Activity启动流程
早就想写这个笔记用于记录这段知识,但是碍于太过庞大所以始终没有进行这段知识的整理
很多博客喜欢画一个时序图展示所有的流程,但是过于庞大,看起来有点吃力,这里我们画多个时序图来展示这个流程
1.app请求AMS启动Activity
在前面章节中介绍过,启动(或跳转)Activity会先配置一个Intent,这个Intent存放的数据可是很丰富了:包含了启动Activity的信息,传递给Activity的数据,甚至还有启动Activity的方式等等.app进程与AMS不处于同一进程,它们之间的通信使用的是binder,Intent会在"binder这条搭建好的公路"上传递到AMS.
?
@Override
public void startActivity(Intent intent, @Nullable Bundle options) {
//省略
if (options != null) {
startActivityForResult(intent, -1, options);
} else {
// Note we want to go through this call for compatibility with
// applications that may have overridden the method.
//重点看这里
startActivityForResult(intent, -1);
//增加了requestCode为-1的参数,代表不需要关注这个Activity的返回数据
}
} public void startActivityForResult(@RequiresPermission Intent intent, int requestCode,
@Nullable Bundle options) {
//主要分析mParent== null的情况
if (mParent == null) {
options = transferSpringboardActivityOptions(options);
//调用mInstrumentation.execStartActivity方法,
Instrumentation.ActivityResult ar =
mInstrumentation.execStartActivity(
this, mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), mToken, this,
intent, requestCode, options);
if (ar != null) {
mMainThread.sendActivityResult(
mToken, mEmbeddedID, requestCode, ar.getResultCode(),
ar.getResultData());
}
//对于requestCode大于0的情况,则把mStartedActivity置为true
if (requestCode >= 0) {
// If this start is requesting a result, we can avoid making
// the activity visible until the result is received. Setting
// this code during onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) or onResume() will keep the
// activity hidden during this time, to avoid flickering.
// This can only be done when a result is requested because
// that guarantees we will get information back when the
// activity is finished, no matter what happens to it.
mStartedActivity = true;
}
cancelInputsAndStartExitTransition(options);
// TODO Consider clearing/flushing other event sources and events for child windows.
} else {
......省略代码
}
}
上面的方法主要做的事情:会根据mParent是否存在执行不同的逻辑,但是最终都会调用到同一方法。咱们主要分析mParent== null的情况。
介绍下mInstrumentation.execStartActivity方法的几个关键参数:
who:类型为Activity
contextThread:类型为IBinder,mMainThread.getApplicationThread()获取的是一个类型为IApplicationThread的对象,这个对象同时也是一个Binder对象,它会被传递给AMS,AMS拿到它可以与app进程进行通信。 mMainThread是ActivityThread的实例,一个进程内就进存在一个
token:类型IBinder,mToken是它的值,在上面原理篇介绍过。
intent:启动信息,参数等都在Intent内
requestCode:若是调用startActivityForResult方法,这个参数有用,否则没用。它若存在会传递给启动的Activity,Activity finish后并且调用了setResult方法,这个参数会被返回。当前值为-1
@UnsupportedAppUsage
public ActivityResult execStartActivity(
Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, Activity target,
Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) {
IApplicationThread whoThread = (IApplicationThread) contextThread;
//省略
try {
intent.migrateExtraStreamToClipData(who);
intent.prepareToLeaveProcess(who);
int result = ActivityTaskManager.getService().startActivity(whoThread,
who.getOpPackageName(), who.getAttributionTag(), intent,
intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(who.getContentResolver()), token,
target != null ? target.mEmbeddedID : null, requestCode, 0, null, options);
checkStartActivityResult(result, intent);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failure from system", e);
}
return null;
}该方法做的事情主要是为intent添加一些额外的信息外,最终通过binder调用把参数发送到系统进程
ActivityTaskManager.getService():获取的是ActivityTaskManagerService在app进程内的代理类的实例,这个代理类实现了IActivityTaskManager,同时它也是BinderProxy类型。
搞一张时序图来看下这个流程,这里只是一个请求流程
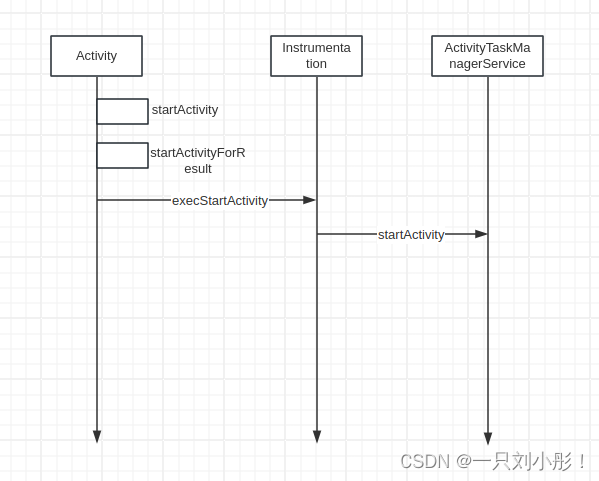
接下来是AMS内部如何处理这个请求??
@Override
public final int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
String callingFeatureId, Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo,
String resultWho, int requestCode, int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo,
Bundle bOptions) {
return startActivityAsUser(caller, callingPackage, callingFeatureId, intent, resolvedType,
resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, startFlags, profilerInfo, bOptions,
UserHandle.getCallingUserId());
}
private int startActivityAsUser(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
@Nullable String callingFeatureId, Intent intent, String resolvedType,
IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode, int startFlags,
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle bOptions, int userId, boolean validateIncomingUser) {
assertPackageMatchesCallingUid(callingPackage);
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("startActivityAsUser");
userId = getActivityStartController().checkTargetUser(userId, validateIncomingUser,
Binder.getCallingPid(), Binder.getCallingUid(), "startActivityAsUser");
// TODO: Switch to user app stacks here.
return getActivityStartController().obtainStarter(intent, "startActivityAsUser")
.setCaller(caller)
.setCallingPackage(callingPackage)
.setCallingFeatureId(callingFeatureId)
.setResolvedType(resolvedType)
.setResultTo(resultTo)
.setResultWho(resultWho)
.setRequestCode(requestCode)
.setStartFlags(startFlags)
.setProfilerInfo(profilerInfo)
.setActivityOptions(bOptions)
.setUserId(userId)
.execute();
}getActivityStartController().obtainStarter方法的介绍。
getActivityStartController()会获取一个ActivityStartController类的实例,ActivityStartController中缓存了ActivityStarter,这样就不需要每次都new一个ActivityStarter出来,浪费宝贵的内存了。
缓存池模式
ActivityStarter obtainStarter(Intent intent, String reason) {
return mFactory.obtain().setIntent(intent).setReason(reason);
}obtainStarter方法会获取一个已有或创建一个新的ActivityStarter类实例,这个类的主要职责就是根据各种信息来决定如何启动Activity,并且根据各种信息来决定是把Activity放在一个新task中还是放在roottask中。
ActivityStarter setProfilerInfo(ProfilerInfo info) {
mRequest.profilerInfo = info;
return this;
}
ActivityStarter setGlobalConfiguration(Configuration config) {
mRequest.globalConfig = config;
return this;
}
ActivityStarter setUserId(int userId) {
mRequest.userId = userId;
return this;
}
最终调用?ActivityStarter 的? execute 方法
int execute() {
try {
省略代码......
