【RT-DETR有效改进】移动设备网络ShuffleNetV1(超轻量化网络主干)
前言
大家好,这里是RT-DETR有效涨点专栏。
本专栏的内容为根据ultralytics版本的RT-DETR进行改进,内容持续更新,每周更新文章数量3-10篇。
专栏以ResNet18、ResNet50为基础修改版本,同时修改内容也支持ResNet32、ResNet101和PPHGNet版本,其中ResNet为RT-DETR官方版本1:1移植过来的,参数量基本保持一致(误差很小很小),不同于ultralytics仓库版本的ResNet官方版本,同时ultralytics仓库的一些参数是和RT-DETR相冲的所以我也是会教大家调好一些参数和代码,真正意义上的跑ultralytics的和RT-DETR官方版本的无区别。
👑欢迎大家订阅本专栏,一起学习RT-DETR👑??
一、本文内容
本文给大家带来的改进内容是ShuffleNetV1,这是一种为移动设备设计的高效CNN架构。它通过使用点群卷积和通道混洗等操作,减少了计算成本,同时保持了准确性,通过这些技术,ShuffleNet在降低计算复杂度的同时,也优化了内存使用,使其更适合低功耗的移动设备,其非常适合轻量化的读者来使用)。本文通过介绍其主要框架原理,然后教你如何添加该网络结构到网络模型中,。接下来,我会展示一下原始版本和我改进后版本在训练上的对比图。之后会在文章中介绍该网络结构,然后教大家如何修改该网络结构,通过修改该主干参数量下降约百分之四十!

目录
二、ShuffleNetV1框架原理
官方论文地址:?官方论文地址
官方代码地址:?官方代码地址

ShuffleNet的创新机制为点群卷积和通道混:使用了新的操作点群卷积(pointwise group convolution)和通道混洗(channel shuffle),以减少计算成本,同时保持网络精度
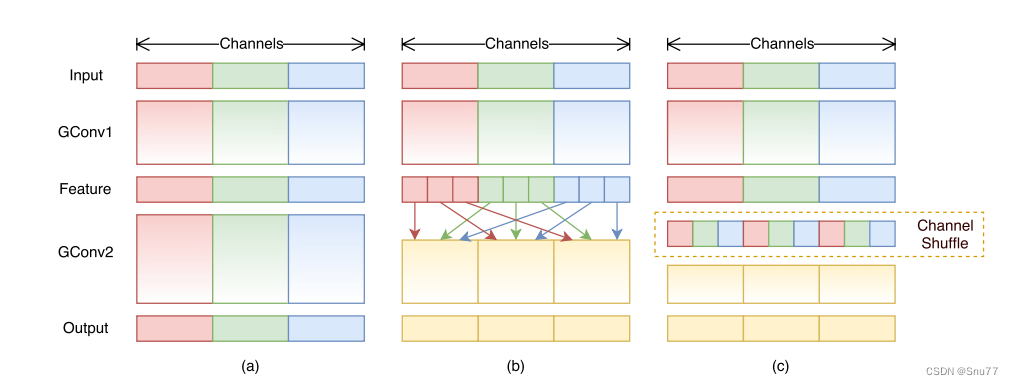
您上传的图片展示的是ShuffleNet架构中的通道混洗机制。这一机制通过两个堆叠的分组卷积(GConv)来实现:
图示(a):展示了两个具有相同分组数量的堆叠卷积层。每个输出通道仅与同一组内的输入通道相关联。
图示(b):在不使用通道混洗的情况下,展示了在GConv1之后,GConv2从不同分组获取数据时输入和输出通道是如何完全相关联的。
图示(c:提供了与(b)相同的实现,但使用了通道混洗来允许跨组通信,从而使网络内更有效和强大的特征学习成为可能。

上面的图片描述了ShuffleNet架构中的ShuffleNet单元。这些单元是网络中的基本构建块,具体包括:
图示(a):一个基本的瓶颈单元,使用了深度可分离卷积(DWConv)和一个简单的加法(Add)来融合特征。
图示(b):在标准瓶颈单元的基础上,引入了点群卷积(GConv)和通道混洗操作,以增强特征的表达能力。
图示(c):适用于空间下采样的ShuffleNet单元,使用步长为2的平均池化(AVG Pool)和深度可分离卷积,再通过通道混洗和点群卷积进一步处理特征,最后通过连接操作(Concat)合并特征。
三、ShuffleNetV1核心代码
下面的代码是整个ShuffleNetV1的核心代码,其中有个版本,对应的GFLOPs也不相同,使用方式看章节四。
# Copyright 2022 Dakewe Biotech Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# ==============================================================================
from typing import Any, List, Optional
import torch
from torch import Tensor
from torch import nn
__all__ = [
"ShuffleNetV1",
"shufflenet_v1_x0_5", "shufflenet_v1_x1_0", "shufflenet_v1_x1_5", "shufflenet_v1_x2_0",
]
class ShuffleNetV1(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
repeats_times: List[int],
stages_out_channels: List[int],
groups: int = 8,
