【记录版】SpringBoot框架中Request请求获取方式及源码解读
SpringBoot + HttpServletRequest
背景: 我们现在有很多WEB项目基于SpringBoot开发,其中接口管理是必不可少的,接口中Request对象是核心内容,我们对参数、属性、header等等元数据的获取和配置都离不开它,常用的Filter、拦截器等操作类也都有它的身影。本篇在此基础上,从源码角度讨论获取Request的三种方式:
方式一、接口方法或全局异常处理方法参数注入
通常在开发简单POST接口时,请求参数或Header等信息都可以用*@RequestBody、@RequestParam、@PathVariable或@RequestHeader*注解直接取值,部分场景下当接口方法参数名和请求体参数名值和类型一致时,也可以赋值,如下所示:
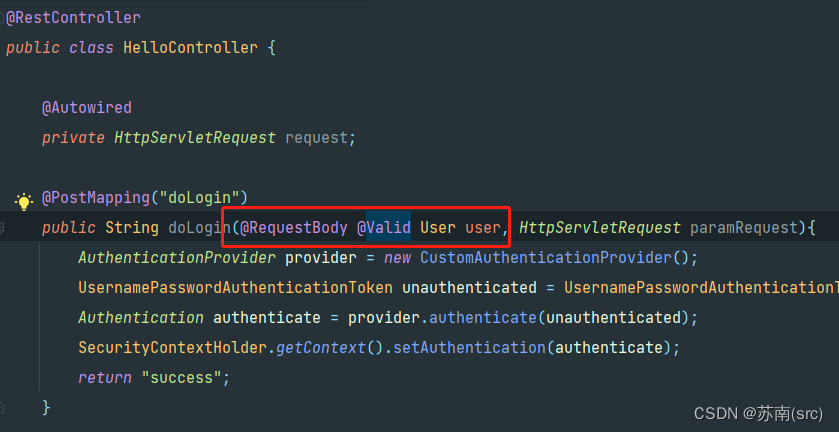
当然最原始的也可用Request实例对象,即在此接口上配置HttpServletRequest参数获取,这是最简单也是最直接的方式。(PS: 接口方法也可设置HttpSession参数控制session逻辑)
源码一、方法参数解析入口类
package org.springframework.web.method.support;
public class InvocableHandlerMethod extends HandlerMethod {
@Nullable
public Object invokeForRequest(NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
// 解析方法所有参数,并将其传给最终的反射方法对象执行invoke操作
Object[] args = this.getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs);
return this.doInvoke(args);
}
}
源码二、方法参数解析类(选一:RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor)
// 方法参数解析接口
public interface HandlerMethodArgumentResolver {
boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter);
@Nullable
Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest, @Nullable WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception;
}
package org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation;
public class RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor extends AbstractMessageConverterMethodProcessor {
......省略......
public Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest, @Nullable WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception {
parameter = parameter.nestedIfOptional();
// 通过转换器将Request中请求流数据转换为对应的实体
Object arg = this.readWithMessageConverters(webRequest, parameter, parameter.getNestedGenericParameterType());
String name = Conventions.getVariableNameForParameter(parameter);
if (binderFactory != null) {
WebDataBinder binder = binderFactory.createBinder(webRequest, arg, name);
if (arg != null) {
// 参数校验
this.validateIfApplicable(binder, parameter);
if (binder.getBindingResult().hasErrors() && this.isBindExceptionRequired(binder, parameter)) {
throw new MethodArgumentNotValidException(parameter, binder.getBindingResult());
}
}
if (mavContainer != null) {
mavContainer.addAttribute(BindingResult.MODEL_KEY_PREFIX + name, binder.getBindingResult());
}
}
return this.adaptArgumentIfNecessary(arg, parameter);
}
// 参数校验
protected void validateIfApplicable(WebDataBinder binder, MethodParameter parameter) {
// 获取参数所有注解,下面将判断是否包含校验类注解
Annotation[] annotations = parameter.getParameterAnnotations();
Annotation[] var4 = annotations;
int var5 = annotations.length;
for(int var6 = 0; var6 < var5; ++var6) {
Annotation ann = var4[var6];
// 此处获取@Valid等校验注解,如果有,binder执行校验并获取校验结果
Object[] validationHints = ValidationAnnotationUtils.determineValidationHints(ann);
if (validationHints != null) {
binder.validate(validationHints);
break;
}
}
}
......省略......
