常用植被物候提取方法
(一)Background
这篇文章介绍的非常全面!!

-
物候的提取通常包含两个步骤:(1)曲线的重构拟合(curve fitting)和 (2)物候矩阵的提取 (phenological metrics extraction)
-
(1)曲线拟合的方法通常有3种方法:(S-G) 滤波法(Savitzky-Golay), 双逻辑斯蒂函数拟合法(Double Logistic)和非对称性高斯函数拟合法(Asumm.Guassian)
-
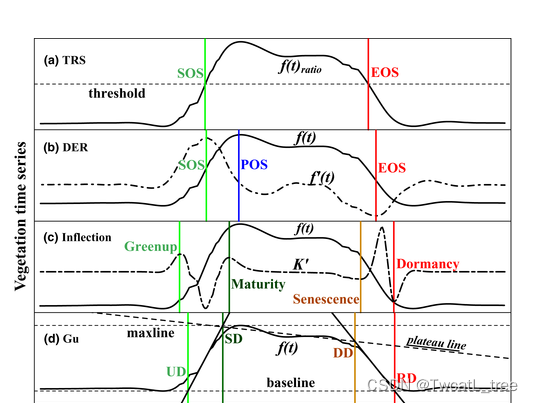
(2)物候矩阵的提取通常有4种方法(如下图)。其中, TRS(动态阈值法,即Seasonal amplitude 季节振幅法)和 Inflection method (无需用户自定义阈值)这两种方法用的比较多

(二)Method
1. 基于TIMESAT的物候提取
[0] 安装包下载:link
[1] TIMESAT安装教程: link
[2] 基于TIMESAT提取物候操作流程: link (ps:文字版的这个教程最详细)
[3] B站视频教学: link (ps: 视频版最详细)
[4] 知乎: link
2. 基于Code的物候提取
[1] Python
- “Phenolopy” package : link (这个原理和TIMESAT一样)
[2] R
- “phenofit” package: link (这个包含的方法最全)
[3] Matlab
- “lsqcurvefit” function (Inflection法,third-order derivative三阶求导)
3. 方法优缺点
-
TIMESAT操作比较简单,默认使用的是第一个Seasonal amplitude 季节振幅法,也就是动态阈值法,需要结合自己的研究区实际,拟定一个合适的动态阈值,可以参考前人研究确定,TIMESAT软件的作者建议可以用0.2(20%振幅)试试
-
phenofit方法比较全
(三)Reference
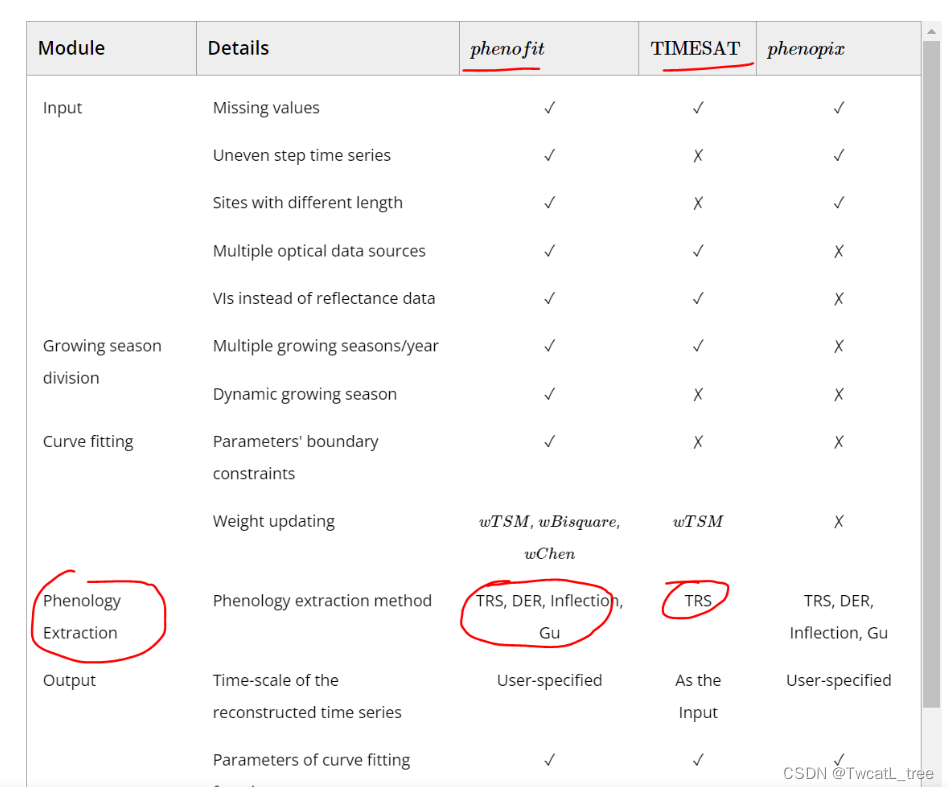
[1] Kong D, McVicar T R, Xiao M, et al. phenofit: An R package for extracting vegetation phenology from time series remote sensing[J]. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 2022, 13(7): 1508-1527.(介绍了不同工具的优缺点)
[2] 刘建文, 周玉科. 站点尺度的青藏高原时序 NDVI 重构方法比较与应用[J]. 地理科学进展, 2018, 37(3): 427-437.(介绍了常用的重构曲线curve fitting的方法)
[3] Wang J, Liu D, Ciais P, et al. Decreasing rainfall frequency contributes to earlier leaf onset in northern ecosystems[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2022, 12(4): 386-392.(基于double-logistic function and dynamic-threshold approach的案例)
[4] Sisheber B, Marshall M, Mengistu D, et al. Tracking crop phenology in a highly dynamic landscape with knowledge-based Landsat–MODIS data fusion[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2022, 106: 102670.(基于S-G and dynamic-threshold approach的案例)
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Pytest框架 之【用例执行顺序】
- 大创项目推荐 深度学习大数据物流平台 python
- 微信扫一扫,ios系统扫码失效解决
- FPGA设计时序约束十四、Set_External_Delay
- Python笔记10-数据可视化练习折线图
- Java实现一个简单的贪吃蛇小游戏
- C# Word Excel Could not load file or assembly ‘office, Version=15
- JRT实现原生Webservice发布
- 12.29_黑马数据结构与算法笔记Java
- [AutoSar]BSW_OS 01 priority ceiling protocol(PCP)