Spring中常见的BeanFactory后处理器
发布时间:2023年12月26日
常见的BeanFacatory后处理器
先给出没有添加任何BeanFactory后处理器的测试代码
public class TestBeanFactoryPostProcessor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();
context.registerBean("config", Config.class);
context.refresh();
for (String beanDefinitionName : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(beanDefinitionName);
}
context.close();
}
}在配置类中我们编写了如下信息
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.zmt.test5")
public class Config {
@Bean
public Bean2 bean2(){
return new Bean2();
}
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean(DataSource dataSource){
SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);
return sqlSessionFactoryBean;
}
@Bean
public DruidDataSource dataSource(){
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("123456");
return dataSource;
}
}同时还有一个Bean1添加了@Component注解并且能够被扫描到,所以理论上来讲,我们可以观察到五个beanName,那么执行测试代码观察输出结果
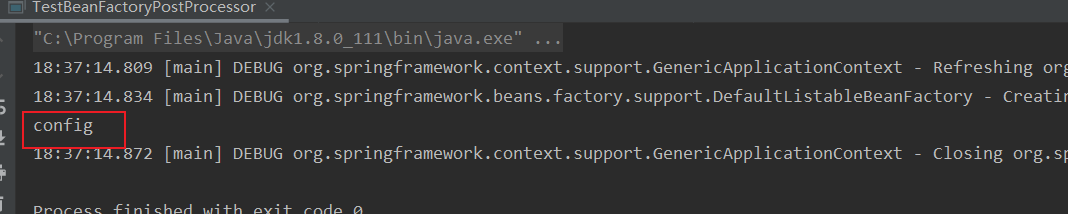
可以看到,这里只输出了一个beanName,我们可以推测出其他注解没有生效,那么接下来我们将常用的BeanFactory后处理器也注册到BeanFactory后,观察输出结果
public class TestBeanFactoryPostProcessor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();
context.registerBean("config", Config.class);
//添加BeanFactory后处理器
context.registerBean(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);//用来解析 @ComponentScan @Bean @Import @ImportResource注解
context.registerBean(MapperScannerConfigurer.class,bd -> {
bd.getPropertyValues().add("basePackage","com.zmt.test.mapper");
});//扫描Mapper,相当于@MapperScan注解
context.refresh();
for (String beanDefinitionName : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(beanDefinitionName);
}
context.close();
}
}添加Spring提供的BeanFactory后处理器之后,可以正常将Bean对象添加到context容器当中了,执行结果如下

接下来我们模拟实现在BeanFactory后处理器当中具体如何解析这些注解。?
模拟实现组件扫描
首先是模拟实现@ComponentScan注解是如何扫描包,获取类资源的
public class TestBeanFactoryPostProcessor {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();
context.registerBean("config", Config.class);
//模拟ConfigurationPostProcessor处理器中如何解析@ComponentScan注解
ComponentScan componentScan = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(Config.class, ComponentScan.class);
if (componentScan != null) {
for (String s : componentScan.basePackages()) {
//将com.zmt.test5.bean转化格式为classpath*:com/zmt/test5/bean/**/*.class
String path = "classpath*:"+s.replace(".", "/")+"/**/*.class";
//创建出一个元数据读取工厂,用来读取类资源信息
CachingMetadataReaderFactory factory = new CachingMetadataReaderFactory();
//通过getResource方法获取到path中的所有类资源
Resource[] resources = context.getResources(path);
for (Resource resource : resources) {
//读取类资源信息
MetadataReader reader = factory.getMetadataReader(resource);
System.out.println("类名:"+reader.getClassMetadata());
System.out.println("是否添加了@Component注解:"+reader.getAnnotationMetadata().hasAnnotation(Component.class.getName()));
System.out.println("是否添加了@Component的派生注解:"+reader.getAnnotationMetadata().hasMetaAnnotation(Component.class.getName()));
}
}
}
context.refresh();
for (String beanDefinitionName : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(beanDefinitionName);
}
context.close();
}
}运行结果如下,可以正常识别类上是否添加了@Component注解或是派生注解

能够扫描到类上添加的注解之后,我们是需要将注解添加到BeanDefinitionMap当中去的,那么继续完善我们的测试方法
public class TestBeanFactoryPostProcessor {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();
context.registerBean("config", Config.class);
//模拟ConfigurationPostProcessor处理器中如何解析@ComponentScan注解
ComponentScan componentScan = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(Config.class, ComponentScan.class);
if (componentScan != null) {
for (String s : componentScan.basePackages()) {
//将com.zmt.test5转化格式为classpath*:com/zmt/test5/**/*.class
String path = "classpath*:" + s.replace(".", "/") + "/**/*.class";
//创建出一个元数据读取工厂,用来读取类资源信息
CachingMetadataReaderFactory factory = new CachingMetadataReaderFactory();
//通过getResource方法获取到path中的所有类资源
Resource[] resources = context.getResources(path);
//创建Bean名称生成器
AnnotationBeanNameGenerator generator = new AnnotationBeanNameGenerator();
for (Resource resource : resources) {
//读取类资源信息
MetadataReader reader = factory.getMetadataReader(resource);
System.out.println("类名1:" + reader.getClassMetadata());
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata = reader.getAnnotationMetadata();
System.out.println("是否添加了@Component注解:" + annotationMetadata.hasAnnotation(Component.class.getName()));
