【学习笔记】-使用LSTM算法实现余额宝资金流入流出预测
发布时间:2024年01月21日
使用LSTM算法实现余额宝资金流入流出预测
关键词:LSTM、基于大规模历史数据预测、MSE
数据来源:[天池大赛-资金流入流出预测-挑战Baseline]
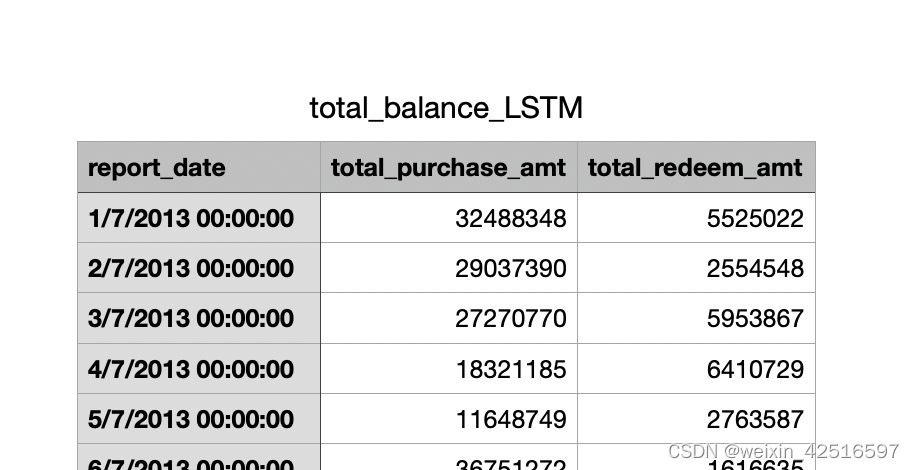
数据预处理:根据数据集进行数据预处理生成每日购入资金总量,最终传入的数据列表如下
模型代码运行过程:
RNN模型运行数据
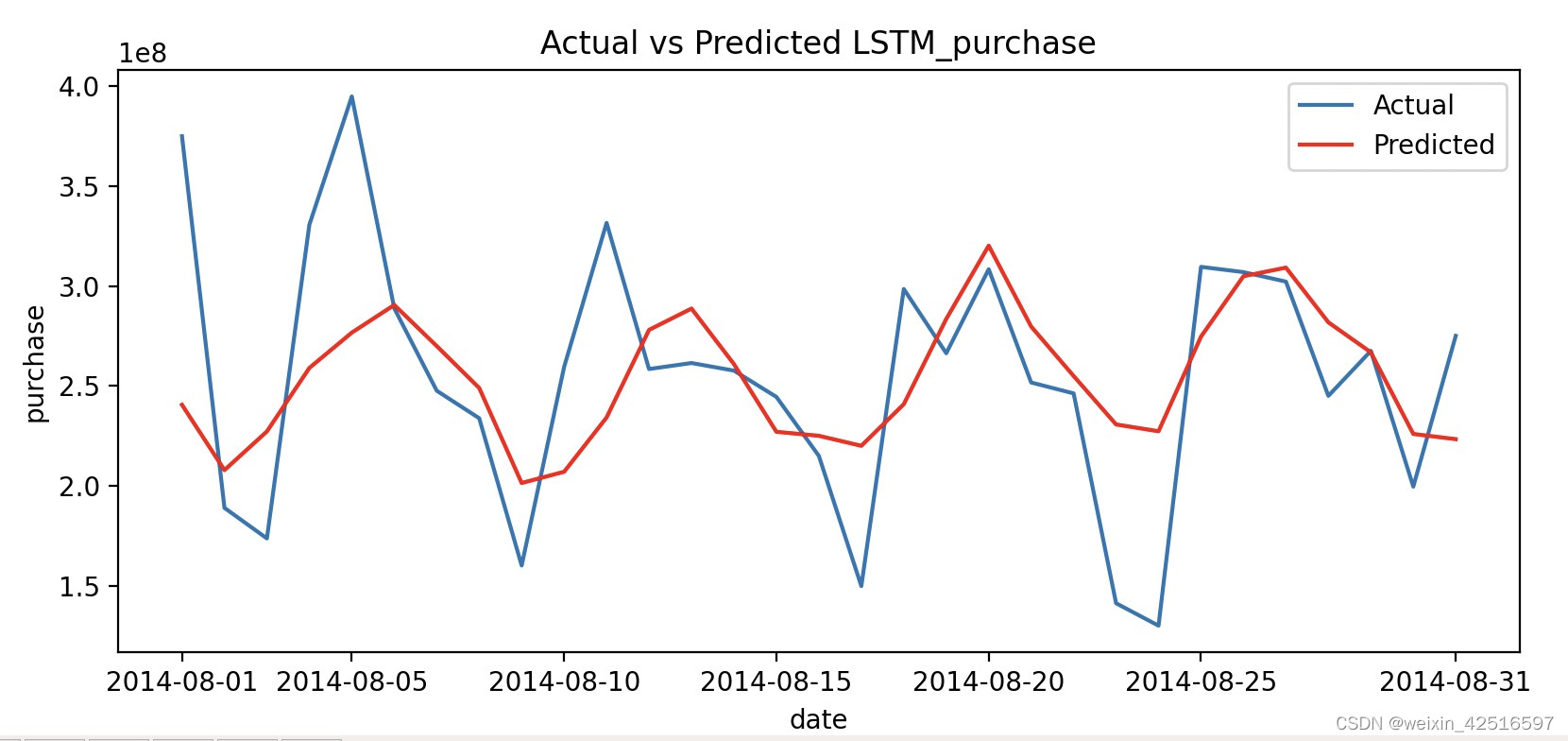
预测数据与原始数据对比图:
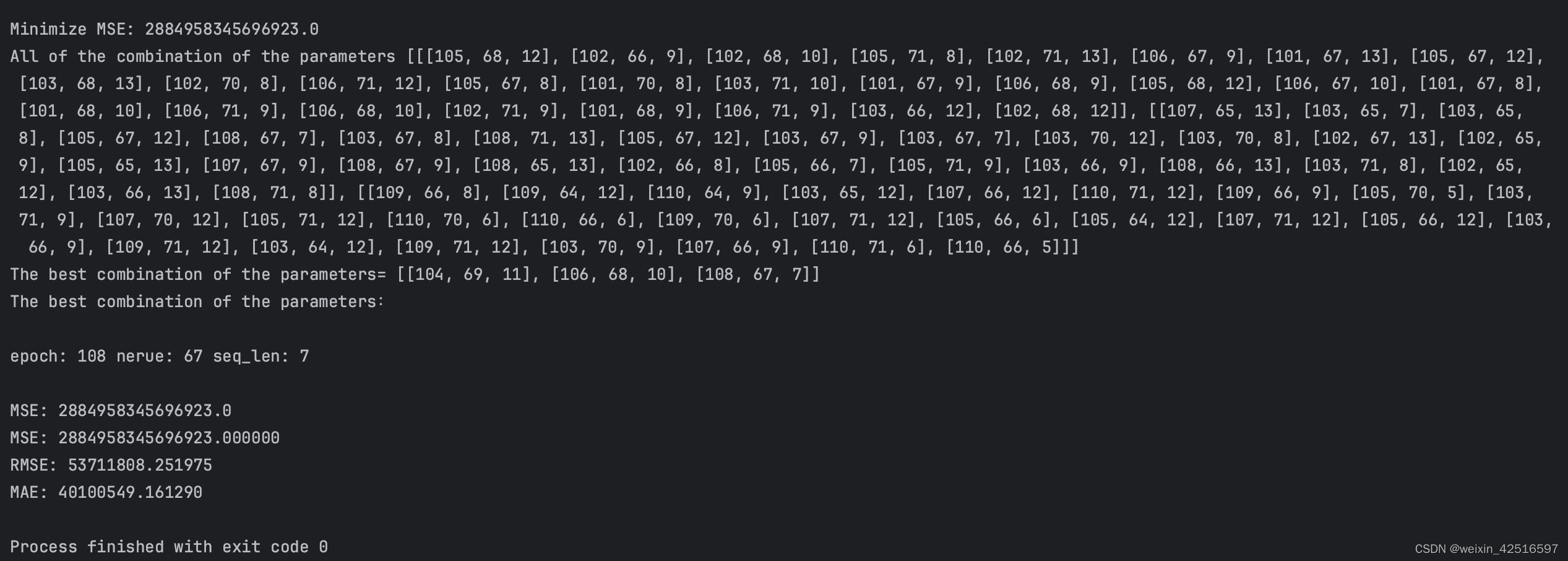
MSE、RMSE、MAE结果:
LSTM模型完整代码:
(数据量较大,代码运行时间较长,需要耐心等待)
#以下部分为项目需要引用的库
from math import sqrt
import numpy
import pandas
from keras.layers import LSTM
from keras.layers import Dense
from keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, mean_absolute_error
from random import choice
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from keras.models import Sequential
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
#设置学习循环的次数(epoch)神经元个数(neure)步长(seq_len)的范围
numpy.random.seed(2019)
epoch_range=[*range(100,200,1)]
neure_range=[*range(10, 128, 1)]
seq_len_range=[*range(5, 50, 1)]
#定义参数组的list
List=[]
combination_all=[]
combination_best=[]
pred_best=[]
pred = []
epoch_best=None
neure_best=None
seq_len_best=None
MSE_best=399044410397529222
def Change_num(index_X,X_all_list):
if(3<=index_X<=(len(X_all_list)-3)):
list_X=X_all_list[index_X-3:index_X+2]
elif(index_X<3):
list_X=X_all_list[:5]
else:
list_X=X_all_list[-5:]
return list_X
#随机生成一组参数值
for i in range(0,1):
epoch=choice(epoch_range)
neure=choice(neure_range)
seq_len=choice(seq_len_range)
List.append(1)
List[i]=[epoch,neure,seq_len]
print(List)
leean=2
#RNN模型主体
class RNNModel(object):
def __init__(self, look_back=1, epochs_purchase=10, batch_size=1, verbose=2, patience=10,
store_result=False,nerue=1):
self.look_back = look_back
self.epochs_purchase = epochs_purchase
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.verbose = verbose
self.store_result = store_result
self.patience = patience
