死锁与读写锁
发布时间:2024年01月06日
一、死锁?
????????死锁(Deadlock)是在并发计算中的一种状态,其中两个或多个进程无法继续执行,因为每个进程都在等待另一个进程释放所占用的资源。这种情况通常发生在系统中的资源分配过程中,其中每个进程都占用一些资源,并且正在等待其他进程释放它们所占用的资源,从而导致所有进程都无法继续执行。?
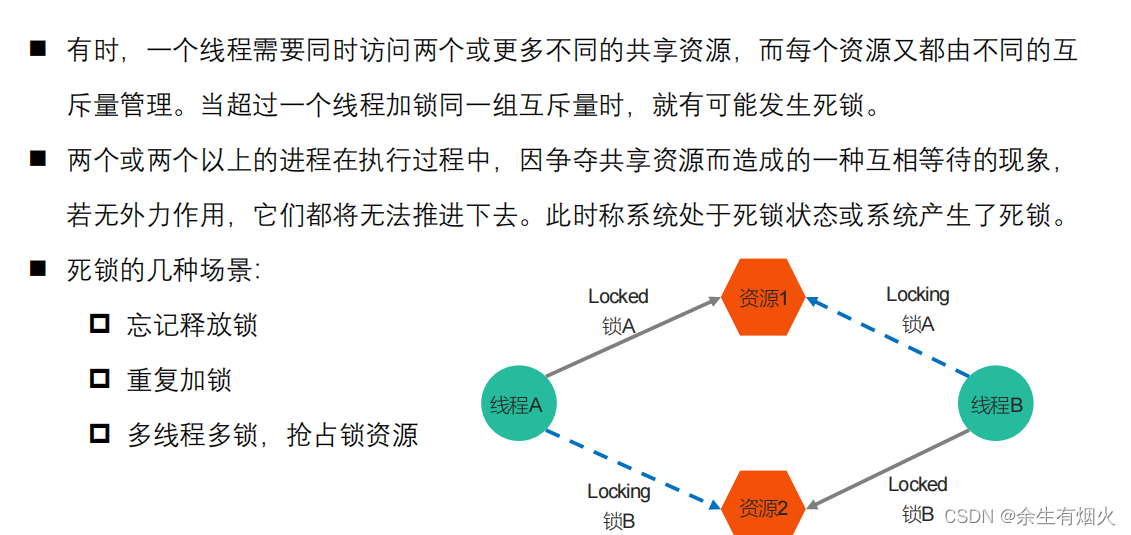
死锁演示 1:? 忘记释放锁及重复加锁
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
// 全局变量,所有的线程都共享这一份资源。
int tickets = 1000;
// 创建一个互斥量
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
void * sellticket(void * arg) {
// 卖票
while(1) {
// 加锁
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if(tickets > 0) {
usleep(6000);
printf("%ld 正在卖第 %d 张门票\n", pthread_self(), tickets);
tickets--;
}else {
// 解锁
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
break;
}
// 解锁
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
return NULL;
}
int main() {
// 初始化互斥量
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
// 创建3个子线程
pthread_t tid1, tid2, tid3;
pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, sellticket, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, sellticket, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid3, NULL, sellticket, NULL);
// 回收子线程的资源,阻塞
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
pthread_join(tid3, NULL);
pthread_exit(NULL); // 退出主线程
// 释放互斥量资源
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
return 0;
}死锁演示 2:? 两个进程争抢资源
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
// 创建2个互斥量
pthread_mutex_t mutex1, mutex2;
void * workA(void * arg) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex1);
sleep(1);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex2);
printf("workA....\n");
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex2);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex1);
return NULL;
}
void * workB(void * arg) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex2);
sleep(1);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex1);
printf("workB....\n");
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex1);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex2);
return NULL;
}
int main() {
// 初始化互斥量
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex1, NULL);
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex2, NULL);
// 创建2个子线程
pthread_t tid1, tid2;
pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, workA, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, workB, NULL);
// 回收子线程资源
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
// 释放互斥量资源
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex1);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex2);
return 0;
}二 、 读写锁
????????当有一个线程已经持有互斥锁时,互斥锁将所有试图进入临界区的线程都阻塞住。但是考
虑一种情形,当前持有互斥锁的线程只是要读访问共享资源,而同时有其它几个线程也想
读取这个共享资源,但是由于互斥锁的排它性,所有其它线程都无法获取锁,也就无法读
访问共享资源了,但是实际上多个线程同时读访问共享资源并不会导致问题。
????????? 在对数据的读写操作中,更多的是读操作,写操作较少,例如对数据库数据的读写应用。
为了满足当前能够允许多个读出,但只允许一个写入的需求,线程提供了读写锁来实现。
????????? 读写锁的特点:
????????????????? 如果有其它线程读数据,则允许其它线程执行读操作,但不允许写操作。
????????????????? 如果有其它线程写数据,则其它线程都不允许读、写操作。
????????????????? 写是独占的,写的优先级高。

/*
读写锁的类型 pthread_rwlock_t
int pthread_rwlock_init(pthread_rwlock_t *restrict rwlock, const pthread_rwlockattr_t *restrict attr);
int pthread_rwlock_destroy(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
int pthread_rwlock_rdlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
int pthread_rwlock_tryrdlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
int pthread_rwlock_wrlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
int pthread_rwlock_trywrlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
int pthread_rwlock_unlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
案例:8个线程操作同一个全局变量。
3个线程不定时写这个全局变量,5个线程不定时的读这个全局变量
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
// 创建一个共享数据
int num = 1;
// pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_rwlock_t rwlock;
void * writeNum(void * arg) {
while(1) {
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&rwlock);
num++;
printf("++write, tid : %ld, num : %d\n", pthread_self(), num);
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);
usleep(100);
}
return NULL;
}
void * readNum(void * arg) {
while(1) {
pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&rwlock);
printf("===read, tid : %ld, num : %d\n", pthread_self(), num);
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);
usleep(100);
}
return NULL;
}
int main() {
pthread_rwlock_init(&rwlock, NULL);
// 创建3个写线程,5个读线程
pthread_t wtids[3], rtids[5];
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
pthread_create(&wtids[i], NULL, writeNum, NULL);
}
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
pthread_create(&rtids[i], NULL, readNum, NULL);
}
// 设置线程分离
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
pthread_detach(wtids[i]);
}
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
pthread_detach(rtids[i]);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
pthread_rwlock_destroy(&rwlock);
return 0;
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/leimeili/article/details/135423724
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 函数式组件
- 热更新相关
- AM3358时钟树遍历与PRU时钟源选择和配置
- Linux中用于自动化交互式程序的工具!expect
- springboot/java/php/node/python在线音乐网站【计算机毕设】
- 基于Ray和vLLM构建70B+模型的开源RLHF全量训练框架
- 【算法】基础算法001之双指针
- java常见面试题:如何使用Java进行JPA框架开发?
- 计算机网络基础——网络拓扑结构介绍及优缺点比较
- C++面试宝典第7题:重载自增自减运算符