final LaunchingState launchingState;
synchronized (mService.mGlobalLock) {
//获取启动者
final ActivityRecord caller = ActivityRecord.forTokenLocked(mRequest.resultTo);
//获取callingUid
final int callingUid = mRequest.realCallingUid == Request.DEFAULT_REAL_CALLING_UID
? Binder.getCallingUid() : mRequest.realCallingUid;
launchingState = mSupervisor.getActivityMetricsLogger().notifyActivityLaunching(
mRequest.intent, caller, callingUid);
}
// If the caller hasn't already resolved the activity, we're willing
// to do so here. If the caller is already holding the WM lock here,
// and we need to check dynamic Uri permissions, then we're forced
// to assume those permissions are denied to avoid deadlocking.
//activityInfo为null 则需要去解析
if (mRequest.activityInfo == null) {
mRequest.resolveActivity(mSupervisor);
}
int res;
//启动的时候使用mService.mGlobalLock锁保持同步
synchronized (mService.mGlobalLock) {
final boolean globalConfigWillChange = mRequest.globalConfig != null
&& mService.getGlobalConfiguration().diff(mRequest.globalConfig) != 0;
final Task rootTask = mRootWindowContainer.getTopDisplayFocusedRootTask();
省略代码......
res = executeRequest(mRequest);
省略代码......
if (mRequest.waitResult != null) {
mRequest.waitResult.result = res;
res = waitResultIfNeeded(mRequest.waitResult, mLastStartActivityRecord,
launchingState);
}
return getExternalResult(res);
}
} finally {
onExecutionComplete();
}
}
mRequest.activityInfo为null,回调用mRequest.resolveActivity(mSupervisor)方法开始解析,会在PMS中根据intent解析出ResolveInfo和ActivityInfo
调用executeRequest方法开始进入下个流程
ResolveInfo
看下它的几个关键属性:
public class ResolveInfo implements Parcelable {
private static final String TAG = "ResolveInfo";
private static final String INTENT_FORWARDER_ACTIVITY =
"com.android.internal.app.IntentForwarderActivity";
/**
* The activity or broadcast receiver that corresponds to this resolution
* match, if this resolution is for an activity or broadcast receiver.
* Exactly one of {@link #activityInfo}, {@link #serviceInfo}, or
* {@link #providerInfo} will be non-null.
*/
public ActivityInfo activityInfo;
/**
* The service that corresponds to this resolution match, if this resolution
* is for a service. Exactly one of {@link #activityInfo},
* {@link #serviceInfo}, or {@link #providerInfo} will be non-null.
*/
public ServiceInfo serviceInfo;
/**
* The provider that corresponds to this resolution match, if this
* resolution is for a provider. Exactly one of {@link #activityInfo},
* {@link #serviceInfo}, or {@link #providerInfo} will be non-null.
*/
public ProviderInfo providerInfo;
/**
* An auxiliary response that may modify the resolved information. This is
* only set under certain circumstances; such as when resolving instant apps
* or components defined in un-installed splits.
* @hide
*/
public AuxiliaryResolveInfo auxiliaryInfo;
/**
* Whether or not an instant app is available for the resolved intent.
*/
public boolean isInstantAppAvailable;
/**
* The IntentFilter that was matched for this ResolveInfo.
*/
public IntentFilter filter;
省略代码......
}
ResolveInfo实现了Parcelable,代表它可以通过binder在进程之间进行传递。在AndroidManifest配置的四大组件解析完后的数据会放入ResolveInfo类中。
如上,它里面的几个关键属性:
activityInfo,serviceInfo,providerInfo:分别代表Activity,Broadcast,Service,ContentProvider
filter:在AndroidManifest里面配置的Intent-filter这一项
用一个AndroidManifest.xml例子来说下ResolveInfo,
AndroidManifest.xml有如下信息:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.lifecycledemo">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/Theme.LifecycleDemo">
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<activity android:name=".SecondActivity"/>
</application>
</manifest>
上面的清单文件信息会被解析成两个ResolveInfo:
其中一个它的activityInfo包含的信息是MainActivity,它的filter包含的信息是action为android.intent.action.MAIN,category为android.intent.category.LAUNCHER。
另一个它的activityInfo包含的信息是SecondActivity,它的filter为null
介绍完ResolveInfo,介绍下ActivityInfo这个类。
ActivityInfo
主要显示它的几个关键属性:
public class ActivityInfo extends ComponentInfo implements Parcelable {
public int theme;
public int launchMode;
public String taskAffinity;
public String name;
public String packageName;
省略代码......
}
ActivityInfo包含了在AndroidManifest里面配置的Activity的信息,它上面的几个属性:
theme:Activity的主题
launchMode:配置的Activity的启动模式
taskAffinity:指定Activity放在哪个名字下面的task
name:Activity的完整的classname
packageName:包名
private int executeRequest(Request request) {
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(request.reason)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Need to specify a reason.");
}
mLastStartReason = request.reason;
mLastStartActivityTimeMs = System.currentTimeMillis();
mLastStartActivityRecord = null;
final IApplicationThread caller = request.caller;
Intent intent = request.intent;
NeededUriGrants intentGrants = request.intentGrants;
String resolvedType = request.resolvedType;
ActivityInfo aInfo = request.activityInfo;
ResolveInfo rInfo = request.resolveInfo;
final IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession = request.voiceSession;
final IBinder resultTo = request.resultTo;
String resultWho = request.resultWho;
int requestCode = request.requestCode;
int callingPid = request.callingPid;
int callingUid = request.callingUid;
String callingPackage = request.callingPackage;
String callingFeatureId = request.callingFeatureId;
final int realCallingPid = request.realCallingPid;
final int realCallingUid = request.realCallingUid;
final int startFlags = request.startFlags;
final SafeActivityOptions options = request.activityOptions;
Task inTask = request.inTask;
int err = ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS;
省略代码......
