Solution {
public:
int longestConsecutive(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_set<int> hash;
for (auto x : nums) hash.insert(x);
int res = 0;
for (auto x : hash) {
if (!hash.count(x - 1)) {
int y = x;
while (hash.count(y + 1)) y ++;
res = max(res, y - x + 1);
}
}
return res;
}
};
八、只出现一次的数字
1. 题目描述

2. 思路分析
(位运算)
- 两个相同的数字经过异或之后会变为0;
- 将数组所有元素异或在一起即可得到出现1次的元素值。
3. 代码实现
class Solution {
public:
int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int res = 0;
for (auto x : nums) res ^= x;
return res;
}
};
九、单词拆分
1. 题目描述

2. 代码实现
class Solution {
public:
bool wordBreak(string s, vector<string>& wordDict) {
int n = s.size();
vector<bool> dp(n+1,false);
dp[0] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(!dp[i])
continue;
for(auto& word : wordDict) {
if((i + word.size()) <= n && s.substr(i,word.size()) == word)
dp[i+word.size()] = true;
}
}
return dp[n];
}
};
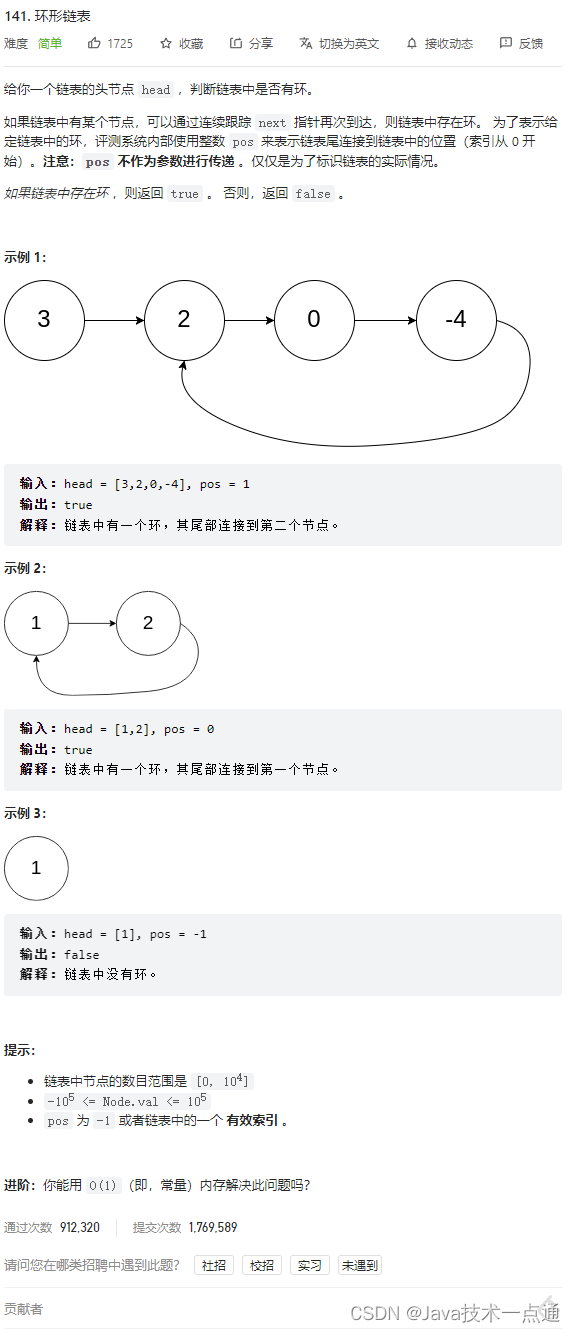
十、环形链表
1. 题目描述
2. 思路分析
- 设置快慢指针,快指针每次走两步,慢指针每次走一步;
- 若两指针相遇,则表示有环存在。
3. 代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
if(head == NULL){
return 0;
}
struct ListNode *first = head,*second = head->next;
while(first != second && second && second->next){
first = first->next;
second = second->next->next;
}
if(second == NULL || second->next == NULL) return 0;
return 1;
}
?
非常感谢您阅读到这里,如果这篇文章对您有帮助,希望能留下您的点赞👍 关注💖 分享👥 留言💬thanks!!!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- UDP Ping程序实现--第5关:客户端向服务器发送消息并接收消息
- 6.C++对象模型
- 实现分布式锁:Zookeeper vs Redis
- Qt/QML编程学习之心得:hicar手机投屏到车机中控的实现(32)
- 鸿蒙和各大厂合作,是不是要火起来
- 基于SSM的学生请假系统设计与实现
- Java语言概述
- MyBatisPlus学习二:常用注解、条件构造器、自定义sql
- Jtti:常见的数据库服务器的启动方法
- 计算机硬件(网络基础)