num_classes: int = 1000,
) -> None:
super(ShuffleNetV1, self).__init__()
in_channels = stages_out_channels[0]
self.first_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, in_channels, (3, 3), (2, 2), (1, 1), bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels),
nn.ReLU(True),
)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d((3, 3), (2, 2), (1, 1))
features = []
for state_repeats_times_index in range(len(repeats_times)):
out_channels = stages_out_channels[state_repeats_times_index + 1]
for i in range(repeats_times[state_repeats_times_index]):
stride = 2 if i == 0 else 1
first_group = state_repeats_times_index == 0 and i == 0
features.append(
ShuffleNetV1Unit(
in_channels,
out_channels,
stride,
groups,
first_group,
)
)
in_channels = out_channels
self.features = nn.Sequential(*features)
self.globalpool = nn.AvgPool2d((7, 7))
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(stages_out_channels[-1], num_classes, bias=False),
)
# Initialize neural network weights
self._initialize_weights()
self.index = stages_out_channels[-3:]
self.width_list = [i.size(1) for i in self.forward(torch.randn(1, 3, 640, 640))]
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> list[Optional[Any]]:
x = self.first_conv(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
results = [None, None, None, None]
for index, model in enumerate(self.features):
x = model(x)
# results.append(x)
if index == 0:
results[index] = x
if x.size(1) in self.index:
position = self.index.index(x.size(1)) # Find the position in the index list
results[position + 1] = x
return results
def _initialize_weights(self) -> None:
for name, module in self.named_modules():
if isinstance(module, nn.Conv2d):
if 'first' in name:
nn.init.normal_(module.weight, 0, 0.01)
else:
nn.init.normal_(module.weight, 0, 1.0 / module.weight.shape[1])
if module.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(module.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(module, nn.BatchNorm2d):
