使用Guava轻松创建和管理不可变集合
第1章:引言
大家好,我是小黑。今天,我们来聊聊一个在Java编程里超有用的话题:使用Guava创建和管理不可变集合。首先,咱们得明白,什么是不可变集合。简单来说,不可变集合就是一旦创建就不能被修改的集合。
为啥要用不可变集合呢?想象一下,你写了一段代码,把一个集合传给了别的方法。如果那个方法不小心改了你的集合,那岂不是一场灾难?但如果你的集合是不可变的,这种情况就绝对不会发生。不可变集合还有助于编写更加清晰、更容易维护的代码,还能提高程序的性能哦。
第2章:Guava不可变集合简介
Guava是Google推出的一个Java库,里面有一堆好用的工具类,其中就包括了不可变集合。Guava的不可变集合和咱们平时用的Java标准库集合有啥不同呢?主要是Guava的集合一旦创建,就不能被修改,这就大大减少了出错的可能性。
来,让我给你演示一下怎么用Guava创建不可变集合。比如说,咱们要创建一个不可变的列表:
import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList;
public class ImmutableDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ImmutableList<String> immutableList = ImmutableList.of("Apple", "Banana", "Cherry");
System.out.println(immutableList);
}
}
这段代码创建了一个包含三种水果名称的不可变列表。你看,使用ImmutableList.of就能轻松创建。这样一来,无论谁拿到这个列表,都不能添加、删除或者修改里面的元素。
同理,不可变的集合(Set)和映射(Map)也可以用类似的方式创建。只要记住,一旦创建,就不能更改了。这样的特性在很多场景下都非常实用,比如在多线程环境下,不可变集合可以保证数据的安全性,防止出现并发修改异常。
第3章:创建不可变集合
让我们来看看不可变列表(ImmutableList)的创建。咱们已经看过最基本的创建方式了,现在再来看点高级的:
import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList;
public class ImmutableListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个不可变列表
ImmutableList<String> immutableList = ImmutableList.<String>builder()
.add("Apple")
.add("Banana")
.add("Cherry")
.build();
System.out.println(immutableList);
}
}
在这个例子中,小黑用了ImmutableList.builder()方法。这个方法特别棒,因为它可以让咱们一步步地添加元素,最后再用build()方法一次性创建不可变列表。
接下来,看看不可变集(ImmutableSet)的创建:
import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableSet;
public class ImmutableSetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个不可变集
ImmutableSet<String> immutableSet = ImmutableSet.of("Apple", "Banana", "Cherry");
System.out.println(immutableSet);
}
}
ImmutableSet.of()方法和列表的创建很像,也是一次性把所有元素传进去。
我们来看看不可变映射(ImmutableMap)的创建:
import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableMap;
public class ImmutableMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个不可变映射
ImmutableMap<String, Integer> immutableMap = ImmutableMap.of("Apple", 1, "Banana", 2, "Cherry", 3);
System.out.println(immutableMap);
}
}
在这个例子中,ImmutableMap.of()方法是用键值对的方式来创建映射的。这里,“Apple”是键,1是它的值,以此类推。
第4章:不可变集合的优势
安全性
首先是安全性。不可变对象是线程安全的,这意味着在多线程环境中,你完全不需要担心并发修改的问题。因为数据一旦创建就不会改变,所以不会出现线程间的冲突。这在编写并发程序时特别有用。
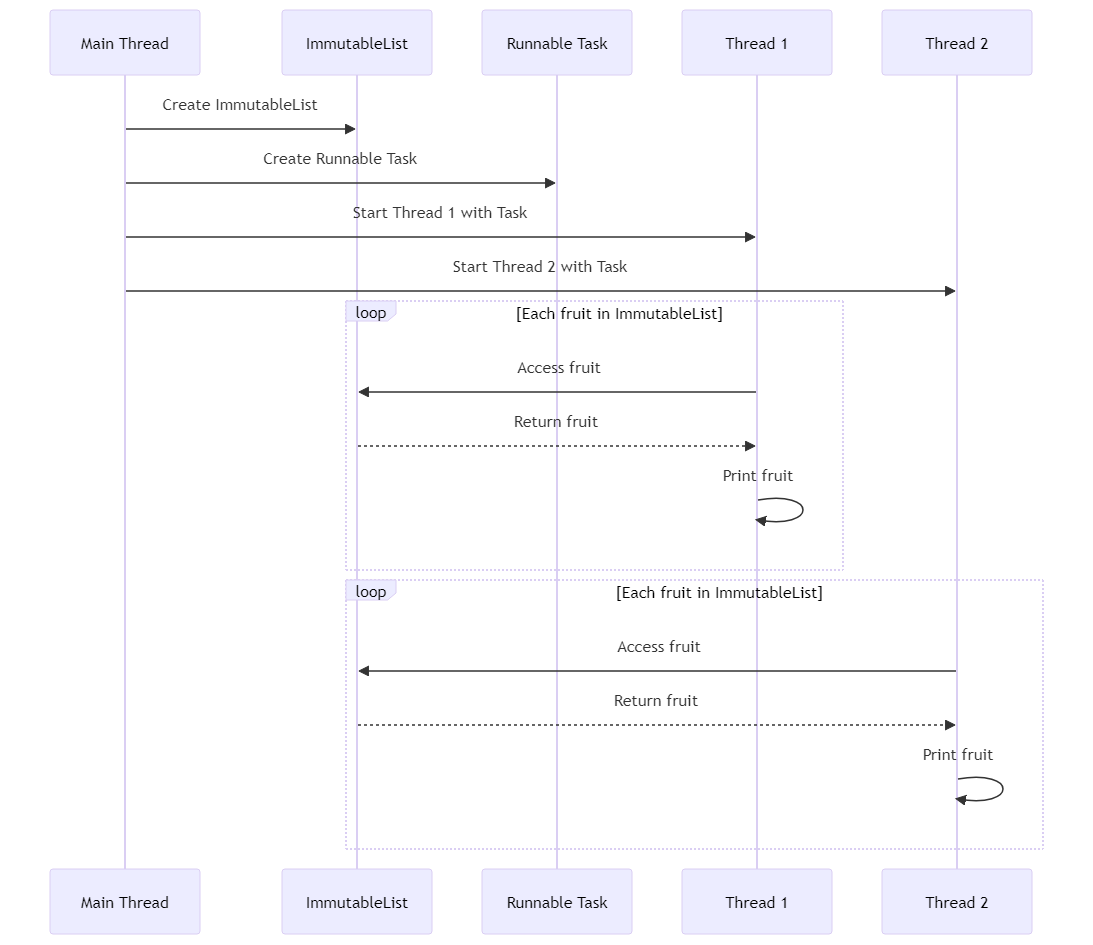
举个例子吧,假设有这样一个场景:
