文件内容的读写
发布时间:2024年01月16日
? 作者:小胡_不糊涂
🌱 作者主页:小胡_不糊涂的个人主页
📀 收录专栏:JavaEE
💖 持续更文,关注博主少走弯路,谢谢大家支持 💖
1. InputStream
从文件(硬盘)中读取内容。
1.1 使用方法
| 修饰符及返回值类型 | 方法签名 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| int | read() | 读取?个字节的数据,返回 -1 代表已经完全读完了 |
| int | read(byte[] b) | 最多读取 b.length 字节的数据到 b中,返回实际读到的数量;-1 代表以及读完了 |
| int | read(byte[] b, int off, int len) | 最多读取 len - off 字节的数据到 b中,放在从 off 开始,返回实际读到的数量;-1 代表以及读完了 |
| void | close() | 关闭字节流 |
InputStream 是?个抽象类,需要使用具体的实现类。在从?件中读取内容时,需要使? FileInputStream。
FileInputStream的构造方法:
| 签名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| FileInputStream(File file) | 利? File 构造?件输?流 |
| FileInputStream(String name) | 利??件路径构造?件输?流 |
上述方法的实现:
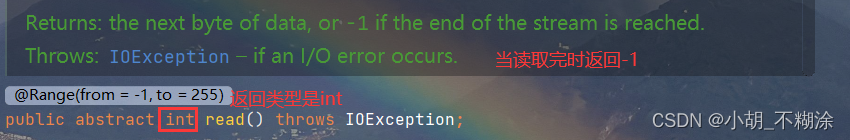
示例一:read()的使用,每次读取一个字符
public static void main(String[] args) {
//先在D目录下创建一个test.txt文件,并写入abc
try(InputStream inputStream=new FileInputStream("D:/test.txt")){
while(true){
int b=inputStream.read();
if(b==-1){//判断是否读完
break;
}
char a=(char)b;//将ASCII值转换为
对应的字符并输出 System.out.println(a);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
上述read的返回值为int型,范围是-1到255:
示例二:read(byte[] b)的使用,一次读取多个字符
public static void main(String[] args) {
//先在D目录下创建一个test.txt文件,并写入abc
try(InputStream inputStream=new FileInputStream("D:/test.txt")){
byte[] b=new byte[1024];
int len=0;
while(true){
len=inputStream.read(b);
if(len==-1){//文件全部读完
break;
}
for(int i=0;i<len;i++) {
System.out.printf("%c",b[i]);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
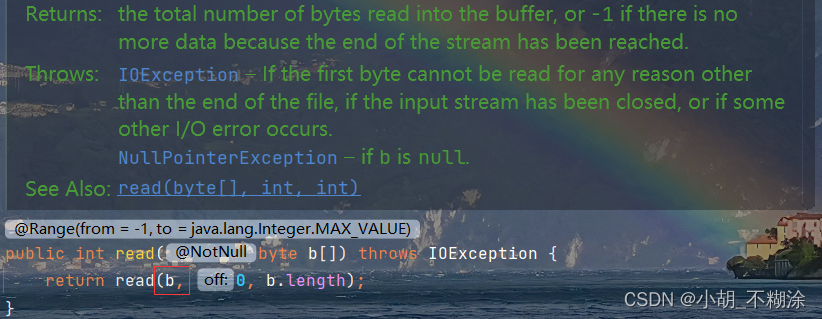
注意:一个Unicode编码的中文字符是2个字节,而UTF-8编码长度是3个字节。
我们也可以利用Scanner进行字符读取:
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(InputStream inputStream=new FileInputStream("D:/test.txt")){
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(inputStream);
String s=scanner.next();
System.out.println(s);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
2. OutputStream
向文件中写入内容。
2.1 使用方法
| 修饰符及返回值类型 | ?法签名 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| void | write(int b) | 写?要给字节的数据 |
| void | write(byte[] b) | 将 b 这个字符数组中的数据全部写? os 中 |
| int | write(byte[] b, int off, int len) | 将 b 这个字符数组中从 off 开始的数据写? os 中,?共写 len 个 |
| void | close() | 关闭字节流 |
| void | flush() | I/O 的速度是很慢的,所以,?多的 OutputStream为了减少设备操作的次数,在写数据的时候都会将数据先暂时写?内存的?个指定区域?,直到该区域满了或者其他指定条件时才真正将数据写?设备中,这个区域?般称为缓冲区。但造成?个结果,就是我们写的数据,很可能会遗留?部分在缓冲区中。需要在最后或者合适的位置,调? flush(刷新)操作,将数据刷到设备中。 |
OutputStream 也是?个抽象类,要使?还需要具体的实现类。当写??件是,需要使?FileOutputStream。
上述方法的实现:
示例一:
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(OutputStream outputStream=new FileOutputStream("D:/test.txt")){
outputStream.write('a');
outputStream.write('b');
outputStream.write('c');
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
OutputStream.flush();
}
示例二:
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(OutputStream outputStream=new FileOutputStream("D:/test.txt")){
byte[] b=new byte[]{(byte)'a',(byte)'b',(byte)'c'};
outputStream.write(b,0,3);
outputStream.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
示例三:写入字符串
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(OutputStream outputStream=new FileOutputStream("D:/test.txt")){
String s="abc";
byte[] b=s.getBytes();
outputStream.write(b);
outputStream.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
示例四:写入中文字符串
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(OutputStream outputStream=new FileOutputStream("D:/test.txt")){
String s="你好";
byte[] b=s.getBytes("utf-8");//写中?的时候使? UTF-8 编码
outputStream.write(b);
outputStream.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
当写入字符串时,总是需要进行转换。所以我们使用PrintWriter类完成输出,PrintWriter 类中提供了print/println/printf 方法。
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(OutputStream outputStream=new FileOutputStream("D:/test.txt")){
PrintWriter writer=new PrintWriter(outputStream);//相当于把字节流转成字符流
writer.printf("hello,world");
writer.flush();//确保数据从缓冲区落到硬盘上
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/iLoyo_/article/details/135626075
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 软测思考题:自动化测试重运行是好是坏?
- RAID5如何优化,可以加快重建速度?
- 外包干了2个多月,技术明显有退步了。。。。。
- 生成式AI改变软件开发模式的机遇和挑战
- linux系统nginx proxy做反向代理
- 中仕教育:考教师编之前需要做哪些准备?
- 人工智能利用深度学习技术增强高级驾驶辅助系统(ADAS)
- Keepalived+Nginx实现高可用(下)
- 页面间动画之放大缩小视图
- 适用于 Mac 的 10 款顶级数据恢复软件分享