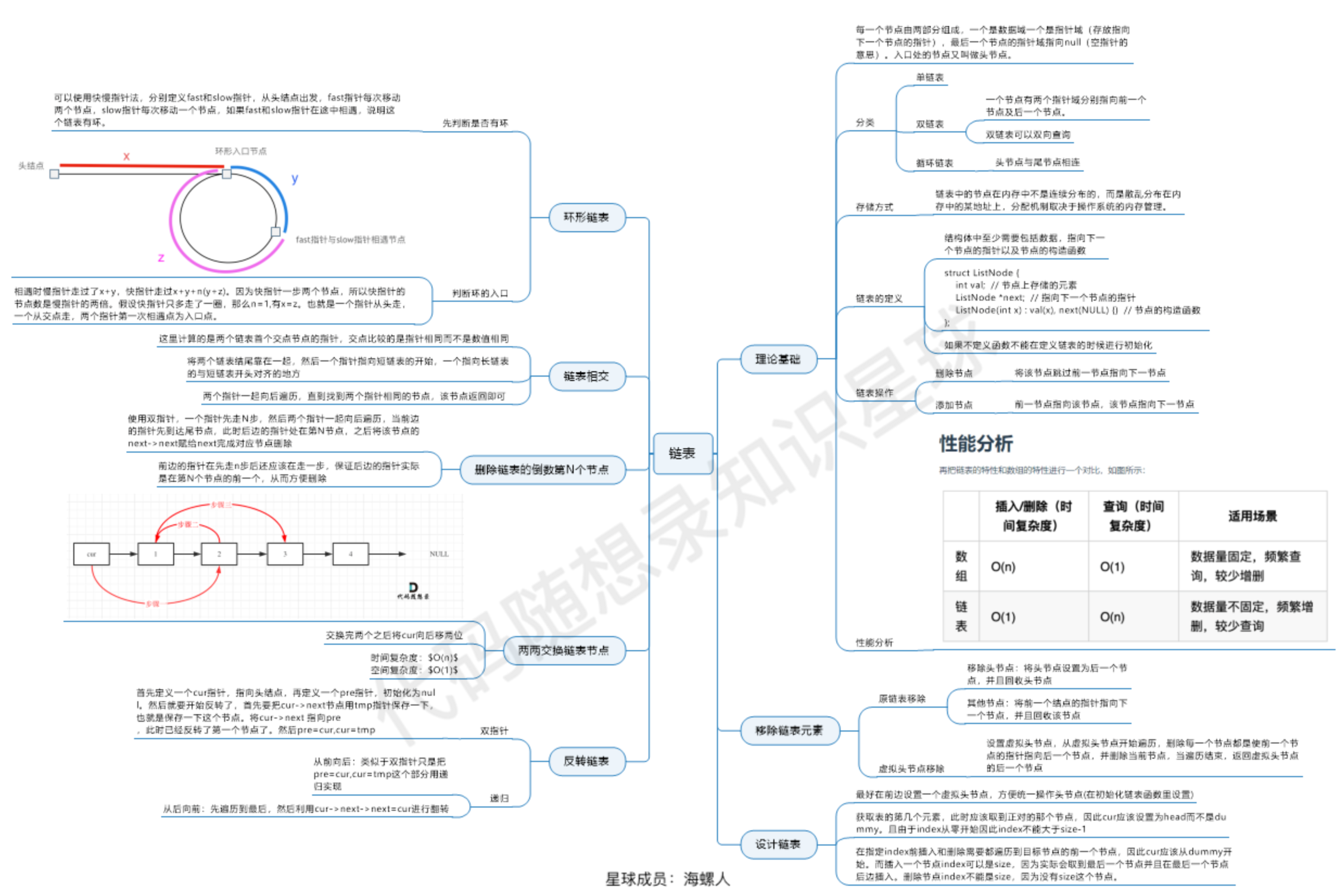
【leetcode】链表总结
发布时间:2023年12月19日
说明:本文内容来自于代码随想录
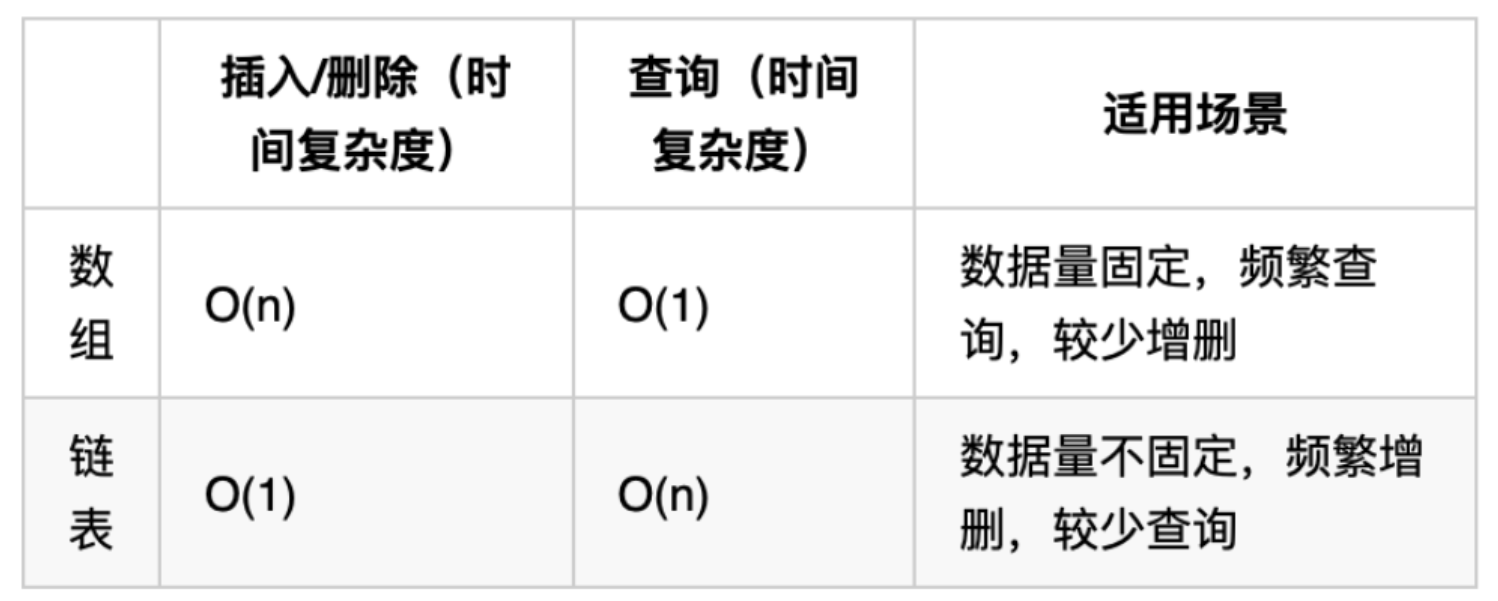
链表基本操作
https://leetcode.cn/problems/design-linked-list/
删除节点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/description/,删除节点,虚拟头节点。定义两个节点,分别为前继节点 pre 和当前节点 cur。当前节点初始化为头节点。每次判断当前节点是否需要删除。若要删除,则将前继节点的下一个指向当前节点的下一个;否则,更新前继节点为当前节点。最后当前节点移动到下一个节点。
要点:
- 头节点的删除和其他节点的删除是不一样的。因为删除是将被删除节点的前继节点指向被删除节点的后继,但是头节点没有前继。所以需要定义一个虚拟头节点,其后继指向 head
- 删除后,新的头节点为虚拟头节点的后继
代码如下:
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
// 前继节点的下一个指向当前节点
// 若当前节点需要删除,则将前继节点的下一个指向当前节点的下一个
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, head); // 虚拟节点,指向头节点
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == val) { // 当前节点需要删除
pre.next = cur.next;
} else { // 当前节点不需要删除,则更新前继节点为当前节点
pre = cur;
}
cur = cur.next; // 当前节点往前移动一位
}
// 最开始,pre.next和dummy指向的实际上是同一个地址。当pre.next发生变化时,dummy.next也发生变化
// 但是pre和dummy不是同一个地址。所以当修改pre = cur时,dummy是不变的。
// 所以最开始如果pre.next发生了更新的话,那么dummy.next也会同步更新,即更新的是头节点。
// 一旦pre发生了更新,则下一次的pre.next更新就不会影响头节点了,影响的是头节点后面的节点。