nn.init.constant_(module.weight, 1)
if module.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(module.bias, 0.0001)
nn.init.constant_(module.running_mean, 0)
elif isinstance(module, nn.BatchNorm1d):
nn.init.constant_(module.weight, 1)
if module.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(module.bias, 0.0001)
nn.init.constant_(module.running_mean, 0)
elif isinstance(module, nn.Linear):
nn.init.normal_(module.weight, 0, 0.01)
if module.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(module.bias, 0)
class ShuffleNetV1Unit(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
in_channels: int,
out_channels: int,
stride: int,
groups: int,
first_groups: bool = False,
) -> None:
super(ShuffleNetV1Unit, self).__init__()
self.stride = stride
self.groups = groups
self.first_groups = first_groups
hidden_channels = out_channels // 4
if stride == 2:
out_channels -= in_channels
self.branch_proj = nn.AvgPool2d((3, 3), (2, 2), (1, 1))
self.branch_main_1 = nn.Sequential(
# pw
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, hidden_channels, (1, 1), (1, 1), (0, 0), groups=1 if first_groups else groups,
bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden_channels),
nn.ReLU(True),
# dw
nn.Conv2d(hidden_channels, hidden_channels, (3, 3), (stride, stride), (1, 1), groups=hidden_channels,
bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden_channels),
)
self.branch_main_2 = nn.Sequential(
# pw-linear
nn.Conv2d(hidden_channels, out_channels, (1, 1), (1, 1), (0, 0), groups=groups, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(True)
def channel_shuffle(self, x):
batch_size, channels, height, width = x.data.size()
assert channels % self.groups == 0
group_channels = channels // self.groups
out = x.reshape(batch_size, group_channels, self.groups, height, width)
out = out.permute(0, 2, 1, 3, 4)
out = out.reshape(batch_size, channels, height, width)
return out