WindowProcessController callerApp = null;
//根据caller获取callerApp
if (caller != null) {
callerApp = mService.getProcessController(caller);
if (callerApp != null) {
callingPid = callerApp.getPid();
callingUid = callerApp.mInfo.uid;
} else {
Slog.w(TAG, "Unable to find app for caller " + caller + " (pid=" + callingPid
+ ") when starting: " + intent.toString());
err = ActivityManager.START_PERMISSION_DENIED;
}
}
//获取userId
final int userId = aInfo != null && aInfo.applicationInfo != null
? UserHandle.getUserId(aInfo.applicationInfo.uid) : 0;
if (err == ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS) {
Slog.i(TAG, "START u" + userId + " {" + intent.toShortString(true, true, true, false)
+ "} from uid " + callingUid);
}
ActivityRecord sourceRecord = null;
ActivityRecord resultRecord = null;
if (resultTo != null) {
//根据resultTo找到sourceRecord,resultTo是一个Token,sourceRecord启动者
sourceRecord = mRootWindowContainer.isInAnyTask(resultTo);
if (DEBUG_RESULTS) {
Slog.v(TAG_RESULTS, "Will send result to " + resultTo + " " + sourceRecord);
}
if (sourceRecord != null) {
//如果是startActivityForResult启动的,则对resultRecord赋值
if (requestCode >= 0 && !sourceRecord.finishing) {
resultRecord = sourceRecord;
}
}
}
final int launchFlags = intent.getFlags();
省略各种出错信息的判断代码......
//根据resultRecord找到resultRootTask
final Task resultRootTask = resultRecord == null
? null : resultRecord.getRootTask();
if (err != START_SUCCESS) {
if (resultRecord != null) {
resultRecord.sendResult(INVALID_UID, resultWho, requestCode, RESULT_CANCELED,
null /* data */, null /* dataGrants */);
}
SafeActivityOptions.abort(options);
return err;
}
省略权限判断等各种其他代码......
//构造ActivityRecord
final ActivityRecord r = new ActivityRecord.Builder(mService)
.setCaller(callerApp)
.setLaunchedFromPid(callingPid)
.setLaunchedFromUid(callingUid)
.setLaunchedFromPackage(callingPackage)
.setLaunchedFromFeature(callingFeatureId)
.setIntent(intent)
.setResolvedType(resolvedType)
.setActivityInfo(aInfo)
.setConfiguration(mService.getGlobalConfiguration())
.setResultTo(resultRecord)
.setResultWho(resultWho)
.setRequestCode(requestCode)
.setComponentSpecified(request.componentSpecified)
.setRootVoiceInteraction(voiceSession != null)
.setActivityOptions(checkedOptions)
.setSourceRecord(sourceRecord)
.build();
mLastStartActivityRecord = r;
//调用startActivityUnchecked方法开始进入下个启动
mLastStartActivityResult = startActivityUnchecked(r, sourceRecord, voiceSession,
request.voiceInteractor, startFlags, true /* doResume */, checkedOptions, inTask,
restrictedBgActivity, intentGrants);
if (request.outActivity != null) {
request.outActivity[0] = mLastStartActivityRecord;
}
return mLastStartActivityResult;
}
该方法主要做了以下工作:
在启动之前,对各种基础的异常进行检测,发现有异常则退出启动Activity流程
检测通过后构造了一个ActivityRecord实例
开始进入启动Activity的流程
构造了一个ActivityRecord实例,对这个实例初始化主要用到了以下参数:
callerApp:WindowProcessController类型,主要是启动者相关的信息
callingPid:启动者的进程id
callingUid:启动者的id,每个安装的app都会分配一个唯一的id,这个id在当前的用户空间内是不会变化的
intent:把intent存起来
aInfo:从AndroidManifest中解析出来的Activity信息
resultRecord:对于startActivityForResult启动activity时候的启动这信息,用于把返回结果返回给resultRecord
requestCode:对于startActivityForResult启动activity时候传递的值
sourceRecord:启动者,代表谁启动了Activity
ActivityRecord就把app进程要启动的Activity及相关的其他信息保存下来了,要注意这里提到的Activity和app进程中要启动的Activity是两码事。
该方法调用startActivityUnchecked方法进入启动的下个流程,调用的时候关键参数有:
r: ActivityRecord类型
sourceRecord:启动者,是一个ActivityRecord
doResume:它的值为true
options:它的值为checkedOptions,checkedOptions的值现在是为null
inTask:代表启动的Activity存放的task,当前它的值为null(因为在初始化ActivityRecord的时候就没有设置它)
?
private int startActivityUnchecked(final ActivityRecord r, ActivityRecord sourceRecord,
IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
int startFlags, boolean doResume, ActivityOptions options, Task inTask,
boolean restrictedBgActivity, NeededUriGrants intentGrants) {
int result = START_CANCELED;
final Task startedActivityRootTask;
省略代码......
try {
mService.deferWindowLayout();
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER, "startActivityInner");
[2.5]
//doResume:true,options值为null,inTask:null
result = startActivityInner(r, sourceRecord, voiceSession, voiceInteractor,
startFlags, doResume, options, inTask, restrictedBgActivity, intentGrants);
} finally {
省略代码......
}
postStartActivityProcessing(r, result, startedActivityRootTask);
return result;
}
int startActivityInner(final ActivityRecord r, ActivityRecord sourceRecord,
IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
int startFlags, boolean doResume, ActivityOptions options, Task inTask,
boolean restrictedBgActivity, NeededUriGrants intentGrants) {
//调用这个方法重置activityStarter的各种数据
setInitialState(r, options, inTask, doResume, startFlags, sourceRecord, voiceSession,
voiceInteractor, restrictedBgActivity);
//设置launchmode
computeLaunchingTaskFlags();
//查找mSourceRootTask
computeSourceRootTask();
mIntent.setFlags(mLaunchFlags);
//获取reusabletask
final Task reusedTask = getReusableTask();
省略冻结task代码......
// Compute if there is an existing task that should be used for.
//如果reusedTask为null,则调用computeTargetTask()方法获取
final Task targetTask = reusedTask != null ? reusedTask : computeTargetTask();
//newTask是否是新task
final boolean newTask = targetTask == null;
mTargetTask = targetTask;
computeLaunchParams(r, sourceRecord, targetTask);
省略代码......