self.nerue = nerue
self.purchase = pandas.read_csv('/Users/Desktop/Purchase Redemption Data/total_balance_LSTM.csv', usecols=[1], engine='python')
#数据标准化
def get_Standard_data(self, data_frame):
# load the data set
data_set= data_frame.values
data_set = data_set.astype('float32')
scaler = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0, 1))
data_set = scaler.fit_transform(data_set)
train_x, train_y, test = self.create_data_set(data_set)
train_x = numpy.reshape(train_x, (train_x.shape[0], 1, train_x.shape[1]))
return train_x, train_y, test, scaler
def create_data_set(self, data_set):
data_x, data_y = [], []
print(self.look_back)
for i in range(len(data_set) - self.look_back - 31):
a = data_set[i:(i + self.look_back), 0]
data_x.append(a)
data_y.append(list(data_set[i + self.look_back: i + self.look_back + 31, 0]))
return numpy.array(data_x), numpy.array(data_y), data_set[-self.look_back:, 0].reshape(1, 1, self.look_back)
#LSTM模型主体
def LSTM_model(self, train_x, train_y, epochs, nerue):
model = Sequential()
model.add(LSTM(nerue, input_shape=(1, self.look_back),return_sequences=True))
model.add(LSTM(32, return_sequences=False))
model.add(Dense(32))
model.add(Dense(31))
model.compile(loss='mse', optimizer='adam')
model.summary()
early_stopping = EarlyStopping('loss', patience=self.patience)
history = model.fit(train_x, train_y, epochs=epochs, batch_size=self.batch_size, verbose=self.verbose,
callbacks=[early_stopping])
return model
def predict(self, model, data):
prediction = model.predict(data)
return prediction
#处理流入数据,划分训练集和测试集,并运行LSTM算法`在这里插入代码片`
def run_purchase(self):
purchase_train_x, purchase_train_y, purchase_test, purchase_scaler = self.get_Standard_data(self.purchase)
purchase_model = self.LSTM_model(purchase_train_x, purchase_train_y, self.epochs_purchase,self.nerue)