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
identify = x
out = self.branch_main_1(x)
out = self.channel_shuffle(out)
out = self.branch_main_2(out)
if self.stride == 2:
branch_proj = self.branch_proj(x)
out = self.relu(out)
out = torch.cat([branch_proj, out], 1)
return out
else:
out = torch.add(out, identify)
out = self.relu(out)
return out
def shufflenet_v1_x0_5(**kwargs: Any) -> ShuffleNetV1:
model = ShuffleNetV1([4, 8, 4], [16, 192, 384, 768], 8, **kwargs)
return model
def shufflenet_v1_x1_0(**kwargs: Any) -> ShuffleNetV1:
model = ShuffleNetV1([4, 8, 4], [24, 384, 768, 1536], 8, **kwargs)
return model
def shufflenet_v1_x1_5(**kwargs: Any) -> ShuffleNetV1:
model = ShuffleNetV1([4, 8, 4], [24, 576, 1152, 2304], 8, **kwargs)
return model
def shufflenet_v1_x2_0(**kwargs: Any) -> ShuffleNetV1:
model = ShuffleNetV1([4, 8, 4], [48, 768, 1536, 3072], 8, **kwargs)
return model
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Generating Sample image
image_size = (1, 3, 640, 640)
image = torch.rand(*image_size)
# Model
model = shufflenet_v1_x0_5()
out = model(image)
print(out)四、手把手教你添加ShuffleNetV1网络结构
下面教大家如何修改该网络结构,主干网络结构的修改步骤比较复杂,我也会将task.py文件上传到CSDN的文件中,大家如果自己修改不正确,可以尝试用我的task.py文件替换你的,然后只需要修改其中的第1、2、3、5步即可。
?修改过程中大家一定要仔细?
4.1 修改一
首先我门中到如下“ultralytics/nn”的目录,我们在这个目录下在创建一个新的目录,名字为'Addmodules'(此文件之后就用于存放我们的所有改进机制),之后我们在创建的目录内创建一个新的py文件复制粘贴进去 ,可以根据文章改进机制来起,这里大家根据自己的习惯命名即可。
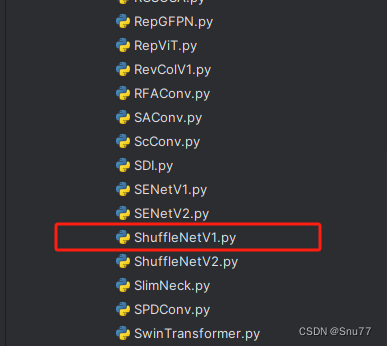
4.2 修改二?
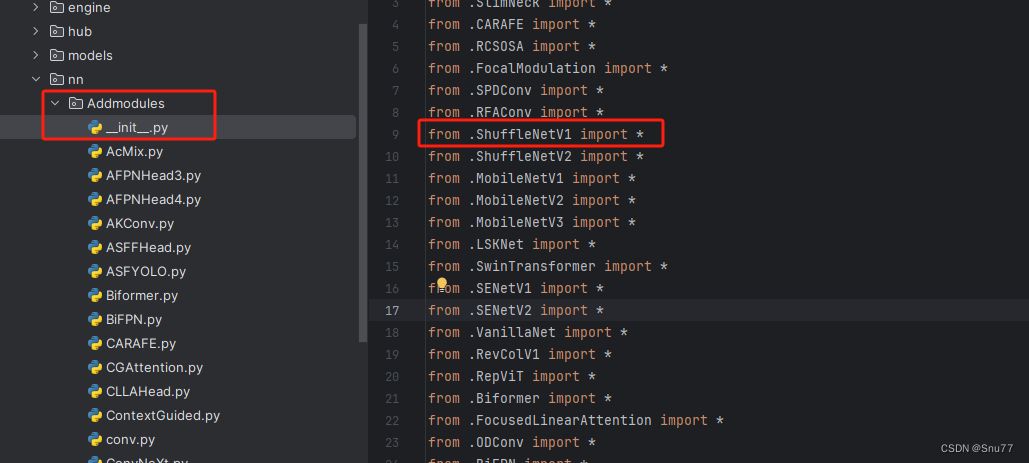
第二步我们在我们创建的目录内创建一个新的py文件名字为'__init__.py'(只需要创建一个即可),然后在其内部导入我们本文的改进机制即可,其余代码均为未发大家没有不用理会!。
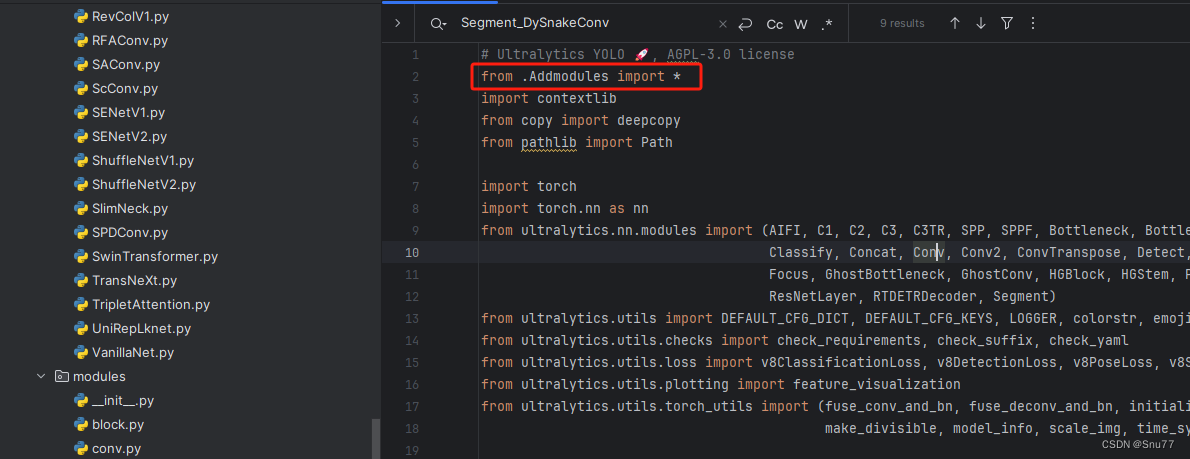
4.3 修改三?
第三步我门中到如下文件'ultralytics/nn/tasks.py'然后在开头导入我们的所有改进机制(如果你用了我多个改进机制,这一步只需要修改一次即可)。
4.4 修改四
添加如下两行代码!!!
 ?
?
4.5 修改五
找到七百多行大概把具体看图片,按照图片来修改就行,添加红框内的部分,注意没有()只是函数名。

elif m in {自行添加对应的模型即可,下面都是一样的}:
m = m(*args)
c2 = m.width_list # 返回通道列表
backbone = True4.6 修改六
用下面的代码替换红框内的内容。?
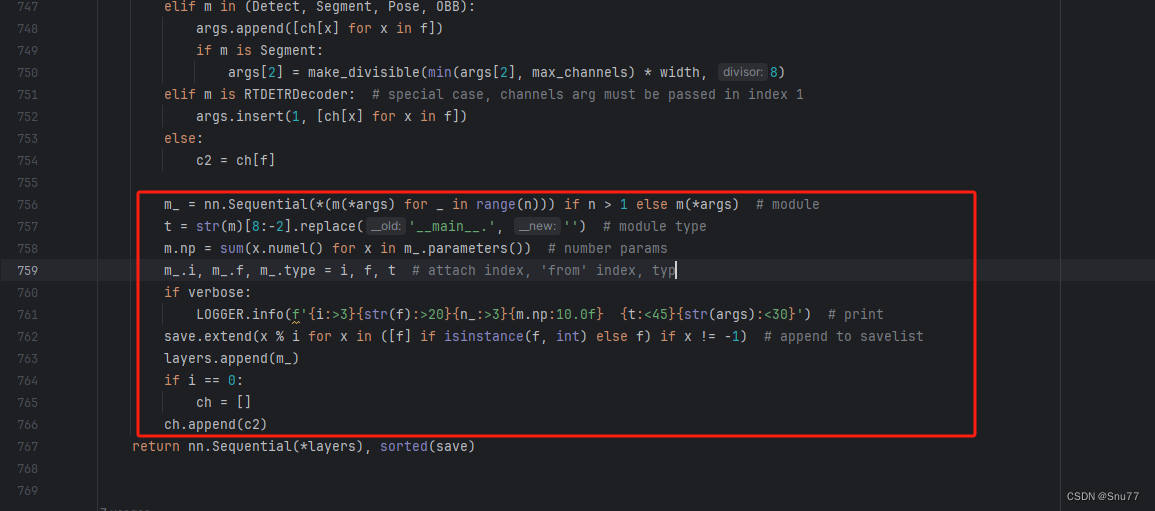 ?