//如果mTargetRootTask为null,则调用getLaunchRootTask方法会获取或者创建一个task
if (mTargetRootTask == null) {
mTargetRootTask = getLaunchRootTask(mStartActivity, mLaunchFlags, targetTask, mOptions);
}
//如果是新的task,则进行创建task流程,并且把ActivityRecord放置在task中
if (newTask) {
final Task taskToAffiliate = (mLaunchTaskBehind && mSourceRecord != null)
? mSourceRecord.getTask() : null;
setNewTask(taskToAffiliate);
} else if (mAddingToTask) {
//把ActivityRecord放置在找到的task中
addOrReparentStartingActivity(targetTask, "adding to task");
}
省略代码......
if (mDoResume) {
final ActivityRecord topTaskActivity =
mStartActivity.getTask().topRunningActivityLocked();
//不关注这块逻辑,直接看下面的else
if (!mTargetRootTask.isTopActivityFocusable()
|| (topTaskActivity != null && topTaskActivity.isTaskOverlay()
&& mStartActivity != topTaskActivity)) {
// If the activity is not focusable, we can't resume it, but still would like to
// make sure it becomes visible as it starts (this will also trigger entry
// animation). An example of this are PIP activities.
// Also, we don't want to resume activities in a task that currently has an overlay
// as the starting activity just needs to be in the visible paused state until the
// over is removed.
// Passing {@code null} as the start parameter ensures all activities are made
// visible.
mTargetRootTask.ensureActivitiesVisible(null /* starting */,
0 /* configChanges */, !PRESERVE_WINDOWS);
// Go ahead and tell window manager to execute app transition for this activity
// since the app transition will not be triggered through the resume channel.
mTargetRootTask.mDisplayContent.executeAppTransition();
} else {
// If the target root-task was not previously focusable (previous top running
// activity on that root-task was not visible) then any prior calls to move the
// root-task to the will not update the focused root-task. If starting the new
// activity now allows the task root-task to be focusable, then ensure that we
// now update the focused root-task accordingly.
//如果mTargetRootTask在mRootWindowContainer不处于focus状态,则调用mTargetRootTask.moveToFront方法把它设置为focus状态
if (mTargetRootTask.isTopActivityFocusable()
&& !mRootWindowContainer.isTopDisplayFocusedRootTask(mTargetRootTask)) {
mTargetRootTask.moveToFront("startActivityInner");
}
// 开始进入下一步的启动Activity操作
mRootWindowContainer.resumeFocusedTasksTopActivities(
mTargetRootTask, mStartActivity, mOptions, mTransientLaunch);
}
}
省略代码......
return START_SUCCESS;
}
startActivityInner方法的逻辑相对复杂,下面先简要的分析下调用的几个方法做的事情:
setInitialState方法
该方法主要对当前ActivityStarter的相关属性进行初始化,介绍下ActivityStarter的几个关键属性:
mStartActivity:代表正在启动的Activity,类型为ActivityRecord
mIntent:存放启动的其他信息
mCallingUid:启动者的uid
mSourceRecord:启动这,类型为ActivityRecord
mLaunchMode:启动模式
mLaunchFlags:启动的flags
mInTask:ActivityRecord放入的task
mNoAnimation:启动过程中是否有动画
mInTask:启动的Activity放入的task
computeLaunchingTaskFlags方法
该方法做的工作是设置mLaunchFlags,依据以下条件进行设置:
如果mSourceRecord为null并且mInTask为不null,在根据一些条件判断是否能使用mInTask(这个暂时不在这节的讨论范围)
如果不满足步骤1,则进入步骤2,把mInTask置为null
如果mInTask为null,则会有如下情况为mLaunchFlags增加FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK
3.1. mSourceRecord为null(这种情况一般发生于比如在Service中或者Broadcast中启动Activity)
3.2. mSourceRecord启动者的启动模式是LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE(singleInstance启动模式代表Activity只能处于自己单独的task中)
3.3. 正在启动的Activity的mLaunchMode是LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE, LAUNCH_SINGLE_TASK中的任意一个
computeSourceRootTask
该方法主要工作是获取mSourceRootTask,简单来介绍下rootTask和task,task不单单可以包含ActivityRecord,它还可以包含task,rootTask就是ActivityRecord的task的task的task等(直到task的parent不是task的时候就结束)
getReusableTask
这个方法的主要工作就是获取是否有可以重用的task,如果有则返回,否则返回null,大概的一个过程如下:
putIntoExistingTask的值主要由 mInTask == null && mStartActivity.resultTo == null来决定,mInTask如果不为null,肯定不需要查找可重用的task了
如果putIntoExistingTask为true,则根据一些条件获取intentActivity
在根据一些条件决定intentActivity是否置为null
如果intentActivity不为null,则把它的task返回
computeTargetTask
该方法的主要工作是获取Activity可以放入的task,分以下条件获取:
根据mInTask,mLaunchFlags,mStartActivity.resultTo,mAddingToTask判断是否需要创建新task,是的话返回null
mSourceRecord不为null的话,返回它的task
mInTask不为null,则返回它
其他情况获取task
startActivityInner方法主要做了以下事情:
根据一些条件来决定是创建一个新的task还是使用已有的task,并且把ActivityRecord放入task中
如果mDoResume为true,则最终会调用mRootWindowContainer.resumeFocusedTasksTopActivities方法进入下一步启动Activity的操作。
调用mRootWindowContainer.resumeFocusedTasksTopActivities方法,来介绍下它的参数:
targetRootTask:Task类型,它的值是mTargetRootTask,正在启动的Activity对应的ActivityRecord已经放入了这个task内
ActivityRecord: ActivityRecord类型,它的值是mStartActivity(保存了正在启动的activity等信息)
targetOptions:ActivityOptions类型,它的值为null
deferPause:代表是否延迟pause top Activity,它的值为false(mTransientLaunch默认是false)
boolean resumeFocusedTasksTopActivities(
Task targetRootTask, ActivityRecord target, ActivityOptions targetOptions,
boolean deferPause) {
if (!mTaskSupervisor.readyToResume()) {
return false;
}
boolean result = false;
//targetRootTask不为null并且targetRootTask是在DisplayArea中是最顶层的roottask,则进入下面逻辑
if (targetRootTask != null && (targetRootTask.isTopRootTaskInDisplayArea()
|| getTopDisplayFocusedRootTask() == targetRootTask)) {
[2.7]
//targetOptions为null,deferPause为false
result = targetRootTask.resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(target, targetOptions,
deferPause);
}
省略代码......
return result;
}
boolean resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(ActivityRecord prev, ActivityOptions options,
boolean deferPause) {
//正在resume top,则直接返回
if (mInResumeTopActivity) {
// Don't even start recursing.
return false;
}
boolean someActivityResumed = false;
try {
// Protect against recursion.
mInResumeTopActivity = true;
//当前的task是叶子task(就是task的孩子都是ActivityRecord),就执行下面逻辑(咱们分析这个流程)
if (isLeafTask()) {
//task是否focus并且可见
if (isFocusableAndVisible()) {
[2.8]
//prev为正在启动的Activity对应的ActivityRecord,options:null,deferPause:false
someActivityResumed = resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(prev, options, deferPause);
}
} else {
//当前的task的孩子还是task,走下面逻辑
int idx = mChildren.size() - 1;
while (idx >= 0) {
final Task child = (Task) getChildAt(idx--);
if (!child.isTopActivityFocusable()) {
continue;
}
if (child.getVisibility(null /* starting */) != TASK_VISIBILITY_VISIBLE) {
break;
}
someActivityResumed |= child.resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(prev, options,
deferPause);
// Doing so in order to prevent IndexOOB since hierarchy might changes while
// resuming activities, for example dismissing split-screen while starting
// non-resizeable activity.
if (idx >= mChildren.size()) {
idx = mChildren.size() - 1;
}
}
}
省略代码......