purchase_predict = self.predict(purchase_model, purchase_test)
purchase = purchase_scaler.inverse_transform(purchase_predict).reshape(31, 1)
test_user = pandas.DataFrame({'report_date': [20140800 + i for i in range(1, 32)]})
test_user['purchase'] = purchase
return test_user['purchase']
if __name__ == '__main__':
real = pandas.read_csv('/Users/Desktop/Purchase Redemption Data/total_balance_test.csv',usecols=[1], engine='python')
#抽取27组epoch、neure、seq_len的参数组合
for i in range(0, 27):
epoch = choice(epoch_range)
neure = choice(neure_range)
seq_len = choice(seq_len_range)
List.append(1)
List[i] = [epoch, neure, seq_len]
print(List)
leean = 2
for f in range(3):
MSE_list = []
pred_all = []
for s in range(27):
initiation = RNNModel(look_back=List[s][2], epochs_purchase=List[s][0], batch_size=14, verbose=0,
patience=50,
store_result=True,nerue=List[s][1])
prediction=initiation.run_purchase()
MSE_list.append(1)
MSE_list[s] = mean_squared_error(real, prediction)
print(MSE_list[s])
pred_all.append(1)
pred_all[s] = prediction
print(MSE_list)
indexs = MSE_list.index(min(MSE_list))
print(indexs)
pred_best.append(1)
pred_best[f] = pred_all[indexs]
epochs, neures, seq_lens = List[indexs][0], List[indexs][1], List[indexs][2]
combination_best.append(1)
combination_best[f] = [epochs, neures, seq_lens]
#计算不同参数的预测模型的预测结果的MSE值,根据MSE值选择最合适的参数组合
if (MSE_list[indexs] < MSE_best):
MSE_best = MSE_list[indexs]
epoch_best = epochs
neure_best = neures
seq_len_best = seq_lens
pred = pred_all[indexs]
print(pred[0])
index_epoch = epoch_range.index(epochs)
del epoch_range[index_epoch]
index_nerue = neure_range.index(neures)
del neure_range[index_nerue]
index_seq_len = seq_len_range.index(seq_lens)
del seq_len_range[index_seq_len]
epoch_new = Change_num(index_epoch, epoch_range)