public class ThreadSafetyDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ImmutableList<String> immutableList = ImmutableList.of("Apple", "Banana", "Cherry");
// 多线程环境下访问不可变列表
Runnable task = () -> {
for (String fruit : immutableList) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " - " + fruit);
}
};
new Thread(task).start();
new Thread(task).start();
}
}
在这个例子中,即使多个线程同时访问immutableList,也不会引发任何问题,因为它是不可变的。
效率
接下来谈谈效率。不可变对象由于状态不变,可以减少内存的占用,因为它们可以被自由地共享。这就意味着在一定条件下,不可变集合比可变集合更加内存高效。
可读性
不可变集合还能提高代码的可读性和维护性。当你看到一个集合是不可变的,你就可以立即确定这个集合在整个生命周期内都不会改变。这就减少了理解和维护代码的复杂性。
使用Guava的不可变集合可以带来很多好处,特别是在处理安全性、效率和可读性方面。虽然它们在某些情况下可能有些限制,但在正确的场景下使用,绝对可以帮助你写出更优雅、更稳定的Java代码。
第5章:使用场景与最佳实践
使用场景
-
常量集合:当你想定义一些永远不变的数据,比如配置项、选项列表等,不可变集合是最佳选择。它们可以公开访问而不用担心被意外修改。
public class Constants { public static final ImmutableList<String> FRUITS = ImmutableList.of("Apple", "Banana", "Cherry"); // 其他常量... } -
类内部状态:在创建类时,使用不可变集合来保存内部状态可以确保类的实例一旦创建就保持不变,这对于创建不可变类(immutable class)非常有用。
public class UserPreferences { private final ImmutableSet<String> preferences; public UserPreferences(Set<String> preferences) { this.preferences = ImmutableSet.copyOf(preferences); } // Getter方法... } -
函数返回值:当函数需要返回集合时,使用不可变集合作为返回类型可以确保调用者不会修改这个集合,从而保证了数据的完整性。
public class ProductService { public ImmutableList<Product> getAvailableProducts() { // 查询并返回产品列表 } }
最佳实践
-
避免预期外的修改:使用不可变集合可以防止调用者意外修改集合内容,从而导致难以追踪的bug。
-
提前拷贝:当从可变集合创建不可变集合时,应当在创建时就进行拷贝,以确保不可变集合的独立性。
public class ConfigLoader { public ImmutableSet<String> loadConfig(Set<String> mutableSet) { return ImmutableSet.copyOf(mutableSet); } } -
在构造函数中使用不可变集合:当创建对象时,可以使用Guava的不可变集合作为构造函数参数,这样可以在对象创建时就确保其不可变性。
public class Employee { private final ImmutableList<String> skills; public Employee(List<String> skills) { this.skills = ImmutableList.copyOf(skills); } // Getter方法... }
第6章:与Java 8及以后版本的整合
利用Streams处理不可变集合
Java 8的Streams API可以和Guava的不可变集合无缝合作。比如说,你可以轻松地将一个不可变集合转换成Stream,进行各种操作,然后再收集回不可变集合。
import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class StreamIntegrationDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ImmutableList<String> immutableList = ImmutableList.of("Apple", "Banana", "Cherry");
// 使用Stream API处理Guava不可变集合
ImmutableList<String> processedList = immutableList.stream()
.filter(s -> s.startsWith("B"))
.collect(ImmutableList.toImmutableList());
System.out.println(processedList);
}
}