} finally {
mInResumeTopActivity = false;
}
return someActivityResumed;
}
private boolean resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(ActivityRecord prev, ActivityOptions options,
boolean deferPause) {
if (!mAtmService.isBooting() && !mAtmService.isBooted()) {
// Not ready yet!
return false;
}
// Find the next top-most activity to resume in this root task that is not finishing and is
// focusable. If it is not focusable, we will fall into the case below to resume the
// top activity in the next focusable task.
//next代表当前task中已经显示的Activity
ActivityRecord next = topRunningActivity(true /* focusableOnly */);
省略代码......
//deferPause的值为false
boolean pausing = !deferPause && taskDisplayArea.pauseBackTasks(next);
//mResumedActivity代表当前task中已经显示的Activity,若不为null,说明在启动其他Activity的时候,需要让mResumedActivity进入pause状态
if (mResumedActivity != null) {
ProtoLog.d(WM_DEBUG_STATES, "resumeTopActivityLocked: Pausing %s", mResumedActivity);
//下面方法会让mResumedActivity进入pause状态,为启动新的Activity做准备
pausing |= startPausingLocked(false /* uiSleeping */, next,
"resumeTopActivityInnerLocked");
}
//如果mResumedActivity正在处于pausing状态,进入下面的逻辑
if (pausing) {
ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_STATES, "resumeTopActivityLocked: Skip resume: need to"
+ " start pausing");
// At this point we want to put the upcoming activity's process
// at the top of the LRU list, since we know we will be needing it
// very soon and it would be a waste to let it get killed if it
// happens to be sitting towards the end.
//next.attachedToProcess()为true,代表next已经启动过了,则更新它的进程等信息
if (next.attachedToProcess()) {
next.app.updateProcessInfo(false /* updateServiceConnectionActivities */,
true /* activityChange */, false /* updateOomAdj */,
false /* addPendingTopUid */);
} else if (!next.isProcessRunning()) {
// Since the start-process is asynchronous, if we already know the process of next
// activity isn't running, we can start the process earlier to save the time to wait
// for the current activity to be paused.
final boolean isTop = this == taskDisplayArea.getFocusedRootTask();
//next.isProcessRunning()为false,代表启动的activity的进程还没被启动,乘mResumedActivity处于pausing的状态,去异步启动进程
mAtmService.startProcessAsync(next, false /* knownToBeDead */, isTop,
isTop ? "pre-top-activity" : "pre-activity");
}
if (lastResumed != null) {
lastResumed.setWillCloseOrEnterPip(true);
}
return true;
} else if (mResumedActivity == next && next.isState(RESUMED)
&& taskDisplayArea.allResumedActivitiesComplete()) {
// It is possible for the activity to be resumed when we paused back stacks above if the
// next activity doesn't have to wait for pause to complete.
// So, nothing else to-do except:
// Make sure we have executed any pending transitions, since there
// should be nothing left to do at this point.
executeAppTransition(options);
ProtoLog.d(WM_DEBUG_STATES, "resumeTopActivityLocked: Top activity resumed "
+ "(dontWaitForPause) %s", next);
return true;
}
省略代码......
//next.attachedToProcess()为true,代表next已经启动过了,执行下面的逻辑,会把让Activity进入resume状态
if (next.attachedToProcess()) {
省略代码......
try {
final ClientTransaction transaction =
ClientTransaction.obtain(next.app.getThread(), next.appToken);
// Deliver all pending results.
ArrayList<ResultInfo> a = next.results;
//a代表从上个Activity是否返回了一些数据
if (a != null) {
final int N = a.size();
if (!next.finishing && N > 0) {
if (DEBUG_RESULTS) Slog.v(TAG_RESULTS,
"Delivering results to " + next + ": " + a);
//从上个Activity返回了数据,则给transaction add一个ActivityResultItem
transaction.addCallback(ActivityResultItem.obtain(a));
}
}
if (next.newIntents != null) {
//若存在newIntents,则add 一个NewIntentItem,这种情况针对的Activity的启动模式是singleTask,singleInstance,singleTop
transaction.addCallback(
NewIntentItem.obtain(next.newIntents, true /* resume */));
}
// Well the app will no longer be stopped.
// Clear app token stopped state in window manager if needed.
next.notifyAppResumed(next.stopped);
EventLogTags.writeWmResumeActivity(next.mUserId, System.identityHashCode(next),
next.getTask().mTaskId, next.shortComponentName);
mAtmService.getAppWarningsLocked().onResumeActivity(next);
next.app.setPendingUiCleanAndForceProcessStateUpTo(mAtmService.mTopProcessState);
next.abortAndClearOptionsAnimation();
//通知Activity进入resume状态
transaction.setLifecycleStateRequest(
ResumeActivityItem.obtain(next.app.getReportedProcState(),
dc.isNextTransitionForward()));
mAtmService.getLifecycleManager().scheduleTransaction(transaction);
ProtoLog.d(WM_DEBUG_STATES, "resumeTopActivityLocked: Resumed %s", next);
} catch (Exception e) {
省略代码......
return true;
}
省略代码......
} else {
省略代码......