}
HandlerMethodArgumentResolver默认有31种,覆盖绝大部分类型参数的解析,使我们从Request的API的操作中解放出来,从而关注业务逻辑的开发和管理,以下仅列出核心解析器:
1、RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor // 支持@RequestBody注解参数解析
2、ServletRequestMethodArgumentResolver //支持ServletRequest、MultipartRequest及HttpSession等参数解析
3、RequestHeaderMethodArgumentResolver // 支持Header参数解析
方法二:方法体内通过RequestContextHolder全局持久化类获取
HttpServletRequest holderRequest = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest();
在SpringBoot项目中,有两处地方进行了上下文保存动作:
1、OrderedRequestContextFilter extends RequestContextFilter implements OrderedFilter 设置
public class RequestContextFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
// 是否线程间传递,适用于后端存在异步线程池场景,需手工开启
private boolean threadContextInheritable = false;
public void setThreadContextInheritable(boolean threadContextInheritable) {
this.threadContextInheritable = threadContextInheritable;
}
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 请求与响应封装体
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = new ServletRequestAttributes(request, response);
// 内存保存
this.initContextHolders(request, attributes);
try {
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
} finally {
// 清除
LocaleContextHolder.resetLocaleContext();
RequestContextHolder.resetRequestAttributes();
attributes.requestCompleted();
}
}
// 请求&响应上下文具体保存逻辑-核心为ThreadLocal
private void initContextHolders(HttpServletRequest request, ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes) {
LocaleContextHolder.setLocale(request.getLocale(), this.threadContextInheritable);
RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(requestAttributes, this.threadContextInheritable);
}
}
OrderedRequestContextFilter是通过SpringBoot自动配置,只要是Web项目都不用手工设置,自动配置源码:
@AutoConfiguration(
after = {DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class, ValidationAutoConfiguration.class}
)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(
type = Type.SERVLET
)
@ConditionalOnClass({Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class})
@AutoConfigureOrder(-2147483638)
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
@Configuration(
proxyBeanMethods = false
)
@Import({EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class})
@EnableConfigurationProperties({WebMvcProperties.class, WebProperties.class})
@Order(0)
public static class WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter implements WebMvcConfigurer, ServletContextAware {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({RequestContextListener.class, RequestContextFilter.class})
@ConditionalOnMissingFilterBean({RequestContextFilter.class})
public static RequestContextFilter requestContextFilter() {
return new OrderedRequestContextFilter();
}
}
}
二、DispatcherServlet执行时设置
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
private void initContextHolders(HttpServletRequest request, @Nullable LocaleContext localeContext, @Nullable RequestAttributes requestAttributes) {
if (localeContext != null) {
LocaleContextHolder.setLocaleContext(localeContext, this.threadContextInheritable);
}
if (requestAttributes != null) {
RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(requestAttributes, this.threadContextInheritable);
}
}
}
三、定义HttpServletRequest类实例变量,通过Spring容器注入,如@Autowired注解修饰
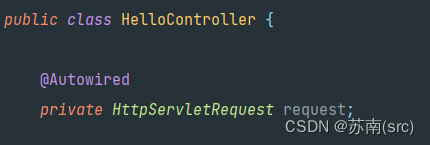
这种方式比较少见,但既然能够使用,说明此时我们看到的request对象,不再是前面方法里获取的Request对象,而是披了一层羊皮的代理对象,这样每个接口获取时才能找到自己的上下文,那它是怎么实现的呢?