neure_new = Change_num(index_nerue, neure_range)
seq_len_new = Change_num(index_seq_len, seq_len_range)
List = []
for y in range(27):
List.append(1)
List[y] = [choice(epoch_new), choice(neure_new), choice(seq_len_new)]
combination_all.append(1)
combination_all[f] = List
print(f, "th selection!\n")
print("epoch:", epoch_best, "nerue:", neure_best, "seq_len:", seq_len_best, "\n")
print("Minimize MSE:", MSE_best)
#输出预测结果最好的的最佳参数组合
print("All of the combination of the parameters", combination_all)
print("The best combination of the parameters=", combination_best)
print("The best combination of the parameters:\n")
print("epoch:", epoch_best, "nerue:", neure_best, "seq_len:", seq_len_best, "\n")
print("MSE:", MSE_best)
#绘制曲线图
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))
plt.plot(real, label='Actual')
plt.plot(pred, color='red', label='Predicted')
plt.xticks()
plt.title('Actual vs Predicted LSTM_purchase')
plt.xlabel('date')
plt.ylabel('purchase')
X=[0,4,9,14,19,24,30]
Y=['2014-08-01','2014-08-05','2014-08-10','2014-08-15','2014-08-20','2014-08-25','2014-08-31']
plt.xticks(X,Y)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
#输出预测结果的MSE、RMSE、MAE值
mseValue = mean_squared_error(real, pred)
rmseValue = sqrt(mean_squared_error(real, pred))
maeValue = mean_absolute_error(real, pred)
print('MSE: %.6f' % mseValue)
print('RMSE: %.6f' % rmseValue)
print('MAE: %.6f' % maeValue)
```
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42516597/article/details/135680611
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 暴雪意图复合,但国内已不是当年的市场
- 个人仿制android QQ、android大作业
- GPT如此火爆的几个重要原因
- 幻兽帕鲁服务器搭建,包教包会
- 软件测试|使用holidays模块处理节假日
- java8 Stream()流 list转map
- VOSviewer分析知网文献以及图片导出
- WTN6040F-8S语音芯片:投篮游戏机新时代引领者
- 使用numpy处理图片——90度旋转
- 【React系列】Hook(一)基本使用