//Activity需要从onCreate方法开始执行
mTaskSupervisor.startSpecificActivity(next, true, true);
}
return true;
}
resumeTopActivityInnerLocked方法的逻辑相对复杂,下面就来介绍下它主要做的事情:
如果正在显示的Activity(mResumedActivity)存在,则需要让它进入pause状态(最终会把这个消息通知到app对应的Activity)
如果正在显示的Activity已处于pausing状态,这时候需要分情况来处理:
2.1 若正在启动的Activity(next)之前已经启动过了,则需要更新它对应的进程状态
2.2 若正在启动的Activity的进程还没有启动,这时候异步启动进程的操作
接着暂停启动Activity的操作,直接返回。那什么时候继续开始启动Activity呢?答案是:当mResumedActivity对应的app端的Activity完全的进入pause状态后,才会接着继续启动Activity。
并且可以借助等待pause完毕的这个时机,更新进程状态或者异步启动进程
如果正在启动的Activity(next)已经启动过了(next.attachedToProcess()这值为true),则会走下面逻辑:
3.1 若从上个Activity返回了数据,则把数据返回给app端的Activity(onActivityForResult方法会被调用)
3.2 若存在newIntents,则把intent返回给app端的Activity(onNewIntent方法会被调用),这种情况针对的Activity的启动模式是singleTask,singleInstance,singleTop
通知app端Activity进入resume状态(onResume方法会被调用)
否则,调用mTaskSupervisor.startSpecificActivity正真进入Activity的启动流程
到这为止的时序图
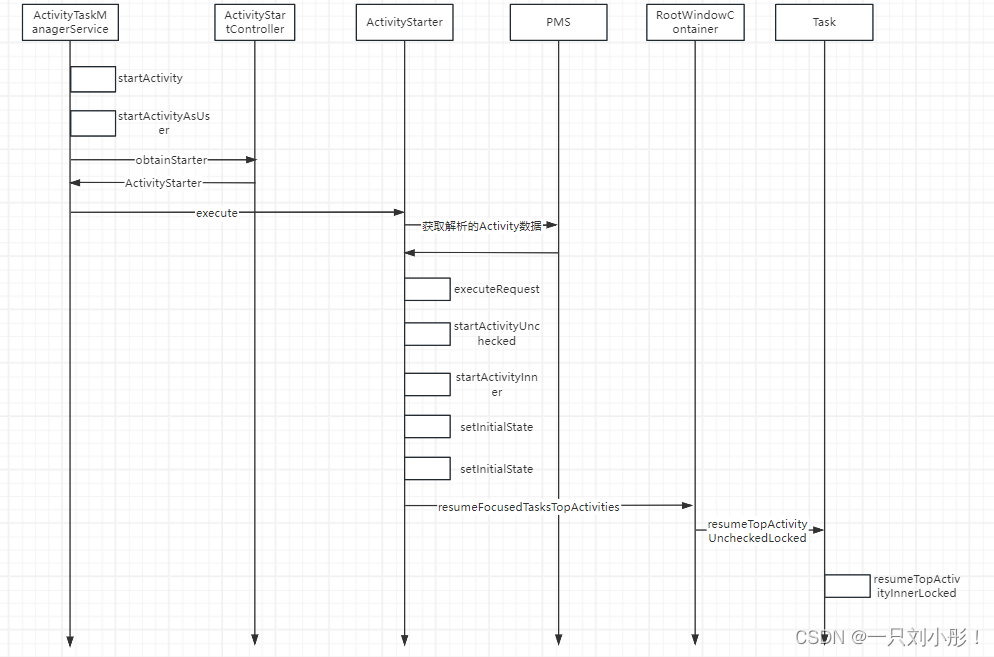
接下来
//r:正在启动的Activity,andResume:当前值为true,checkConfig:当前值true
void startSpecificActivity(ActivityRecord r, boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) {
// Is this activity's application already running?
final WindowProcessController wpc =
mService.getProcessController(r.processName, r.info.applicationInfo.uid);
boolean knownToBeDead = false;
//对应的app进程是否启动,启动则进入下面逻辑
if (wpc != null && wpc.hasThread()) {
try {
[2.10]
realStartActivityLocked(r, wpc, andResume, checkConfig);
return;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when starting activity "
+ r.intent.getComponent().flattenToShortString(), e);
}
// If a dead object exception was thrown -- fall through to
// restart the application.
knownToBeDead = true;
}
r.notifyUnknownVisibilityLaunchedForKeyguardTransition();
final boolean isTop = andResume && r.isTopRunningActivity();
//异步启动进程
mService.startProcessAsync(r, knownToBeDead, isTop, isTop ? "top-activity" : "activity");
}
//r:正在启动的Activity,proc:对应的进程,andResume:true,checkConfig:true
boolean realStartActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, WindowProcessController proc,
boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) throws RemoteException {
if (!mRootWindowContainer.allPausedActivitiesComplete()) {
// While there are activities pausing we skipping starting any new activities until
// pauses are complete. NOTE: that we also do this for activities that are starting in
// the paused state because they will first be resumed then paused on the client side.
ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_STATES,
"realStartActivityLocked: Skipping start of r=%s some activities pausing...",
r);
return false;
}
final Task task = r.getTask();
final Task rootTask = task.getRootTask();
beginDeferResume();
// The LaunchActivityItem also contains process configuration, so the configuration change
// from WindowProcessController#setProcess can be deferred. The major reason is that if
// the activity has FixedRotationAdjustments, it needs to be applied with configuration.
// In general, this reduces a binder transaction if process configuration is changed.
proc.pauseConfigurationDispatch();
try {
r.startFreezingScreenLocked(proc, 0);
// schedule launch ticks to collect information about slow apps.
r.startLaunchTickingLocked();
//设置了proc后,r.attachedToProcess()的值就为true
r.setProcess(proc);
// Ensure activity is allowed to be resumed after process has set.
if (andResume && !r.canResumeByCompat()) {
andResume = false;
}
省略代码......
try {
//proc.hasThread()代表app端是否活着
if (!proc.hasThread()) {
throw new RemoteException();
}
List<ResultInfo> results = null;
List<ReferrerIntent> newIntents = null;
if (andResume) {
// We don't need to deliver new intents and/or set results if activity is going
// to pause immediately after launch.
results = r.results;
newIntents = r.newIntents;
}
if (DEBUG_SWITCH) Slog.v(TAG_SWITCH,
"Launching: " + r + " savedState=" + r.getSavedState()
+ " with results=" + results + " newIntents=" + newIntents
+ " andResume=" + andResume);
EventLogTags.writeWmRestartActivity(r.mUserId, System.identityHashCode(r),
task.mTaskId, r.shortComponentName);
if (r.isActivityTypeHome()) {
// Home process is the root process of the task.
updateHomeProcess(task.getBottomMostActivity().app);
}
mService.getPackageManagerInternalLocked().notifyPackageUse(
r.intent.getComponent().getPackageName(), NOTIFY_PACKAGE_USE_ACTIVITY);
r.forceNewConfig = false;
mService.getAppWarningsLocked().onStartActivity(r);
r.compat = mService.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.info.applicationInfo);
// Because we could be starting an Activity in the system process this may not go
// across a Binder interface which would create a new Configuration. Consequently
// we have to always create a new Configuration here.
final Configuration procConfig = proc.prepareConfigurationForLaunchingActivity();
final MergedConfiguration mergedConfiguration = new MergedConfiguration(
procConfig, r.getMergedOverrideConfiguration());
r.setLastReportedConfiguration(mergedConfiguration);
logIfTransactionTooLarge(r.intent, r.getSavedState());
if (r.isEmbedded()) {
// Sending TaskFragmentInfo to client to ensure the info is updated before
// the activity creation.
mService.mTaskFragmentOrganizerController.dispatchPendingInfoChangedEvent(
r.getOrganizedTaskFragment());
}
// Create activity launch transaction.