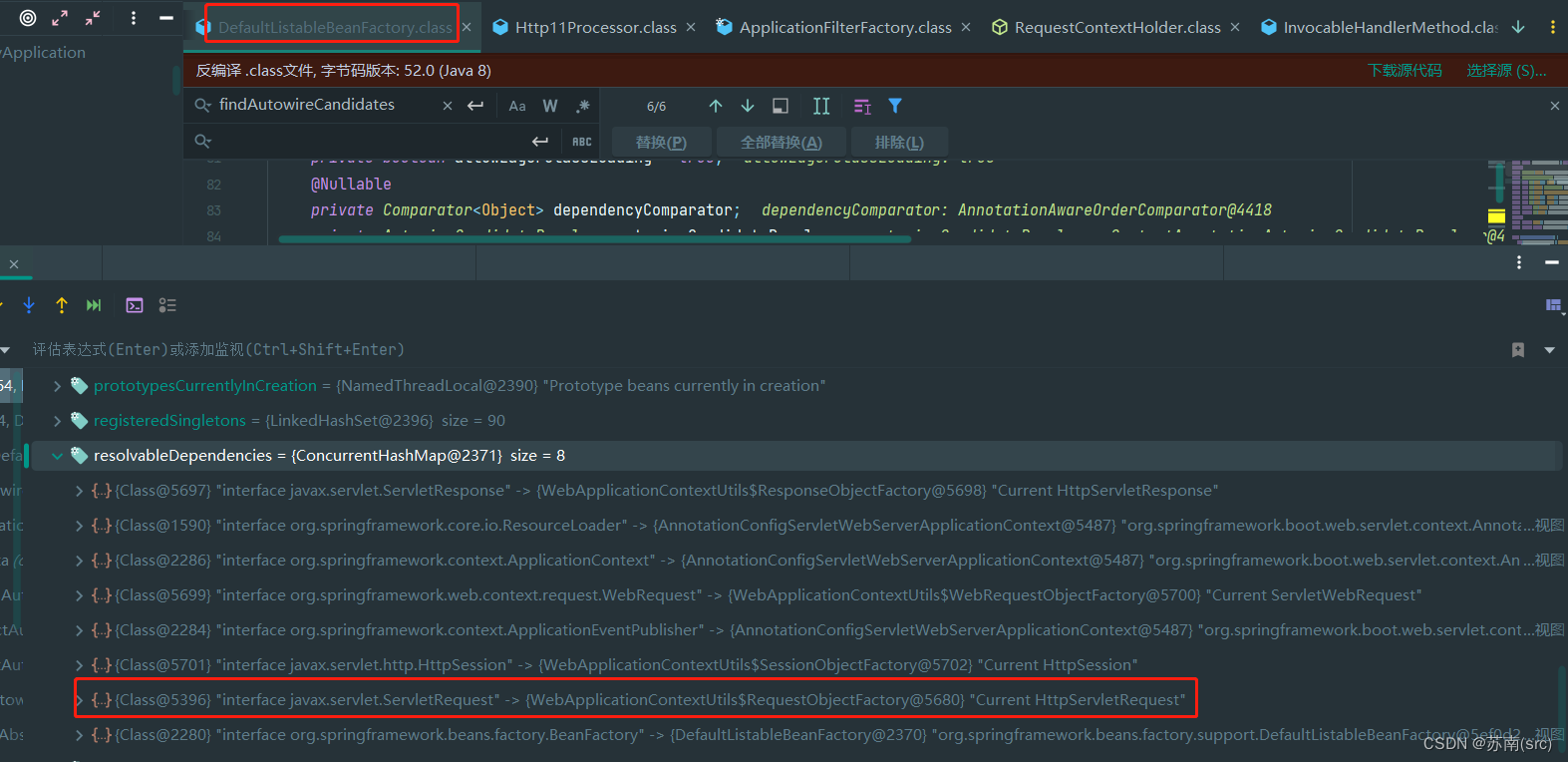
熟悉Spring框架的话,就会知道容器在实例化外部控制器实例时,会在BeanPostProcessor等处优先处理需要注入的实例,当需要注入实例到Request变量时,BeanFactory会自动处理:
// Bean实例化时会执行
public class DefaultListableBeanFactory extends AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory implements ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, BeanDefinitionRegistry, Serializable {
// beanName为外部类名称,requiredType为HttpServletRequest.class
protected Map<String, Object> findAutowireCandidates(@Nullable String beanName, Class<?> requiredType, DependencyDescriptor descriptor) {
String[] candidateNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(this, requiredType, true, descriptor.isEager());
Map<String, Object> result = CollectionUtils.newLinkedHashMap(candidateNames.length);
// BeanFactory所有缓存的resolvableDependencies,具体见如上截图中8个依赖
Iterator var6 = this.resolvableDependencies.entrySet().iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object> classObjectEntry = (Map.Entry)var6.next();
Class<?> autowiringType = (Class)classObjectEntry.getKey();
if (autowiringType.isAssignableFrom(requiredType)) {
Object autowiringValue = classObjectEntry.getValue();
// 此处根据变量类型,获取对应的ObjectFactory工厂,再生成对应的Proxy
autowiringValue = AutowireUtils.resolveAutowiringValue(autowiringValue, requiredType);
if (requiredType.isInstance(autowiringValue)) {
result.put(ObjectUtils.identityToString(autowiringValue), autowiringValue);
break;
}
}
}
..........