?
if isinstance(c2, list):
m_ = m
m_.backbone = True
else:
m_ = nn.Sequential(*(m(*args) for _ in range(n))) if n > 1 else m(*args) # module
t = str(m)[8:-2].replace('__main__.', '') # module type
m.np = sum(x.numel() for x in m_.parameters()) # number params
m_.i, m_.f, m_.type = i + 4 if backbone else i, f, t # attach index, 'from' index, type
if verbose:
LOGGER.info(f'{i:>3}{str(f):>20}{n_:>3}{m.np:10.0f} {t:<45}{str(args):<30}') # print
save.extend(
x % (i + 4 if backbone else i) for x in ([f] if isinstance(f, int) else f) if x != -1) # append to savelist
layers.append(m_)
if i == 0:
ch = []
if isinstance(c2, list):
ch.extend(c2)
if len(c2) != 5:
ch.insert(0, 0)
else:
ch.append(c2)4.7 修改七?
修改七这里非常要注意,不是文件开头YOLOv8的那predict是400+行的RTDETR的predict!!!初始模型如下,用我给的代码替换即可!!!
 ?
?
代码如下->
def predict(self, x, profile=False, visualize=False, batch=None, augment=False, embed=None):
"""
Perform a forward pass through the model.
Args:
x (torch.Tensor): The input tensor.
profile (bool, optional): If True, profile the computation time for each layer. Defaults to False.
visualize (bool, optional): If True, save feature maps for visualization. Defaults to False.
batch (dict, optional): Ground truth data for evaluation. Defaults to None.
augment (bool, optional): If True, perform data augmentation during inference. Defaults to False.