return dummy.next;
}
在头部插入节点
public ListNode insertHead(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(val);
newNode.next = head; // 新节点的后继指向旧头节点
head = newNode; // 更新头节点为新节点
return head;
}
反转链表
思路:
- 用两个指针分别指向前一个 pre 和当前节点 cur,当前节点初始化为头节点 pre=head
- 每次操作,头节点指向前一个,cur.next = pre,然后 pre 和 cur 分别前进一个单位
- 由于改变了 cur 的下一个之后,前进的时候就无法找到原来的下一个了,所以需要在操作之前暂存下一个 next = cur.next
动画:
https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/gifs/206.%E7%BF%BB%E8%BD%AC%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8.gif
迭代版
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
// 保存cur的下一个节点
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
递归版
public ListNode reverse(ListNode pre, ListNode cur) {
if (cur == null) return pre;
// 反转
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
return reverse(cur, next);
}
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
return reverse(pre, cur);
}
交换成对节点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/description/

交换涉及到 3 步,所以需要 3 个指针 pre, cur, next,分别表示上一个的前继、上一个、下一个(注意图中的 cur 指的是这里的 pre,图里的 1 是这里的 cur,图里的 2 是这里的 next):
- 上一个的后继指向下一个的后继,cur.next = next.next
- 下一个的后继指向上一个,next.next = cur
- 上一个的前继的后继指向下一个,pre.next = next
// 交换
cur.next = next.next;
next.next = cur;
pre.next = next;
注意需要更新头节点,即:当第一次交换完之后,更新头节点为 next
删除链表倒数第 n 个节点
链表相交
环形链表
总结
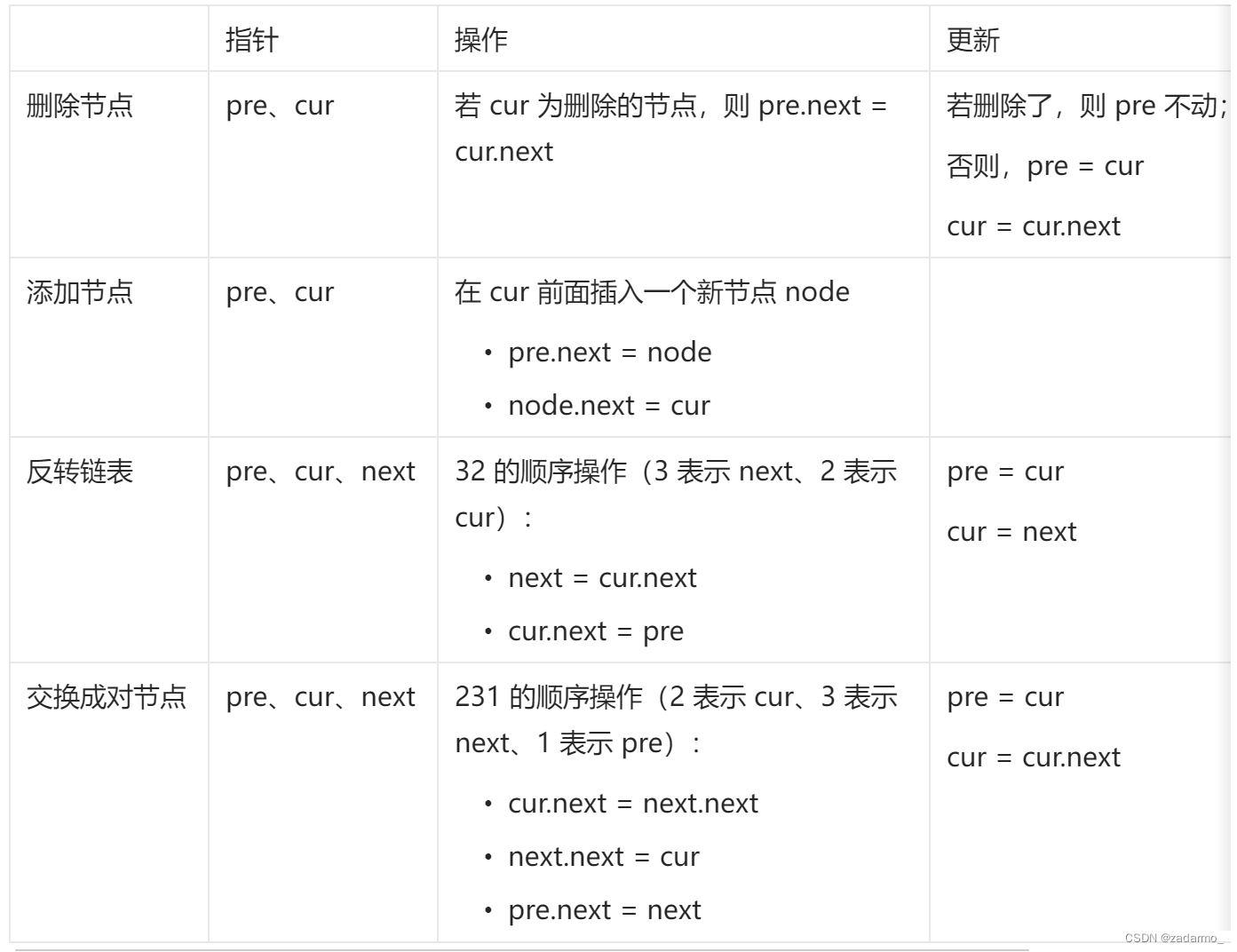
哑节点(dummy node)在链表中很常用,比如:
- 删除节点,涉及到 2 个节点,当前节点 cur 和当前节点的前继 pre。如果删除的是头节点,就没有前继,所以需要哑节点
- 交换节点,涉及到 3 个节点,当前节点 cur、当前节点的前继 pre、当前节点的后继 next。类似的,头节点没有前继,所以需要哑节点
说明:由于这些操作有可能会修改头节点,所以在操作的时候,除了哑节点 dummy,还要定义 pre 节点:
- 初始化,pre = dummy
- 后续的操作中,只移动 pre,dummy 保持不变
- 由于第一次 pre 和 dummy 的后继指向的是同一个,所以 pre 的后继更新了,dummy 的后继也会更新,即达到了更新头节点的目的。后续移动 pre 之后,pre 的后继和 dummy 的后继就不是同一个了, dummy 的后继就不会在更新了
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/destiny_balabala/article/details/135030166
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- GBASE南大通用数据库GBase 8s常见问题讲堂 --查看表中数据量与表占用空间
- spring见解2基于注解的IOC配置
- 抖店常见基础问题,实操经验,新手必看!
- 6.3 多线程的安全与应用
- [Application] The app delegate must implement the window property if ..... 错误
- 德特森:电动蝶阀打不开的原因有哪些?
- 洛谷 P8823
- CentOS7自动备份数据库到git
- 传奇服务器搭建
- vue3中组合式api的常用方法