//ClientTransaction主要用于添加各种callback以及Activity要执行的生命周期方法,它会通过binder传递到app进程
//proc.getThread()获取的是IApplicationThread的实例,主要通过它给app发送消息,r.appToken发送给app的token
final ClientTransaction clientTransaction = ClientTransaction.obtain(
proc.getThread(), r.appToken);
final boolean isTransitionForward = r.isTransitionForward();
//add一个LaunchActivityItem类型的callback
clientTransaction.addCallback(LaunchActivityItem.obtain(new Intent(r.intent),
System.identityHashCode(r), r.info,
// TODO: Have this take the merged configuration instead of separate global
// and override configs.
mergedConfiguration.getGlobalConfiguration(),
mergedConfiguration.getOverrideConfiguration(), r.compat,
r.getFilteredReferrer(r.launchedFromPackage), task.voiceInteractor,
proc.getReportedProcState(), r.getSavedState(), r.getPersistentSavedState(),
results, newIntents, r.takeOptions(), isTransitionForward,
proc.createProfilerInfoIfNeeded(), r.assistToken, activityClientController,
r.createFixedRotationAdjustmentsIfNeeded(), r.shareableActivityToken,
r.getLaunchedFromBubble()));
// Set desired final state.
final ActivityLifecycleItem lifecycleItem;
if (andResume) {
//因为andResume为true,进入这,构造一个ResumeActivityItem实例,Activity的onResume方法被执行
lifecycleItem = ResumeActivityItem.obtain(isTransitionForward);
} else {
//否则构造一个PauseActivityItem实例,Activity的onPause方法会被执行
lifecycleItem = PauseActivityItem.obtain();
}
clientTransaction.setLifecycleStateRequest(lifecycleItem);
// Schedule transaction.
//clientTransaction会被传递到app进程
mService.getLifecycleManager().scheduleTransaction(clientTransaction);
省略代码......
} catch (RemoteException e) {
省略代码......
}
} finally {
endDeferResume();
proc.resumeConfigurationDispatch();
}
r.launchFailed = false;
省略代码......
return true;
}
该方法主要做的事情是把各种数据整理收集好后,通过binder发送到app进程,那就来看下这个过程:
1.获取一个ClientTransaction实例
通过ClientTransaction.obtain方法获取一个ClientTransaction实例,为了避免浪费内存从缓存池中获取,ClientTransaction代表要传递给app的事务,它可以包含多个callback和一个lifecycleStateRequest。
来介绍下ClientTransaction.obtain这个方法它的参数:
client:IApplicationThread类型,AMS通过它把消息发送给app,它的值是proc.getThread()
activityToken:IBinder类型,它的值是r.appToken。AMS并没有把ActiviityRecord传递给app(传过去不安全),而是把ActiviityRecord的appToken传递过去,简单看下这个appToken
static class Token extends IApplicationToken.Stub {
private WeakReference<ActivityRecord> weakActivity;
private final String name;
private final String tokenString;
Token(Intent intent) {
name = intent.getComponent().flattenToShortString();
tokenString = "Token{" + Integer.toHexString(System.identityHashCode(this)) + "}";
}
private void attach(ActivityRecord activity) {
if (weakActivity != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Already attached..." + this);
}
weakActivity = new WeakReference<>(activity);
}
private static @Nullable ActivityRecord tokenToActivityRecordLocked(Token token) {
if (token == null) {
return null;
}
ActivityRecord r = token.weakActivity.get();
if (r == null || r.getRootTask() == null) {
return null;
}
return r;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(128);
sb.append("Token{");
sb.append(Integer.toHexString(System.identityHashCode(this)));
sb.append(' ');
if (weakActivity != null) {
sb.append(weakActivity.get());
}
sb.append('}');
return sb.toString();
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}ActivityRecord的appToken是一个类型为Token的实例。Token它继承了IApplicationToken.Stub说明它是一个IBinder类型,它用弱引用的方式持有ActivityRecord,appToken作为一个“令牌”被传递到app进程,就是告诉app,我给了你一个token,如果想给我发送消息,就带上这个token,我就能通过token找到ActivityRecord了(tokenToActivityRecordLocked方法)
最后把clientTransaction发送给app
调用mService.getLifecycleManager().scheduleTransaction(clientTransaction)方法把clientTransaction发送到app端那么如何发送的?
public class ClientTransaction implements Parcelable, ObjectPoolItem {
省略
进行传递
public void schedule() throws RemoteException {
mClient.scheduleTransaction(this);
}
省略
/** Obtain an instance initialized with provided params. */
这里会将app的 IApplicationThread 对象传进来
public static ClientTransaction obtain(IApplicationThread client, IBinder activityToken) {
ClientTransaction instance = ObjectPool.obtain(ClientTransaction.class);
if (instance == null) {
instance = new ClientTransaction();
}
instance.mClient = client;
instance.mActivityToken = activityToken;
return instance;
}
}该段时序图如下?
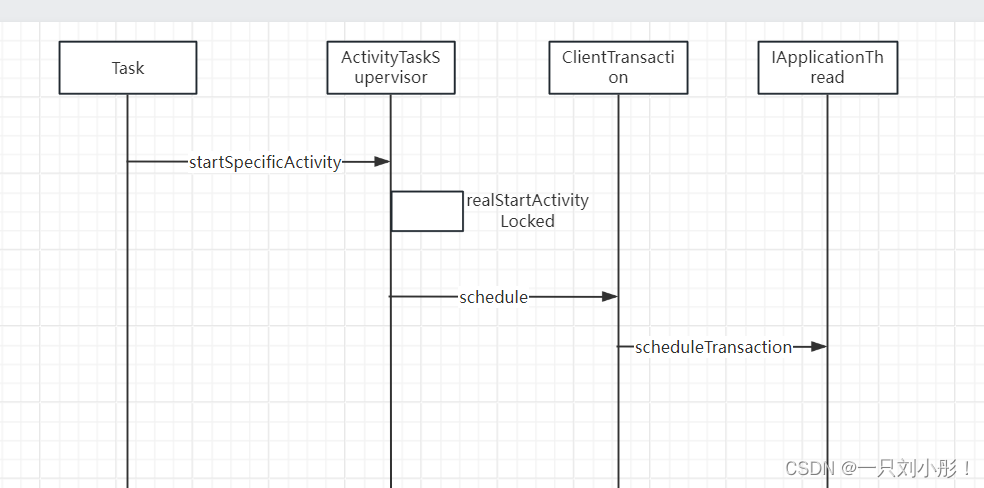
@Override
public Activity handleLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r,
PendingTransactionActions pendingActions, Intent customIntent) {
省略代码......