embed (list, optional): A list of feature vectors/embeddings to return.
Returns:
(torch.Tensor): Model's output tensor.
"""
y, dt, embeddings = [], [], [] # outputs
for m in self.model[:-1]: # except the head part
if m.f != -1: # if not from previous layer
x = y[m.f] if isinstance(m.f, int) else [x if j == -1 else y[j] for j in m.f] # from earlier layers
if profile:
self._profile_one_layer(m, x, dt)
if hasattr(m, 'backbone'):
x = m(x)
if len(x) != 5: # 0 - 5
x.insert(0, None)
for index, i in enumerate(x):
if index in self.save:
y.append(i)
else:
y.append(None)
x = x[-1] # 最后一个输出传给下一层
else:
x = m(x) # run
y.append(x if m.i in self.save else None) # save output
if visualize:
feature_visualization(x, m.type, m.i, save_dir=visualize)
if embed and m.i in embed:
embeddings.append(nn.functional.adaptive_avg_pool2d(x, (1, 1)).squeeze(-1).squeeze(-1)) # flatten
if m.i == max(embed):
return torch.unbind(torch.cat(embeddings, 1), dim=0)
head = self.model[-1]
x = head([y[j] for j in head.f], batch) # head inference
return x4.8 修改八
我们将下面的s用640替换即可,这一步也是部分的主干可以不修改,但有的不修改就会报错,所以我们还是修改一下。
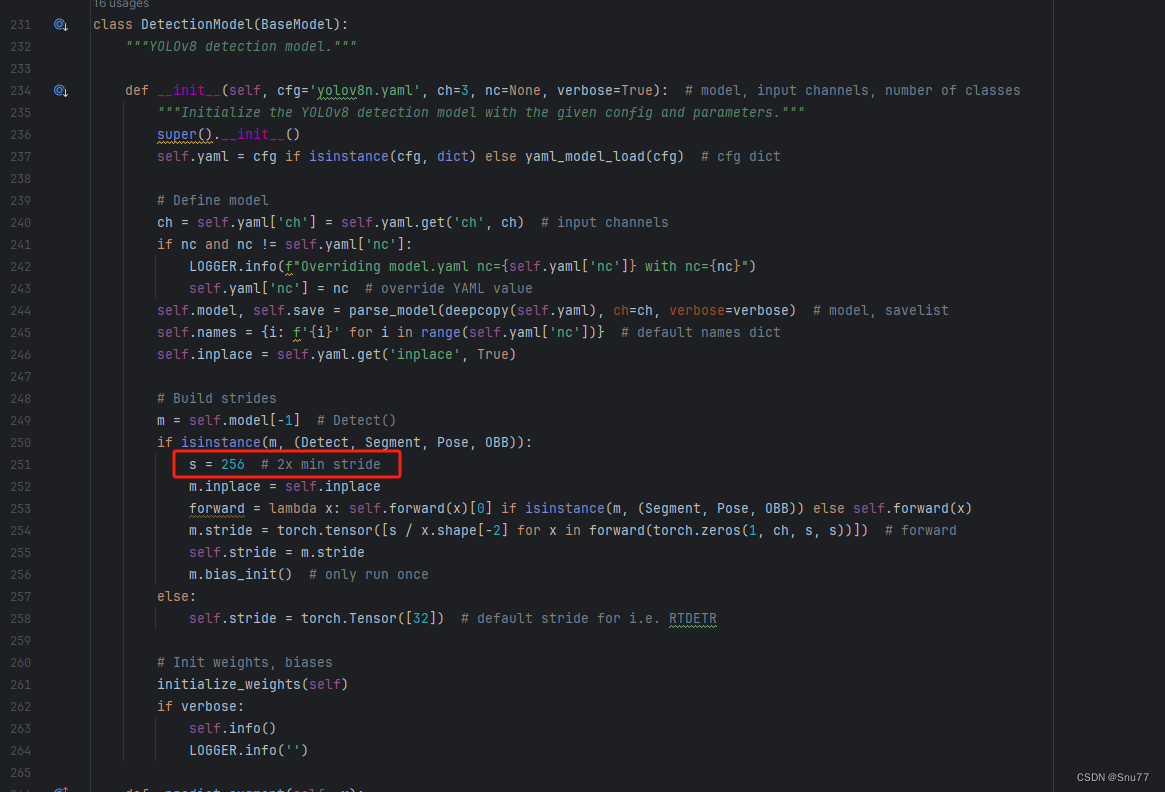
4.9 RT-DETR不能打印计算量问题的解决
计算的GFLOPs计算异常不打印,所以需要额外修改一处,?我们找到如下文件'ultralytics/utils/torch_utils.py'文件内有如下的代码按照如下的图片进行修改,大家看好函数就行,其中红框的640可能和你的不一样, 然后用我给的代码替换掉整个代码即可。
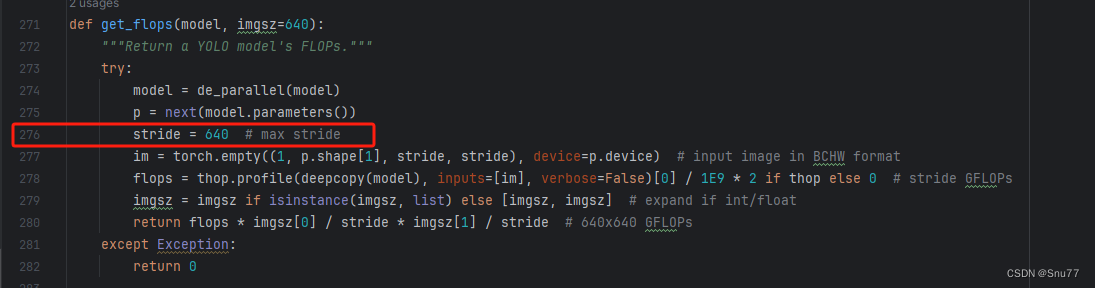
def get_flops(model, imgsz=640):
"""Return a YOLO model's FLOPs."""