}
}
abstract class AutowireUtils {
public static Object resolveAutowiringValue(Object autowiringValue, Class<?> requiredType) {
if (autowiringValue instanceof ObjectFactory && !requiredType.isInstance(autowiringValue)) {
ObjectFactory<?> factory = (ObjectFactory)autowiringValue;
if (!(autowiringValue instanceof Serializable) || !requiredType.isInterface()) {
return factory.getObject();
}
// 此处使用JDK动态代理
autowiringValue = Proxy.newProxyInstance(requiredType.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{requiredType}, new ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler(factory));
}
return autowiringValue;
}
}
// 私有静态内部类封装InvocationHandler具体的反射调用内容,配合JDK动态代理生成代理类
private static class ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private final ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory;
ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler(ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory) {
this.objectFactory = objectFactory;
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
switch (method.getName()) {
case "equals":
return proxy == args[0];
case "hashCode":
return System.identityHashCode(proxy);
case "toString":
return this.objectFactory.toString();
default:
try {
return method.invoke(this.objectFactory.getObject(), args);
} catch (InvocationTargetException var6) {
throw var6.getTargetException();
}
}
}
}
}
ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler是处理封装类,具体逻辑为ObjectFactory实现类提供
public abstract class WebApplicationContextUtils {
public static void registerWebApplicationScopes(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, @Nullable ServletContext sc) {
beanFactory.registerScope("request", new RequestScope());
beanFactory.registerScope("session", new SessionScope());
if (sc != null) {
ServletContextScope appScope = new ServletContextScope(sc);
beanFactory.registerScope("application", appScope);
sc.setAttribute(ServletContextScope.class.getName(), appScope);
}
// 此处注册Request执行的工厂类
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ServletRequest.class, new RequestObjectFactory());
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ServletResponse.class, new ResponseObjectFactory());
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(HttpSession.class, new SessionObjectFactory());
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(WebRequest.class, new WebRequestObjectFactory());
if (jsfPresent) {
WebApplicationContextUtils.FacesDependencyRegistrar.registerFacesDependencies(beanFactory);
}
}
}
Request代理类真实执行逻辑:
public abstract class WebApplicationContextUtils {
private static class RequestObjectFactory implements ObjectFactory<ServletRequest>, Serializable {
// ObjectFactory核心就是getObject方法,封装实例创建的过程
public ServletRequest getObject() {
// 实际获取的还是RequestContextHolder缓存的Request对象
return WebApplicationContextUtils.currentRequestAttributes().getRequest();
}
}
}
总结:
1、一般需求场景,直接在接口方法上标注HttpServletRequest对象即可
2、如果需要在任意场景使用HttpServletRequest对象,方法二和方法三都可,方法三使用更加简洁
3、方法二和方法三底层都依赖ThreadLocal,如果后台使用异步线程池,需要手工设置inheritable属性为true
4、从方法一中,我们可以学到接口方法可以定义多个我们需要的上下文参数,如HttpSession;从方法三中我们可以学习到全局使用Request、Response、Session等8个对象。
5、方法三虽然涉及Bean生命周期、JDK动态代理等底层知识,但实际内容还是围绕RequestContextHolder做的封装,使用时更加方便,全局场景推荐使用此方式。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- FreeRTOS学习--56讲 软件定时器
- 透过许战海矩阵洞察安记食品增长战略
- 智能农业大棚环境监测数据分析系统(开题+源码)
- SQL 语言详解
- 工业4.0对制造业的深度影响:库米超声波焊接机与库米多工位转盘螺丝机的革新技术
- 服务器运维小技巧(一)——如何进行远程协助
- 第五章[列表]:5.12:元组的操作
- 基于Java学生成绩管理系统设计与实现(源码+部署文档)
- 《微信小程序开发从入门到实战》学习五十一
- outlook邮箱群发邮件方法?邮箱如何群发?