WindowManagerGlobal.initialize();
// Hint the GraphicsEnvironment that an activity is launching on the process.
GraphicsEnvironment.hintActivityLaunch();
//开始启动Activity
[3.5]
final Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent);
省略代码......
return a;
}
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
ActivityInfo aInfo = r.activityInfo;
if (r.packageInfo == null) {
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfo(aInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo,
Context.CONTEXT_INCLUDE_CODE);
}
//ComponentName封装了mPackage和mClass,component是真正Activity的对应的信息,先从r.intent.getComponent()获取
ComponentName component = r.intent.getComponent();
if (component == null) {
//没获取到从PMS中去解析
component = r.intent.resolveActivity(
mInitialApplication.getPackageManager());
r.intent.setComponent(component);
}
//如果targetActivity存在,则从targetActivity获取
if (r.activityInfo.targetActivity != null) {
component = new ComponentName(r.activityInfo.packageName,
r.activityInfo.targetActivity);
}
//初始化appContext它的类型是ContextImpl,像Activity调用到的Context的方法最终都是通过ContextImpl来实现的
ContextImpl appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r);
Activity activity = null;
try {
//获取ClassLoader,来加载Activity
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = appContext.getClassLoader();
//mInstrumentation.newActivity方法中通过反射来实例化一个Activity
activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(
cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
StrictMode.incrementExpectedActivityCount(activity.getClass());
r.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(cl);
r.intent.prepareToEnterProcess(isProtectedComponent(r.activityInfo),
appContext.getAttributionSource());
if (r.state != null) {
r.state.setClassLoader(cl);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate activity " + component
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
try {
//尝试去make Application(一般情况下都已经创建成功了),如果存在直接返回
Application app = r.packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Performing launch of " + r);
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(
TAG, r + ": app=" + app
+ ", appName=" + app.getPackageName()
+ ", pkg=" + r.packageInfo.getPackageName()
+ ", comp=" + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString()
+ ", dir=" + r.packageInfo.getAppDir());
if (activity != null) {
CharSequence title = r.activityInfo.loadLabel(appContext.getPackageManager());
Configuration config =
new Configuration(mConfigurationController.getCompatConfiguration());
if (r.overrideConfig != null) {
config.updateFrom(r.overrideConfig);
}
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Launching activity "
+ r.activityInfo.name + " with config " + config);
Window window = null;
if (r.mPendingRemoveWindow != null && r.mPreserveWindow) {
window = r.mPendingRemoveWindow;
r.mPendingRemoveWindow = null;
r.mPendingRemoveWindowManager = null;
}
// Activity resources must be initialized with the same loaders as the
// application context.
appContext.getResources().addLoaders(
app.getResources().getLoaders().toArray(new ResourcesLoader[0]));
appContext.setOuterContext(activity);
//attach方法把各种数据传递给activity
activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token,
r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent,
r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config,
r.referrer, r.voiceInteractor, window, r.configCallback,
r.assistToken, r.shareableActivityToken);
if (customIntent != null) {
activity.mIntent = customIntent;
}
r.lastNonConfigurationInstances = null;
checkAndBlockForNetworkAccess();
activity.mStartedActivity = false;
int theme = r.activityInfo.getThemeResource();
if (theme != 0) {
activity.setTheme(theme);
}
if (r.mActivityOptions != null) {
activity.mPendingOptions = r.mActivityOptions;
r.mActivityOptions = null;
}
activity.mLaunchedFromBubble = r.mLaunchedFromBubble;
activity.mCalled = false;
//下面是根据r.isPersistable(),分别调用Activity的onCreate方法
if (r.isPersistable()) {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state, r.persistentState);
} else {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state);
}
//如果自己实现的Activity的onCreate方法没有调用父类的onCreate方法,则抛异常
if (!activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
" did not call through to super.onCreate()");
}
r.activity = activity;
mLastReportedWindowingMode.put(activity.getActivityToken(),
config.windowConfiguration.getWindowingMode());
}
r.setState(ON_CREATE);
// updatePendingActivityConfiguration() reads from mActivities to update
// ActivityClientRecord which runs in a different thread. Protect modifications to
// mActivities to avoid race.
synchronized (mResourcesManager) {
//AMS传递过来的token作为key,r作为value存放在mActivities中
mActivities.put(r.token, r);
}
} catch (SuperNotCalledException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to start activity " + component
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
return activity;
}
该方法是启动Activity的核心方法主要做了以下几件事:
获取到ComponentName,它包含了真正Activity的包名,class信息
使用ClassLoader,通过反射对第1步的类进行实例化,会实例化一个Activity
尝试创建/获取Application的实例
通过Activity的attach方法把各种信息传递给它
调用Activity的onCreate方法
AMS传递过来的token作为key,r作为value存放在mActivities中(这样通过tokenActivityRecord和ActivityClientRecord就建立了关系)
最后分析下mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate这个方法
?
final void performCreate(Bundle icicle) {
performCreate(icicle, null);
}
@UnsupportedAppUsage(maxTargetSdk = Build.VERSION_CODES.R, trackingBug = 170729553)
final void performCreate(Bundle icicle, PersistableBundle persistentState) {
if (Trace.isTagEnabled(Trace.TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER)) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER, "performCreate:"
+ mComponent.getClassName());
}
dispatchActivityPreCreated(icicle);
mCanEnterPictureInPicture = true;
// initialize mIsInMultiWindowMode and mIsInPictureInPictureMode before onCreate
final int windowingMode = getResources().getConfiguration().windowConfiguration
.getWindowingMode();
mIsInMultiWindowMode = inMultiWindowMode(windowingMode);
mIsInPictureInPictureMode = windowingMode == WINDOWING_MODE_PINNED;
restoreHasCurrentPermissionRequest(icicle);
//onCreate方法被调用
if (persistentState != null) {
onCreate(icicle, persistentState);
} else {
onCreate(icicle);
}
EventLogTags.writeWmOnCreateCalled(mIdent, getComponentName().getClassName(),
"performCreate");
mActivityTransitionState.readState(icicle);
mVisibleFromClient = !mWindow.getWindowStyle().getBoolean(
com.android.internal.R.styleable.Window_windowNoDisplay, false);
mFragments.dispatchActivityCreated();
mActivityTransitionState.setEnterActivityOptions(this, getActivityOptions());
dispatchActivityPostCreated(icicle);
到此Activity的onCreate方法被调用,因为clientTransaction.setLifecycleStateRequest(lifecycleItem),lifecycleItem是ResumeActivityItem类型,Activity的onResume方法也会被调用,这个流程就不分析了.
借鉴的原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/niurenwo/article/details/127896874
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!