try:
model = de_parallel(model)
p = next(model.parameters())
# stride = max(int(model.stride.max()), 32) if hasattr(model, 'stride') else 32 # max stride
stride = 640
im = torch.empty((1, 3, stride, stride), device=p.device) # input image in BCHW format
flops = thop.profile(deepcopy(model), inputs=[im], verbose=False)[0] / 1E9 * 2 if thop else 0 # stride GFLOPs
imgsz = imgsz if isinstance(imgsz, list) else [imgsz, imgsz] # expand if int/float
return flops * imgsz[0] / stride * imgsz[1] / stride # 640x640 GFLOPs
except Exception:
return 0
4.10 可选修改
有些读者的数据集部分图片比较特殊,在验证的时候会导致形状不匹配的报错,如果大家在验证的时候报错形状不匹配的错误可以固定验证集的图片尺寸,方法如下?->
找到下面这个文件ultralytics/models/yolo/detect/train.py然后其中有一个类是DetectionTrainer class中的build_dataset函数中的一个参数rect=mode == 'val'改为rect=False

五、ShuffleNetV1的yaml文件
5.1 yaml文件
大家复制下面的yaml文件,然后通过我给大家的运行代码运行即可,RT-DETR的调参部分需要后面的文章给大家讲,现在目前免费给大家看这一部分不开放。
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# RT-DETR-l object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For details see https://docs.ultralytics.com/models/rtdetr
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n-cls.yaml' will call yolov8-cls.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
l: [1.00, 1.00, 1024]
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, shufflenet_v1_x2_0, []] # 4
head:
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1, None, 1, 1, False]] # 5 input_proj.2
- [-1, 1, AIFI, [1024, 8]] # 6
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]] # 7, Y5, lateral_convs.0
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']] # 8
- [3, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1, None, 1, 1, False]] # 9 input_proj.1
- [[-2, -1], 1, Concat, [1]] # 10
- [-1, 3, RepC3, [256, 0.5]] # 11, fpn_blocks.0
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]] # 12, Y4, lateral_convs.1
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']] # 13
- [2, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1, None, 1, 1, False]] # 14 input_proj.0
- [[-2, -1], 1, Concat, [1]] # 15 cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, RepC3, [256, 0.5]] # X3 (16), fpn_blocks.1
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 17, downsample_convs.0
- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # 18 cat Y4
- [-1, 3, RepC3, [256, 0.5]] # F4 (19), pan_blocks.0
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 20, downsample_convs.1
- [[-1, 7], 1, Concat, [1]] # 21 cat Y5
- [-1, 3, RepC3, [256, 0.5]] # F5 (22), pan_blocks.1
- [[16, 19, 22], 1, RTDETRDecoder, [nc, 256, 300, 4, 8, 3]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
5.2 运行文件
大家可以创建一个train.py文件将下面的代码粘贴进去然后替换你的文件运行即可开始训练。
import warnings
from ultralytics import RTDETR
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = RTDETR('替换你想要运行的yaml文件')
# model.load('') # 可以加载你的版本预训练权重
model.train(data=r'替换你的数据集地址即可',
cache=False,
imgsz=640,
epochs=72,
batch=4,
workers=0,
device='0',
project='runs/RT-DETR-train',
name='exp',
# amp=True
)5.3 成功训练截图
下面是成功运行的截图(确保我的改进机制是可用的),已经完成了有1个epochs的训练,图片太大截不全第2个epochs了。?

?
六、全文总结
从今天开始正式开始更新RT-DETR剑指论文专栏,本专栏的内容会迅速铺开,在短期呢大量更新,价格也会乘阶梯性上涨,所以想要和我一起学习RT-DETR改进,可以在前期直接关注,本文专栏旨在打造全网最好的RT-DETR专栏为想要发论文的家进行服务。
?
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- OpenAI的DALL·e2生成的AI图像有时会带有偏见或NSFW
- LeetCode每日一题.04(不同路径)
- maven、springboot项目编译打包本地jar、第三方jar包
- 基于springBoot + Vue电影售票系统分前后台【完整源码+数据库】
- 安科瑞AEM“电碳表”实现碳结算功能的多功能电力仪表
- 力扣(leetcode)第412题Fizz Buzz(Python)
- php 微信分享可编辑分享标题、内容、图标
- 第二百七十七回
- Java期末复习题之GUI
- 启发式教学是什么