在这个例子里,小黑先把一个不可变列表转换成了Stream,然后用filter方法筛选出以"B"开头的元素,最后再收集回一个不可变列表。这就是Java 8 Stream和Guava不可变集合强强联合的例子。
使用Lambda表达式
Java 8的Lambda表达式也可以和Guava的不可变集合很好地结合。它们可以使得对集合的操作更加简洁。
import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList;
public class LambdaIntegrationDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ImmutableList<String> immutableList = ImmutableList.of("Apple", "Banana", "Cherry");
// 使用Lambda表达式遍历不可变集合
immutableList.forEach(fruit -> System.out.println("Fruit: " + fruit));
}
}
在这个例子中,咱们使用了forEach方法和Lambda表达式来遍历不可变集合。这种方式比传统的for循环更简洁,更易读。
Guava的不可变集合与Java 8及以后版本的特性相结合,可以提供更强大的数据处理能力,同时让代码变得更加简洁和易于理解。
第7章:避免常见陷阱
不可变集合不等于只读集合
首先要清楚,Guava的不可变集合和只读集合不是一回事。不可变集合是在创建时就确定了内容,而只读集合只是不能修改,其底层数据可能被其他引用修改。看个例子:
import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class ImmutableVsReadOnly {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("Apple");
list.add("Banana");
// 创建只读集合
List<String> readOnlyList = Collections.unmodifiableList(list);
// 创建不可变集合
ImmutableList<String> immutableList = ImmutableList.copyOf(list);
// 修改原始列表
list.add("Cherry");
// 只读集合的内容发生了变化
System.out.println("Read-only list: " + readOnlyList);
// 不可变集合的内容没变
System.out.println("Immutable list: " + immutableList);
}
}
这个例子展示了只读集合和不可变集合的区别。当原始集合修改时,只读集合的内容也会跟着变,但不可变集合的内容不会变。
注意构建时的副作用
在使用ImmutableList.builder()或类似的构建器时,要注意不要引入副作用。比如,不要在添加元素的过程中修改这些元素。
// 错误示范:在构建不可变集合时修改元素
ImmutableList.Builder<String> builder = ImmutableList.builder();
for (String fruit : fruits) {
modifyFruit(fruit); // 不应在这里修改fruit
builder.add(fruit);
}
小心空指针异常
Guava的不可变集合在创建时会对元素进行非空校验,这意味着如果你试图添加一个null元素,它会立即抛出NullPointerException。
// 这将抛出NullPointerException
ImmutableList<String> list = ImmutableList.of("Apple", null, "Cherry");
第8章:总结
选择不可变集合不仅仅是为了编码的方便,更重要的是它们提供了额外的安全性、效率和可维护性。在多线程环境下,不可变集合几乎是必不可少的,因为它们天生就是线程安全的。此外,它们还能帮助减少bug和意外行为,尤其是在大型和复杂的项目中。
要注意,在某些情况下,使用不可变集合可能会有性能开销,特别是在需要频繁修改集合的场景中。因此,选择合适的数据结构和集合类型对于任何项目都至关重要。
希望这篇博客能够帮助你更好地理解Guava的不可变集合,让你在Java编程的道路上更进一步。如果你有任何问题或者想深入讨论,欢迎在评论区留言,小黑很乐意和你一起探讨和学习!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 浅谈AcrelEMS-CIA机场智慧能源管平台解决方案-安科瑞 蒋静
- 生信技能34 - 通过UCSC单条染色体Fasta序列构建hg19参考序列及其索引
- 一文读懂SSL证书
- 集合框架(Set Map List)
- 原码、反码、补码、移码
- 获取 jira filter issue count 方法
- Qt 中文处理
- Android 10.0 系统语言随sim卡语言自适应变化功能实现
- k-Wave仿真例程:对圆形换能器记录的光声波场进行时间反转重建
- VUE中的8种常规通信方式