System.out.println("是否添加了@Component的派生注解:" + annotationMetadata.hasMetaAnnotation(Component.class.getName()));
if (annotationMetadata.hasAnnotation(Component.class.getName()) ||
annotationMetadata.hasMetaAnnotation(Component.class.getName())) {
//如果该类添加了注解,需要添加到BeanDefinitionMap当中去,生成BeanDefinition对象
AbstractBeanDefinition bd = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(reader.getClassMetadata().getClassName())
.getBeanDefinition();
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getDefaultListableBeanFactory();
//生成Bean名称
String name = generator.generateBeanName(bd,beanFactory);
System.out.println("name:"+name);
//将BeanDefinition注册到beanFactory
beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition(name,bd);
}
}
}
}
context.refresh();
for (String beanDefinitionName : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(beanDefinitionName);
}
context.close();
}
}我们通过打断点查看beanFactory中是否将BeanDefinition信息注册到BeanDefinitionMap当中去,结果如下
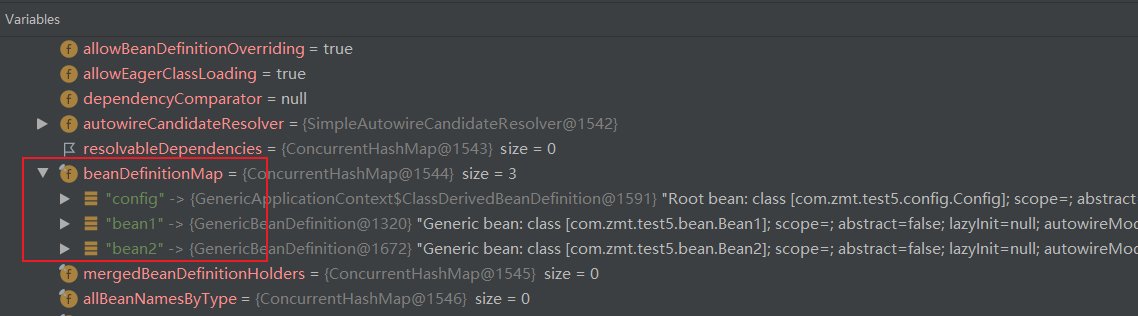
至此已经实现了组件扫描,但是目前我们的实现是在容器初始化 [refresh()方法] 之前就做好了,我们应该将这些实现抽取到一个BeanFactory后处理器当中,等待refresh()方法回调,因此我们将这些实现代码放入一个组件扫描后处理器。
public class ComponentScanPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override //在执行context.refresh()方法时回调该方法
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory configurableListableBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
try {
ComponentScan componentScan = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(Config.class, ComponentScan.class);
if (componentScan != null) {
for (String s : componentScan.basePackages()) {
//将com.zmt.test5转化格式为classpath*:com/zmt/test5/**/*.class
String path = "classpath*:" + s.replace(".", "/") + "/**/*.class";
//创建出一个元数据读取工厂,用来读取类资源信息
CachingMetadataReaderFactory factory = new CachingMetadataReaderFactory();
//通过getResource方法获取到path中的所有类资源
Resource[] resources = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources(path);
//创建Bean名称生成器
AnnotationBeanNameGenerator generator = new AnnotationBeanNameGenerator();
for (Resource resource : resources) {
//读取类资源信息
MetadataReader reader = factory.getMetadataReader(resource);
System.out.println("类名1:" + reader.getClassMetadata());
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata = reader.getAnnotationMetadata();
System.out.println("是否添加了@Component注解:" + annotationMetadata.hasAnnotation(Component.class.getName()));
System.out.println("是否添加了@Component的派生注解:" + annotationMetadata.hasMetaAnnotation(Component.class.getName()));
if (annotationMetadata.hasAnnotation(Component.class.getName()) ||
annotationMetadata.hasMetaAnnotation(Component.class.getName())) {
//如果该类添加了注解,需要添加到BeanDefinitionMap当中去,生成BeanDefinition对象
AbstractBeanDefinition bd = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(reader.getClassMetadata().getClassName())
.getBeanDefinition();
if (configurableListableBeanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory){
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = (DefaultListableBeanFactory) configurableListableBeanFactory;
String name = generator.generateBeanName(bd,beanFactory);
System.out.println("name:"+name);
beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition(name,bd);
}
}
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}修改此时的测试代码,将我们自定义的BeanFactory后处理器注册到context当中?
public class TestBeanFactoryPostProcessor {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();
context.registerBean("config", Config.class);
//模拟ConfigurationPostProcessor处理器中如何解析@ComponentScan注解
context.registerBean(ComponentScanPostProcessor.class);
context.refresh();
for (String beanDefinitionName : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(beanDefinitionName);
}
context.close();
}
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/zmbwcx/article/details/135231648
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- ref和$refs,$nextTick异步更新
- 流动的边框用css怎么实现
- 基于简化版python+VGG+MiniGoogLeNet的智能43类交通标志识别—深度学习算法应用(含全部python工程源码)+数据集+模型(三)
- 日本yolov8用户案例
- 【Linux】初识命令行
- leetCode算法—3.无重复字符的最长子串
- 接口芯片选型分析 四通道差分驱动可满足ANSI TIA/EIA-422-B 和ITU V.11 的要求 低功耗,高速率,高ESD
- 揭秘大数据时代的内存数据存储、数据缓存:redis缓存框架!
- 计算机毕业设计选题分享-spring boot疾病查询网站01548(赠送源码数据库)JAVA、PHP,node.js,C++、python,大屏数据可视化等
- 司铭宇老师:销售团队培训课程体系